Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise Notes Chapter - 14 Surface Areas and Volumes
Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise Notes Chapter - 14 Surface Areas and Volumes
Uploaded by
ROOPAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise Notes Chapter - 14 Surface Areas and Volumes
Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise Notes Chapter - 14 Surface Areas and Volumes
Uploaded by
ROOPACopyright:
Available Formats
CLASS X CBSE PATTERN CHAPTERWISE NOTES
CHAPTER - 14 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES
INTRODUCTION
All of us know about the basic shapes that we encounter in daily life. The common shapes are
cylinders, cubes, cuboids, cones and spheres. Now let us have a brief insight into the technical
parameters of these shapes. The dimensions encountered while viewing a cube are length,
breadth and height. The cube is a three dimensional view of a square in two dimensions .The
length, breadth and height have equal measurements in a cube. The case of a cuboid is different.
The cuboid is a three dimensional view of a rectangle in two dimensions. The dimensions of
length, breadth and height in a cuboid have different measurements.
When we consider a cylinder, it has two dimensions like radius and height. Height here refers to
the vertical height of the cylinder. In a cone, there are three dimensions to be considered namely
the radius, vertical height and the slant height. A sphere is easier to be analyzed. Only one
dimension which is the radius is to be considered in the case of a sphere.
There are two areas namely the lateral surface area and the total surface area to be considered in
the case of a cuboid and a cube.
There are two different types of areas like the curved surface area and total surface area to be
considered in the case of cylinder ,cone and sphere.
Here, in this chapter we are going to discuss problems related to areas and volumes of the basic
shapes.
AREA AND VOLUME OF A CUBE
When we look at a cube, we can see that there are six faces ,twelve edges and eight vertices in a
cube. The surface area formulas for a cube are given below:
(i) The lateral surface area of a cube = 4 X a2 where 'a' is the side of a cube.
Note: There are 4 sides seen laterally excluding the top and bottom.
(ii) The total surface area of a cube = 6 X a2 where 'a' is the side of a cube
(iii) The volume of a cube = a3 , where ‘a’ is the side of a cube.
AREA AND VOLUME OF A CUBOID
The case of a cuboid is different where length, breadth and height are different.
The cuboid also has 6 faces,8 vertices and 12 edges as in the case of a cube.
Total surface area of a cuboid = 2 *(lb + bh +lh) where l, b and h are the length , breadth and
height of a cuboid respectively.
Volume of a cuboid = l* b* h where l, b and h are the length, breadth and height of a cuboid
respectively.
AREA AND VOLUME OF CYLINDER
The cylinder has a curved surface and the height to be considered in the case of a cylinder is the
vertical height. The area to be considered in this case is of the curved surface and the total
surface. The cylinder may be hollow inside or solid.
The curved surface area of hollow cylinder = 2*π*R*h +2*π*r*h
Where,’R’ is the external radius of the hollow cylinder and ‘r’ is the internal radius of the
hollow cylinder.
‘h’ is the vertical height of the hollow cylinder.
Here, in this case the external surface area and the internal surface area are considered.
The curved surface area of a solid cylinder = 2*π*r*h
Where ‘r and ‘h’ are the radius of base and height of the solid cylinder respectively.
The total surface area of a hollow cylinder = 2*π*R*h + 2*π*r*h +2 *π*(R2 - r2)
Where ‘R’,’r’ and ‘h’ are the external radius ,internal radius and the vertical height of the hollow
cylinder respectively.
The total surface area of the solid cylinder = 2 *π*r*(h + r)
Where ‘r’ is the base radius and ‘h’ is the vertical height of the solid cylinder.
The volume of a hollow cylinder = π*h *(R2-r2)
Where ‘R’ and ‘r’ are the external and internal radii of the hollow cylinder respectively.
The volume of a solid cylinder = π*r2* h
Where ‘r’ is the base radius and ‘h’ is the vertical height of the solid cylinder.
