Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Uploaded by
rob fagfaceCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tuckman 1965 Developmental Sequence in Small Groups PDFDocument16 pagesTuckman 1965 Developmental Sequence in Small Groups PDFRaluca Daminescu100% (7)
- Plant Competition Lab ReportDocument10 pagesPlant Competition Lab Reportapi-313931206100% (1)
- Paul Ricoeur's Oneself As AnotherDocument10 pagesPaul Ricoeur's Oneself As AnotherAna DincăNo ratings yet
- Reference Card (PDQ Sheet) : Week 1: Statistical Inference For One and Two Popula-Tion VariancesDocument50 pagesReference Card (PDQ Sheet) : Week 1: Statistical Inference For One and Two Popula-Tion Variancesbusiness docNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing RoadmapDocument2 pagesHypothesis Testing RoadmapRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Metacognition PDFDocument311 pagesApplied Metacognition PDFNawel Zoghlami100% (3)
- Chapter Three Statistical Inference in Simple Linear Regression ModelDocument33 pagesChapter Three Statistical Inference in Simple Linear Regression ModeleferemNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Class 2Document23 pagesWeek 6 Class 2anon_711312801No ratings yet
- 8 - Part - 2 - Hypo - Z - Test - Beta - N - and - T - Test.9188.1587301904.1057 2Document36 pages8 - Part - 2 - Hypo - Z - Test - Beta - N - and - T - Test.9188.1587301904.1057 2Pun AditepNo ratings yet
- Engineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 8Document13 pagesEngineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 8EICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- ECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 6Document73 pagesECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 6OREJESU EUNICE OJUTIKUNo ratings yet
- G. Hypothesis Testing-1Document21 pagesG. Hypothesis Testing-1Lahiru PrasangaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestDocument49 pagesHypothesis Testwindi apriliaNo ratings yet
- Statistika: Hypothesis TestingDocument50 pagesStatistika: Hypothesis TestingSuryati PurbaNo ratings yet
- 20230820025153_WEEK 12Document28 pages20230820025153_WEEK 12richiealdo7No ratings yet
- Stat 410 Tutorial Week 6Document4 pagesStat 410 Tutorial Week 6S CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Monica Joyce Naperi - Adaptive-Teaching-Guide-TemplateDocument9 pagesMonica Joyce Naperi - Adaptive-Teaching-Guide-TemplateMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3Abdii Dhufeera100% (2)
- Basics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeDocument34 pagesBasics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeshanNo ratings yet
- PPT05 - Hypothesis Test For Mean - One SampleDocument31 pagesPPT05 - Hypothesis Test For Mean - One SampleaekimNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis - STAT510Document43 pagesRegression Analysis - STAT510Vivian TranNo ratings yet
- EC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Document29 pagesEC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Nagmani KumarNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 Ex-I CorrDocument2 pages2022-23 Ex-I CorrAzer TyuiopNo ratings yet
- Walpole Chapter 10Document13 pagesWalpole Chapter 10Mehmet PolatNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics II Chapter 11 Distribution-Free InferenceDocument94 pagesApplied Statistics II Chapter 11 Distribution-Free InferenceJose Ruben Sorto BadaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis FormulationDocument16 pagesHypothesis FormulationFantayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Sign Test, Kolmogorov Test and Jarque-Bera TestDocument27 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Sign Test, Kolmogorov Test and Jarque-Bera TestJune SabatinNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: Lecture Notes No. 7 M235Document63 pagesHypothesis Testing: Lecture Notes No. 7 M235محمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Hypothesis Testing With One SampleDocument6 pagesChapter 7: Hypothesis Testing With One SamplenootiNo ratings yet
- II-4 B Basic Statistics - COLLADO Pages 9-10Document2 pagesII-4 B Basic Statistics - COLLADO Pages 9-10trishaNo ratings yet
