Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Block 2.2 - Mental/Defense Mechanism
Block 2.2 - Mental/Defense Mechanism
Uploaded by
Dylan Mansilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesThe document discusses different types of defense mechanisms. It defines defense mechanisms as involuntary coping strategies that distort reality to reduce anxiety. Defense mechanisms are classified into four types: narcissistic-psychotic, immature, neurotic, and mature. Examples of immature defenses discussed include denial, distortion, hypochondriasis, introjection, and passive aggression. Projection and denial are provided as examples of narcissistic-psychotic defenses.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of defense mechanisms. It defines defense mechanisms as involuntary coping strategies that distort reality to reduce anxiety. Defense mechanisms are classified into four types: narcissistic-psychotic, immature, neurotic, and mature. Examples of immature defenses discussed include denial, distortion, hypochondriasis, introjection, and passive aggression. Projection and denial are provided as examples of narcissistic-psychotic defenses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesBlock 2.2 - Mental/Defense Mechanism
Block 2.2 - Mental/Defense Mechanism
Uploaded by
Dylan MansillaThe document discusses different types of defense mechanisms. It defines defense mechanisms as involuntary coping strategies that distort reality to reduce anxiety. Defense mechanisms are classified into four types: narcissistic-psychotic, immature, neurotic, and mature. Examples of immature defenses discussed include denial, distortion, hypochondriasis, introjection, and passive aggression. Projection and denial are provided as examples of narcissistic-psychotic defenses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
PSYCH TRANS 2
ego cannot recognize, therefore reduce
ILO ILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE O F MED ICINE
anxiety.
Molo, Iloilo City
S.Y. 2018-2019
Examples of Projection
BATCH 2021 “OH MY GOD, SHE’S SO FAT/UGLY/SLUTTY!”
DISCIMUS SAPIENCIA UT VIRTUS o You might have felt an immense
sense of distaste and dislike for
this person, when in fact this is
a projection mechanism veiling
PSYCHIATRY your own deeper body-image
BLOCK 2 issues. Likely, you are deeply
insecure about your own body,
LE CTUR ER: DR. V AR GA S and thus unconsciously project
MAIN TOPIC: MENTAL/ DEFENSE MECHANISM this loathing to others.
“THAT IS GROSS/BAD, GET IT AWAY FROM
Outline
ME.”
I. Definition of Defense Mechanisms
II. Classifications of Defense Mechanisms
o What we react the most strongly to
III. Narcissistic-Psychotic Defenses says the most about what we place
IV. Immature Defenses the most importance in. For
V. Neurotic Defenses instance, if we can’t stand
VI. Mature Defenses watching sex on TV, this could very
well be a reflection of a hidden
DEFINITION OF DEFENSE MECHANISMS sexual shame or insecurity we in
ourselves.
Adaptive involuntary coping mechanisms that distort
“HE/SHE IS HAVING AN AFFAIR.”
our perception of reality in order to reduce subjective
o The fear that your partner/spouse
distress, anxiety, and depression.
is having an affair or is
If such changes in reality are not “distorted” and untrustworthy is often a reflection
“denied”, they can result in disabling anxiety and of the way you feel about yourself.
depression, or both. All normal people functioning in
Unconscious strategies that protect us from threats to relationships feel attracted to
our self-esteem and other sources of anxiety. other people at one point or
These involuntary mental mechanisms: another, and sometimes this self-
o Restore psychological homeostasis discovery is met with fear and
o Provide a mental time-out to adjust to shame which is then often
sudden changes in reality and self-image projected onto the other partner.
(example: winning the lottery, unexpected
accident or a diagnosis of an incurable illness) 2. Denial
Sometimes, people will accept reality and the
CLASSIFICATIONS OF DEFENSE MECHANISMS seriousness of the fact, but they will deny
George Vaillant classified defense mechanisms into four types: their own responsibility and instead blame
I. Narcissistic-Psychotic Defenses other people or other outside forces.
II. Immature Defenses Inability to accept reality
III. Neurotic Defenses If some situation is just too much to handle,
IV. Mature Defenses the person just refuses to experience it; the
person will continue to deny existence or
truth because it is too uncomfortable to face.
