Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDF
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDF
Uploaded by
Valery LizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDF
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDF
Uploaded by
Valery LizCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter
1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.1 Basic Geometric Definitions
Answers
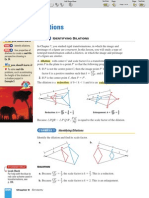
Possible Answers for 1-4. Answers may vary.
1. 2.
D
B C
A
E
3. 4.
G
X W
Y Q
Z
P
5. This problem describes any quadrilateral with the diagonals drawn in.
6. 𝑊𝑋, 𝑋𝑊, 𝑊𝑌, 𝑌𝑊, 𝑋𝑌, 𝑌𝑋 and line m.
7. 𝑇𝑅, 𝑇𝑆, 𝑅𝑇, and 𝑆𝑇.
8. Plane V, Plane RST, Plane RTS, Plane STR, Plane SRT, Plane TSR, and Plane TRS.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 1
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
9. A soccer field is like a plane since it is a flat two-dimensional surface. Student could
also say it is a rectangle.
10. Possible Answers sun rays, laser beam, the hands on a clock, foul lines on a baseball
field, the light from a flashlight.
11. A line and a plane intersect at a point.
12. A postulate is assumed true and a theorem must be proven true. All postulates, by
definition, are true. You must be told (or shown in a proof) that a theorem is true before
you can use it in a proof or otherwise.
13. Possible Answer 𝑃𝑄 intersects 𝑅𝑆 at point Q.
14. Possible Answer 𝐴𝐶 and 𝐴𝐵 are coplanar but point D is not.
15. Possible Answers Points E and H lie in Plane J, but 𝐸𝐹 and 𝐻𝐺 do not. Points E and
H are coplanar, but 𝐸𝐹 and 𝐻𝐺 are non-coplanar.
16. Possible Answer 𝐼𝑀, 𝐼𝐿, 𝐼𝐾, and 𝐼𝐽 have I as the endpoint, but J, K, L and M are non-
collinear.
17. True.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 2
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
18. False. To make this a true statement, it should say three non-collinear points determine
a plane. If three points are collinear, then they can be in infinitely many planes.
19. False. See the picture.
20. False. To make this a true statement, it should say a line segment is the set of infinitely
many collinear points between two endpoints.
21. False, by definition a point is “zero dimensional” and does not take up space.
22. True.
23. False. See the picture.
24. False, the endpoint, A, must be first.
25. True.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 3
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.2 Distance Between Two Points
Answers
For questions 1-8, your answers may vary, depending on the size of paper you printed
these questions on. These answers are for 100% on a 8.5” x 11” piece of paper.
1. 2.75 in
2. 4.9 cm
3. 4.125 in
4. 8.2 cm
B A T
5.
6. O is the midpoint. LO = OT = 8 cm.
T A Q
7. a)
b) TA + AQ = TQ
c) TQ = 15 in
H M A
8. a)
b) HM + MA = HA
c) MA = 11 cm
M I T
9. a)
b) MI + IT = MT
c) MI = 19 cm
A B C D
10.
BC = 8 cm, BD = 25 cm, CD = 17 cm
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 4
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
F H E G
11.
FE = 8 in, 13 in = HG, FG = 17 in
12. x = 3, HJ = 21 units, JK = 12
13. x = 11, HJ = 52 units, JK = 79 units
14. 13 units
15. 5 units
16. 9 units
17. 5 units
18.
19. SV = 6 units, TS = 23 units, RS = 17 units, TV = 29 units
20. x=3
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 5
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.3 Congruent Angles and Angle Bisectors
Answers
1. PS
2. 90°
3. 45°
4. 45°
5. x = 20°
6. x = 14°
7. True
8. False
9. False; it divides an angle into two congruent angles.
10. True
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 6
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.4 Midpoints and Segment Bisectors
Answers
1. (students may not have angle markings)
A D
B C
2. 𝑉𝑆 and 𝑄𝑇
3. 𝑉𝑆 bisects 𝑄𝑇
4. 𝑄𝑇 bisects 𝑉𝑆 You could also say that the lines bisect each other from what we know in
#3.
