Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANA: Calculation View Creation
Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANA: Calculation View Creation
Uploaded by
shree.patil20028558Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANA: Calculation View Creation
Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANA: Calculation View Creation
Uploaded by
shree.patil20028558Copyright:
Available Formats
Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling with SAP HANA
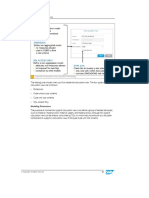
Figure 47: Advanced Data Processing Capabilities
SAP HANA has built-in, advanced data processing capabilities. These include textual, spatial,
and predictive functions. Calculation views can easily call these native SAP HANA functions,
so applications can leave all the complex processing to SAP HANA.
Core Modeling Versus Advanced Modeling
The term, core modeling (sometimes called view modeling), refers to the development of
models that handle common analytical functions. These functions include filtering,
aggregation, calculations, and so on.
When we develop models to handle advanced analytical scenarios, such as predictive, spatial,
textual, and graph, we refer to this type of modeling as advanced modeling. For now, we will
focus on core modeling.
Core modeling in SAP HANA begins with the creation of a calculation view.
Note:
In earlier releases of SAP HANA, calculations views were part of a family called
Information Views. There were originally three members of that family; Attribute
View, Analytic View, and Calculation View.
Each of these view types had its own unique features, and typically, all three view
types were required. However, since the calculation view has inherited all the
features of the two other views, we no longer develop attribute or analytic views. In
fact these types of views can be migrated to calculation views using the supplied
tools. The calculation view can now do it all, which means we no longer have to be
concerned about which view type to use.
Calculation View Creation
When you create a calculation view, you choose various combinations of settings. These
settings define four basic types of calculation view.
© Copyright. All rights reserved. 69
You might also like
- Tech M Certificate - WFHDocument1 pageTech M Certificate - WFHshree.patil2002855873% (15)
- Power BI Interview QuestionsDocument39 pagesPower BI Interview QuestionsGOMTI100% (1)
- 3.3 Up & Running With Power BI Desktop PDFDocument109 pages3.3 Up & Running With Power BI Desktop PDFJason Araos Fuentes100% (3)
- Data Modeling with SAP BW/4HANA 2.0: Implementing Agile Data Models Using Modern Modeling ConceptsFrom EverandData Modeling with SAP BW/4HANA 2.0: Implementing Agile Data Models Using Modern Modeling ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Determine Whether This Statement Is True or False.: Unit 3: Learning Assessment - AnswersDocument1 pageDetermine Whether This Statement Is True or False.: Unit 3: Learning Assessment - Answersshree.patil2002855825% (4)
- Determine Whether This Statement Is True or False.: Unit 3: Learning Assessment - AnswersDocument1 pageDetermine Whether This Statement Is True or False.: Unit 3: Learning Assessment - Answersshree.patil2002855825% (4)
- 02-HOPEX IT Architecture - Training Handout PDFDocument121 pages02-HOPEX IT Architecture - Training Handout PDFJR BorgNo ratings yet
- Oracle Hyperion Planning 11 Essentials Exam TopicsDocument1 pageOracle Hyperion Planning 11 Essentials Exam Topicsadisun21No ratings yet
- PowerBI Advanced Analytics With PowerBIDocument18 pagesPowerBI Advanced Analytics With PowerBIBruce Ge100% (7)
- Getting Started With Strategic PlanningDocument9 pagesGetting Started With Strategic PlanningAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Splunk Dashboards Quick Reference GuideDocument6 pagesSplunk Dashboards Quick Reference Guidesavsabien97267% (3)
- 03 Sap Ha100Document40 pages03 Sap Ha100Angel Luis Hernandez SalazarNo ratings yet
- 2015 Improving Business Intelligence Applications by Using New Generation of Web and Mobile TechnologiesDocument9 pages2015 Improving Business Intelligence Applications by Using New Generation of Web and Mobile Technologiesimygad53No ratings yet
- What Is Currency Conversion Currency Conversion Currency ConversionDocument2 pagesWhat Is Currency Conversion Currency Conversion Currency ConversionMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Calculation View Step by StepDocument19 pagesCalculation View Step by Stepannesree100% (1)
