Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDF
Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDF
Uploaded by
Syarfa FurzanneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDF
Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDF
Uploaded by
Syarfa FurzanneCopyright:
Available Formats
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 1
SEKOLAH MENENGAH TEKNIK JOHOR BAHRU
MODUL PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA SPM 2018
KERTAS 2 BHGN B DAN C
BAHAGIAN B
F4: CHEMICAL BONDS: JOHOR SET 1
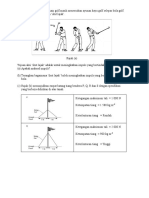
1. Diagram 7 shows the chemical symbols which represent three elements P, Q and R. These
letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan simbol kimia yang mewakili tuga unsur P, Q dan R. Huruf ini bukan simbol
sebenar bagi unsur.
(a) State which elements that can form ionic and covalent compound when combined.
Nyatakan unsur-unsur yang manakah boleh membentuk sebatian ionik dan kovalen apabila ia
berpadu. [2 marks]
(b) Based on Diagram 7, explain how two compounds in question 7(a) can be formed from these
elements. The two compounds should have different type of bonds.
Berdasarkan Rajah 7, terangkan bagaimanakan dua sebatian dalam soalan 7(a) ini boleh
terbentuk. Dua sebatian ini sepatutnya mempunyai ikatan yang berbeza. [10 marks]
(c) Compare and explain the physical properties between the ionic compound and covalent
compound. Your answer should consist of the following:
Bandingkan dan jelaskan ciri-ciri fizikal antara sebatian ion dengan sebatian kovalen. Jawapan
anda perlu mengandungi perkara berikut:
• Melting point and boiling point
Takat lebur dan takat didih
• Electrical conductivity
Kekonduksian elektrik [8 marks]
F5: CARBON COMPOUNDS: JOHOR SET 1
2. (a) Diagram 8 shows the structural formulae of hydrocarbon of compounds P and Q.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan formula struktur bagi sebatian hidrokarbon P dan Q.
Diagram 8 / Rajah 8
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 2
Compound P is a highly volatile, flammable organic liquid with petroleum like odour. Compound
P is insoluble in water and less dense than water.
Uses: formulation of glue and leather products.
Sebatian P mudah meruwap, cecair organik yang mudah terbakar dengan bau serupa petroleum.
Sebatian P tidak larut dalam air dan kurang tumpat daripada air.
Penggunaan: bahan untuk membuat pelekat dan bahan-bahan dari kulit.
Compound Q is a colourless, highly volatile, flammable organic liquid with petroleum-like odor. It
is insoluble in water and less dense than water.
Uses: solvent and chemical antiseptic.
Sebatian Q merupakan cecair tidak berwarna, mudah meruwap, cecair organik yang mudah
terbakar dengan bau serupa petroleum. Sebatian Q tidak larut dalam air dan kurang tumpat
daripada air.
Penggunaan: pelarut dan antiseptik kimia.
Compare and contrast these two hydrocarbons based on their structure formulae.
Banding dan bezakan kedua-dua hidrokarbon ini berdasarkan formula strukturnya. [4 marks]
(b) Table 8 shows the properties of four organic compounds. Each compound has three carbon
atoms per molecule.
Jadual 8 menunjukkan sifat empat sebatian organik. Setiap sebatian mempunyai tiga atom
karbon per molekul.
Organic compound Properties
Sebatian organik Sifat
W Miscible with water in all proportions. Burns with blue flame to form
carbon dioxide and water.
Larut campur dengan air dalam semua bahagian. Terbakar dengan
nyalaan biru menghasilkan karbon dioksida dan air.
X Low melting and boiling points. Insoluble in water but dissolve in
organic solvents. Does not undergoes halogenation reaction
Takat lebur dan didih yang rendah. Tidak larut dalam air tetapi larut
dalam pelarut organik. Tidak menjalankan tindak balas penghalogenan
Y Insoluble in water. Decolourises the purple colour of acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution.
Tidak larut dalam air. Menyahwarnakan warna ungu larutan kalium
manganat(VII) berasid.
Z Insoluble in water. Sweet smell.
Tidak larut. Berbau wangi.
Based on table, state the names for the homologous series for compounds W, X, Y and Z.
Berdasarkan jadual, nyatakan nama bagi siri homolog untuk sebatian W, X, Y and Z. [4 marks]
(c) Diagram 8.2 shows the conversion of an organic compound from one homologous series to
another.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan penukaran sebatian organik daripada satu siri homolog kepada yang
lain.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 3
(i) Based on Diagram 8.2
• Draw the structural formulae and state the names of compound A, compound B and ester C.
• Write the chemical equation to show the conversion of compound A to compound B.
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.2
• Lukiskan formula struktur dan nyatakan nama sebatian A, sebatian B dan ester C.
• Tuliskan persamaan kimia untuk menunjukkan penukaran sebatian A kepada sebatian B.
[8 marks]
(ii) Alkenes burnt completely in oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide gas. By using the
hydrocarbon in the diagram above, write a balanced chemical equation for the complete
combustion for that hydrocarbon. Calculate the percentage of carbon in the hydrocarbon.
Alkene terbakar secara lengkap dalam oksigen untuk menghasilkan air dan gas karbon dioksida.
Dengan menggunakan hidrokarbon dalam rajah di atas, tuliskan satu persamaan kimia lengkap
bagi pembakaran lengkap hidrokarbon tersebut. Hitung peratus karbon bagi hidrokarbon.
[ Relative atomic mass / Jisim atom relatif : C = 12 , H = 1 ] [4 marks]
F4: SALTS: KEDAH
3. Diagram 7.1 shows eight test tubes containing lead(II) chromate(VI) precipitate. The
experiment was carried out to construct an ionic equation for the formation of lead (II)
chromate(VI).
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan lapan tabung uji mengandungi mendakan plumbum(II) kromat(VI).
Eksperimen tersebut telah dijalankan untuk membina persamaan ion bagi pembentukan
plumbum(II) kromat(VI).
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 4
Eight test tubes of the same size were labelled 1 to 8.
A fixed volume of 5.0 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 potassium chromate(VI), K2CrO4 solution was placed
in each test tube.
1.0 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 solution X was added into test tube 1. 2.0 cm3 into test tube 2 and so on
until 8.0 cm3 was added into test tube 8.
The heights of the precipitate formed in each test tube were measured.
Lapan buah tabung yang sama saiz dilabelkan dengan 1 hingga 8.
Isipadu tetap 5.0 cm3 larutan kalium kromat(VI), K2CrO4 1.0 mol dm-3 dimasukkan dalam setiap
tabung uji.
1.0 cm3 larutan larutan X, 1.0 mol dm-3 ditambah ke dalam tabung uji 1. 2.0 cm3 ke dalam tabung
uji 2, dan seterusnya sehingga 8.0 cm3 ditambah ke dalam tabung uji 8.
Tinggi mendakan yang terbentuk dalam setiap tabung uji diukur.
The results are shown in Table 7.
Keputusan ditunjukkan dalam Jadual 7.
(a) Named solution X.
Based on Table 7, plot a graph of the height of the precipitate against volume of solution X on
the graph paper.
Namakan larutan X.
Berdasarkan Jadual 7, plotkan satu graf tinggi mendakan melawan isipadu larutan X pada kertas
graf.
[4 marks]
(b)(i) Identify the colourless solution above the precipitate in the test tube.
Determine the volume of solution X that had reacted completely with 5.0 cm3 of 1.0 moldm-3
potassium chromate(VI) solution.
Using the volume obtained, calculate the number of moles of lead (II) ions and chromate(VI)
ion that are required for the formation of lead(II) chromate(VI).
Kenalpasti larutan tidak berwarna di atas mendakan dalam tabung uji itu.
Tentukan isipadu larutan X yang telah bertindak balas lengkap dengan 5.0 cm3 larutan kalium
kromat(VI) 1.0 moldm-3.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 5
Dengan menggunakan isipadu yang diperolehi, hitungkan bilangan mol bagi ion plumbum(II) dan
ion kromat(VI) yang diperlukan untuk pembentukan plumbum(II) kromat(VI).
[4 marks]
(ii) Write the ionic equation for the formation of lead(II) chromate(VI).
Tulis persamaan ion bagi pembentukan plumbum(II) kromat(VI) [2 marks]
(c)
Based on Diagram 7.2:
Berdasarkan Rajah 7.2:
(i) Identify salt P, gas Q and R precipitate.
Kenal pasti garam P, gas Q dan mendakan R. [3 marks]
(ii) Write a chemical equation for the formation of R precipitate.
Tulis persamaan kimia bagi pembentukan mendakan R. [2 marks]
(iii) Copper(II) salt is a soluble salt. Describe briefly a chemical test to verify the cation and
anion present in aqueous solution of the salt.
Garam kuprum(II) adalah garam terlarutkan. Huraikan secara ringkas ujian kimia untuk
mengesahkan kehadiran kation dan anion yang hadir dalam larutan akueus garam tersebut.
[5 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 6
F5: REDOKS: KEDAH
4. Diagram 8.1 shows the change of ion of iron as a redox reaction.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan pertukaran ion bagi besi sebagai suatu tindak balas redoks.
(a) Based on the reaction in Diagram 8.1:
Berdasarkan tindak balas dalam Rajah 8.1:
(i) State the change in oxidation number of iron and bromine.
Nyatakan perubahan nombor pengoksidaan besi.dan bromin
(ii) State the role of bromine water
Nyatakan peranan air bromin
(iii) State the colour change of the solution
Nyatakan perubahan warna larutan tersebut [4 marks]
(b) One of the method used to prevent iron from corrosion is tin plating. Diagram 8.2 shows a
food can that is electroplated with tin.
Salah satu kaedah digunakan untuk menghalang besi daripada terkakis adalah penyaduran timah.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan satu tin makanan yang disadurkan dengan timah
Explain why food in a dented can should not be consumed.
Write the half equation for the reaction that occurs.
Terangkan mengapa makanan dalam tin yang kemek tidak boleh digunakan.
Tulis setengah persamaan bagi tindak balas yang terlibat. [6 marks]
(c) Diagram 8.3 shows the apparatus set-ups and observations for redox reaction involving
metal X.
Rajah 8.3 menunjukkan susunan radas dan pemerhatian bagi tindak balas redoks yang
melibatkan logam X.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 7
Set Set up of apparatus Observation
Susunan radas Pemerhatian
I Brown precipitate produce
Mendakan perang
terbentuk
II Pink colour formed
Warna merah jambu
terbentuk
Diagram 8.3 / Rajah 8.3
Based on the observations, suggest metal X and explain the observations in Set I and Set II
include the half-equation.