5. x = 12
6. (3, −5)
7. (1.5, −6)
8. (5, 5)
9. (−4.5, 2)
10. (−0.5, −2)
11. B is (7, 10)
12. A is (6, 9)
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 7
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.5 Angle Measurement
Answers
1. m∠LMN = 32°
2. x = 15°
3. False, B is the vertex.
4. True
5. True
6. False, it is equal to the sum of the smaller angles within it.
7. 8.
9. 10.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 8
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
11. 12.
For questions 13-16, student answers might be off by 1° or 2°.
13. 40°
14. 122°
15. 18°
16. 87°
17. x = 10°
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 9
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.6 Angle Classification
Answers
1. False, two angles could be 5° and 30°.
2. False, it is a straight angle.
3. True
4. True
5. Acute
6. Obtuse
7. Obtuse
8. Acute
9. Obtuse
10. Acute
11. Possible Answer
S
Q
R 160°
100° P
T
O
12. m∠QOP = 100°
13. m∠QOT = 130°
14. m∠ROQ = 30°
15. m∠SOP = 70°
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 10
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.7 Complementary Angles
Answers
1. 86 °
2. 1 °
3. 36 °
4. 58 °
5. 63 °
6. 90° − ( x + y )°
7. 90° − z° or (90 − z ) °
8. ∠INJ and ∠KNJ
9. m∠KNJ = 27°
10. False, they add up to 90 °
11. False, they can be the sum of any two angles where their sum is 90 ° .
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 11
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.8 Supplementary Angles
Answers
1. 66 °
2. 169 °
3. 89 °
4. 96 °
5. 123 °
6. 180° − x° or (180 − x ) °
7. 180° − ( x + y )°
8. Possible Answer ∠JNI and ∠INM
9. 117 °
10. True
11. x = 17°
12. x = 10.5°
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 12
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.9 Linear Pairs
Answers
1. False, they are supplementary.
2. True
3. False, they are next to each other.
4. True
5. False, they can form linear pairs, but not all the time.
6. x = 34°
7. 119 °
8. 147 °
9. 66 °
10. 173 °
11. 1°
12. 180° − z ° or (180 − z ) °
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 13
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.10 Vertical Angles
Answers
1. Possible Answer ∠INJ and ∠MNL
2. m∠MNL = 63°
3. True
4. 64 °
5. 42 °
6. 27 °
7. 21 °
8. 32 °
9. 4°
10. 21 °
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 14
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.11 Triangle Classification
Answers
1. Acute scalene
2. Equiangular equilateral
3. Right isosceles
4. Obtuse scalene
5. Acute isosceles
6. Obtuse isosceles
7. No, because a right angle is 90 ° and an obtuse angle is greater than 90 ° . That would
be a sum greater than 180 ° and a triangle’s three angles must add up to exactly 180 ° .
8. No, same reasoning as #7. Two obtuse angles would add up to be greater than 180 ° .
9. True.
10. False, triangles are named after the largest angle.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 15
Chapter 1 – Basics of Geometry Answer Key
1.12 Polygon Classification
Answers
1. Concave pentagon
2. Convex octagon
3. Convex 17-gon
4. Convex decagon
5. Concave quadrilateral
6. Concave hexagon.
7. A is not a polygon because two of the sides do not meet at a vertex; B is not a polygon
because one side is curved; C is not a polygon because it is not closed.