- SAP HANA Cloud - Foundation - Unit 4Document19 pagesSAP HANA Cloud - Foundation - Unit 4ahyuliyanovNo ratings yet
- Sap Hana Modeling Doc-1216Document69 pagesSap Hana Modeling Doc-1216tariqibnazizNo ratings yet
- Dark Modern and Elegant Company Profile PresentationDocument21 pagesDark Modern and Elegant Company Profile PresentationMais alhawamdehNo ratings yet
- Sap Hana Interview ImpDocument11 pagesSap Hana Interview ImpMani KandanNo ratings yet
- The 4+1 View Model of ArchitectureDocument9 pagesThe 4+1 View Model of Architecturemoody_mannu100% (1)
- SAP HANA CurriculumDocument5 pagesSAP HANA CurriculumdasuooNo ratings yet
- Reading Sample Sap Press Sap Analytics CloudDocument37 pagesReading Sample Sap Press Sap Analytics CloudSalah BAKIRNo ratings yet
- Embedded Analytics The Jewel of Your S4hana InvestmentDocument4 pagesEmbedded Analytics The Jewel of Your S4hana InvestmentFITA fashionNo ratings yet
- Reading Sample: "Implementing Analytical Apps" Index The AuthorDocument35 pagesReading Sample: "Implementing Analytical Apps" Index The AuthorNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Attribute ViewDocument26 pagesSAP HANA Attribute ViewSittipat ArtNo ratings yet
- 20 Data Models Stored ProceduresDocument26 pages20 Data Models Stored ProceduresSARGURUNo ratings yet
- Simulating With Value Driver TreesDocument10 pagesSimulating With Value Driver Treesbessma.bakriNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Topic of SAP HANA Modeling ViewsDocument16 pagesWelcome To The Topic of SAP HANA Modeling Viewspavani shettyNo ratings yet
- Best Practice For Data Modeling With HANA PDFDocument52 pagesBest Practice For Data Modeling With HANA PDFsabrina100% (7)
- Lectura3 The 41 View Model of ArchitectureDocument16 pagesLectura3 The 41 View Model of Architectureorejas123No ratings yet
- Building Advanced Formula Data ActionsDocument15 pagesBuilding Advanced Formula Data Actionsbessma.bakriNo ratings yet
- Professional Program in Data Science and Machine Learning: - ML EngineerDocument4 pagesProfessional Program in Data Science and Machine Learning: - ML EngineerMANPREET SODHINo ratings yet
- The 41 View Model of ArchitectureDocument16 pagesThe 41 View Model of ArchitectureAlexander BukowskiNo ratings yet
- Sap Hana DocsDocument9 pagesSap Hana Docsanandnishchal90No ratings yet
- Mastering Object-Oriented Analysis and Design With UMLDocument20 pagesMastering Object-Oriented Analysis and Design With UMLChi Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1Srilakshmi MaduguNo ratings yet
- B071H6YNMNDocument395 pagesB071H6YNMNbhabhijee100% (2)
- SAP Analytics Cloud - IntroductionDocument5 pagesSAP Analytics Cloud - Introductionsrianurag87No ratings yet
- 1.4 Mejora en El Uso de VistasDocument12 pages1.4 Mejora en El Uso de VistasOmar CruzNo ratings yet
- Sap HanaDocument4 pagesSap HanaPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Calc View Star Join PDFDocument74 pagesCalc View Star Join PDFRavi RoshanNo ratings yet
- SAP CDS - CDS Vs Calculation ViewDocument5 pagesSAP CDS - CDS Vs Calculation ViewtovinonNo ratings yet
- DEV475_04_Analysis&DesignDocument25 pagesDEV475_04_Analysis&Designlmi20111No ratings yet
- Advanced Analytics With Power BIDocument18 pagesAdvanced Analytics With Power BIramu9999No ratings yet
- Power BI Class NotesDocument18 pagesPower BI Class Notesramu9999No ratings yet
- Difference Between BW, BW On HANA and Native HANADocument2 pagesDifference Between BW, BW On HANA and Native HANASourabhNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Calculation ViewDocument3 pagesSAP HANA Calculation ViewEli_HuxNo ratings yet
- OOM Module 4Document66 pagesOOM Module 4narendraupNo ratings yet
- Reading Sample Sap Press Designing Dashboards With Sap Analytics CloudDocument24 pagesReading Sample Sap Press Designing Dashboards With Sap Analytics CloudSalah BAKIRNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnalyticsDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Analyticsanil kumarNo ratings yet
- SAP SACS21 EN Col37Document122 pagesSAP SACS21 EN Col37Burak YüceNo ratings yet
- 502 Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument110 pages502 Object Oriented Analysis and DesignRekha JaiswarNo ratings yet
- Architectural Blueprints - The "4+1" View Model of Software ArchitectureDocument16 pagesArchitectural Blueprints - The "4+1" View Model of Software ArchitectureRonald N Meza CNo ratings yet
- Pattern Recognition AssignmentsDocument8 pagesPattern Recognition AssignmentsJahan ChawareNo ratings yet