NARCISSISTIC-PSYCHOTIC DEFENSES
It will only last as long as we can hold onto
1. Projection our distorted belief that we are fine, when in
Involves transferring unwanted aspects of reality, we are not
the self onto others Functions to protect the ego from things with
Much of what we criticize in other may which the individual cannot cope
reflect something we’re hiding from
ourselves Examples of Denial
Projection works by allowing the expression “No, I’m just a social smoker.”
of the desire or impulse, but in a way that the
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 7|16
PSYCH TRANS 2
A person who is functioning alcoholic will 2. Hypochondriasis
often simply deny they have a drinking Exaggerating or overemphasizing an illness
problem, pointing to how well they function for the purpose of evasion
in their job and relationships. Responsibility can be avoided, guilt can be
They might admit that they do use drugs or circumvented
alcohol, but will claim that his substance
abuse is not a problem. 3. Introjection
In chronic or terminal illnesses, people with Internalizing the qualities of an object
such illnesses may think, “It’s not so bad. I’ll Identifying with the aggressor
get over it,” and refuse to make any lifestyle A focus on negative or feared traits, i.e. if you
changes. are afraid of someone, you can practically
conquer that fear by becoming more like
3. Distortion them
Grossly reshaping the experience of external
reality to suit inner needs 4. Passive aggression
Is about being passive, appearing to be OK
Example of Distortion with things and saying “yes”
A singer who is not told at an audition that The passive aggressive will say “yes” to
she needs a lot of work to make her voice requests even if they don’t want to do them.
stronger remembers the audition as notable They often lack the strength to stand up for
for receiving only positive feedback. themselves and say no assertively.
IMMATURE DEFENSES
Examples of Passive Aggression
Common in preadolescent years
Deliberately pissing someone off out of anger
Related to intimacy or its loss
but pretending you didn’t know it would
bother them
Examples of Immature Defenses
o When she was trying to study, I
Acting out
blasted my music as loud as I could
Blocking
Not answering the phone to avoid someone
Hypochondriasis and pretending you simply weren’t able to
Introjection talk to them.
Passive-aggressive behavior Agreeing to help someone because you don’t
Regression have enough guts to say no and then doing a
Somatization sloppy job because you never really wanted
Schizoid fantasy to help
Deliberately hurting someone or something
1. Acting out but pretending it was an accident
Performing an extreme behavior in order to Agreeing to do something and then
express thoughts or feelings the person feels procrastinating such that the thing is not
incapable of otherwise expressing done on time or at all.
When a person acts out, it can act as a o The person may tell you it is fine to
pressure release, and often help the attend your friend’s party, but he
individual feel calmer and peaceful once does not start getting ready to go on
again. time and runs an hour late.
As a passive aggressive, I…
Examples of Acting Out o Hide my hostility by seeming
Instead of saying, “I’m angry with you,” a someone I dislike, and am unable to
person who acts out may throw a book at the be honest with the person.
person, or punch a hole through the wall o Say I agree with something but don’t
A child’s temper tantrum is a form of acting follow through because I don’t agree
out when he or she doesn’t get is or her way with it.
with a parent. o Try to please people by agreeing to
Self-injury may also be a form of acting-out, their plan of action, yet actually
expressing in physical pain what one cannot doing the opposite.
stand to feel emotionally.
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 8|16
PSYCH TRANS 2
o Act one way, which is true to my Traumatic events manifested themselves
inner feelings, yet say another. physically
o Avoid conflict at all cost by giving in
to others, then procrastinate and Example of Somatization
never do what I agreed to do. A person experienced paralysis on one side,
o Am angry, but afraid to show my which linked to a dream in which she felt
anger, so I quietly take my revenge paralyzed while trying to fend off a snake
by doing the opposite. from her bed-bound father.
Passive aggressive think in a very specific
way 7. Schizoid fantasy
o I must avoid an argument, fight, or “Finding a happy place”
conflict at all costs. People retreat into a fantasy world in order
o I never “win” in confrontation. to escape from reality, a way to escape real
o I must please people by telling them problems.
what they want to hear. In some cases, this may be beneficial:
o No one wants to know how I feel. thinking about an upcoming vacation, or a
o No one will understand how I feel. reward from work when it gets too stressful,
is a healthy use of fantasy.