- Z Test ProportionsDocument9 pagesZ Test ProportionsSunita BasakNo ratings yet
- Test Concerning Mean: Lesson Note #Document4 pagesTest Concerning Mean: Lesson Note #iqrakonain1No ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document39 pagesLecture 14JING NIENo ratings yet
- L2 - Hypothesis TestingDocument62 pagesL2 - Hypothesis TestingMan Ho LiNo ratings yet
- A Handout On Statistical Approach To Nonparametric MethodsDocument62 pagesA Handout On Statistical Approach To Nonparametric Methodsudita.iitismNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Applied StatisticsDocument23 pagesUnit-4 Applied StatisticsRidham chitreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: One-Parameter Models: Lecture 3.2: Inference For Poisson ModelDocument16 pagesChapter 3: One-Parameter Models: Lecture 3.2: Inference For Poisson Modelxiuxian liNo ratings yet
- ZCVZCVZXVCDocument66 pagesZCVZCVZXVCDiovinyl KartilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 105 4Document20 pagesChapter 4 105 4masrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Lecture BDS 9-23-24 PrintDocument13 pagesLecture BDS 9-23-24 PrintVictor Van der WelNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For The Mean (Small Samples)Document40 pagesHypothesis Testing For The Mean (Small Samples)ANCHURI NANDININo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Complete SlidesDocument54 pagesHypothesis Testing Complete Slidesghabel11No ratings yet
- 07 Test On Proportions - StudentDocument5 pages07 Test On Proportions - StudentRaihanil JannahNo ratings yet
- 6.2009 Hypothesis Testing-Binomial SDocument6 pages6.2009 Hypothesis Testing-Binomial Sfabremil7472100% (2)
- Hypothesis Testing ReviewDocument5 pagesHypothesis Testing ReviewhalleyworldNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Statistics-1-1Document35 pagesHypothesis Statistics-1-111- NikunjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document12 pagesLecture 03B SRINATH ACHARYNo ratings yet
- STAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847Document19 pagesSTAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847azmina rahamanNo ratings yet
- Stats Sums and FormulasDocument28 pagesStats Sums and FormulasShruti ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- QM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDocument1 pageQM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- QM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDocument1 pageQM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- Alternative Hypothesis TestingDocument2 pagesAlternative Hypothesis TestingtocharivaniNo ratings yet
- Cheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamDocument4 pagesCheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamM.Ilham PratamaNo ratings yet
- Applications Noncentral T Distribution PDFDocument22 pagesApplications Noncentral T Distribution PDFMelo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Section V Notes With Answers - PDF BDocument8 pagesSection V Notes With Answers - PDF BDeivid William TorresNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hypothesis TestingDocument42 pagesBasics of Hypothesis TestingRandy NatalNo ratings yet
- Final Term Biostatistics PDFDocument7 pagesFinal Term Biostatistics PDFSarmad HussainNo ratings yet
- MAT 3 12th WKDocument22 pagesMAT 3 12th WKparulanirvinjohnNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Random Processes - Lecture-05: Course Code: ECE-215Document14 pagesProbability Theory and Random Processes - Lecture-05: Course Code: ECE-215mail2megp6734No ratings yet
- Topic 6A Hypotheses TestingDocument41 pagesTopic 6A Hypotheses TestingMATHAVAN A L KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Calibration PDFDocument8 pagesCalibration PDFAldo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- T Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectDocument10 pagesT Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectPayal DhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Valed-001 Self-Learning Module 2 Hazel Kim M. Cudia: Teachers Copy (Values Education)Document35 pagesValed-001 Self-Learning Module 2 Hazel Kim M. Cudia: Teachers Copy (Values Education)Celina Atayde HermosillaNo ratings yet