Berdasarkan pemerhatian, cadangkan logam X dan huraikan pemerhatian dalam Set I dan Set
II beserta dengan setengah persamaan. [10 marks]
F4: STRUKTUR ATOM: MRSM
5. Diagram 7.1 shows an article on Health Effects of Mothballs.
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan satu artikel berkaitan Kesan Kesihatan Ubat Gegat.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 8
(a)(i) Based on article shown in Diagram 7.1, mothballs are commonly used as the main
insecticide to repel cockroaches.
Name the process involved and explain how the mothballs vapour act as insecticide by using
Kinetic Theory of Matter.
Berdasarkan artikel dalam Rajah 7.1, ubat gegat kebiasaannya digunakan sebagai insektisid
untuk menghalau lipas.
Namakan proses yang terlibat dan terangkan bagaimana wap ubat gegat bertindak sebagai
insektisid menggunakan Teori Kinetik Jirim. [4 marks]
(ii) Solid mothballs melt into liquid when heated in water bath.
Diagram 7.2 shows the heating curve of the solid mothballs.
Pepejal ubat gegat melebur menjadi cecair apabila dipanaskan dalam kukus air.
Rajah 7.2 menunjukkan lengkungan pemanasan pepejal ubat gegat.
Based on Diagram 7.2, describe the curve from the region of P to Q and the region of R to S. In
your description include:
Berdasarkan Rajah 7.2, huraikan lengkung dari bahagian P ke Q dan dari bahagian R ke S.
Dalam huraian anda sertakan:
• state of matter
keadaan jirim
• movement of the particles
pergerakan zarah-zarah
• diagram of particles arrangement
gambarajah susunan zarah-zarah [6 marks]
(b) Diagram 7.3 shows subatomic particles in the nucleus of three carbon atoms.
Rajah 7.3 menunjukkan zarah subatom di dalam nukleus bagi tiga atom karbon.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 9
(i) What can be deduced from Diagram 7.3?
Explain your answer.
Apakah kesimpulan berdasarkan Rajah 7.3?
Terangkan jawapan anda. [2 marks]
(ii) Compare and contrast the three carbon atoms in terms of:
Banding dan bezakan ketiga –tiga atom tersebut dari segi:
• Number of proton
Bilangan proton
• Number of neutron
Bilangan neutron
• Number of electron
Bilangan elektron
• Physical properties
Sifat fizikal
• Chemical properties
Sifat kimia [5 marks]
(iii) Draw the atomic structure of carbon-14.
Lukiskan struktur atom bagi karbon-14. [3 marks]
F5: SALTS: MRSM
6. (a) Diagram 8.1 shows two methods of preparing salts in the laboratory.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan dua kaedah penyediaan garam-garam di dalam makmal
The following are three examples of salts that can be prepared using either Method I or Method
II.
Berikut adalah tiga contoh garam yang boleh disediakan sama ada menggunakan Kaedah I atau
Kaedah II.
Barium sulphate, BaSO4 Copper(II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2 Magnesium chloride, MgCl2
Barium sulfat, BaSO4 Kuprum(II) nitrat, Cu(NO3)2 Magnesium klorida, MgCl2
(ii) From the given examples, identify the salts that can be prepared by using the methods as
shown in Diagram 8.1.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 10
Daripada contoh-contoh yang diberikan, kenalpasti garam-garam yang boleh disediakan melalui
kaedah-kaedah seperti di dalam Rajah 8.1. [2 marks]
(ii) State the reactants for the preparation of salt in Method II.
Nyatakan bahan tindak balas bagi penyediaan garam dalam Kaedah II. [2 marks]
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows the graph of the height of precipitate against the volume of potassium
iodide solution used to construct the ionic equation for the formation of lead(II) iodide through
continuous variation method using 0.2 mol dm-3 potassium iodide solution and 5 cm3 of 0.1 mol
dm-3 salt P solution.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan graf tinggi mendakan melawan isipadu larutan kalium iodida yang
digunakan untuk membina persamaan ion bagi pembentukan plumbum(II) iodida melalui
kaedah perubahan berterusan menggunakan larutan kalium iodida 0.2 mol dm-3 dan 5 cm3
larutan garam P 0.1 mol dm-3.
(i) Name the salt P solution.
Namakan larutan garam P.[1 mark]
(ii) Based on Diagram 8.2 determine,
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.2 tentukan,
• the number of moles of Pb2+ ions and I ¯ ions that reacted completely in the reaction.
bilangan mol bagi ion Pb2+ dan ion I ¯ yang bertindak balas dengan lengkap dalam tindak balas
itu.
• the simplest mole ratio of Pb2+ ions to I ¯ ions in the reaction.
nisbah mol yang teringkas bagi ion Pb2+ kepada ion I ¯ dalam tindak balas itu.
• ionic equation for the reaction.
persamaan ion bagi tindak balas itu [5 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 11
(c) Diagram 8.3 shows the reaction scheme of white solid W.
Rajah 8.3 menunjukkan tindak balas bagi pepejal putih W.
Based on diagram 8.3
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.3
(i) Identify substances V, W, Y and Z
Kenalpasti bahan V, W, Y, dan Z [4 marks]
(ii) Describe a chemical test to verify the cation and anion in solution Y.
Huraikan ujian kimia untuk mengesahkan kehadiran kation dan anion di dalam larutan Y.
[6 marks]
F4: ELECTROCHEMISTRY: PERLIS
7. (a) A group of students carry out an electrolysis of ethanoic acid solution, CH3COOH by
using carbon electrodes.
Sekumpulan pelajar menjalankan suatu elektrolisis larutan asid etanoik, CH3COOH,
menggunakan elektrod karbon.
By using your knowledge of factors affecting the selective discharge of ions at the electrodes,
Dengan menggunakan pengetahuan anda tentang faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi pemilihan
ion untuk dinyahcaskan di elektrod,
(i) Identify the ion that is selectively discharge at anode and cathode.
Kenal pasti ion yang dipilih menyahcas di anod dan katod.
(ii) Write half equation for the reactions occurred at anode and cathode.
Tuliskan persamaan setengah yang berlaku di anod dan katod.
(iii) Describe a chemical test to verify the product formed at cathode.
Huraikan satu ujian kimia bagi mengesahkan hasil yang terbentuk di katod.
[6 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 12
(b) Table 3.1 shows the apparatus set-up to electroplate iron spoon.
Jadual 3.1 menunjukkan susunan radas bagi menyadurkan sudu besi.
Observation on
iron spoon
Set Apparatus set up
Pemerhatian
Set Susunan radas
terhadap sudu
besi
A
A shiny grey solid
Silver Iron spoon deposited
Sudu besi Pepejal kelabu
I Argentum
berkilat terenap
Silver nitrate
solution
Larutan
argentum nitrat
Silver
Iron spoon Argentum No changes
II Sudu besi Tiada perubahan
Silver nitrate
solution
Larutan
argentum nitrat
Table 3.1 / Jadual 3.1
Based on the observation in Table 3.1, explain the differences in Set I and Set II.
Berdasarkan pemerhatian dalam Jadual 3.1, terangkan mengapa terdapat
perbezaan dalam Set I dan Set II.
[4 marks]
(c) Table 3.2 shows the apparatus set-up and observation for four different of cells using
1.0 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulphate solution
Jadual 3.2 menunjukkan susunan radas dan pemerhatian bagi empat sel yang
berbeza menggunakan larutan kuprum(II) sulfat 1.0 mol dm-3.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 13
Cell Set up of apparatus Susunan Observation
Sel radas Pemerhatian
I Anode:
A
Anod:
Bubbles of gas released
Gelembung-gelembung
C arbon
C arbon gas terbebas
Karbon
Karbon Electrolyte:
Elektrolit:
Copper(II) sulphate
solution The intensity of blue
Larutan kuprum ( II) colour of copper(II)
sulphate solution
sulfat
decreases Keamatan
warna biru larutan
kuprum(II) sulfat
berkurang
II
Anode :
A
Anod :
Copper plate becomes
thinner
Copper
Copper Kepingan kuprum menipis
Kuprum
Kuprum
Electrolyte:
Copper(II) su lphate Elektrolit:
solution The intensity of blue
Larutan kuprum ( II ) colour of copper(II)
sulfat sulphate solution remain
Keamatan warna biru
larutan kuprum(II) sulfat
kekal
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 14
III Anode:
Anod:
V
Magnesium plate
becomes thinner
Kepingan magnesium
Copper menipis
Mag nesium Kuprum
Mag n esium Electrolyte:
Elektrolit:
Copper(II) sulphate The intensity of blue
colour of copper(II)
solution
sulphate solution
Larutan kuprum ( II )
decreases
sulfat
Keamatan warna biru
larutan kuprum(II) sulfat
berkurang
Anode:
IV V Anod:
Copper plate becomes
thinner
Copper Kepingan kuprum menipis
Silver Kuprum
Argentum Electrolytes :
Elektrolit:
Copper(II) The intensity of blue
sulphate solution colour of copper(II)
Larutan sulphate solution
kuprum ( II ) sulfat increases
Keamatan warna biru
larutan kuprum(II) sulfat
bertambah
Table 3.2 / Jadual 3.2
Based on Table 3.2:
Berdasarkan Jadual 3.2:
Explain why there are differences in the observation between
Terangkan mengapa terdapat perbezaan pemerhatian di antara
(i) Cell I and Cell II
Sel I dan Sel II
(ii) Cell III and Cell IV
Sel III dan Sell IV [10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 15
F5: REDOX: PERLIS
8 (a) Diagram 7 shows the apparatus set-up and the observations of three sets of the
experiments to study the displacement of halogen. The products formed are then added
with 1,1,1-trichloroethane.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan susunan radas dan pemerhatian bagi tiga set eksperimen untuk
mengkaji penyesaran halogen. Kemudian, hasil yang terbentuk ditambah dengan
1,1,1-trikloroetana.
Set
I II III
Set
Y 2 water Y 2 water Z 2 water
Air Y 2 Air Y 2 Air Z 2
KX solution KZ solution KY solution
Larutan KX Larutan KZ Larutan KY
Colourless solution turns No change. Forms a Colourless solution turns
brown. The product layer of brown colour in brown. The product
forms a layer of purple 1,1,1-trichloroethane. forms a layer of brown
colour in 1,1,1- Tiada perubahan. colour in 1,1,1-
trichloroethane. Membentuk lapisan trichloroethane.
Larutan tidak berwarna berwarna perang dalam Larutan tidak berwarna
menjadi perang. Hasil 1,1,1trikloroetana. menjadi perang. Hasil
membentuk lapisan membentuk lapisan
berwarna ungu dalam berwarna perang dalam
1,1,1-trikloroetana. 1,1,1trikloroetana.
Diagram 7 / Rajah 7
(i) State the name of halogen X, halogen Y and halogen Z.