5. Regression It may become part of the problem:
Moving oneself back to a once secure place imagining the worst consequences may lead
when experiencing an insecure state of to fear, or reliving a bad situation may lead to
emotion anger and depression; imagining solutions to
Reversion to an earlier stage of development problems instead of actually solving them can
in the face of unacceptable thoughts or have negative consequences.
impulses In younger children, for example, if they are
When we are troubled or frightened, our having a hard time at school, they might
behaviors often become more childish or convince themselves that they are spies, or
primitive have superpowers like superman.
Ann Freud call this defense mechanism
regression, suggesting that people act out NARCISSISTIC DEFENSES
behaviors from the stage of psychosexual
development in which they are fixated. Common in neurotic disorders
For example:
o An individual fixated at the oral Examples of Narcissistic Defenses
stage might begin eating or smoking Controlling
excessively, or might become very Displacement
verbally aggressive. Dissociation
o A fixation at the anal stage might Externalization
result in excessive tidiness or Inhibition
messiness. Intellectualization
Isolation
Examples of Regression Rationalization
A child may begin to suck their thumb again Reaction formation
or wet the bed Repression
Teenagers ma giggle uncontrollably when Sexualization
introduced into a social situation involving
the opposite sex 1. Displacement
An adult may regress when under a great Redirection of an impulse (usually
deal of stress, refusing to leave their bed and aggression) onto a powerless substitute
engage in normal, everyday activities. target
Transferring of one’s aggression from one
6. Somatization target to another, usually more innocent
Occurs when the internal conflicts between target
the drives of the Id, Ego and Super Ego take
on physical characteristics
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 9|16
PSYCH TRANS 2
Example of Displacement 5. Rationalization
A worker, angry at his boss, obviously unable Justifying one’s own negative actions,
to direct his anger and hostility to his thoughts and experiences
intended target, comes home and yells at his “Make excuses”
wife. Involves explaining an unacceptable behavior
She, now also angry and upset, displaces her or feeling in a rational or logical manner,
anger on the child, who then further avoiding the true reasons for the behavior
displaces it on their pet dog. Protects self-esteem and self-concept
Most often, we take out our frustrations on When confronted by success or failure,
the people we love. people ten d to attribute achievement to
their own qualities and skills while failure are
2. Dissociation blamed on other people or outside forces
People who use dissociation as a defense
mechanism tend to momentarily lose their Examples of Rationalization
connection to the world around them. A person who has been turned down for a
They may feel separated from the outside date might rationalize the situation by saying
world, as though they exist in another realm. they were not attracted to the other person
Dissociation often helps people to cope with anyway.
uncomfortable situations by “removing” A student might blame a poor exam score on
themselves from them. the instructor rather than his lack of
They may enter a state of daydreaming, preparation.
staring into space and letting their mind You lose your temper in front of people you
wander until someone nudges them, want to like and respect you. To make
prompting them to acknowledge reality once yourself feel better, you mentally attribute
more. your outburst to a situation outside your
control, and twist things so that you can
3. Intellectualization blame someone else for provoking you.
Thinking is used to avoid feeling Bob has been dumped by his girlfriend,
Involves removing one’s self emotionally Susan. Instead of moving on and accepting
from a stressful event the end of his relationship with Susan, he
Excludes unpleasant urges from full continues to rationalize the break-up by
awareness by removing their affective charge telling people that Susan only broke up with
him because she was having a bad day, or
Examples of Intellectualization reassuring himself that everyone breaks up
A person who has just been diagnosed with a sooner or later. By doing this, he is able to
terminal illness might focus on learning avoid the emotional pain and the thought of
everything about the disease in order to his own incompetence as a mate.
avoid distress ad remain distant from the
reality of the situation. 6. Reaction Formation
A woman who has been raped seeks out Reduces anxiety by taking up the opposite
information on another cases and the feeling, impulse, or behavior
psychology of rapists and victims. She takes According to Freud, reaction formation is
self-defense classes in order to feel better used to hide true feelings by behaving in the
(rather than more directly addressing the exact opposite manner.
psychological and emotional issues.)