- BC0160011 - Disha JainDocument3 pagesBC0160011 - Disha JainVIVEKANANDAN JVNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & ReliabilityDocument2 pagesQuality Assurance & ReliabilityNishit KarkarNo ratings yet
- Holzhey-Kunz - Two Ways of Combining Philosophy and Psychopathology of Time ExperiencesDocument17 pagesHolzhey-Kunz - Two Ways of Combining Philosophy and Psychopathology of Time ExperiencesBreno Costa100% (1)
- IB Chem2tr Assess EasgDocument13 pagesIB Chem2tr Assess EasgRNo ratings yet
- Criminological Research 2Document3 pagesCriminological Research 2Vin Sab100% (4)
- (BS EN ISO 10360-8 - 2013) - Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) - Acceptance and Reverification Tests For Coordinate Measuring Systems (CMS) - CMMs With Optical Distance Senso PDFDocument62 pages(BS EN ISO 10360-8 - 2013) - Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) - Acceptance and Reverification Tests For Coordinate Measuring Systems (CMS) - CMMs With Optical Distance Senso PDFAugusto Maury ToledoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Good AssessmentDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of Good AssessmentGhan PrathamaNo ratings yet
- Lectre2 - Roots of Social PsychologyDocument11 pagesLectre2 - Roots of Social PsychologyMalay Kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Toward A Theory of Managing Organizational ConflictDocument20 pagesToward A Theory of Managing Organizational ConflictAahil RazaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Performance Appraisal System On Staff Performance inDocument16 pagesEffect of Performance Appraisal System On Staff Performance inAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- VV AA - Michel Foucault Philosopher PDFDocument369 pagesVV AA - Michel Foucault Philosopher PDFAntonio Pepe Giménez VascoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 by Hasan MaridiDocument233 pagesGeneral Physics 1 by Hasan MaridiEmily Tercio100% (1)
- Students' Perception On Collaborative Grouping As A Learning Strategy in Pasig Catholic College SCHOOL YEAR 2018 - 2019Document50 pagesStudents' Perception On Collaborative Grouping As A Learning Strategy in Pasig Catholic College SCHOOL YEAR 2018 - 2019Angelie De La PazNo ratings yet
- Ujian Pra Untuk Topik Unit Dan Pengukuran: Pre Test For Unit and Measurement TopicDocument5 pagesUjian Pra Untuk Topik Unit Dan Pengukuran: Pre Test For Unit and Measurement TopicZa Liza MNorNo ratings yet
- Psychology Essay Questions 1Document9 pagesPsychology Essay Questions 1keyas143No ratings yet
- Scheidegger 2004 MorphotectonicsDocument201 pagesScheidegger 2004 Morphotectonicsluis100% (1)
- Tabulation of DataDocument19 pagesTabulation of DataAJAY SINGH MAURYA100% (1)
- Quantum Physics Berkeley Physics Course Eyvind WichmanDocument444 pagesQuantum Physics Berkeley Physics Course Eyvind WichmanVeerareddy Vippala100% (3)
- Training The Antifragile Athlete - A Preliminary Analysis of Neuromuscular Training Effects On Muscle Activation DynamicsDocument22 pagesTraining The Antifragile Athlete - A Preliminary Analysis of Neuromuscular Training Effects On Muscle Activation DynamicsGoranMarkovicNo ratings yet
- Dato Mokhtar Bin Hashim & Anor V Public ProsDocument57 pagesDato Mokhtar Bin Hashim & Anor V Public Prossaifuddin_zain100% (1)
- Freedom of Will and DeterminismDocument11 pagesFreedom of Will and DeterminismTanya MiyaNo ratings yet
- ARDL Models-Bounds TestingDocument17 pagesARDL Models-Bounds Testingmzariab88% (8)
- Jurnal Mia BismillahDocument8 pagesJurnal Mia BismillahDede SumiaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inferences Solved PaperDocument7 pagesStatistical Inferences Solved PaperMubarakNo ratings yet
- Experimental Psychology: Ma'Am Lois LopezDocument74 pagesExperimental Psychology: Ma'Am Lois LopezDrixson DwightNo ratings yet
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Uploaded by
rob fagfaceOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Hypothesis Testing: Cee 3040 - Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
Uploaded by
rob fagfaceCopyright:
Available Formats
CEE 3040 - UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS IN ENGINEERING
