Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology
Uploaded by
Pau De GuzmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology
Uploaded by
Pau De GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Ophthalmology – Lens: allows for fine focusing of light
Ophthalmology- the study of the eye, including diseases – Retina: lines the inside of the back part
of the eye and their respective treatments of the eye
Optometrist- examines people’s eyes to diagnose vision – Macula: center area of the retina
problems and eye diseases
– Optic nerve: transmits nerve signals of
Optician- person who dispenses lenses and other optical images to the brain
devices
The Visual Process
Ophthalmologist- an MD who performs eye surgery, as
well as diagnoses and treats eye diseases and injuries Light → cornea → pupil → lens → retina →
photoreceptor layer → optic nerve → brain
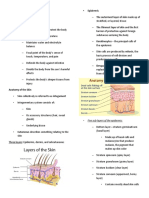
Anatomy of the Eye
Common Visual Disorders
• The Outer Structures
• Myopia: nearsightedness
– Orbit: bony socket that holds the eye
• Hyperopia: farsightedness
– Lacrimal gland: the gland that secretes
• Astigmatism: irregular conformation of the
tears
cornea
– Nasolacrimal ducts: drains tears into
• Presbyopia: “aging eyes”
nose
– Eyelids: folds of skin that protect the • Diplopia: double vision
eye • Amblyopia: “lazy eye”
– Meibomian glands: secrete oils to Treatments
lubricate the eyelids
• Corrective lenses (glasses, contacts)
– Eyelashes: hair attached to the eyelids
to protect the eye • Surgical Treatments:
• Other Structures – LASIK: corrects the shape of the cornea
with a laser and microkeratome
– Cornea: “window of the eye”
– PRK: corrects the shape of the cornea
– Sclera: “white of the eye” but without cutting (as in LASIK)
– Extraocular muscles: move the eye in – RK: radial incisions placed into the
different directions cornea to correct myopia
– Conjunctiva: keeps bacteria and foreign – AK: curved patterns placed into the
material out of the eye cornea to correct astigmatism
– Iris: colored part; controls light that – LTK: treats hyperopia using a YAG laser
enters the eye shrinking collagen in the cornea
– Pupil: central opening that allows light – CK: uses low-level frequency waves to
to enter the eye shrink the collagen in the cornea
– ICL: injectable lens that unfolds to Diagnostic Studies and Procedures
correct nearsightedness
• Assessing Visual Acuity
Common Structural Diseases and Disorders
– Snellen chart
• Chalazion: a cyst caused by enlargement of a
meibomian gland – Refraction
• Dilated examination: examination of back of
• Blepharitis: inflammation of the lid margins
the eye with ophthalmoscope
• Entropion: abnormal inward curling of the
• Slit-lamp examination: can examine eyes under
eyelid
high magnification
• Ectropion: abnormal outward curling of the
• Visual field testing:
eyelid
• Conjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva; - Amsler grid: detects macular problems
“pink eye” - Perimetry test: tests peripheral vision
Applanation tonometry: measures balance
• Scleritis: inflammation of the sclera of pressure to detect glaucoma
• Superficial punctate keratitis: inflammation Gonioscopy: evaluates angle between
and death of cells on the cornea cornea and iris for glaucoma
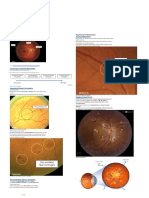
Fluorescein angiography: captures photos
• Keratoconus: a change in shape of the cornea
of retinal vasculature
to cone-shaped
Corneal topography: analyzes the curvature
• Cataract: clouding of the lens of the cornea
• Glaucoma: increased eye pressure due to
inadequate drainage of aqueous humor
• Diabetic retinopathy: macular edema and
vision loss caused by diabetes
• Age-related macular (AMD) degeneration:
malfunction of rods and cones, causing vision
loss
- Dry form:
• most common: 90% of cases
• cells of the macula begin to break down
• drusen form under the retina
- Wet form:
• considered to be advanced AMD
• blood vessels leak fluid and blood,
causing damage to the macula
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Expository Writing ModuleDocument30 pagesExpository Writing ModulePau De Guzman38% (8)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Case of George EthicsDocument4 pagesThe Case of George EthicsPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Laser Therapy For Posterior Segment DiseasesDocument37 pagesLaser Therapy For Posterior Segment DiseasesHerin Natalia100% (2)
- M1 Pre-Task: The Trolley ProblemDocument20 pagesM1 Pre-Task: The Trolley ProblemPau De Guzman75% (4)
- M3 Lesson 1: Reason and Impartiality - While Task 1: Case Study: What Should We Do?Document3 pagesM3 Lesson 1: Reason and Impartiality - While Task 1: Case Study: What Should We Do?Pau De Guzman100% (1)