You might also like
- 2.12.4 Test (TST) - Triangles (Test)Document10 pages2.12.4 Test (TST) - Triangles (Test)Charlotte Hargrove100% (2)
- Maths Project - PrantarDocument12 pagesMaths Project - Prantarprantarchakraborty.2006No ratings yet
- Cylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDocument5 pagesCylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDeviana DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Areas and Volumes ReportDocument13 pagesCylinder Areas and Volumes ReportJorge EsperidaNo ratings yet
- Surface-Area Jiwanwala FaridkotDocument12 pagesSurface-Area Jiwanwala Faridkotapi-3731257No ratings yet
- And VolumesDocument31 pagesAnd Volumesdev mittalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationDocument4 pagesA Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationAnjana mohandas WarrierNo ratings yet
- Cylinder - WikipediaDocument39 pagesCylinder - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Cone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HDocument31 pagesCone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9PDocument17 pagesSurface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9Pmahindra100% (1)
- Solid Geometry-3d PDFDocument27 pagesSolid Geometry-3d PDFpraveenshridharNo ratings yet
- CylinderDocument10 pagesCylinderSara XhaferiNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument17 pagesSurface Area and Volumeidrive12345678No ratings yet
- Ch-13 Maths NotesDocument6 pagesCh-13 Maths NotesJsjn NNo ratings yet
- Common Solid FiguresDocument6 pagesCommon Solid FiguresERLIZA ROSETENo ratings yet
- NOTE-Surface Area and VolumeDocument1 pageNOTE-Surface Area and VolumeSadiq NavalurNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume of 3d FiguresDocument13 pagesSurface Area and Volume of 3d Figuresapi-3731257100% (15)
- Maths Class 9 Notes For Volume and Surface AreaDocument5 pagesMaths Class 9 Notes For Volume and Surface AreaMd. Humayun KabirNo ratings yet
- Math ProjectDocument39 pagesMath Projectidod2307No ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument5 pagesGeometry FormulasAlyzza Rose Pampliega LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulasDocument25 pagesMensuration FormulasIsrar Ahmad100% (1)
- Cone and CylinderDocument17 pagesCone and CylindervinayaroraknpNo ratings yet
- Document 11Document6 pagesDocument 11Astitva KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Surface Area and VolumeDocument57 pagesClass 9th Surface Area and VolumemalakepayalNo ratings yet
- Word Problem ExamplesDocument18 pagesWord Problem ExamplesselventhiraNo ratings yet
- How To Find Volume of A CylinderDocument4 pagesHow To Find Volume of A Cylinderapi-174648067No ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument17 pagesSurface Area and VolumeNishant Malhotra100% (2)
- The Diagram Given Here Is of A Right Circular CylinderDocument2 pagesThe Diagram Given Here Is of A Right Circular CylinderRevaldy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface AreaDocument18 pagesVolume and Surface AreaPrabhakar Chowdary ChintalaNo ratings yet
- CURVED SURFACE SOLIDS Chapter 6Document35 pagesCURVED SURFACE SOLIDS Chapter 6tikafebriani52No ratings yet
- Course Hero 43Document4 pagesCourse Hero 43Maria Helen MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Area of Some Rectilinear FiguresDocument7 pagesArea of Some Rectilinear Figuressureshkthakur100% (1)
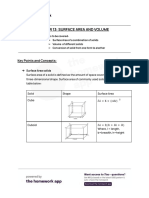
- Chapter 13: Surface Area and Volume: Key Points and ConceptsDocument8 pagesChapter 13: Surface Area and Volume: Key Points and ConceptssudhaNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument29 pagesMensurationSilparajaNo ratings yet
- ConeDocument6 pagesConeNaeem RazaNo ratings yet
- Cube Definition: Surface Area Formula For The CubeDocument3 pagesCube Definition: Surface Area Formula For The CubeJohn Joshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Surface Area & Volume Surface Area & Volume of 3-D Objects: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSurface Area & Volume Surface Area & Volume of 3-D Objects: ObjectiveShrey GuptaNo ratings yet
- Compilation in Solid GeometryDocument7 pagesCompilation in Solid GeometryBeepoy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Chap 13Document14 pagesChap 13P RASHMITHANo ratings yet
- Mensuration ProjectDocument4 pagesMensuration ProjectJatin NayyarNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexDocument9 pagesThree-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexAlí PabónNo ratings yet
- Cylinders: The Cylinder Area FormulaDocument2 pagesCylinders: The Cylinder Area Formulah8alfredNo ratings yet
- Solid MensurationDocument60 pagesSolid MensurationBenePicar100% (2)
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Do You Know What A Cylinder IsDocument3 pagesDo You Know What A Cylinder IsMaria AngelLuna GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume Class 10 PDF - Docx 1Document12 pagesSurface Area and Volume Class 10 PDF - Docx 1ABHISHEK J KNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument5 pagesGeometrylolileeNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formula For Bank Exams: Mensuration Shapes Two-Dimensional (2D) FiguresDocument4 pagesMensuration Formula For Bank Exams: Mensuration Shapes Two-Dimensional (2D) FiguresSagar Kumar PahiNo ratings yet
- Geometrical ShapesDocument10 pagesGeometrical ShapesEJ CastroNo ratings yet