Lec. Notes #31
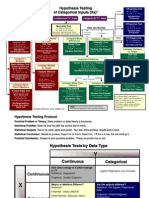
Steps in Constructing a Hypothesis Test
1. Select Ho and Ha -- what is to be decided?
2. Select test statistic to summarize the available data (Z, T, c2, F and others)
3. Specify a and thus determine rejection region before test is conducted. Test criterion is now set.
4. Evaluate b in repeated use – is this going to work?
5. Compute test statistics. Reject? Compute P-value.
Hypothesis Testing
Possible states of nature: Ho and Ha
Possible decisions: accept or reject Ho
f(x|Ha) f(x|Ho)
Ho#True#######Ha#True#
Accept#Ho# 1 α" β"
#
#Reject#Ho# α"a# 1 β"
α c β
Type I error a = P[ Reject Ho | Ho true ]
Type II error b = P[ Accept Ho | Ho false ]
Power = 1 – b = P[ Reject Ho | Ho false ] Positive viewpoint
Formalization of Test
X − µo X − µo
Test Statistic: Ztest = OR Tn-1 =
σ n S n
or other statistics for two-sample & nonparametric tests
Decision Rule t-test
if Tn-1 < ta,n-1 Accept Ho : µ = µ o
if Tn-1 > ta,n-1 Reject Ho Ha: µ > µo, or
Ha: µ = µa where µa is greater than µo
Value of b
X − µo
b = P[ Accept Ho | Ha ] = P[ ≤ tα ,n−1 | Ha: µ > µo ]
S n
% X −µ n(µ a − µ o ) (
a
' + *
' σ n σ
= P ≤ tα ,n−1 * Requires non-central t-distribution
' Sσ *
' *
& )
depends upon degrees of freedom n-1 and distance d = (µa – µo)/s. See Fig. A.17.
Can also be used to determine required sample size for fixed a and b.
P-values
Smallest value of a such that evidence would result in rejection of Ho.
P-value = "Attained significance level of test." For NORMAL tests:
P-value = 1 – F(z) one-sided upper-tailed, Ha: µ > µo
P-value = 2 F(–|z|) two-sided
P-value = F(z) one-sided lower-tail, Ha: µ < µo
You might also like
- Tuckman 1965 Developmental Sequence in Small Groups PDFDocument16 pagesTuckman 1965 Developmental Sequence in Small Groups PDFRaluca Daminescu100% (7)
- Plant Competition Lab ReportDocument10 pagesPlant Competition Lab Reportapi-313931206100% (1)
- Paul Ricoeur's Oneself As AnotherDocument10 pagesPaul Ricoeur's Oneself As AnotherAna DincăNo ratings yet
- Reference Card (PDQ Sheet) : Week 1: Statistical Inference For One and Two Popula-Tion VariancesDocument50 pagesReference Card (PDQ Sheet) : Week 1: Statistical Inference For One and Two Popula-Tion Variancesbusiness docNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing RoadmapDocument2 pagesHypothesis Testing RoadmapRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Metacognition PDFDocument311 pagesApplied Metacognition PDFNawel Zoghlami100% (3)
- Chapter Three Statistical Inference in Simple Linear Regression ModelDocument33 pagesChapter Three Statistical Inference in Simple Linear Regression ModeleferemNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Class 2Document23 pagesWeek 6 Class 2anon_711312801No ratings yet
- 8 - Part - 2 - Hypo - Z - Test - Beta - N - and - T - Test.9188.1587301904.1057 2Document36 pages8 - Part - 2 - Hypo - Z - Test - Beta - N - and - T - Test.9188.1587301904.1057 2Pun AditepNo ratings yet
- Engineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 8Document13 pagesEngineering Prob & Stat Lecture Notes 8EICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- ECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 6Document73 pagesECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 6OREJESU EUNICE OJUTIKUNo ratings yet
- G. Hypothesis Testing-1Document21 pagesG. Hypothesis Testing-1Lahiru PrasangaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestDocument49 pagesHypothesis Testwindi apriliaNo ratings yet
- Statistika: Hypothesis TestingDocument50 pagesStatistika: Hypothesis TestingSuryati PurbaNo ratings yet
- 20230820025153_WEEK 12Document28 pages20230820025153_WEEK 12richiealdo7No ratings yet
- Stat 410 Tutorial Week 6Document4 pagesStat 410 Tutorial Week 6S CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Monica Joyce Naperi - Adaptive-Teaching-Guide-TemplateDocument9 pagesMonica Joyce Naperi - Adaptive-Teaching-Guide-TemplateMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3Abdii Dhufeera100% (2)
- Basics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeDocument34 pagesBasics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeshanNo ratings yet
- PPT05 - Hypothesis Test For Mean - One SampleDocument31 pagesPPT05 - Hypothesis Test For Mean - One SampleaekimNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis - STAT510Document43 pagesRegression Analysis - STAT510Vivian TranNo ratings yet
- EC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Document29 pagesEC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Nagmani KumarNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 Ex-I CorrDocument2 pages2022-23 Ex-I CorrAzer TyuiopNo ratings yet