8. 2 diagonals 9. 5 diagonals 10. 9 diagonals
11. Nonagon: 21, Decagon: 35, Undecagon: 44, Dodecagon: 54
12. True
13. False, a star is a concave polygon.
14. True, see the picture.
CK-‐12 Basic Geometry Concepts 16
You might also like
- Earth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionDocument11 pagesEarth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionCharles Carpo67% (3)
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- MS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)Document158 pagesMS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)adar100% (1)
- Service Tower Problem - Solutions: Adapted From Module 2: Worksheet 6 in Precalculus: Pathways To CalculusDocument5 pagesService Tower Problem - Solutions: Adapted From Module 2: Worksheet 6 in Precalculus: Pathways To Calculusapi-287216602100% (1)
- Algebra 2 QuestionDocument9 pagesAlgebra 2 QuestionGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Night Chapter 1 Summary 1Document1 pageNight Chapter 1 Summary 1Elizabeth LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsLymenson BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsHammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Geometry Rules PDFDocument21 pagesGeometry Rules PDFVadlamudiMohanKumarNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 PDFDocument715 pagesAlgebra 1 PDFEfraín Antonio Jovél100% (2)
- Grade 8 Cartoon Dilation Rubric and InstructionsDocument8 pagesGrade 8 Cartoon Dilation Rubric and Instructionsapi-424017280No ratings yet
- CK 12 TrigonometryDocument552 pagesCK 12 TrigonometryjesusNo ratings yet
- SPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDDocument50 pagesSPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDJay B Gayle0% (1)
- ML Geometry 8-7 DilationsDocument8 pagesML Geometry 8-7 Dilationsashish663No ratings yet
- Abstract Algebra For Beginners - BeachyDocument177 pagesAbstract Algebra For Beginners - Beachycantor2000100% (1)
- Prob and Stats Notes PDFDocument12 pagesProb and Stats Notes PDFSivagami SaminathanNo ratings yet
- Day 38 Right Triangle TrigDocument32 pagesDay 38 Right Triangle TrigArchessNo ratings yet
- Similar Triangles r1 PDFDocument34 pagesSimilar Triangles r1 PDFjayroe ramosNo ratings yet
- Teaching GeometryDocument17 pagesTeaching Geometryanglo phile100% (1)
- Algebra 2Document40 pagesAlgebra 2Kevin BookerNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Flowchart 3Document10 pagesTrigonometry Flowchart 3Harshavardhan A100% (1)
- Geometry Curriculum MapDocument15 pagesGeometry Curriculum MapFosheeMNo ratings yet
- Batdangthuc DDTHDocument40 pagesBatdangthuc DDTHTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- Ratios Choice BoardDocument1 pageRatios Choice BoardKaitlyn AprilNo ratings yet
- Activities On Slope - Intercept FormDocument4 pagesActivities On Slope - Intercept FormJenelyn PonesNo ratings yet
- CMO Olympiad Book For Class 7Document13 pagesCMO Olympiad Book For Class 7KarthikaNo ratings yet
- Mock AP Exam 3 Review - MC ProblemsDocument36 pagesMock AP Exam 3 Review - MC ProblemsMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit Lessons On TransformationsDocument29 pagesUnit Lessons On TransformationsmagdammNo ratings yet
- Study BooksDocument6 pagesStudy BooksAster PhoenixNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistics PDFDocument40 pages1 Statistics PDFHue HueNo ratings yet
- History Alive Chapter 9 Guided NotesDocument9 pagesHistory Alive Chapter 9 Guided NotesBenbrandstraderNo ratings yet
- Math in Our World: Section 2-1Document38 pagesMath in Our World: Section 2-1Khemme Lapor Chu UbialNo ratings yet
- Force Relationship Between Mass Foce AccelerationDocument26 pagesForce Relationship Between Mass Foce AccelerationPauling ChiaNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Algebra Curriculum MapDocument9 pages8th Grade Algebra Curriculum Mapapi-264569685No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Gleancoe BookDocument84 pagesChapter 5 Gleancoe BookPablo UlisesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry-Word-Problems L v6 s1 PDFDocument7 pagesTrigonometry-Word-Problems L v6 s1 PDFAnonymous csfnVOKP6No ratings yet
- JC Math SyllabusDocument20 pagesJC Math Syllabusseeker103No ratings yet
- Mathematical LogicDocument113 pagesMathematical LogicRaduC43100% (1)
- School of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsDocument20 pagesSchool of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsThalika RuchaiaNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument133 pagesGeometryagonza70100% (1)
- 6.1 - Radian Measure and Arc Length Math 30-1Document14 pages6.1 - Radian Measure and Arc Length Math 30-1Math 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNo ratings yet
- Hands On GeometryDocument9 pagesHands On Geometrytina_cardone1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Polynomial Functions PDFDocument59 pagesChapter 4 Polynomial Functions PDFBuddy DavisonNo ratings yet