Example of Formation Reaction
4. Isolation You secretly harbor lustful feelings toward
Leads a person to separate ideas or feelings someone you should probably stay away
from the rest of their thoughts from. You don’t want to admit to these
feelings, so you instead express the very
Example of Isolation opposite of those feelings. This object of your
A person with a particularly stressful job may lust now becomes the object of your bitter
use isolation to separate their work from hatred.
their family, avoiding the stress affecting
their relationships.
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 10|16
PSYCH TRANS 2
You treat someone you strongly dislike in an 2. Anticipation
excessively friendly manner in order to hide Involves rehearsing possible outcomes in
your true feelings. one’s mind or telling oneself that will not be
as bad as they imagine
7. Repression
“Putting away” Example of Anticipation
Acts to keep information out of conscious A person with a phobia of dentists might
awareness anticipate an appointment to have a tooth
To keep disturbing or threatening thoughts removal by telling themselves that the
from becoming conscious procedure will be over in just a few minutes,
Note: These memories just don’t disappear; and reminding themselves that they have
they continue to influence our behavior. had one previously without any problems.
Examples of Repression 3. Humor
A person who has repressed memories of Hiding of one’s anxiety by expressing an
abuse suffered as a child may later have outward sense of humor about an
difficulty forming relationships. emotionally tolling event
Bob has been dumped by his girlfriend, Using comedy to overly express feelings and
Susan. Instead of moving on and accepting thoughts without personal discomfort and
the end of his relationship with Susan, he without producing an unpleasant effect on
goes on with his life avoiding any thoughts others
that have to do with his past relationship with
Susan. Example of Humor
MATURE DEFENSES Bob has been dumped by his girlfriend,
Susan. Instead of moving on and accepting
Healthy and adaptive mechanisms the end of his relationship with Susan, he
Useful in the integration of personal needs and jokes with his friends and tells them he might
motives, social demands, and interpersonal relations be the ugliest son of a gun in town, and that’s
why she dumped him. By doing this, Bob is
Examples of Mature Defenses covering up his pain and anxiety with a false
Altruism sense of humor.
Anticipation
Asceticism 4. Sublimation
Humor Involves transforming unacceptable desires
Sublimation into constructive and socially acceptable
Suppression forms
This is similar to displacement, but takes
1. Altruism place when we manage to displace our
An act of goodwill towards another person, emotions into a constructive rather that
known as altruism behavior, can be used as a destructive activity.
way of diffusing a potentially anxious
situation Examples of Sublimation
It involves getting pleasure from giving to Many great artists and musicians have had
others what the individual would have unhappy lives and have used the medium of
received. art of music to express themselves.
Sport is another example of putting our
Example of Altruism emotions (e.g. aggression) into something
A former alcoholic serves as an Alcoholics constructive.
Anonymous sponsor to a new member – A surgeon who takes hostile impulses and
achieving a transformative process that may converts them into “cutting” other people in
be lifesaving to both giver and receiver. a way that is perfectly acceptable in society.
The deaf, angry, and lonely Beethoven
transformed his pain into triumph by putting
Schiller’s “Ode to Joy” to music.
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 11|16
PSYCH TRANS 2
5. Suppression
Occurs consciously
Involves attempting not to think about a
memory or feelings when an uneasy thought
enters their mind or they might preoccupy
their minds by undertaking an unrelated task
to distract themselves
A person may also suppress feelings of love or dislike towards a
person, behaving normally towards them as though they felt
dispassionate towards them.