- Walpole Chapter 10Document13 pagesWalpole Chapter 10Mehmet PolatNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics II Chapter 11 Distribution-Free InferenceDocument94 pagesApplied Statistics II Chapter 11 Distribution-Free InferenceJose Ruben Sorto BadaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis FormulationDocument16 pagesHypothesis FormulationFantayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Sign Test, Kolmogorov Test and Jarque-Bera TestDocument27 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Sign Test, Kolmogorov Test and Jarque-Bera TestJune SabatinNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: Lecture Notes No. 7 M235Document63 pagesHypothesis Testing: Lecture Notes No. 7 M235محمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Hypothesis Testing With One SampleDocument6 pagesChapter 7: Hypothesis Testing With One SamplenootiNo ratings yet
- II-4 B Basic Statistics - COLLADO Pages 9-10Document2 pagesII-4 B Basic Statistics - COLLADO Pages 9-10trishaNo ratings yet
- Z Test ProportionsDocument9 pagesZ Test ProportionsSunita BasakNo ratings yet
- Test Concerning Mean: Lesson Note #Document4 pagesTest Concerning Mean: Lesson Note #iqrakonain1No ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document39 pagesLecture 14JING NIENo ratings yet
- L2 - Hypothesis TestingDocument62 pagesL2 - Hypothesis TestingMan Ho LiNo ratings yet
- A Handout On Statistical Approach To Nonparametric MethodsDocument62 pagesA Handout On Statistical Approach To Nonparametric Methodsudita.iitismNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Applied StatisticsDocument23 pagesUnit-4 Applied StatisticsRidham chitreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: One-Parameter Models: Lecture 3.2: Inference For Poisson ModelDocument16 pagesChapter 3: One-Parameter Models: Lecture 3.2: Inference For Poisson Modelxiuxian liNo ratings yet
- ZCVZCVZXVCDocument66 pagesZCVZCVZXVCDiovinyl KartilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 105 4Document20 pagesChapter 4 105 4masrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Lecture BDS 9-23-24 PrintDocument13 pagesLecture BDS 9-23-24 PrintVictor Van der WelNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For The Mean (Small Samples)Document40 pagesHypothesis Testing For The Mean (Small Samples)ANCHURI NANDININo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Complete SlidesDocument54 pagesHypothesis Testing Complete Slidesghabel11No ratings yet
- 07 Test On Proportions - StudentDocument5 pages07 Test On Proportions - StudentRaihanil JannahNo ratings yet
- 6.2009 Hypothesis Testing-Binomial SDocument6 pages6.2009 Hypothesis Testing-Binomial Sfabremil7472100% (2)
- Hypothesis Testing ReviewDocument5 pagesHypothesis Testing ReviewhalleyworldNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Statistics-1-1Document35 pagesHypothesis Statistics-1-111- NikunjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document12 pagesLecture 03B SRINATH ACHARYNo ratings yet
- STAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847Document19 pagesSTAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847azmina rahamanNo ratings yet
- Stats Sums and FormulasDocument28 pagesStats Sums and FormulasShruti ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- QM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDocument1 pageQM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- QM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDocument1 pageQM Hypothesis Testing SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- Alternative Hypothesis TestingDocument2 pagesAlternative Hypothesis TestingtocharivaniNo ratings yet
- Cheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamDocument4 pagesCheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamM.Ilham PratamaNo ratings yet
- Applications Noncentral T Distribution PDFDocument22 pagesApplications Noncentral T Distribution PDFMelo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Section V Notes With Answers - PDF BDocument8 pagesSection V Notes With Answers - PDF BDeivid William TorresNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hypothesis TestingDocument42 pagesBasics of Hypothesis TestingRandy NatalNo ratings yet
- Final Term Biostatistics PDFDocument7 pagesFinal Term Biostatistics PDFSarmad HussainNo ratings yet
- MAT 3 12th WKDocument22 pagesMAT 3 12th WKparulanirvinjohnNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Random Processes - Lecture-05: Course Code: ECE-215Document14 pagesProbability Theory and Random Processes - Lecture-05: Course Code: ECE-215mail2megp6734No ratings yet