Nyatakan nama bagi halogenX, halogen Y dan halogen Z.
Arrange X, Y and Z in descending order of their reactivity.
Susun X, Y dan Z dalam tertib kereaktifan menurun. [4 marks]
(ii) By using the reaction in set I, explain the meaning of redox reaction in terms
of the oxidation number. Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Dengan menggunakan tindak balas dalam set I, terangkan maksud tindak
balas redoks dari segi nombor pengoksidaan. Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi
tindak balas itu. [5 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 16
(b) Table 4 shows the results of two experiments to study the effects of metals P and Q
on the rusting of iron.
Jadual 4 menunjukkan keputusan bagi dua eksperimen untuk mengkaji kesan
logam P dan logam Q terhadap pengaratan besi.
Experiment Observation
Eksperimen Pemerhatian
I Hot agar solution containing
potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
and phenolphthalein
Larutan agar-agar panas
mengandungi larutan kalium Dark blue spots formed.
heksasianoferat(III) dan Tompok biru tua
fenolftalein terbentuk.
Iron nail
Paku besi
Metal P
Logam P
II Hot agar solution containing
potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
and phenolphthalein
Larutan agar-agar panas Pink colour formed.
mengandungi larutan kalium Warna merah jambu
heksasianoferat(III) dan terbentuk.
fenolftalein
Iron nail
Paku besi
Metal Q
Logam Q
Table 4 / Jadual 4
(i) Explain why there is a difference in observations in both experiments and
include the half equations.
Terangkan mengapa terdapat perbezaan pemerhatian dalam kedua-dua
eksperiment dan sertakan setengah persamaan. [8 marks]
(ii) State the metal that is oxidised in both experiments.
Nyatakan logam yang dioksidakan dalam kedua-dua eksperimen.
Arrange in descending order metals P, Q and iron based on the
electropositivity of the metals.
Susunkan secara menurun logam P, logam Q dan besi berdasarkan
keelektropositifan logam. [3 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 17
F5: RATE OF REACTION: TERENGGANU
9 (a) Food stored in a refrigerator last longer than food stored in a kitchen cabinet.
Explain why.
Makanan yang disimpan di dalam peti sejuk tahan lebih lama daripada makanan
yang disimpan dalam kabinet dapur. Terangkan mengapa.
[4 marks]
(b) Table 7 shows the information for three sets of experiment to investigate factors
affecting the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid.
Jadual 7 menunjukkan maklumat bagi tiga set eksperimen untuk menyiasat faktor-
faktor yang mempengaruhi kadar tindak balas antara kalsium karbonat dengan asid
hidroklorik.
Time taken to collect
40 cm3 of carbon
dioxide gas (s)
Experiment Reactants Masa yang diambil
Eksperimen Bahan tindak balas untuk mengumpul 40
cm3 gas karbon
dioksida (s)
50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3
Excess calcium
hydrochloric acid
Set I Carbonate powder 33
50 cm3 asid hidroklorik
Serbuk kalsium
1.0 mol dm-3
karbonat berlebihan
50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3
Excess calcium
hydrochloric acid
Set II carbonate chip 45
50 cm3 asid hidroklorik
Ketulan kalsium
1.0 mol dm-3
karbonat berlebihan
25 cm3 of 2.0 mol dm-3
Excess calcium
hydrochloric acid
Set III carbonate powder 25
25 cm3 asid hidroklorik
Serbuk kalsium
2.0 mol dm-3
karbonat berlebihan
Table 7 / Jadual 7
(i) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between calcium carbonate and
hydrochloric acid.
Calculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gas produced in Set I.
[Given that the molar volume of gas is 24 dm3 mol-1 at room conditions]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 18
Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas antara kalsium karbonat dengan
asid hidroklorik. Hitungkan isipadu maksimum bagi gas karbon dioksida yang
terhasil dalam Set I.
[Diberi isipadu molar bagi gas ialah 24 dm3 mol-1 pada keadaan bilik] [5 marks]
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction for Set II.
Hitungkan kadar tindak balas purata bagi Set II. [1 mark]
(iii) Based on the information in Table 7, compare the rate of reaction between
• Set I and Set II
• Set I and Set III
By using the collision theory, explain your answers.
Berdasarkan maklumat dalam Jadual 7, bandingkan kadar tindak balas antara
• Set I dan Set II
• Set I dan Set III
Dengan menggunakan teori perlanggaran, terangkan jawapan anda.
[10 marks]
F5: REDOX: TERENGGANU
10. (a) Diagram 8 shows the apparatus set-up for redox reactions involving electron
transfer at a distance.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan susunan radas bagi tindak balas redoks yang melibatkan
pemindahan elektron pada satu jarak.
Based on Diagram 8, explain how the transfer of electron occurred.
In your description state the substance that undergoes oxidation and reduction.
Berdasarkan Rajah 8, terangkan bagaimana pemindahan elektron itu berlaku.
Dalam penerangan anda nyatakan bahan yang mengalami pengoksidaan dan
penurunan. [4 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 19
(b) The Prime Minister of Malaysia, YAB Tun Dr.Mahathir Bin Mohamad had visited to
Japan on 10-12 June 2018. In his visit, he has suggested to produce national car
2.0.
You are selected to work at the car factory.
Suggest the way to control the rusting and give a reason for your answer of the
following parts of cars:
• Gear and engine
• Car body
• Tire rim
Perdana Menteri Malaysia, YAB Tun Dr. Mahathir Bin Mohamad telah membuat
lawatan ke negara Jepun pada 10-12 Jun 2018. Dalam lawatan itu beliau telah
mencadangkan untuk mengeluarkan kereta nasional 2.0.
Anda telah dipilih untuk bekerja di kilang kereta itu.
Cadangkan cara untuk mengawal pengaratan dan berikan satu sebab bagi jawapan
anda pada bahagian-bahagian kereta berikut:
• Gear dan enjin
• Badan kereta
• Rim tayar [6 marks]
(c) Table 8 shows the apparatus set-up and observation of two set of experiments, Set
I and Set II for the reaction between metal X and metal Y with copper(II) oxide.
Jadual 8 menunjukkan susunan radas dan pemerhatian dua set eksperimen, Set I
dan Set II bagi tindak balas antara logam X dan logam Y dengan kuprum(II)
oksida.
Apparatus set up Observation
Set
Susunan radas Pemerhatian
Mixture of metal X and A glow spreads to the whole
copper(II) oxide. mixture.Black solid change
Campuran logam X dan to brown solid.
Kuprum(II) oksida
I Baraan merebak ke
seluruhan campuran.
Pepejal hitam bertukar ke
pepejal perang
II Mixture of metal Y and
copper(II) oxide. No change
Campuran logam Y Tiada perubahan
dan Kuprum(II) oksida
Table 8 / Jadual 8
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 20
Suggest metal X and metal Y.
Explain the observation for set I and set II. In your answer state
• the substance that is oxidised
• the substance that is reduced
• oxidising agent and reducing
• change in oxidation number of copper.
Cadangkan logam X dan logam Y.
Terangkan pemerhatian bagi set I dan set II. Dalam jawapan anda nyatakan
• bahan yang dioksidakan
• bahan yang diturunkan
• agen pengoksidaan dan agen penurunan.
• perubahan nombor pengoksidaan kuprum. [10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 21
BAHAGIAN C
F4: SALT: JOHOR SET 1
1. Salts played an important part of human life. Salts is used in many areas such as fertilizers in
agricultural, painting, industry, medicine and cooking.
Garam memainkan peranan penting dalam kehidupan manusia. Garam digunakan dalam pelbagai
bidang seperti baja dalam pertanian, mengecat. industry, perubatan dan memasak.
(a) Explain what is meant by salt.
Terangkan apa yang di maksudkan dengan garam.
[2 marks]
(b) Describe how you can prepare a sample of magnesium carbonate from magnesium oxide
Huraikan bagaimana anda dapat menyediakan satu sampel garam magnesium karbonat dari
magnesium oksida
[10 marks]
2+ 2+ 2+ 3+
(c) You are given four solutions containing Zn , Pb , Mg and Al ions in different unlabeled
beakers. Describe how you carry out analysis to differentiate the ions in each solution.
Anda dibekalkan empat larutan yang mengandungi ion Zn2+, Pb2+, Mg2+ dan Al 3+ dalam bikar
berlainan yang tidak di label. Huraikan bagaimana anda menjalankan analisis untuk
mengenalpasti ion dalam setiap larutan.
[8 marks]
F5: REDOKS: JOHOR SET 1
2. (a) Diagram 10 shows two electrolytic cells of A and B.
Rajah 10 menunjukkan dua sel elektrolitik A dan B
Compare and contrast the reactions in Cell A and Cell B.
Your answer should include observation, half equation and redox reactions at anode electrode.
Banding dan bezakan tindak balas dalam Sel A dan Sel B.
Jawapan anda hendaklah mengandungi pemerhatian, setengah persamaan dan tindak balas
redoks yang berlaku pada elektrod anod.
[10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 22
(b)
The displacement of iodine, I2 from potassium iodide, KI
solution by halogen Y is a redox reaction.
Penyesaran iodin, I2 daripada larutan kalium iodida oleh halogen Y
adalah tindak balas redoks.
Based on the above statement, design an experiment to verify the reaction that occurred is a
redox reaction. In your description, include the following.
Berdasarkan penytaan di atas, rancangkan satu eksperimen untuk mengesahkan bahawa tindak
balas yang berlaku adalah tindak balas redoks. Dalam penerangan anda, sertakan yang berikut
• Name of suitable halogen Y
Nama halogen Y yang sesuai
• Procedure
Prosedur
• Test to identify the ion that is produced
Ujian untuk mengenalpasti ion yang terhasil
• Explanation on oxidation and reduction process
Penerangan berkaitan proses pengoksidaan dan penurunan
• Ionic equations
Persamaan ion
[10 marks]
F4: ACIDS AND BASES / SALT: KEDAH
3. Diagram 9.1 shows a jelly fish.
Rajah 9.1 menunjukkan seekor obor-obor
(a) The sting of a jelly-fish is alkaline and can cause pain. Suggest one substance that can be
applied to the skin to relieve the pain without causing further injury. Give three reasons for your
suggestion.
Sengatan obor-obor adalah beralkali dan boleh menyebabkan kesakitan. Cadangkan satu bahan
yang boleh disapu pada kulit untuk mengurangkan rasa sakit tanpa menyebabkan kecederaan
yang seterusnya. Beri tiga sebab bagi cadangan anda. [4 marks]
(b) Table 9.2 shows information about of acid P and acid Q
Jadual 9.2 menunjukkan maklumat tentang asid P dan asid Q.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 23
Acid P Q
Asid
Uses of acid
Kegunaan asid
pH value 5 1
Nilai pH
Table 9.2 / Jadual 9.2
By naming an example for each acid, explain why the pH values are different.