BATCH 2021-DSV | ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE OF MEDICINE 12|16
You might also like
- McWilliams' Defensive Functioning - Table by BeierDocument3 pagesMcWilliams' Defensive Functioning - Table by BeierCLD100% (1)
- GABBARD - Term Psychodynamic Psychotherapy (Extrait) - 1Document6 pagesGABBARD - Term Psychodynamic Psychotherapy (Extrait) - 1Moëa NmtNo ratings yet
- IG Sarason (Theory) PDFDocument57 pagesIG Sarason (Theory) PDFDaril Inocencio0% (1)
- Why Punctuality Is ImportantDocument4 pagesWhy Punctuality Is ImportantHumpyCreatureNo ratings yet
- Philippine Center For AutismDocument5 pagesPhilippine Center For AutismdianamusniNo ratings yet
- Theories of Human Develoment - Prof SE NkoanaDocument21 pagesTheories of Human Develoment - Prof SE Nkoananokwandankosi222No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - Defense Mechanism 2014ADocument4 pagesPsychiatry - Defense Mechanism 2014AbunteekNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Defense Mechanism and Crisis InterventionDocument3 pagesTask 3 Defense Mechanism and Crisis InterventionRosevick BadocoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewerDocument20 pagesPsychiatric Nursing ReviewerLezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- Negative StigmaDocument6 pagesNegative StigmaCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Defense Mechanism, Psychological Perspective and Fields of PsychologyDocument46 pagesDefense Mechanism, Psychological Perspective and Fields of PsychologyVince Dulay100% (1)
- Text 3. Ego Defense Mechanisms: DisplacementDocument4 pagesText 3. Ego Defense Mechanisms: DisplacementAnja MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- Ncmpsy4 MidtermsDocument11 pagesNcmpsy4 MidtermsDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Defense MechanismsDocument2 pagesDefense MechanismsJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- Defense Mechanism, Psychological Perspective and Fields of PsychologyDocument46 pagesDefense Mechanism, Psychological Perspective and Fields of PsychologyVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Defense MechanismDocument3 pagesDefense MechanismCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic Theory - FreudDocument40 pagesPsychoanalytic Theory - FreudMuzzammil Mehboob0% (1)
- Personality DisordersDocument3 pagesPersonality Disordersvzantua.k11831205No ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosteraisyahNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic Approach To CounselingDocument25 pagesPsychoanalytic Approach To CounselingMarilyn A. Bayhi100% (1)
- Unit 5 Family InfluencesDocument25 pagesUnit 5 Family Influencesshubhii1997No ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The SelfYay or Nay Panel DiscussionNo ratings yet
- 100 Defense MechanismDocument15 pages100 Defense MechanismEm Manuel100% (4)
- Defense MechanismsDocument8 pagesDefense Mechanismsraudadaimon0No ratings yet
- Defense Description Example: DisplacementDocument5 pagesDefense Description Example: DisplacementTeyen MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Psychology1Document26 pagesPsychology1Arriana JutajeroNo ratings yet
- Zachary Feder The Message of AutoimmunityDocument10 pagesZachary Feder The Message of AutoimmunitygenerjustnNo ratings yet
- Defense MechanismDocument24 pagesDefense MechanismVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument22 pagesTheories of PersonalityJacqueline Marie G. MilladoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Humanistic Theory PDFDocument4 pages4 - Humanistic Theory PDFpawansdube100% (1)
- TablesDocument4 pagesTablesColeen DajonNo ratings yet
- 1 Universal Bioethcal PrinciplesDocument2 pages1 Universal Bioethcal PrincipleschelseyNo ratings yet
- The Ego by Anna FreudDocument9 pagesThe Ego by Anna FreudyogimanmanNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 A Lec / W3 / Akba: TheoryDocument3 pagesNCM 117 A Lec / W3 / Akba: TheoryAngeli Kristiana AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DistortionDocument1 pageCognitive DistortionAhmad Shahril Ab Halim100% (1)
- LibidoDocument6 pagesLibidoNISHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Crisis and Crisis InterventionDocument7 pagesCrisis and Crisis InterventionAud SyneNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis: Uncovering The Mysteries of The Unconscious MindDocument15 pagesPsychoanalysis: Uncovering The Mysteries of The Unconscious MindRhea AlumNo ratings yet
- PSYC A333F Lecture 8Document51 pagesPSYC A333F Lecture 8trudyNo ratings yet
