Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Chemistry
Introduction To Chemistry
Uploaded by
bangtanswifue -Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Chemistry
Introduction To Chemistry
Uploaded by
bangtanswifue -Copyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY 5 MAIN PRINCIPLES OF LEUCIPPUS DEMOCRITUS
The study of composition of matter and the changes that 1. All matter is made up of atoms that are too tiny to see by the
matter undergoes. naked eye & can’t be broken down further into smaller portions.
Explains the natural world. 2. Atoms are in constant motion around an empty space that
Prepares people for career opportunities. they called void.
Produces informed citizens. 3. Atoms are completely solid. [ false ]
4. Atoms are uniformed with no internal structure.
TWO DIVISION OF CHEMISTRY
5. Atoms can come in different shape and sizes. [ true ]
Pure Chemistry - research driven by facts and theories
Applied Chemistry -application of pure chemistry. Epicurus of Samos - popularized atomism.
- Developed the ideas of Leucippus and Democritus.
FIVE TRADITIONAL AREAS OF STUDY
- According to him atoms have diffeferent weights, same
Inorganic chemistry -study of chemicals that do not
speed regardless of its size.
contain carbon. ( diamond, sulfur, silver)
- Plato and aristotle opposed his ideas.
Organic chemistry -all about carbon based compounds.
Empedocles - a certain matter is composed of only four
( Alcohol, Polymers, Vitamins, Human, Coal, Methane )
elements. Plato and Aristotle agreed with him.
Analytical Chemistry - study of the quality and quantity of
Aristotle - continuous theory that matter can be divided
components of different substances.
indefinitely w/o changing the fundamental characteristics.
Biochemistry- study of the living system or the living
- The fifth element is Aether.
things or anything that has life. (biomolecule, lipids)
All theories are based on logic
Physical chemistry - study of the mechanism, rates, and
energetics of chemical reaction. 5 STATES OF MATTER
1. Bose-Einstein condensate - is a very odd condition in which
NATURE OF MATTER
all atoms atain the same quantum-mechanical state. This state is
The earliest belief of the Greek philosophers was that
matter is just a single element. only found within a minute portion of absolute 0.
2. Solids - are materials with a defined volume and shape.
GREEK PHILOSOPHERS Resistant to outside forces, tend to keep their shape and mass.
6th century 3. Liquids - are non-compressible materials that take shape of
Anaximenex - concluded that everything in the world is their containers and have a free surface.
composed of air. 4. Gases - expand to fill the size and shape of their containers.
Thales of Miletus - the nature of matter was a single They tend to have relitively low density levels.
material substance: water. 5. Plasma - are ionized (electrically charged) gases that possess
Heraclitus - remembered for his cosmology, in which fire an equal number of positive and negative charges.
forms the basic material principle of an orderly universe.
ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS
Empedocles - Empedocles devised the theory that all
substances are made of four pure, indestructible elements: Division of Matter
air, fire, water, and earth.
Pure substance - uniform, Mixtures - a physical blend
5th century definite composition, of two or more pure
samples have the same substances.
Leucippus - originated the theory of atomism. properties.
Democritus - student of Leucippus. Heterogenous -
Elements - one kind of atom components are in different
- Developed the concept of the atom. that cannot be broken down phases, therefore
by physical or chemical components are visible
- In every matter there is a certain portion of it that
means.
is a tiny particle that is indestructible or uncuttable. Homogenous - the same;
Compounds - 2 or more uniform composition; a
kinds of atoms; can be solution (solute+solvent)
broken down into elements
by chemical means.
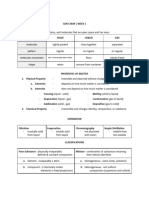
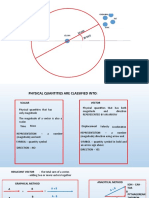
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Extensive - affected if you Intensive - qualities that
change the amount of won’t change even if the
matter. amount of matter does
Physical - can be observed Chemical - the ability of a
or measured with your five substance to undergo a
senses. specific chemical change.
CHANGES IN MATTER
Physical changes - the composition of the material does
not change; may or may not be reversible.
