Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ideal Verses Actual Rankine Cycle: Rankine Cycle Is A Known Mechanical Cycle Which Is Being Commonly Used in The
Ideal Verses Actual Rankine Cycle: Rankine Cycle Is A Known Mechanical Cycle Which Is Being Commonly Used in The
Uploaded by
Kantha RaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ideal Verses Actual Rankine Cycle: Rankine Cycle Is A Known Mechanical Cycle Which Is Being Commonly Used in The
Ideal Verses Actual Rankine Cycle: Rankine Cycle Is A Known Mechanical Cycle Which Is Being Commonly Used in The
Uploaded by
Kantha RaoCopyright:
Available Formats
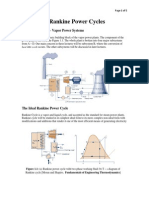
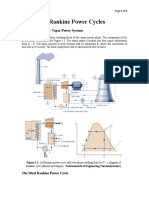
Ideal Verses Actual Rankine Cycle
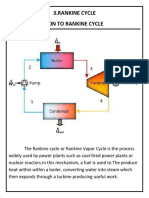
Rankine Cycle is a known mechanical cycle which is being commonly used in the power
plants for converting the pressure energy of steam into mechanical energy using steam
turbines. Major components of it are rotating steam turbine and boiler pump and stationary
condenser and boiler.
A boiler is used for heating the water for generation of steam at required pressure and
temperature as per the requirement of the turbine for power generation. Turbine exhaust is
directed to the radial or axial flow condenser for condensing the steam to condensate and
recycled back to the boiler through boiler pumps for heating again.
The efficiency of the ideal Rankine cycle as described in the earlier section is close to the efficiency
of Carnot Cycle. But in real plants, each stage of the Rankine cycle is associated with some
irreversible processes and thus the efficiency of the actual Rankine cycle is far lower than the ideal
Rankine cycle efficiency.
Given below Fig. 1-a and Fig 1-b represents the Rankine cycle on P-v and T-s diagram
Rankine Cycle Representation are as follows on P-v and T-s diagrams:
Ideal Rankine Cycle 1-2‘-b-3‘-4‘-1
Actual Rankine Cycle 1-2-b-3-4-1
Critical Point (CP) is in centre of the curve as shown in Fig 1-a and 1-b above. The curved lines on the left
side of the CP are saturated- liquid lines and the region/area to the left of these lines are called as sub-
cooled liquid regions.
Similarly curved lines on the right side of the CP are saturated- vapour lines and the region/area to the
right of these lines are called as super-heat vapour regions.
Energy Analysis of Ideal Rankine Cycle
All components of Rankine cycle (boiler, turbine, condenser and pump) are examples of
steady flow process and to be analysed accordingly. Energy balance for the Ideal cycle is as
follows:
Ideal Rankine Cycle Components Heat Work
Boiler feed Pump Wpump-in
Boiler /addpost/images/4-10-15-6.gif
Turbine
Condenser
Thermal efficiency of Ideal Rankine cycle
You might also like
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine Cycledeepakkesri260% (1)
- Steam Power Plants (System)Document58 pagesSteam Power Plants (System)Hafzal Gani100% (2)
- Actual VS Ideal Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesActual VS Ideal Rankine CycleFarah Khan FairyNo ratings yet
- Ciclo Rankine WilkinsDocument49 pagesCiclo Rankine WilkinsluisNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument7 pagesCollectionRohan RustagiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: TutorialDocument13 pagesFaculty of Engineering: TutorialDavid ChikuseNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines FundamentalsDocument51 pagesSteam Turbines Fundamentalssevero97100% (2)
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine CycleGeçmiş GölgelerNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument5 pagesRankine CycleRohit JainNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument26 pagesThermodynamicsManikanta Reddy100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Rankine Cycle in EnglishDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Rankine Cycle in EnglishRahmandan HafidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Rankine Power CyclesDocument5 pagesLecture 1 - Rankine Power CyclesMuhammad Alam Zaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclesbmmla100% (1)
- The Four Processes in The Rankine CycleDocument3 pagesThe Four Processes in The Rankine CyclesahiiiiNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsDocument44 pagesCh1 - Steam Power PlantsSyahir LokhmanNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)Document11 pagesRankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)bnida99No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Steam Turbine - Rankine CycleDocument41 pagesChapter 2 - Steam Turbine - Rankine CycleAnthony AbourahalNo ratings yet