- 3d Mensuration 41Document5 pages3d Mensuration 41PRAKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesAbdella KarimeNo ratings yet
- WK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dDocument61 pagesWK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dHoneybunch beforeNo ratings yet
- Mensuration BasicsDocument9 pagesMensuration BasicsKimberly ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Volume BolaDocument14 pagesVolume BolaLyfia SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Concept CirclesDocument36 pagesConcept CirclesPartha MajumderNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Geometry: Keerti Vardhan MadaharDocument8 pagesCalculus and Geometry: Keerti Vardhan MadaharReko BasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument31 pagesChapter - 13 Surface Areas and VolumesYash Goyal100% (1)
- Surface Area of Pyramids Cylinders and Cones Notes and ExamplesDocument17 pagesSurface Area of Pyramids Cylinders and Cones Notes and Examplesapi-308587685No ratings yet
- Conic Section Maths Project PDFDocument13 pagesConic Section Maths Project PDFSiva Kumar75% (4)
- Q N F F, The Bearing Capacity Factor Is F and The Product of Bearing QDocument2 pagesQ N F F, The Bearing Capacity Factor Is F and The Product of Bearing QROOPANo ratings yet
- Steel 9Document6 pagesSteel 9ROOPANo ratings yet
- Construction 2Document1 pageConstruction 2ROOPANo ratings yet
- 50 PSF 10 PSF: DL DLDocument1 page50 PSF 10 PSF: DL DLROOPANo ratings yet
- Steel 8Document2 pagesSteel 8ROOPANo ratings yet
- New Steel DesignDocument5 pagesNew Steel DesignROOPANo ratings yet
- New 8.3-2Document4 pagesNew 8.3-2ROOPANo ratings yet
- Wood DesignDocument4 pagesWood DesignROOPANo ratings yet
- Soil MaterialDocument3 pagesSoil MaterialROOPANo ratings yet
- CE6501-Structural Analysis-IDocument17 pagesCE6501-Structural Analysis-IROOPANo ratings yet
- Ce 8502 Structural AnalysisDocument2 pagesCe 8502 Structural AnalysisROOPA100% (1)
- Chapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Document18 pagesChapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Jesse McClureNo ratings yet
- LinesDocument27 pagesLinesicynitrogen9087No ratings yet
- Math Olimpiade Grade 5-1Document4 pagesMath Olimpiade Grade 5-1sofia milatinaNo ratings yet
- Math 4-Quarter 3 Week 1-Module 1Document19 pagesMath 4-Quarter 3 Week 1-Module 1jgorpiaNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Intergral Tententu - Volume Benda PutarDocument20 pagesAplikasi Intergral Tententu - Volume Benda PutarRita SuzanaNo ratings yet
- 2023 MATHEMATICS F2 QS T2 Exam Teacher - Co - .KeDocument17 pages2023 MATHEMATICS F2 QS T2 Exam Teacher - Co - .KePaul MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 03Document2 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions - DPP 03jeemainsmaterial97No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Circles AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Circles AnswersSandeep BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Geometry (SC)Document3 pagesGrade 4 - Geometry (SC)Ml PhilNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument3 pagesCirclesericmilamattimNo ratings yet
- Geometry Section 4 3Document7 pagesGeometry Section 4 3api-262621710No ratings yet
- G9MATH - T6.2 Similar PolygonsDocument30 pagesG9MATH - T6.2 Similar Polygonsdenzxx100% (1)
- To Draw Their Projections Means F.V, T.V. & S.V. What Is Usually Asked in The Problem?Document37 pagesTo Draw Their Projections Means F.V, T.V. & S.V. What Is Usually Asked in The Problem?Amit MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 10 - Straight Lines Revision NotesRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- CrystallographyDocument68 pagesCrystallographyMajid AliNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Transformations GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesThird Space Learning Transformations GCSE Worksheetmiapeachapplepiko000279001No ratings yet
- 8 1 MathsEnglishDocument96 pages8 1 MathsEnglishRaman VenmarathoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Hyperbolic FunctionDocument10 pagesChapter 1-Hyperbolic Functionhiromiebizuka11No ratings yet
- Edp Midterms Reviewer 1Document29 pagesEdp Midterms Reviewer 1gabbycervantes30No ratings yet
- Oblique TrianglesDocument18 pagesOblique TrianglesGilbertNo ratings yet
- Assignments QuadrilateralsDocument46 pagesAssignments Quadrilateralsmark joseph pamplonaNo ratings yet
- Aa Sss and Sas SimilarityDocument24 pagesAa Sss and Sas SimilarityJay Jexter SeldaNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9 Semester 2Document198 pagesMath Grade 9 Semester 2sarat135790No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Pea306Document127 pagesUnit 4 Pea306Aryan Rathore100% (1)
- TriangleDocument16 pagesTriangleShruti PatelNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry - October 30 2019Document80 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry - October 30 2019Gerelizza Angga100% (1)
- Polygon Polygon Note Taking Note Taking Activity Activity: Angela Lianne de AlaDocument6 pagesPolygon Polygon Note Taking Note Taking Activity Activity: Angela Lianne de AlaPrincess Vallery LuckmanNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelDocument19 pagesParallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelPenke Mejado BelenNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 10 Maths SA 2 Set 3Document3 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 10 Maths SA 2 Set 3sasankasahu36No ratings yet