Dengan menamakan satu contoh bagi setiap asid, terangkan mengapa nilai pH adalah berbeza.
[6 marks]
(c) Diagram 9.3 shows a dry zinc sulphate salt.
Rajah 9.3 menunjukkan garam zink sulfat kering.
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
Zinc sulphate salt can be prepared by adding solid X into acid Y solution. Suggest a suitable
solid X and acid Y.
Describe how you can prepare a dry zinc sulphate salt by using solid X and acid Y.
Garam zink sulfat boleh disediakan dengan menambahkan pepejal X ke dalam larutan asid Y.
Cadangkan pepejal X dan larutan asid Y yang digunakan.
Huraikan bagaimana anda dapat menyediakan garam zink sulfat yang kering dengan
menggunakan pepejal X dan larutan asid Y. [10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 24
F5: CARBON COMPOUNDS: KEDAH
4. Diagram 10.1 shows the conversion of few carbon compounds with less than four carbon
atoms.
Rajah 10.1 menunjukkan penukaran beberapa sebatian karbon yang mempunyai atom karbon
kurang daripada empat.
(a) Based on Diagram 10.1:
Berdasarkan Rajah 10.1:
(i) Identify reaction I, reaction II and homologous series of compound P.
Kenalpasti tindak balas I, tindak balas II dan siri homolog bagi sebatian P.
(ii) By using suitable number of carbon atom, draw the structural formula of compound P,
carboxylic acid Q and alkene W.
Dengan menggunakan bilangan atom karbon yang sesuai, lukiskan formula struktur bagi
sebatian P, asid karbosilik Q dan alkena W. [6 marks]
(iii) By using compound P and alkene W that obtained in 10(a)(ii), describe how to conduct
reaction II in the laboratory. In your description, include:
Labeled diagram
Procedure
Chemical equation
Chemical test to proof the product
Dengan menggunakan sebatian P dan alkena W yang diperolehi di 10(a)(ii), huraikan
bagaimana tindak balas II dijalankan dalam makmal. Dalam huraian anda, sertakan:
Gambar rajah berlabel
Prosedur
Persamaan kimia
Ujian kimia untuk mengesahkan hasil tindak balas [10 marks]
(b) Diagram 10.2 shows a product of uses of an example of carboxylic acid.
Rajah 10.2 menunjukkan suatu produk daripada kegunaan sejenis asid karbosilik
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 25
Suggest the carboxylic acid and a reagent that can be used to produce carboxylic acid Q from
compound P. Write the chemical equation involved in this conversion.
Cadangkan nama asid karboksilik tersebut. Nyatakan suatu bahan yang boleh digunakan untuk
menghasilkan asid ini. Tulis persamaan kimia yang terlibat. [4 marks]
F5: CARBON COMPOUNDS: KELANTAN
5. (a) Edham telah diarahkan oleh gurunya supaya menjalankan ujian ke atas dua jenis
hidrokarbon yang mempunyai kumpulan berfungsi yang berbeza iaitu sebatian hidrokarbon X dan
Y. Sehubungan dengan itu, beliau telah menjalankan tiga tindak balas untuk membezakan sifat
kimia bagi dua hidrokarbon tersebut.
Jadual 9.1 menunjukkan pemerhatian hasil daripada ujian yang telah dijalankan.
Tindak balas Pemerhatian
Hidrokarbon X Hidrokarbon Y
Pembakaran Nyalaan kuning lebih berjelaga Nyalaan kuning berjelaga
Penambahan air bromin Warna perang air bromin Warna perang air bromin
menjadi tidak berwarna kekal tidak berubah
Penambahan larutan Warna ungu larutan kalium Warna ungu larutan kalium
kalium manganat(VII) manganat(VII) berasid manganat(VII) berasid kekal
berasid menjadi tidak berubah
tidak berwarna
(i) Berdasarkan maklumat dalam Rajah 9.1, sebatian X dan Y masing-masing mempunyai enam
atom karbon, cadangkan sebatian X dan sebatian Y.
Nyatakan formula molekul sebatian X dan sebatian Y seterusnya lukis formula struktur bagi
kedua-dua sebatian X dan Y. [6 markah]
(ii) Pembakaran sebatian X menghasilkan lebih banyak jelaga berbanding sebatian X. Jelaskan.
[ Jisim Atom Relatif : H = 1C = 12 ] [4 markah]
(b) Faqihah sangat menggemari kuih traditional iaitu tapai pulut. Pada suatu hari, Faqihah
meminta ibunya menyediakan makanan tersebut untuk jamuan hari raya di sekolahnya.
Berdasarkan situasi itu, nyatakan nama tindak balas yang berlaku bagi menyediakan kuih
tradisional itu.
Sebagai seorang murid, huraikan penyediaan etanol dalam makmal sekolah yang
mengandungi perkara yang berikut:
(i) senarai bahan
(ii) susunan radas
(ii) prosedur
(iii) persamaan tindak balas [10 markah]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 26
F5: THERMOCHEMISTRY: KELANTAN
6. (a) Sekumpulan murid menjalankan eksperimen untuk menentukan haba pembakaran
propanol. Didapati 0.60 g propanol terbakar lengkap dan haba yang terbebas digunakan untuk
memanaskan 200 cm3 air. Haba pembakaran propanol, C3H7OH ialah – 2017 kJmol-1
[ muatan haba tentu = 4.2 Jg-1 ºC-1, Jisim atom relatif : H = 1, C = 12, O = 16 ]
Hitung kenaikkan suhu air dan lukis gambar rajah aras tenaga bagi pembakaran propanol.
[6 markah]
(b) Butana, C4H10 merupakan gas yang digunakan untuk memasak. Manakala petrol pula
mengandungi oktana, C8H18 digunakan sebagai bahan api bagi kereta. Carta bar dalam Rajah
10.1 menunjukkan nilai haba pembakaran bagi butana dan oktana.
Berdasarkan rajah 10.1, terangkan perbezaan nilai haba pembakaran bagi butana dan oktana.
[4 markah]
(c) Bioetanol (C2H5OH) merupakan salah satu bahan bakar alternatif yang lebih mesra alam dan
mudah diperoleh dari tumbuhan seperti pokok tebu dan ubi kayu.
Rajah 10.2 menunjukkan bioetanol digunakan sebagai bahan api.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 27
Huraikan satu eksperimen untuk menentukan haba pembakaran bioetanol.
Huraian anda haruslah mengandungi prosedur dan langkah pengiraan.
[Jisim atom relatif : H = 1, C = 12]
[ Muatan haba tentu larutan = 4.2 J g-1 ⁰C-1] [10 markah]
F4: CHEMICAL BONDS: MRSM
7. Diagram 9.1 shows the three element cards, X, Y and Z. X and Y can react with Z to form
different type of compounds.
Gambarajah 9.1 menunjukan tiga kad unsur, X, Y dan Z. X dan Y boleh bertindakbalas dengan
Z membentuk sebatian yang berbeza.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 28
(a)(i) Write the electron arrangement of atoms X, Y and Z.
Tuliskan susunan elektron bagi atom-atom X, Y dan Z. [3 marks]
(ii) Based on Diagram 9.1, suggest any two suitable elements that can react to form a
compound.
State the type of bond formed and explain the formation of the compound.
Berdasarkan Rajah 9.1, cadangkan dua unsur yang sesuai bertindak balas membentuk suatu
sebatian.
Nyatakan jenis ikatan yang terbentuk dan terangkan pembentukan sebatian tersebut.[7 marks]
(b) Diagram 9.2 shows the arrangement of particle for two types of compound.
Rajah 9.2 menunjukkan susunan zarah dua jenis sebatian.
Describe an experiment to differentiate the compounds based on:
Huraikan eksperimen untuk membezakan kedua-dua sebatian tersebut
berdasarkan:
• solubility in water
keterlarutan di dalam air
• melting point or boiling point
takat lebur atau takat didih.
In your description include:
Huraian anda haruslah mengandungi perkara berikut:
• Example of compound T and compound V
Contoh sebatian T dan sebatian V
• Procedure of experiment
Kaedah ekperimen
• Observation
Pemerhatian
• Conclusion
Kesimpulan [10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 29
8. Diagram 10.1 shows the information about complete combustion of methane.
Rajah 10.1 menunjukkan maklumat berkenaan pembakaran lengkap metana
ENERGY PROFILE DIAGRAM
RAJAH PROFIL TENAGA:
THERMOCHEMICAL EQUATION
PERSAMAAN TERMOKIMIA:
(a) Based on Diagram 10.1, verify the heat of combustion of methane by using the following
formula, Energy change, ΔH = Ex - Ey and identify the type of reaction.
Berdasarkan Rajah 10.1, tentusahkan haba pembakaran metana menggunakan formula,
Perubahan tenaga, ΔH = Ex - Ey dan kenalpasti jenis tindak balas tersebut. [4 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 30
(b) Diagram 10.2 shows the cross section of apparatus set-up for two sets of experiment to
determine the heat of reaction.
Rajah 10.2 menunjukkan keratan rentas susunan radas bagi dua set ekperimen untuk
menentukan haba tindakbalas
(ii) Based on Diagram 10.2, compare Set I and Set II in terms of:
Berdasarkan Rajah 10.2, bandingkan antara Set I dan Set II dari segi:
• Heat change in the reaction
Perubahan tenaga haba dalam tindakbalas
• Change in total energy content of reactants and total energy content of products
Perubahan jumlah kandungan tenaga bagi bahan tindakbalas dan hasil tindakbalas.[2 marks]
(ii) Hydrochloric acid in Set I is replaced with 100 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 of copper(II) sulphate
solution. The initial temperature of solution recorded is 28.0 °C and the highest temperature of
the mixture is 40.0 °C.
Calculate the heat of reaction in this experiment.
[Specific heat capacity of solution, c = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1]
Asid hidroklorik didalam Set I digantikan dengan 100 cm3larutan kuprum(II) sulfat 1.0 mol dm-3.
Suhu awal larutan direkodkan adalah 28.0 °C dan suhu tertinggi campuran adalah 40.0 °C.
Hitung haba tindakbalas bagi eksperimen ini.
[Muatan haba tentu bagi air, c = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1] [4 marks]
(c) A student carried out an experiment to determine the heat of precipitation of zinc carbonate.
Describe an experiment to determine the heat of precipitation of zinc carbonate.
Your answer should include the following:
Seorang pelajar menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk menentukan haba pemendakan zink
karbonat.
Huraikan eksperimen untuk menentukan haba pemendakan zink karbonat.