- Topic 6A Hypotheses TestingDocument41 pagesTopic 6A Hypotheses TestingMATHAVAN A L KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Calibration PDFDocument8 pagesCalibration PDFAldo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- T Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectDocument10 pagesT Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectPayal DhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Valed-001 Self-Learning Module 2 Hazel Kim M. Cudia: Teachers Copy (Values Education)Document35 pagesValed-001 Self-Learning Module 2 Hazel Kim M. Cudia: Teachers Copy (Values Education)Celina Atayde HermosillaNo ratings yet
- BC0160011 - Disha JainDocument3 pagesBC0160011 - Disha JainVIVEKANANDAN JVNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & ReliabilityDocument2 pagesQuality Assurance & ReliabilityNishit KarkarNo ratings yet
- Holzhey-Kunz - Two Ways of Combining Philosophy and Psychopathology of Time ExperiencesDocument17 pagesHolzhey-Kunz - Two Ways of Combining Philosophy and Psychopathology of Time ExperiencesBreno Costa100% (1)
- IB Chem2tr Assess EasgDocument13 pagesIB Chem2tr Assess EasgRNo ratings yet
- Criminological Research 2Document3 pagesCriminological Research 2Vin Sab100% (4)
- (BS EN ISO 10360-8 - 2013) - Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) - Acceptance and Reverification Tests For Coordinate Measuring Systems (CMS) - CMMs With Optical Distance Senso PDFDocument62 pages(BS EN ISO 10360-8 - 2013) - Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) - Acceptance and Reverification Tests For Coordinate Measuring Systems (CMS) - CMMs With Optical Distance Senso PDFAugusto Maury ToledoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Good AssessmentDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of Good AssessmentGhan PrathamaNo ratings yet
- Lectre2 - Roots of Social PsychologyDocument11 pagesLectre2 - Roots of Social PsychologyMalay Kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Toward A Theory of Managing Organizational ConflictDocument20 pagesToward A Theory of Managing Organizational ConflictAahil RazaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Performance Appraisal System On Staff Performance inDocument16 pagesEffect of Performance Appraisal System On Staff Performance inAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- VV AA - Michel Foucault Philosopher PDFDocument369 pagesVV AA - Michel Foucault Philosopher PDFAntonio Pepe Giménez VascoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 by Hasan MaridiDocument233 pagesGeneral Physics 1 by Hasan MaridiEmily Tercio100% (1)
- Students' Perception On Collaborative Grouping As A Learning Strategy in Pasig Catholic College SCHOOL YEAR 2018 - 2019Document50 pagesStudents' Perception On Collaborative Grouping As A Learning Strategy in Pasig Catholic College SCHOOL YEAR 2018 - 2019Angelie De La PazNo ratings yet
- Ujian Pra Untuk Topik Unit Dan Pengukuran: Pre Test For Unit and Measurement TopicDocument5 pagesUjian Pra Untuk Topik Unit Dan Pengukuran: Pre Test For Unit and Measurement TopicZa Liza MNorNo ratings yet
- Psychology Essay Questions 1Document9 pagesPsychology Essay Questions 1keyas143No ratings yet
- Scheidegger 2004 MorphotectonicsDocument201 pagesScheidegger 2004 Morphotectonicsluis100% (1)
- Tabulation of DataDocument19 pagesTabulation of DataAJAY SINGH MAURYA100% (1)
- Quantum Physics Berkeley Physics Course Eyvind WichmanDocument444 pagesQuantum Physics Berkeley Physics Course Eyvind WichmanVeerareddy Vippala100% (3)
- Training The Antifragile Athlete - A Preliminary Analysis of Neuromuscular Training Effects On Muscle Activation DynamicsDocument22 pagesTraining The Antifragile Athlete - A Preliminary Analysis of Neuromuscular Training Effects On Muscle Activation DynamicsGoranMarkovicNo ratings yet
- Dato Mokhtar Bin Hashim & Anor V Public ProsDocument57 pagesDato Mokhtar Bin Hashim & Anor V Public Prossaifuddin_zain100% (1)
- Freedom of Will and DeterminismDocument11 pagesFreedom of Will and DeterminismTanya MiyaNo ratings yet
- ARDL Models-Bounds TestingDocument17 pagesARDL Models-Bounds Testingmzariab88% (8)
- Jurnal Mia BismillahDocument8 pagesJurnal Mia BismillahDede SumiaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inferences Solved PaperDocument7 pagesStatistical Inferences Solved PaperMubarakNo ratings yet
- Experimental Psychology: Ma'Am Lois LopezDocument74 pagesExperimental Psychology: Ma'Am Lois LopezDrixson DwightNo ratings yet