Chemical changes - chemical reactions; new product =
new composition; represented by chemical equation.
- Reaction - Products; Mass of products = mass of
reactants ( Law of Conservation of Mass)
FOUR CLUES OF CHEMICAL CHANGE
1. There is a transfer of energy.
2. There is a change in color.
3. A gas is produced.
4. A precipitate forms ( a solid with low solubility )
THE NAMING OF MATTER
Chemical symbols - J.J Berzelius (1779-1848)
Chemical formulas - chemical symbol, subscript
IUPAC - International Union of Pure and Applied Chem.
THE PERIODIC TABLE
In organizing the element, the elements are in group based
on their properties.
Dmitri Mendeleev (1934-1907) - predicted properties of
undiscovered elements. ( Periodic table - 1869 )
- organized by increasing atomic mass.
- Elements with similar properties are grouped together.
J.W Dobereiner (1780-1849) - grouped elements into
triads ( 1829 )
Now, elements are arranged in orders of increasing atomic
number.
There is a periodic repitition of their physical and
chemical properties ( the periodic law )
Metals - conductors, high scheen, solid at room temperature,
ductile , malleable.
Metalloids - mixture of metal and nonmetal, also called
semimentals.
Nonmetals - solids, liquids, but mostly gases; properties vary
considerably.
You might also like
- Jcpds CardDocument148 pagesJcpds CardSanchit100% (3)
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument54 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerJohn Eivhon Festijo0% (2)
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notesbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Chemistrylecturewps OfficeDocument12 pagesChemistrylecturewps Officeniconiconii BANGTANXARMYNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument46 pagesScience Reviewerrowannenicole.jaudianNo ratings yet
- Science REVIEWERDocument8 pagesScience REVIEWERJoannah PinoteNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChemistryDocument17 pages1 - ChemistryJOANA ESTINOCONo ratings yet
- Chemistry For EngineersDocument5 pagesChemistry For EngineersErgie PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Chem (Lec)Document2 pagesChem (Lec)Dalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryAndrei Angelo PantigNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 3Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 3shareeandradaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Nature and States of MatterDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Nature and States of MatterReinn DionisioNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1Document6 pagesStudy Guide 1Rochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Gen. ChemDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Gen. Chemsunny sonejaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Reviewerback upNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerJohn Nicolo P. GurangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Matter - Its Properties and MeasurementDocument54 pagesChapter 1: Matter - Its Properties and MeasurementJan Rovyn Javier100% (1)
- What Is ChemistryDocument20 pagesWhat Is ChemistryMohammad Ryyan PumbagulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Course Lecturer: Jasmin Šutković 4th March 2015Document32 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Course Lecturer: Jasmin Šutković 4th March 2015Esmira Melić ŠutkovićNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesC15 Notes CH1 IntroductionArnieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year MTDocument12 pagesChemistry 1st Year MTENo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry ReviewerTala CodiemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Medical ChemistryDocument165 pagesLecture 1 Medical ChemistryCypher Soth ViNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerDocument9 pagesQuarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerRussel LaugoNo ratings yet
- Substance - Is A Type of Matter That Has TheDocument2 pagesSubstance - Is A Type of Matter That Has TheMeow NyawNo ratings yet
- Pre Middle Test Chemistry Feodora Shintia GitaDocument5 pagesPre Middle Test Chemistry Feodora Shintia GitaFeodora NicoleNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem ReviewerShane PangatoNo ratings yet
- Biochem LecDocument10 pagesBiochem LecRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryVincent LagunillaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 1 Atom Electronic ConfigDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY 1 Atom Electronic ConfigcavalyaffaNo ratings yet
- Matter and It - S Properties Learning Material PDFDocument12 pagesMatter and It - S Properties Learning Material PDFikennahtNo ratings yet