- 7th and 8th Grade Math Integer RulesDocument3 pages7th and 8th Grade Math Integer RulesjanetNo ratings yet
- Math 26 Midyear 2016 Course GuideDocument4 pagesMath 26 Midyear 2016 Course GuideHasmaye PintoNo ratings yet
- Geometry 1-1Document41 pagesGeometry 1-1api-293865618No ratings yet
- All Solutions 1078Document88 pagesAll Solutions 1078Anonymous 7CxwuBUJz3No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 PDFDocument44 pagesAlgebra 2 PDFAlan HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Develpment of Algebra 1995Document25 pagesDevelpment of Algebra 1995Hector VasquezNo ratings yet
- CalcIII Complete SolutionsDocument384 pagesCalcIII Complete SolutionsToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- 1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesZenic TzyNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Vocab CardsDocument15 pagesAlgebra 1 Vocab Cardsjoero51No ratings yet
- Geometry Lesson 11 V2-Proofs Using LogicDocument12 pagesGeometry Lesson 11 V2-Proofs Using Logicezmoreldo100% (3)
- Indiana University: New Portraits of the Bloomington CampusFrom EverandIndiana University: New Portraits of the Bloomington CampusNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument16 pagesCirclePaul PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key CK-12 Chapter 03 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument12 pagesAnswer Key CK-12 Chapter 03 Basic Geometry ConceptsAlyssa GrayNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Chapter 2F5Document28 pagesMathematics Chapter 2F5Rita LauNo ratings yet
- Miii Sample 2011Document24 pagesMiii Sample 2011Nilanjan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Linear FunctionDocument6 pagesTutorial 3 Linear FunctionBorhan Nordin DaudNo ratings yet
- An Accuate and Rapid Method For The Design of Super Sonice NozzlesDocument58 pagesAn Accuate and Rapid Method For The Design of Super Sonice NozzlesThet ZinNo ratings yet
- National University: Syllabus Subject: MathematicsDocument3 pagesNational University: Syllabus Subject: MathematicsFathmaakter JuiNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Axiomatic MethodDocument26 pagesThe Rise of Axiomatic MethodMichael Bahian Dodongan100% (1)
- Projection of Point and LinesDocument38 pagesProjection of Point and LinesmatetipraveenNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry: Direction Cosines and LinesDocument6 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry: Direction Cosines and LinesRahul Jha0% (1)
- AIEEE 2012 Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAIEEE 2012 Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsAjay Singh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Complex NumbersDocument3 pagesFiitjee: Complex NumbersSaravanan BNo ratings yet
- Moulded and Displacement DimensionsDocument7 pagesMoulded and Displacement DimensionsHabibah Dwi SalmaNo ratings yet
- Well TestingDocument21 pagesWell TestingOvaid Mehmood100% (1)
- Projection of Straight Line: - A Straight Line Can Be Kept in SIXDocument9 pagesProjection of Straight Line: - A Straight Line Can Be Kept in SIXAravamudhanNo ratings yet
- ComprehensiveDocument5 pagesComprehensivesunshine_avenueNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Design of The Question PaperDocument14 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Design of The Question PaperArjit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Solving and Graphing Linear Equations: Focused Learning Lessons For Mathematics AlgebraDocument14 pagesLesson 4: Solving and Graphing Linear Equations: Focused Learning Lessons For Mathematics AlgebraandhodgeNo ratings yet
- 9709 w04 QP 1Document4 pages9709 w04 QP 1michael hengNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Neutral Geometry Projective Geometry and Differential GeometryDocument12 pagesModule 5 Neutral Geometry Projective Geometry and Differential GeometryDanilyn SukkieNo ratings yet
- Slope HomeworkDocument4 pagesSlope HomeworkRC GonzalezNo ratings yet
- SPE 173103 PA - Microguide PDFDocument10 pagesSPE 173103 PA - Microguide PDFRichard AldazNo ratings yet
- A3 Vertical Planner Maths MypDocument7 pagesA3 Vertical Planner Maths Mypapi-414612775No ratings yet
- Dream World School, Ballari, KarnatakaDocument61 pagesDream World School, Ballari, Karnatakassewbay bayNo ratings yet
- The Project For Human Resource Development Scholarship by Japanese Grant Aid (JDS)Document7 pagesThe Project For Human Resource Development Scholarship by Japanese Grant Aid (JDS)Can Dinh ThuNo ratings yet
- CH 02 - Scalars & VectorsDocument8 pagesCH 02 - Scalars & VectorsMisa InafNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsAlwin Asuncion100% (1)
- GeometryDocument60 pagesGeometryAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Drawing Isometric Piping PDFDocument6 pagesDrawing Isometric Piping PDFgamin0% (1)