Jawapan anda perlu mengandungi perkara berikut:
• Suggest the suitable reactants required
Cadangkan bahan tindak balas yang sesuai
• Procedure
Prosedur
• Chemical equation
Persamaan kimia [10 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 31
9 The following equation represents the reaction between magnesium and acid P. Acid P is
a monoprotic acid.
Persamaan berikut mewakili tindak balas antara magnesium dengan asid P. Asid P
adalah asid monobes.
Mg + Acid P → Salt Q + H2
Mg + Asid P → Garam Q + H2
Based on the equation,
Berdasarkan persamaan itu,
(a) (i) Suggest acid P and identify salt Q.
Cadangkan asid P dan kenal pasti garam Q. [2 marks]
(ii) From your answer in 9(a)(i) , write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Daripada jawapan anda di 9(a)(i) , tulis persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas itu.
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 8 shows a flow chart of magnesium salts.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan carta alir bagi garam magnesium
MgSO 4
+ Solution R
Lauran R Salt
MgCl 2
MgCO 3 + Garam
Reaction I
Mg(NO 3) 2 Tindak balas I
Reaction II + Acid W
Tindak balas II + Asid W
Magnesium salt
Garam magnesium
Diagram 8 / Rajah 8
All the three salts, MgSO4, MgCl2 and Mg(NO3)2 in Diagram 8 can be converted to MgCO3
by reaction I, then MgCO3 reacts with acid W to form a Magnesium salt through
reaction II.
Ketiga-tiga garam, MgSO4, MgCl2 dan Mg(NO3)2 dalam Rajah 8 boleh ditukar kepada
MgCO3 melalui tindak balas I, kemudian MgCO3 bertindak balas dengan asid W
membentuk satu garam magnesium melalui tindak balas II.
(i) By choosing one of the three salts in Diagram 8, suggest solution R to prepare
magnesium carbonate, MgCO3.
Write the chemical equation involved and describe a laboratory experiment to
prepare magnesium carbonate, MgCO3.
Dengan memilih satu garam di Rajah 8, cadangkan larutan R untuk menyediakan
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 32
magnesium karbonat, MgCO3.
Tulis persamaan kimia yang terlibat dan huraikan eksperimen makmal untuk
menyediakan magnesium karbonat, MgCO3. [8 marks]
(ii) Suggest acid W to prepare any one of the three magnesium salt in Diagram 8.
Write a chemical equation involved and describe a laboratory experiment to
prepare the salt.
Cadangkan asid W untuk menyediakan salah satu daripada tiga garam
magnesium di Rajah 8.
Tulis persamaan kimia yang terlibat dan huraikan eksperimen makmal untuk
menyediakan garam itu. [8 marks]
10. Mr. Ali is a rubber plantation entrepreneur. Rubber factory A wants to buy latex in liquid
form while rubber factory B wants to buy latex in solid form to produce tyres.
En. Ali adalah seorang pengusaha ladang getah. Kilang getah A mahu membeli lateks
dalam bentuk cecair manakala kilang getah B mahu membeli lateks dalam bentuk
pepejal untuk pembuatan tayar.
Diagram 9 shows a flow chart to prepare the rubber for rubber factory A and rubber factory
B by Mr. Ali.
Rajah 9 menunjukkan carta alir untuk menyediakan getah bagi kilang getah A dan kilang
getah B oleh En. Ali.
(a) (i) Based on the Diagram 9, suggest solution X, solution Y and process Z.
Berdasarkan Rajah 9, cadangkan larutan X, larutan Y dan proses Z. [3 marks]
(ii) Explain
Terangkan
1. why physical state of latex different when solution X and solution Y are added into
fresh latex.
kenapa keadaan fizikal lateks berbeza apabila larutan X dan larutan Y ditambahkan
ke dalam lateks segar.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 33
2. how process Z can increase the elasticity of natural rubber.
bagaimana proses Z boleh meningkatkan kekenyalan getah asli.
[9 marks]
(b)
Vulcanised rubber is more elastic than natural rubber.
Getah tervulkan lebih kenyal daripada getah asli.
Describe an experiment to verify the above statement by listing the materials and
apparatus.
Huraikan satu eksperimen untuk menentusahkan pernyataan di atas dengan
menyenaraikan bahan dan radas. [8 marks]
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 34
BAHAGIAN B
1. (a) Ionic : P and R Covalent : Q and R
(b) P and R
1. Electron arrangement of P atom is 2.8.2 and R atom is 2.6
2. To achieve stable octet electron arrangement
3. P atom donates 2 electrons to form P2+ // P à P2+ + 2e
4. R atom receives 2 electrons to form R2- // R + 2e à R2-
5. P2+ and R2- are attracted to each other with strong electrostatic forces of attraction to form
ionic compound with formula PR
6.
Q and R
1. Electron arrangement of Q atom is 2.4 and R atom is 2.6
2. To achieve stable octet electron arrangement
3. Q atom contributes 4 electrons for sharing and R atom contributes 2 electrons for sharing
4. One Q atom and two R atoms share electrons
5. A compound with the formula QR2 is formed
6.
(c)
Properties Ionic compound Covalent compound
Melting point and High Low
boiling point
Explanation Positive and negative ions are Molecules are attracted by weak
attracted by strong electrostatic intermolecular forces / van der
forces of attraction. Waals forces.
More heat energy is required to Less heat energy is required to
overcome the strong forces overcome the weak forces
Electrical Can conduct electricity in molten Cannot conduct electricity in any
conductivity and aqueous state state
Explanation There are free moving ions which Exist as molecules, no ion present
can carry electrical charges to carry electrical charges
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 35
2. (a) 1. P and Q have 6 carbon atoms.
2. P is an unsaturated hydrocarbon (alkenes) which has a double bond.
3. Q is saturated hydrocarbon (alkane) with single bond only.
4. P has 14 hydrogen atoms & Q has 12 hydrogen atoms
(b) W = Alcohol X = Alkanes Y = Alkenes Z = Ester
(c)(i) Structured formula for compound A = CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Name A = Butanol
Structured formula for compound B = CH3CH2CH2COOH
Name B = Butanoic acid
Structured formula for Ester C = CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH2CH2CH3
Name ester C = Butyl butanoate
C4H9OH + 2[O] → C3H7COOH + H2O
Correct chemical formula for reactants and products
Balanced chemical equation
(ii) C4H8 + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 4H2O
Correct chemical formula for reactants and products
Balanced chemical equation
Percentage of carbon C4H8
= 4(12) / [ 4(12) + 8(1) ] x 100%
= [ 48 / 56 ] x 100%
= 85.7%
3. (a) 1. Lead (II) nitrate
Graph:
2. Correct axis with unit
3. Correct and Smooth line
4. Correct scale
(b)(i) 1. Potassium nitrate
2. Volume of Pb(NO3)2 = 5 cm3
3. No of mole Lead(II) ion = 1 x 5 // 0.005
1000
4. No of mole Chromate(VI) ion = 1 x 5 // 0.005
1000
(ii) Pb2+ + CrO42- → PbCrO4
1. Correct formulae of reactants and product
2. Balanced chemical equation
(c)(i) 1. Salt P = Copper(II) carbonate / CuCO3
2. Gas Q = Carbon dioxide
3. R precipitate = Calcium sulphate
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 36
(ii) CuSO4 + Ca(NO3)2 → CaSO4 + Cu(NO3)2
1. Correct formulae of reactants and products
2. Balanced chemical equation
(iii) Confirmatory test for cation:
1. Add ammonia// sodium hydroxide solution until excess
2. Blue precipitate formed dissolves in excess ammonia to
produce dark blue solution // blue precipitate does not dissolve
in excess NaOH indicates the presence of Cu2+ ion.
Confirmatory test for anion:
3. Add hydrochloric acid.
4. Add barium chloride solution.
5. White precipitate formed indicate the presence of SO42- ion
4. (a) 1. Change in oxidation number of iron is +2 to +3
2. Change in oxidation number of bromine 0 to -1
3. Bromine water as oxidizing agent
4. Green solution turns brown solution
(b) 1. When food can dent, the tin plate is crack and form small hole and the ion is exposed.
2. Iron atom will donates/releases 2 electrons to form iron(II) ions
3. Fe → Fe2+ + 2e
4. In food can also have water and some oxygen gas. The water and oxygen gas gain electron
to formed hydroxide ion
5. Iron(II) ion will combine with hydroxide ion to form iron(II) hydroxide.
6. Fe2+ + 2OH- → Fe(OH)2
7. Fe(OH)3 are oxidized by oxygen to form brown solid which is iron(III) oxide /rust.
(c) 1. Metal X is Mg/ Zn / Al
Set I
2. Metal X more electropositive than copper
3. X is oxidized // X atom loses electron to form X2+
X → X2+ + 2e
4. Cu2+ is reduced / receives electrons to form copper atom
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu
5. Brown precipitate formed is copper
Set II
6. Metal X more electropositive than iron
7. Rusting does not occur
8. X is oxidized / X atom loses electron to form X2+
X → X2+ + 2e
9. Oxygen and water is reduced /receive electron to form OH ¯ ion / O2 + 2H2O + 4e → 4OH ¯
10. Pink colour shows the presence of OH ¯
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 37
5. (a)(i) P1. Diffusion
P2. The mothballs vapour particles/molecules are tiny and discrete
P3. which move freely/randomly in between the air particles/molecules
P4. From the higher concentration area/region to the lower concentration area/region
(ii)
(b)(i) P1. Atoms are isotopes
P2. Atoms have the same number of proton but different number of neutron
adp: atoms for P2
a: Atoms have the same proton number but different nucleon number
(ii)
a: any specific chemical reaction of carbon.
Eg: Carbon reacts with oxygen produces carbon dioxide
(iii) P1. Nucleus is shown (labeled/shaded)
P2. Number of proton & neutron is shown in the nucleus
P3. Correct number of shells and its electrons
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 38
6. (a)(i) Method I: Copper(II) nitrate / magnesium chloride
Method II– Barium sulphate
a: formula
(ii) Reactants for insoluble salt: any suitable answer
P1. Soluble barium salt – Barium nitrate / Barium chloride
P2. Soluble sulphate salt – Sodium sulphate // potassium sulphate // ammonium sulphate etc.
a: formula
(b)(i) Lead(II) nitrate r: formula
(ii) P1. No. of moles of Pb2+ = 0.1 x 5 = 0.0005 mole
1000
P2. No. of moles of I ¯ = 0.2 x 5 = 0.001 mole
1000
P3. 0.0005 moles of Pb2+ reacts completely with 0.001 moles of I ¯
1 moles of Pb2+ reacts with 2 moles of I ¯ .