- Jasper Van B Arrieta Bsme-IvDocument6 pagesJasper Van B Arrieta Bsme-IvJasper Van ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsDocument43 pagesCh1 - Steam Power PlantsShiau Fen100% (1)
- Vapour Power CycleDocument41 pagesVapour Power CycleSaiVelamalaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Steam Power PlantsDocument44 pagesCh1 - Steam Power Plantsaminjoe93100% (1)
- Power PlantDocument63 pagesPower PlantSatheesh Sekar100% (4)
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine CycleAshish GargNo ratings yet
- Further Thermodynamics Steam Turbine PlantsDocument38 pagesFurther Thermodynamics Steam Turbine Plantsamdan srlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Analysis of Steam Power Plant CycleDocument61 pagesChapter 2 - Analysis of Steam Power Plant Cyclerrhoshack100% (1)
- Thermal EngineeringDocument6 pagesThermal EngineeringGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclerr1819No ratings yet
- 1 Rankine CycleDocument19 pages1 Rankine CycleAshwin kumarNo ratings yet
- 3.rankine Cycle 3.1 Introduction To Rankine CycleDocument12 pages3.rankine Cycle 3.1 Introduction To Rankine Cycleyashwanthyadavr123No ratings yet
- Exp#5-Operating Characteristics of A Steam Power Plant: The Analysis of Rankine CyclerDocument26 pagesExp#5-Operating Characteristics of A Steam Power Plant: The Analysis of Rankine CyclerTakiyahJacksonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument8 pagesChapter 10: Vapor and Combined Power CyclesAhmad SairafiNo ratings yet
- Coal Fired Power Plants: Background Thermodynamics and IntroductionDocument43 pagesCoal Fired Power Plants: Background Thermodynamics and IntroductionDurgesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument8 pagesRankine CyclesupriyasarkarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle and Its Utility in Thermal Power Plant - A Theoretical ApproachDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Rankine Cycle and Its Utility in Thermal Power Plant - A Theoretical ApproachAnonymous sG3iVImJNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesThermodynamicsNicole Andrei BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1c - The Rankine Cycle 3 PDFDocument19 pagesLesson 2.1c - The Rankine Cycle 3 PDFBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Cycles Part 1Document7 pagesSteam Power Cycles Part 1UNIQUE INDIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3smisosphamandla30No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Rankine Power CyclesDocument6 pagesLecture 1 - Rankine Power CyclesMuhammad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science (UGC Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesMadanapalle Institute of Technology & Science (UGC Autonomous) Department of Mechanical EngineeringHarsha DadanaNo ratings yet
- Presentation estDocument29 pagesPresentation estgunjanmeet.kaur5No ratings yet
- 1-3 Advanced Steam Power CyclesDocument14 pages1-3 Advanced Steam Power CyclesGeethika Nayanaprabha100% (1)
- Energy Systems Steam Cycles PolimiDocument19 pagesEnergy Systems Steam Cycles PolimiDevin Ardisa ThiodorusNo ratings yet
- Assignment in ME 312Document23 pagesAssignment in ME 312jasperNo ratings yet
- 01-Steam Power Plant 26 OctDocument64 pages01-Steam Power Plant 26 OcthuusenaliNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Rankine CycleDocument27 pagesActivity 3 Rankine CycleTricia IbabaoNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 12-05-2023 18.51Document10 pagesCamScanner 12-05-2023 18.51thelostconjectureNo ratings yet
- Fernandez John Ralph L. 3 - Argon Assignment No. 1 (Pps Prelim) Rankine CycleDocument2 pagesFernandez John Ralph L. 3 - Argon Assignment No. 1 (Pps Prelim) Rankine CycleFernandez John Ralph L.No ratings yet
- 18me42 Atd Module 3Document23 pages18me42 Atd Module 3Shaik SulemanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-: Ideal Reverse Brayton CycleDocument7 pagesLecture-: Ideal Reverse Brayton Cycleabrar alhadadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Power CyclesDocument23 pagesChapter 2-Power CyclesbaseakelNo ratings yet
- I.C Engines: Classification, Working PrinciplesDocument8 pagesI.C Engines: Classification, Working PrinciplesSony RamaNo ratings yet
- Power Cycles: Q W Q W Cost BenefitDocument3 pagesPower Cycles: Q W Q W Cost BenefitMaey AkimNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Steam Power PlantDocument60 pagesChap 1 - Steam Power PlantMuhammad Qusyairi100% (2)
- Kalina Cycle Power PlantDocument5 pagesKalina Cycle Power PlantArie OrsandNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document24 pagesUnit - 1rajeshwari100% (2)
- 01-NORA - Steam Power PlantDocument51 pages01-NORA - Steam Power PlantmasrizaNo ratings yet