- Newton Learning Material PDFDocument12 pagesNewton Learning Material PDFikennahtNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesMatter and Its Properties Properties of MattermiahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisDocument9 pagesChapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisYhena ChanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer: Mass - Amount of Matter Constant Weight - Force That The Gravity ExertsDocument13 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer: Mass - Amount of Matter Constant Weight - Force That The Gravity ExertsMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Science 8 5Document9 pagesScience 8 5Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Aspect of General Science: Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesChemistry Aspect of General Science: Learning ObjectivessannaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience ReviewerIT'S JAY STEPHEN0% (1)
- Gen Chem 1 (1s Midterms)Document5 pagesGen Chem 1 (1s Midterms)Princess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter I. Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesChapter I. Introduction To Organic ChemistryAun eeNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- 1-Properties of MatterDocument32 pages1-Properties of MatterTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument3 pagesGen ChemJanice RiliNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notesdeveravanessa01No ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry ReviewerJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- Eng EconoDocument7 pagesEng EconoDUMAGCAO, LAURENCE ROBERT R.No ratings yet
- Class 9 - Chemistry Book-Federal-BoardDocument25 pagesClass 9 - Chemistry Book-Federal-BoardShaista HabibNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories and StructureDocument14 pagesAtomic Theories and StructureShanen May Apostol Ampatin IINo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Document25 pagesLecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Louise Nicole CastroNo ratings yet
- Matter Can Exist in One of Three Main States: Solid, Liquid, or GasDocument7 pagesMatter Can Exist in One of Three Main States: Solid, Liquid, or GasFrancys Angella QuisanNo ratings yet
- Pop Sheet 3Document4 pagesPop Sheet 3pang batzNo ratings yet
- Conceptual and Functional Chemistry-Book SummaryDocument8 pagesConceptual and Functional Chemistry-Book SummaryJehan CodanteNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDocument52 pagesSome Basic Concept of ChemistryjabNo ratings yet
- 1 ChemistryDocument13 pages1 ChemistryAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- HES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3Document1 pageHES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- 3.1.3 CM Cardboard 04dkDocument6 pages3.1.3 CM Cardboard 04dkbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- HES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-5Document1 pageHES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-5bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Personal Statement: Adm-Adm 07F Documented Information Effective March 1, 2021Document4 pagesPersonal Statement: Adm-Adm 07F Documented Information Effective March 1, 2021bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- UCSP Reviewer - FinalsDocument1 pageUCSP Reviewer - Finalsbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notesbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- HES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-1Document1 pageHES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-1bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Chapter Assesment 2 (Gen-Chem)Document1 pageChapter Assesment 2 (Gen-Chem)bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Center of MassDocument1 pageCenter of Massbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Philippine: Al Majd Fntemational CurriculumDocument1 pagePhilippine: Al Majd Fntemational Curriculumbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- 1421-Article Text-5000-1-10-20161030Document10 pages1421-Article Text-5000-1-10-20161030bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- The Three Following Requirements of Academic WritingDocument3 pagesThe Three Following Requirements of Academic Writingbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument2 pagesABSTRACTbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Pre-Conquest PeriodDocument6 pagesPre-Conquest Periodbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- CHAPTER III New StudentsDocument3 pagesCHAPTER III New Studentsbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Frances Reyes AquinoDocument2 pagesFrances Reyes Aquinobangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- National Artist For MusicDocument2 pagesNational Artist For Musicbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- 465 Homosexualmarriage 2Document2 pages465 Homosexualmarriage 2bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Fall Semester Review KEYDocument8 pagesFall Semester Review KEYbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Vector Simplified SDocument15 pagesVector Simplified Sbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Worksheet Uniform Circular MotionDocument1 pageWorksheet Uniform Circular Motionbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Displacement, Time, Average Velocity, Instantaneous VelocityDocument13 pagesDisplacement, Time, Average Velocity, Instantaneous Velocitybangtanswifue -100% (1)