P4. Simplest ratio Pb2+ : I ¯ is 1:2
P5. Pb2+ + 2 I ¯ → PbI2
(c)(i) Gas V : carbon dioxide
Solid W : Zinc carbonate
Salt Y : Zinc nitrate
Solid Z: Zinc Oxide
(ii) P1 : Pour solution Y into two different test tubes
P2 : Add drop by drop of ammonia solution until in excess and shake.
P3 : White precipitate is formed and dissolve in excess ammonia.
P4 : Add 2 cm3 dilute sulphuric acid followed by 2 cm3 iron(II) sulphate
P5: Add concentrated sulphuric slowly// slant the test tube carefully
P6: A brown ring is formed
7.
(a)(i) Anode: OH-
Cathode: H+
(ii) Anode : 4OH- → O2 + H2O + 4e
Cathode : 2H+ + 2e → H2
(iii) Insert a lighted wooden splinter into the mouth of the test tube.
A pop sound is produced
(b) In Set I :
- Iron spoon is connected at cathode
- The position of Ag+ ion is lower than H+ ion in electrochemical series. Ag+
ion is selectively discharged to form silver atom // Ag+ + e → Ag
In Set II :
- Iron spoon is placed at anode
- No silver atom formed
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 39
(c)(i) In Cell I
- OH- is discharged at anode because the position of OH- is lower than NO3- in
ECS
- Oxygen gas is formed // 4OH- → O2 + 2H2O + 4e
- The concentration of Cu2+ decreases because Cu2+ is discharged to form
copper atom at cathode// Cu2++ 2e → Cu
In Cell II
- copper anode ionises to form Cu2+ ion because copper is active
electrode// Cu →Cu2+ + 2e
- The concentration of Cu2+ unchanged because the rate of copper anode
ionises to form Cu2+ ion is the same as the rate of Cu2+ ion accept electron to
form copper at cathode
(ii) In Cell III
- Magnesium is more electropositive than copper
- Magnesium atom ionises to form Mg2+ // Mg → Mg2+ + 2e
- The concentration of Cu2+ decreases because Cu2+ is discharged to form
copper at copper electrode (positive terminal)//
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu
In Cell IV
- Copper is more electropositive than silver
- Copper atom ionises to form Cu2+// Cu→ Cu2+ + 2e
- The concentration of Cu2+ increases because copper ionises to form Cu2+
at copper electrode (negative terminal) // Cu → Cu2+ + 2e
8 (a)(i) X: Iodine
Y: Bromine
Z: Chlorine
Z→Y → X
(ii) 1. KX undergoes oxidation because the oxidation number of X increases
from –1 to 0.
2. Y2 undergoes reduction because the oxidation number of Y decreases
from 0 to –1.
3. Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneous.
4. Correct formulae of reactants and products.
5. Balanced equation : 2KX + Y2 → 2KY + X2 // 2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 40
(b)(i) Set I:
1. Iron rusts.
2. Iron is more electropositive than P.
3. Iron releases electron to form Fe2+ ion formed. Iron is oxidised.
4. Fe → Fe2+ + 2e
Set II:
5. Iron does not rust.
6. Iron is less electropositive than Q.
7. Oxygen accept electron to form OH–
8. O2 + 2H2O + 4e → 4 OH–
(ii) Set I: Iron is oxidised.
Set II: Metal Q is oxidised.
Q → Iron → P
9.
(a)
Food stored in a refrigerator Food stored in a kitchen
Makanan disimpan dalam cabinet
peti sejuk Makanan disimpan dalam
kabinet dapur
1.The temperature is lower 1.The temperature is higher
Suhu lebih rendah Suhu adalah lebih tinggi
2. Bacterial activity is lower 2.Bacterial activity is higher.
Aktiviti bakteria adalah lebih Aktiviti bakteria lebih tinggi
rendah
3. Less toxin is produced by the 3. More toxin is produced by
Bacteria. bacteria
Kurang toksin dihasilkan oleh . Lebih toksin dihasilkan oleh
bakteria bakteria
4. The rate of food spoilage is 4. The rate of food spoilage is
lower. higher.
Kadar kerosakan makanan Kadar kerosakan makanan
adalah lebih rendah. adalah lebih tinggi
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 41
(b) (i) CaCO3 + 2HCl→ CaCl2 + CO2 +H2O
[Correct chemical formula]
[Balanced equation]
Number of moles of HCl = 50 x 1.0 // 0.05 mol
1000
0.05 mol HCl → 0.025 mol CO2
Volume of CO2 = 0.025 x 24 // 0.6 dm3
(ii) Set II
Average rate of reaction = 40
45
= 0.889 cm3 s-1
(iii) Set I and Set II
1. The rate of reaction of Set I is higher than Set II.
Kadar tindak balas Set I lebih tinggi daripada Set II.
2. In Set I, the size of calcium carbonate used is smaller.
Dalam Set I, saiz kalsium karbonat yang digunakan lebih
kecil.
3. The total surface area of calcium carbonate powder is larger .
Jumlah luas permukaan serbuk kalsium karbonat lebih
besar.
4. The frequency of collisions between calcium carbonate and
hydrogen ion is higher.
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara kalsium karbonat dan ion
hydrogen lebih tinggi.
5. The frequency of effective collisions increases.
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan meningkat.
Set I and Set III
1. The rate of reaction of Set III is higher than Set I.
Kadar tindak balas Set III lebih tinggi daripada Set I
2. In Set III, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is higher .
Dalam Set III, kepekatan asid hidroklorik lebih tinggi.
3. The number of hydrogen ions per volume is higher
Bilangan ion hidrogen per isipadu lebih tinggi.
4. The frequency of collisions between calcium carbonate and
hydrogen ion is higher.
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara kalsium karbonat dan ion
hidrogen lebih tinggi.
5. The frequency of effective collisions increases.
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan meningkat.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 42
10.
(a) Fe2+ ion release electron to form Fe3+ //
Ion Fe2+ membebaskan elektron membentuk ion Fe3+
Fe2+ ion undergoes oxidation //
Ion Fe2+ mengalami pengoksidaan
MnO4 – ion accept electron to form Mn2+ ion //
Ion MnO4 – menerima elektron membentuk ion Mn2+
MnO4 – ion undergoes reduction //
Ion MnO4 – mengalami penurunan
(b)
Part The way Reason
Bahagian Cara Sebab
Gear and Put grease// Moving parts or engine//bahagian enjin
engine// Letak gris yang bergerak
Gear dan
enjin
Paints // Prevent water and air from reaching
Car body// Cat the surface of iron//
Badan kereta Mencegah air dan udara sampai ke
permukaan besi
Tire rim // Alloying// To increase resistance the rusting//to
Rim tayar Pengaloian improve appearance//
Meningkatkan rintangan terhadap
pengaratan // kelihatan lebih menarik
(c) 1.Metal X : [Any metal above copper in the reactivity
series . Example : Zinc ]
Logam X : [ Sebarang logam di atas kuprum dalam siri
kereaktifan. Contoh : zink ]
2. Metal Y : : [Any metal below copper in the reactivity
series . Example : Silver ]
Logam Y : [ Sebarang logam di bawah kuprum dalam
siri kereaktifan. Contoh : argentum ]
Set I
3. The reaction occurred // Tindak balas berlaku
4. Metal X above copper in the reactivity series//Logam X
di atas kuprum dalam siri kereaktifan .
5. Metal X is oxidised to form oxide of metal X // Logam X
Dioksidakan membentuk oksida logam X.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 43
6. Copper(II) oxide is reduced to copper //
Kuprum(II)oksida diturunkan kepada kuprum
7. Copper (II) oxide is oxidising agent // kuprum(II)oksida
ialah agen pengoksidaan.
8. Metal X is reducing agent // logam X ialah agen
penurunan
9. Change in oxidation number of copper from +2 to 0 //
Perubahan dalam nombor pengoksidaan kuprum dari
+2 ke 0
Set II
10. The reaction did not occur because metal Y below copper in the reactivity
series.//
Tindak balas tidak berlaku sebab logam Y dibawah kuprum dalam siri
kereaktifan
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 44
BAHAGIAN C
1. (a) Salt is a substance formed when hydrogen ion from acid is replaced by metal ion or
ammonium ion
(b) 1. React excess magnesium oxide with nitric acid or hydrochloric acid
2. MgO + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O
Correct chemical formula for reactants and products
Balanced chemical equation
3. Filter out the mixture to remove excess magnesium oxide powder.
4. Add sodium carbonate solution into the filtrate containing magnesium chloride solution.
Double decomposition reaction occurs and insoluble magnesium carbonate is precipitated
5. MgCl2 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2NaCl
Correct chemical formula for reactants and products
Balanced chemical equation
6. Filter the mixture. The insoluble magnesium carbonate is collected in filter paper
7. Rinse magnesium carbonate with distilled water
8. The magnesium carbonate is dried by pressing between two filter papers.
(c) 1. Pour each solution into four different test tubes
2. Add sodium hydroxide solution until in excess
3. The solution which produces a white precipitate that is insoluble in excess NaOH solution
contain Mg 2+ ion
4. The Zn 2+, Pb2+, and Al3+ ions forms white precipitates that dissolves in excess NaOH
solution. Thus Mg2+ is identified.
5. Pour the remaining three solutions into 3 different test tubes. Add ammonia solution. The
solution which forms white precipitate which dissolves in excess ammonia solutions contain Zn2+
ion. Zn 2+ ion is identified.