- Mahesh Kumar Sap Consultant: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesMahesh Kumar Sap Consultant: Career ObjectivejamallamudimNo ratings yet
- ASUG83664 - Sales Outlook With SAP Analytics CloudDocument35 pagesASUG83664 - Sales Outlook With SAP Analytics CloudmiteshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Ssas 2016Document49 pagesSsas 2016Lilantha Lakmal GallabaNo ratings yet
- CDS ViewDocument103 pagesCDS Viewthanhtbt100% (4)
- Fundamental Design Concepts (PSE SE)Document47 pagesFundamental Design Concepts (PSE SE)Rahul LokeshNo ratings yet
- Mind Map in Software DevelopmentDocument9 pagesMind Map in Software DevelopmentNazmudin FirdaosNo ratings yet
- Power BI DAX Essentials Getting Started with Basic DAX Functions in Power BIFrom EverandPower BI DAX Essentials Getting Started with Basic DAX Functions in Power BINo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer.: Unit 3: Learning AssessmentDocument1 pageChoose The Correct Answer.: Unit 3: Learning Assessmentshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Tech M Certificate - Ai 101Document1 pageTech M Certificate - Ai 101shree.patil200285580% (1)
- Glo PDFDocument1 pageGlo PDFshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lesson 2: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3 Lesson 2: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- How To Master Strategic ThinkingDocument2 pagesHow To Master Strategic Thinkingshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With Sap HanaDocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With Sap Hanashree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- GROW Model WorksheetDocument4 pagesGROW Model Worksheetshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANA: Graph ModelingDocument1 pageLesson: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANA: Graph Modelingshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- For Company Acme. The Conditions Can Also Be More Complex Such As Olive Can View Company Acme Data But Only Between 2017-2018 - A User Can Have Multiple AnalyticDocument1 pageFor Company Acme. The Conditions Can Also Be More Complex Such As Olive Can View Company Acme Data But Only Between 2017-2018 - A User Can Have Multiple Analyticshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- SAP HANA Modeling EditorDocument1 pageSAP HANA Modeling Editorshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANADocument1 pageLesson: Advanced Analytics With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANADocument1 pageUnit 3: Analytical Processing With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANADocument1 pageLesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANADocument1 pageLesson: Understanding Core Modeling With SAP HANAshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- SAP HANA Graph Processing Powers Real-Time, High-Performance Business Charts, and DashboardsDocument1 pageSAP HANA Graph Processing Powers Real-Time, High-Performance Business Charts, and Dashboardsshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Roles: Unit 4: Workstream OverviewDocument1 pageRoles: Unit 4: Workstream Overviewshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Exploring SAP Activate ElementsDocument1 pageLesson: Exploring SAP Activate Elementsshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Understanding New Implementation S/4HANA Cloud Single-Tenant EditionDocument1 pageLesson: Understanding New Implementation S/4HANA Cloud Single-Tenant Editionshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Transition PathsDocument1 pageUnit 5: Transition Pathsshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Sap Build: Lesson: Introducing The Design and Configuration WorkstreamDocument1 pageSap Build: Lesson: Introducing The Design and Configuration Workstreamshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 4: Workstream OverviewDocument1 pageUnit 4: Workstream Overviewshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Lesson: Outlining The Key Characteristics of SAP ActivateDocument1 pageLesson: Outlining The Key Characteristics of SAP Activateshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Unit 4: Workstream OverviewDocument1 pageUnit 4: Workstream Overviewshree.patil20028558No ratings yet
- Introducing The Integration Workstream: Unit 4 Lesson 8Document1 pageIntroducing The Integration Workstream: Unit 4 Lesson 8shree.patil20028558No ratings yet