- Example of Instantaneous VelocityDocument5 pagesExample of Instantaneous Velocitybangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Kinetics For Benzene#ethylene Reaction in Near-Critical RegionsDocument8 pagesKinetics For Benzene#ethylene Reaction in Near-Critical RegionsDulce GradillaNo ratings yet
- HIRA and Process Life CycleDocument36 pagesHIRA and Process Life Cycleنايف الخالديNo ratings yet
- Study of Intermediate Stages in The Kaolin - Metakaolin TransformationDocument10 pagesStudy of Intermediate Stages in The Kaolin - Metakaolin TransformationRalucaNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaDocument14 pagesAlkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaomarnajimNo ratings yet
- دوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Document59 pagesدوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Doha LababnehNo ratings yet
- St. John of Buug Foundation Inc.: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSt. John of Buug Foundation Inc.: Objectivestammy a. romuloNo ratings yet
- Food Science and Technology International-2004-Bautista-Ortín-287-95Document9 pagesFood Science and Technology International-2004-Bautista-Ortín-287-95Ximena CáceresNo ratings yet
- Final Sif Report 2022 23Document52 pagesFinal Sif Report 2022 23Shazia FatimaNo ratings yet
- Routine & Preventive MaintenanceDocument8 pagesRoutine & Preventive Maintenancevinay956No ratings yet
- Extraction and Characterization of Asphaltenes From Different Crude Oils and SolventsDocument7 pagesExtraction and Characterization of Asphaltenes From Different Crude Oils and SolventsJesseNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Emilia, Lia Destiarti, AdhitiyawarmanDocument10 pagesIndonesian Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Emilia, Lia Destiarti, Adhitiyawarmanjoenni hansNo ratings yet
- Split Tensile Strength-Flexural TestDocument15 pagesSplit Tensile Strength-Flexural TestHVRANANo ratings yet
- Pexgol Engineering GuideDocument88 pagesPexgol Engineering GuideGiann CarlosNo ratings yet
- M-Dinitrobenzene From Nitrobenzene by Substitution ReactionDocument22 pagesM-Dinitrobenzene From Nitrobenzene by Substitution ReactionFarheen BehlimNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: ObjectiveMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- ME 40 Thermodynamics PDFDocument3 pagesME 40 Thermodynamics PDFkakiNo ratings yet
- Creatine Kinase: Store at 2-8ºCDocument4 pagesCreatine Kinase: Store at 2-8ºCLaboratorios HerliNo ratings yet
- K02083 - 20180605141639 - Pure Substances and Physical MixturesDocument7 pagesK02083 - 20180605141639 - Pure Substances and Physical MixturesaiynaNo ratings yet
- ANRORC MechanismDocument3 pagesANRORC MechanismLuis Felipe Mera GrandasNo ratings yet
- 2022 Dedza District Mock (Chemistry Paper II)Document6 pages2022 Dedza District Mock (Chemistry Paper II)makudavieNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Peta #2.2 - Ice Cream MakingDocument6 pagesGen Chem 2 Peta #2.2 - Ice Cream MakingDaiyu 'No ratings yet
- Predicting Hardness by The Grossman H-Value HOT SEATDocument3 pagesPredicting Hardness by The Grossman H-Value HOT SEATetxeanaNo ratings yet
- Efka PU 4047: Technical InformationDocument2 pagesEfka PU 4047: Technical InformationAniket PatelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: To Identify The Cation and Anion in Copper Sulphate PentahydrateDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 1: Aim: To Identify The Cation and Anion in Copper Sulphate PentahydrateElite GamingNo ratings yet
- Mixture/: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskDocument4 pagesMixture/: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskCarissa Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Ios-Mat-0207 (Aa-2291517-4)Document77 pagesIos-Mat-0207 (Aa-2291517-4)hai nguyenNo ratings yet
- (Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology) J. Paulo Davim - Introduction To Mechanical Engineering-Springer International Publishing (2018) PDFDocument372 pages(Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology) J. Paulo Davim - Introduction To Mechanical Engineering-Springer International Publishing (2018) PDFSillas Souza OliveiraNo ratings yet
- BG 7 387 2010Document8 pagesBG 7 387 2010abhishek ranjanNo ratings yet
- High Content Screening A Powerful Approach To Systems Cell Biology and Phenotypic Drug Discovery 2nd Edition Paul A. JohnstonDocument54 pagesHigh Content Screening A Powerful Approach To Systems Cell Biology and Phenotypic Drug Discovery 2nd Edition Paul A. Johnstondarlene.cumming380100% (10)