6. The remaining 2 solutions either Pb 2+ or Al 3+ ion.
7. Pour the two solution into 2 different test tubes. Add potassium iodide solution.
8. The Pb2+ ion forms yellow precipitate with KI solution where Al3+ ion does not
2. (a)
Cell A Cell B
Ions in electrolyte Cu2+ , H+ , SO4 2-, OH ̅
Ion selectively None. OH ̅ ion
discharged Because copper is Because position of OH ̅ ion
at anode active electrode. is lower than SO42- ion in
electrochemical series
Observation at anode Anode P: Copper Anode X: colourless gas
becomes thinner bubbles released
Half equation Anode P: Anode X:
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e 4OH ̅ → O2 + 2H2O + 4e
Reaction at anode Anode P: Copper Anode X: OH ̅ ion release
release electron to electrons to form Oxygen
form Cu2+ ion // gas and water // Oxidation
Copper atom is oxidised to occur
Cu2+ ion // oxidation occur
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 45
(b) 1. Halogen Y: Bromine water // Chlorine water
Procedure
2. Pour 2 cm3 of potassium iodide into test tube
3. Add 2 cm3 of chlorine water // bromine water into the test tube.
4. Add 1,1,1 – trichloroethane // tetrachloromethane to the test tube and shake the test tube
5. Put a stopper to the test tube
6. Observation : The purple layer formed at the bottom of the test tube.
Explanation on oxidation and reduction processes
7. Iodide ion releases electrons/ is oxidise to produce iodine
8. Iodide ion is reducing agent
9. Chlorine water//Bromine water receive electron // is reduced to produce chloride ion //
bromide ion
10. Chlorine water // Bromine water is oxidising agent
11. Ionic equation: Cl2 + 2 I ̅ → I2 + 2Cl ̅
3. (a) 1. Substance: Vinegar
2. Vinegar is acidic thus can neutralise the alkaline sting.
3. Vinegar is a weak acid that will not burn the skin.
4. Vinegar is also easily available.
(b) 1. Example of P: Ethanoic acid
2. Example of Q: Sulphuric acid
3. P is a weak acid while Q is strong acid
4. Q ionised completely in water and produced high concentration of H+ ions
5. P ionised partially in water and produced low concentration of H+ ions
6. The higher the concentration of H+ ions the lower pH value
(c) 1. Suggestion solid X: zinc oxide//zinc carbonate//zinc
2. Acid Y: Sulphuric acid
Preparation of zinc sulphate
3. Pour (50-100 cm3) of (0.1-1.0moldm-3) sulphuric acid into a beaker and heat slowly.
4. Add zinc oxide//zinc carbonate//zinc powder into the acid and stir
5. Stop adding zinc oxide//zinc carbonate//zinc powder when solid cannot dissolve/ in excess.
6. Filter the mixture
7. Transfer the filtrate to a evaporating dish and heat until saturated
8. Cool down to room temperature.
9. Filter to obtain the crystal form.
10. Dry the crystal by pressing between filter paper.
4. (a)(i) Reaction I = oxidation
Reaction II = dehydration
Homologous series = alcohol
Accept : 2 or 3 carbon atom only
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 46
Labeled diagram
1. Functional diagram
2. Label: glass wool, ethanol, porcelain chip//alumina//other
substance, water, boiling tube
Procedure
3. Some glass wool is placed in a boiling tube
4. Using a dropper, some ethanol is added into the boiling tube to wet the glass wool
5. The boiling tube is clamped horizontally and unglazed porcelain chip are placed in the mid-
section of boiling tube.
6. The boiling tube is closed with a stopper fitted with a delivery tube and the other hand of
delivery tube is placed under an inverted test tube filled with water.
7. The unglazed porcelain chips are heated strongly. When the porcelain chips are hot, the
flame is shifted to gently heat the glass wool to vaporize the ethanol.
Chemical equation
8. C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O
Chemical test to proof the product
9. Flow the gas produced in a test tube contain bromine water // acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution.
10. If ethene produced then brown bromine water /purple acidified potassium manganate(VII)
solution turns colourless
(b) 1. Q = Ethanoic acid
2. Acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution// potassium dicromate(VI) solution.//Ethanol
C2H5OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O
3. Correct formulae of reactant and product
4. Balanced chemical equation
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 47
5. (a)(i) Sebatian X : heksena Sebatian Y : heksana
Formula molekul sebatian X : C6H12
Formula molekul sebatian Y : C6H14
(ii) P1 : JMR heksena = 84
JMR heksana = 86
P2 : % C heksena = (72 ÷ 84) x 100 % = 85.71%
P3 : % C heksana = (72 ÷ 86) x 100 % = 83.72%
P4 : Peratus kandungan karbon mengikut jisim bagi heksena lebih tinggi berbanding heksena
(b) P1 : Penapaian / Fermentasi
P2 : senarai bahan : glukosa , yis, air suling, air kapur.
P3 : Radas berfungsi
P4 : Berlabel
Prosedur
P5 : 200 cm3 air suling disukat dan dituang ke dalam kelalang kon
P6 : 20 g glukosa ditimbang dan dimasukkan ke dalam kelalang kon
P7 : 10 g yis ditimbang dan dimasukkan ke dalam kelalang kon
P8 : Kelalang kon ditutup dan dibiarkan selama tiga hari ditempat hangat / pada suhu 35oC
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 48
Persamaan tindakbalas
P9 : Betul bahan dan hasil
P10 : Persamaan seimbang
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
6. (a)(i) Bilangan mol : 0.60 / 60 = 0.01 mol
Haba yang dibebaskan
Q = ΔH x n
= 2017 x 0.01
= 20.17 kJ / 20170 J
Kenaikkan suhu
Ɵ = Q / mc
= 20170 / ( 200 x 4.2)
= 24.0 ⁰C
(ii)
(b)
Butana Oktana
Nilai haba pembakaran 2900 kJ mol-1 5500 kJ mol-1
Saiz molekul / Bilangan Kecil / mengandungi bilangan Lebih besar / bilangan atom
atom karbon dan atom karbon & hidrogen kurang karbon & hidrogen lebih banyak
hidrogen berbanding oktana berbanding butana
semasa pembentukan haba dibebaskan kurang
haba dibebaskan lebih banyak
ikatan berbanding oktana
Haba pembakaran Lebih rendah Lebih tinggi
(c) Prosedur
1. Sukat [50 – 250] cm3 air dan tuangkan ke dalam tin kuprum.
2. Rekodkan suhu awal air.
3. Timbang dan catat jisim awal pelita dan bioetanol.
4. Letakkan pelita dibawah tin kuprum dan nyalakan sumbu.
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 49
5. Kacau air itu.
6. Apabila suhu meningkat [20 – 50] ⁰C, padam nyalaan dan rekod bacaan suhu tertinggi
air.
7. Timbang pelita dan rekod jisim akhir.
Keputusan
8. Jisim pelita + bioetanol sebelum pemanasan = M1 g
Jisim pelita + bioetanol selepas pemanasan = M2 g
Bilangan mol
= M1 – M2 // M1 – M2 = n
Jisim molar 46
9. Suhu permulaan/awal air = T1⁰C
Suhu tertinggi air = T2⁰C
10. Haba yang dibebaskan
Q = mcƟ = 100 x 4.2 x [T2 – T1]
11. Haba pembakaran bioetanol
100 x 4.2 x [T2 – T1]
ΔH = - ----------------------------- = q kJmol-1
M1 – M2
46
Haba pembakaran bioetanol ialah – q kJ mol-1
7. (a)(i) P1. X: 2.8.1
P2. Y: 2.4
P3. Z: 2.8.7
OPTION 1
P1. X and Z formed ionic bond
P2. To achieve [stable] octet electron arrangement
P3. X atom release/donate one [valence] electron to form X+ ion.
P4. Z atom gain/receive one electron to form Z ¯ ion
P5. X+ ion and Z ¯ ion are attracted by strong electrostatic force
P6 & P7. Diagram
• Correct number of shells and electron
• Labeled nucleus and charge of ions
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 50
OPTION 2
P1. Y and Z form covalent bond
P2. To achieve [stable] octet electron arrangement
P3. One atom Y contribute 4 electrons while
P4. each atom Z contribute 1 electron
P5. One atom Y share 1 pair of electrons each with four atom Z
P6 & P7. Diagram
• Correct number of shells and electron
• Labeled nucleus and correct number of atom
(b) Compound T: Sodium chloride/magnesium chloride, etc.
Compound V: Hexane
a: any ionic and covalent compound
Experiment 1: Melting point or boiling point
Procedure:
1) Place half spatula of compound T and pour compound V in evaporating dish separately
2) Leave aside / heat for [5-10] minutes
3) Observe and record the change
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 51
Experiment 2: Solubility in water
Procedure:
1) Pour 5 cm3 of water into two different test tubes
2) Place half spatula of compound T and 2 cm3 of compound V into each test tube separately
and shake
3) Observe and record the change
Conclusion:
Compound T is ionic compound and compound V is covalent compound.
8. (a) P1. Total energy absorbed, Ex = 1740 + 994 = 2734 kJ
P2. Total energy released, Ey = 1606 + 1856 = 3462 kJ of energy
P3. Energy change, ΔH = Ex - Ey
= 2734 – 3462
= - 728 kJ mol-1
P4. Exothermic reaction
(b)(i)
(ii) P1. Number of mole CuSO4 = 100 𝑥 1.0 = = 0.1 mol
1000
P2. Heat released = 100 x 4.2 x 12 = 5040 J
P3. [Displacement] of 0.1 mol Cu → 5040 J heat released
[Displacement] of 1 mol Cu → 5040 𝑥 1
0.1
= 50400 J
P4. ΔH = - 50.4 kJ mol-1
(c) P1.Soluble salt 1: suitable carbonate salt solutions to produce precipitate/ insoluble salt
Sample Answer:
Sodium carbonate solution/ ammonium carbonate solution/potassium carbonate solution.
P2. Soluble salt 2: suitable zinc salt solutions to produce precipitate/ insoluble salt
Sample answer:
Zinc nitrate solution/zinc sulphate solution/zinc chloride solution
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 52
Procedure:
P3. Measure [25-200] cm3 of [0.1-2.0] moldm-3 zinc nitrate solution.
P4. Pour into a polystyrene cup.
P5. Measure [25-200] cm3 of [0.1-2.0] moldm-3 sodium carbonate solution.
P6. Pour into a different polystyrene cup.
P7. Measure the initial temperature of both solutions.
P8. Pour sodium carbonate solution quickly into zinc nitrate solution.[a: vice versa]
P9. Stir the mixture.
P10. Record the highest/maximum temperature.[r: final temperature]
P11. Zn(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 → ZnCO3 + 2NaNO3
9.
(a)(i) Hydrochloric acid //nitric acid // ethanoic acid
magnesium chloride// magnesium nitrate // magnesium ethanoate
(ii) Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 //
Mg + 2HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + H2 //
Mg + 2CH3COOH → Mg(CH3COO)2 + H2
- Correct formula of reactants and products
- Balance chemical equation
(b)(i) Sample answer:
Magnesium chloride, MgCl2
Solution R : sodium/potassium/ammonium carbonate
Sample answer:
MgCl2 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2NaCl
Procedure :
1. [20-100] cm3 of MgCl2 solution [0.5 - 2.0] mol dm-3 is
poured into a beaker
2. [20-100] cm3 of Na2CO3 solution [0.5 - 2.0] mol dm-3 is
added into MgCl2 solution
3. The mixture is stirred
4. The mixture is filtered
5. The residue is rinsed and dried.
(ii) Sample answer:
Sulphuric acid is used to prepare MgSO4
Sample answer :
H2SO4 + MgCO3 → MgSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Procedure:
1. [50-100] cm3 of sulphuric acid [0.5-2.0] mol dm-3 is poured into a
beaker .