- Situation A:: M5 Lesson 1: Theories of Justice - While Task 1Document2 pagesSituation A:: M5 Lesson 1: Theories of Justice - While Task 1Pau De Guzman100% (1)
- M4 Post-TaskDocument2 pagesM4 Post-TaskPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Process of Writing For Non-Writers - PPSXDocument53 pagesProcess of Writing For Non-Writers - PPSXPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Reading Material - Skeletal SystemDocument38 pagesReading Material - Skeletal SystemPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Medical Technology vs. Coronavirus Pre-Writing Who?Document2 pagesSubject Title: Medical Technology vs. Coronavirus Pre-Writing Who?Pau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- BSMT2C DE GUZMAN OutlineDocument1 pageBSMT2C DE GUZMAN OutlinePau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- General Surgery ConceptsDocument4 pagesGeneral Surgery ConceptsPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Epidermis: - Five Sub-Layers of The EpidermisDocument7 pagesEpidermis: - Five Sub-Layers of The EpidermisPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- National Geographic USA 11.2022Document136 pagesNational Geographic USA 11.2022Manuel Salas Arroyo100% (1)
- Persea Americana (Written Report)Document6 pagesPersea Americana (Written Report)Fathiah NhNo ratings yet
- Normal Macular ThicknessDocument6 pagesNormal Macular ThicknessSara BkrNo ratings yet
- Passmedicine MRCP Notes-OphthalmologyDocument31 pagesPassmedicine MRCP Notes-OphthalmologyHashim Ahmad50% (2)
- MedicineDocument49 pagesMedicinesnagltNo ratings yet
- Biology Eye NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Eye NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Macular Buckle in Myopia: Pradeep Susvar and S. Vinay KumarDocument4 pagesMacular Buckle in Myopia: Pradeep Susvar and S. Vinay KumarMohammad A. BawtagNo ratings yet
- 21 Masterclass NLE Gapuz 2 - HANDOUTSDocument16 pages21 Masterclass NLE Gapuz 2 - HANDOUTSLimuel dale CaldezNo ratings yet
- WBI05 Energy Exercise and Co-OrdiantionDocument172 pagesWBI05 Energy Exercise and Co-OrdiantionOxygen CarbonNo ratings yet
- OptiVisum LLC Releases Plant Based OptiVisum Drops For Restoring Visual AcuityDocument2 pagesOptiVisum LLC Releases Plant Based OptiVisum Drops For Restoring Visual AcuityPR.comNo ratings yet
- Funduscopy of Retinal Pathologies PDFDocument4 pagesFunduscopy of Retinal Pathologies PDFavininditaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNo ratings yet
- Lisa A. Kurtz - Visual Perception Problems in Children With AD - HD, Autism, and Other Learning Disabilities-Jessica Kingsley Pub (2006)Document108 pagesLisa A. Kurtz - Visual Perception Problems in Children With AD - HD, Autism, and Other Learning Disabilities-Jessica Kingsley Pub (2006)César AugustoNo ratings yet
- Case 29.07.09Document51 pagesCase 29.07.09kanavgNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye ReportDocument46 pagesBionic Eye ReportJHANSI .NNo ratings yet
- Icd Mata No Nama Penyakit Kode IcdDocument5 pagesIcd Mata No Nama Penyakit Kode IcdElNo ratings yet
- Restore Your Lost Vision - The Three-Step Program To Regain Your Sight (PDFDrive)Document198 pagesRestore Your Lost Vision - The Three-Step Program To Regain Your Sight (PDFDrive)prateek mehndirattaNo ratings yet
- 5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersDocument5 pages5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Unilateral Retinitis Pigmentosa: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument8 pagesUnilateral Retinitis Pigmentosa: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureWidyawati SasmitaNo ratings yet
- CarotenoidsDocument22 pagesCarotenoidsVanitha Reddy P100% (4)
- Classification: Associated ProblemsDocument13 pagesClassification: Associated ProblemsYrraFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Macular DegenerationDocument5 pagesMacular DegenerationPauleen Jambora RodilNo ratings yet
- Cookies ThesisDocument36 pagesCookies ThesisNegero Ararso100% (1)
- RetinaDocument4 pagesRetinaSyam k rajNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument15 pagesVisual PathwaymohhammadfaisaalNo ratings yet
- The Beneficial Role of Lutein and Zeaxanthin in Cataracts: ReviewDocument7 pagesThe Beneficial Role of Lutein and Zeaxanthin in Cataracts: ReviewLavinia BaleaNo ratings yet
- Funduscopy of Retinal PathologiesDocument4 pagesFunduscopy of Retinal PathologiesAvinindita Nura LestariNo ratings yet
- Myopic Degeneration - Myopic CrescentsDocument3 pagesMyopic Degeneration - Myopic CrescentsFerdinando BaehaNo ratings yet
- The Utility of Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Neuro-OphthalmologyDocument19 pagesThe Utility of Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Neuro-OphthalmologyA. JumeauNo ratings yet