2. Magnesium carbonate is added bit by bit into the acid until excess
3. The mixture is filtered
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
PECUTAN AKHIR KIMIA 2018 53
4. The filtrate is heated in evaporating dish until saturated
5. The saturated solution is allowed to cool at room temperature
6. Filter the magnesium sulphate crystal.
10 (a)(i) Solution X: ammonia solution//sodium hydroxide? //any akalis
Solution: ethanoic acid//methanoic acid// any weak acids any strong
acids
Process Z: vulcanization
(ii) 1. solution Y contains OH- /hydroxide ions
2. OH- does not neutralize negative charges on protein membrane
3. rubber molecules do not coagulate
4. solution X contains H+ /hydrogen ions
5. H+ neutralizes negative charges on protein membrane
6. rubber particles collide with each other and break the membrane
7. rubber molecule coagulate
(iii) 1. sulphur atoms form cross-linkages between rubber
molecules// cross-linkages between rubber molecules//
sulphur atoms are added to double bond in rubber
molecules
2. reduce the rubber molecules from sliding
(b) 1. materials : natural rubber strip, vulcanized rubber strip
2. apparatus: ruler, weight, retort stand clip
3. measure the original length of the natural rubber by using ruler
4. Hang a natural rubber strip to the retort stand by using two clips
5. a weight is then hung on the rubber strip and the length is
measured
6. a weight is removed and the length is measured again
7. steps 1 to 6 are repeated using vulcanized rubber
8. the observation is recorded
PANITIA KIMIA SMTJB
You might also like
- Jawapan - Modul Excellent KimiaDocument25 pagesJawapan - Modul Excellent KimiaSHESASHTHINY A/P MANICKA RAO Moe0% (1)
- Kimia Tingkatan 5 Bab 2Document24 pagesKimia Tingkatan 5 Bab 2hariprem2667% (9)
- KIMIA T4 KSSM BAB 8 Bahan Buatan Dalam IndustriDocument64 pagesKIMIA T4 KSSM BAB 8 Bahan Buatan Dalam IndustriFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- 9.3 AloiDocument12 pages9.3 AloiismalindaNo ratings yet
- Bahagian B Ikut Lajak FizikDocument3 pagesBahagian B Ikut Lajak FizikDarlene CatrinaNo ratings yet
- Bab 7 - Respirasi Sel-NewDocument33 pagesBab 7 - Respirasi Sel-NewNurul Fatihah Binti MamatNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Unsur PeralihanDocument14 pages4.7 Unsur Peralihansedan091No ratings yet
- Kertas P2 PPT Fiz F4 2018 Group Fiz MalayDocument36 pagesKertas P2 PPT Fiz F4 2018 Group Fiz MalayZhess BugNo ratings yet
- K@MPoI FIZIK EDISI 2023Document120 pagesK@MPoI FIZIK EDISI 2023raihanNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Trial SPM Fizik 2023 TC Bee KisasDocument442 pagesKoleksi Trial SPM Fizik 2023 TC Bee Kisasmunxin02No ratings yet
- Bab 4 Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument40 pagesBab 4 Jadual Berkala Unsurtheebighaa100% (2)
- Percubaan Kimia Johor 2010 Kertas 2 With AnswerDocument34 pagesPercubaan Kimia Johor 2010 Kertas 2 With Answersensnaliquid100% (1)
- SOALANDocument7 pagesSOALANVERONICA A/P FRANCIS MoeNo ratings yet
- Kimia SlideDocument43 pagesKimia SlideRajasree Karunamoorthy0% (1)
- PEKA Formula EmpirikDocument3 pagesPEKA Formula Empirikfaiz_fatihah2954100% (2)
- Kimia K2 Putrajaya 2022Document24 pagesKimia K2 Putrajaya 2022Jing Yun NgNo ratings yet
- Modul Bitara Biologi T4Document113 pagesModul Bitara Biologi T4ZULAIKHA BINTI YAHAYA KAMALUDDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Formula Molekul, Formula Empirik Dan Formula StrukturDocument2 pagesFormula Molekul, Formula Empirik Dan Formula StrukturVinohthini RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Cahaya Naskah GuruDocument30 pagesBab 5 Cahaya Naskah GuruNoor Athirah100% (1)
- Soalan Peperiksaan Pat Kimia t4 2021 k2 Modul 2Document30 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Pat Kimia t4 2021 k2 Modul 2Nur Farhana Binti Mohamad MokhtarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGI Jwp-1Document79 pagesBIOLOGI Jwp-1Cikgu Zurina BishanNo ratings yet
- Kimia Amali 1 - GaramDocument14 pagesKimia Amali 1 - GaramMing Kevin100% (2)
- Latihan Soalan Berformat SPM Kertas 2 Bahagian ADocument10 pagesLatihan Soalan Berformat SPM Kertas 2 Bahagian AChewLee Tan100% (1)
- Konsep Mol Dalam Persamaan KimiaDocument2 pagesKonsep Mol Dalam Persamaan KimiaHamidah MANo ratings yet
- T5 B2 Sebatian Karbon KSSM (Blog)Document12 pagesT5 B2 Sebatian Karbon KSSM (Blog)syaNo ratings yet
- Soalan-Nombor PengoksidaanDocument8 pagesSoalan-Nombor PengoksidaanCheng LinglingNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Kimia SPM 2022Document12 pagesJawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Kimia SPM 2022MUHAMMAD HAZRIQ BIN ARIS JABATAN SAINS100% (1)
- Bab 3 Kertas 2Document14 pagesBab 3 Kertas 2Noor Hidayah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan BM K1 Modul Oasis '21Document65 pagesSkema Jawapan BM K1 Modul Oasis '21Cikgu MaiNo ratings yet
- Empirical Formula NotaDocument7 pagesEmpirical Formula NotaNor AfidahNo ratings yet
- Biologi Tingkatan 4 Lat Formatif 10.2Document1 pageBiologi Tingkatan 4 Lat Formatif 10.2wanhaziraaNo ratings yet
- PeneutralanDocument10 pagesPeneutralansclau78No ratings yet
- 02 - Super SBP Kimia TG 5 (Jawapan) 3rd 24-11-22Document18 pages02 - Super SBP Kimia TG 5 (Jawapan) 3rd 24-11-22Ammar RusyaidiNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Document291 pagesModul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Farihah Ha50% (4)
- Asid Dan Bes PrintDocument16 pagesAsid Dan Bes PrintRohayati Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 2B09 (20M) Daya Impuls - SPM2011Document5 pages2B09 (20M) Daya Impuls - SPM2011RossniePijieNo ratings yet
- Kimia Tingkatan 4 Bab 6 ElektrokimiaDocument18 pagesKimia Tingkatan 4 Bab 6 ElektrokimiaEizyan Lattive100% (20)
- Folio Kimia Bab 5Document14 pagesFolio Kimia Bab 5Farhana UmairahNo ratings yet
- Modul Analisis BertopikDocument78 pagesModul Analisis BertopikAqif ZarifNo ratings yet
- Whole Book Answers PDFDocument178 pagesWhole Book Answers PDFHaavinesh Ganesh100% (1)
- 3.3 Haba PenyesaranDocument10 pages3.3 Haba PenyesaranNajwaAbdullah100% (1)
- 2.4 Isomer Dan Penamaan Mengikut IUPACDocument20 pages2.4 Isomer Dan Penamaan Mengikut IUPACNurul Nadiah SharifNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Esei 2021Document78 pagesKoleksi Esei 2021Mohamad Rizal MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Sebatian KarbonDocument13 pagesBab 4 Sebatian KarbonNur Ardellaa100% (1)
- Latihan 5.4 (Jawapan)Document5 pagesLatihan 5.4 (Jawapan)BENNY LAU XUE ZHENG Moe100% (1)
- B6A - Elektrolisis NotaDocument18 pagesB6A - Elektrolisis NotaMichael WeissNo ratings yet
- JawapanBab4 PDFDocument36 pagesJawapanBab4 PDFkokseemailNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Formula Kanta Nipis 2020 JawapanDocument4 pages6.4 Formula Kanta Nipis 2020 JawapanNora HafizanNo ratings yet
- Eksperimen Kimia Tingkatan 4Document53 pagesEksperimen Kimia Tingkatan 4Azri LokmanNo ratings yet
- Sifat Kimia Unsur Kumpulan 17 Dalam Periodic TableDocument10 pagesSifat Kimia Unsur Kumpulan 17 Dalam Periodic TableZee ZaaraNo ratings yet
- Soalan BIOLOGI 2.pdf SITI NOOR ASSERA BINTI AWANGDocument27 pagesSoalan BIOLOGI 2.pdf SITI NOOR ASSERA BINTI AWANGIt's nuhaNo ratings yet
- Kegunaan Siri HomologDocument6 pagesKegunaan Siri Homolognajihah mgNo ratings yet
- Chemquest 2024 - CG AduraDocument161 pagesChemquest 2024 - CG AduraJyisnuuNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik k2 Smka Sabk 2023Document14 pagesSkema Fizik k2 Smka Sabk 2023Thesha SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Biot4 6.4 Pembahagian Sel (BM)Document8 pagesBiot4 6.4 Pembahagian Sel (BM)Che SalNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Kimia KSSMDocument26 pagesPersamaan Kimia KSSMsitiNo ratings yet
- k2 f4 BC KIMIADocument12 pagesk2 f4 BC KIMIAAzalida Md YusofNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 - Esei - ALL CompileDocument106 pagesKertas 2 - Esei - ALL Compilezulskb78No ratings yet
- K2 KedahDocument29 pagesK2 Kedahryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Bahan Xclusive PerakDocument19 pagesBahan Xclusive PerakFNo ratings yet
- Templat Pelaporan PBD KSSM Tingkatan 4 SainsDocument26 pagesTemplat Pelaporan PBD KSSM Tingkatan 4 SainsSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Manual PBD Kimia Tingkatan 4 PLG LATESTDocument16 pagesManual PBD Kimia Tingkatan 4 PLG LATESTSyarfa Furzanne100% (1)
- Manual PBD Kimia Tingkatan 4 PLG LATESTDocument16 pagesManual PBD Kimia Tingkatan 4 PLG LATESTSyarfa Furzanne100% (1)
- Templat Pelaporan PBD Kimia Ting 4Document22 pagesTemplat Pelaporan PBD Kimia Ting 4Syarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Modul Analisis Bertopik Tingkatan 5 2017 PDFDocument40 pagesModul Analisis Bertopik Tingkatan 5 2017 PDFSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Program Sepanjang Tahun Panitia Sains 2020Document1 pageProgram Sepanjang Tahun Panitia Sains 2020Syarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 RuangDocument7 pagesBab 6 RuangSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Keraktifan LogamDocument32 pagesBab 4 Keraktifan LogamSyarfa Furzanne0% (1)
- Laporan 12perjumpaanDocument16 pagesLaporan 12perjumpaanSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet
- Soalan Kemahiran Berfikir Aras TinggiDocument2 pagesSoalan Kemahiran Berfikir Aras TinggiSyarfa FurzanneNo ratings yet