- Ways To Overcome Emotional and Psychological TraumDocument5 pagesWays To Overcome Emotional and Psychological TraumJosé Ángel Pérez TapiasNo ratings yet
- File 1404755176Document6 pagesFile 1404755176Mico MasamayorNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders ExercisesDocument6 pagesPersonality Disorders ExercisesPolina AndreevaNo ratings yet
- Bantolo Bsn305 NCPDocument4 pagesBantolo Bsn305 NCPIrish BantoloNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Models and Relevance To Nursing PracticeDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Models and Relevance To Nursing PracticeJewel Yap100% (1)
- WINNICOTT, Donald W. - 1974.-Fear-of-Breakdown.-International-Review-of-Psychoanalysis.-1-103-7 PDFDocument5 pagesWINNICOTT, Donald W. - 1974.-Fear-of-Breakdown.-International-Review-of-Psychoanalysis.-1-103-7 PDFFelipe Garzon SutNo ratings yet
- The Humanistic Approach - Anushka and ShaswatiDocument13 pagesThe Humanistic Approach - Anushka and ShaswatiadeshNo ratings yet
- Ahuja Defence Mechanisms AhujqDocument4 pagesAhuja Defence Mechanisms AhujqEchoNo ratings yet
- Social ThinkingDocument5 pagesSocial Thinkingjonizaaspe78No ratings yet
- Dissociation and Trauma: in Young PeopleDocument4 pagesDissociation and Trauma: in Young Peopleyeney armenterosNo ratings yet
- Eng Lit 7 Archetypal - Marxist and PsychoDocument42 pagesEng Lit 7 Archetypal - Marxist and PsychoEllie MontalbanNo ratings yet
- The Superpower of Validation:: Jill Rathus Alec MillerDocument19 pagesThe Superpower of Validation:: Jill Rathus Alec Miller水野午後No ratings yet
- Shame and AttachmentDocument9 pagesShame and Attachmentciobanusimona259970No ratings yet
- Handouts For Emotional Self in UTSDocument2 pagesHandouts For Emotional Self in UTSTuppidNo ratings yet
- Parts: of PsycheDocument10 pagesParts: of PsycheFlower100% (2)
- Stress & CopingDocument24 pagesStress & Copingohemgee wowNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Soc ScieDocument4 pagesFinal Examination Soc ScieMatuzalm BobilesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - PerdevDocument10 pagesReviewer - PerdevFrencyJhonSanJuanNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Definitions, Contexts, Neural Correlates and Strategic TherapyDocument16 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Definitions, Contexts, Neural Correlates and Strategic TherapySATRIO BAGAS SURYONEGORONo ratings yet
- Cognitive Distortions Handout TemplateDocument3 pagesCognitive Distortions Handout TemplateLand Bank CatanauanNo ratings yet
- Pathologies of the Self: Exploring Narcissistic and Borderline States of MindFrom EverandPathologies of the Self: Exploring Narcissistic and Borderline States of MindNo ratings yet
- Shadow Work: The Ultimate Guide to Integrating Your Dark Side (A Guide to Integrating Your Dark Side for Spiritual Awakening)From EverandShadow Work: The Ultimate Guide to Integrating Your Dark Side (A Guide to Integrating Your Dark Side for Spiritual Awakening)No ratings yet
- Workbook & Summary - The Gift Of Fear - Based On The Book By Gavin De BeckerFrom EverandWorkbook & Summary - The Gift Of Fear - Based On The Book By Gavin De BeckerNo ratings yet
- NSAIDs and DMARDs - Dr. FabilaDocument9 pagesNSAIDs and DMARDs - Dr. FabilaDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic & Pituitary Hormone DrugsDocument29 pagesHypothalamic & Pituitary Hormone DrugsDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Agents For BoneDocument43 pagesAgents For BoneDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid and Thyroid DrugsDocument36 pagesAnti-Thyroid and Thyroid DrugsDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Block 2.1 - Abdominal, Rectal Injury (Dr. Lozada) - 2Document6 pagesSurgery Block 2.1 - Abdominal, Rectal Injury (Dr. Lozada) - 2Dylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Dystocia Due To Abnormalities of The Bony and Soft Parts PassagesDocument4 pagesDystocia Due To Abnormalities of The Bony and Soft Parts PassagesDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Emg Conceptos - Nerve Conduction StudiesDocument23 pagesEmg Conceptos - Nerve Conduction StudiesDeborah SalinasNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 NotesDocument4 pagesExam 1 Noteshenry EkwuemeNo ratings yet
- Inquirybased Learning MIDYEAR INSET2023Document30 pagesInquirybased Learning MIDYEAR INSET2023Cynthia LuayNo ratings yet
- Andi Learning ManagementDocument26 pagesAndi Learning ManagementFikri SeptianNo ratings yet
- LabChart Spike HistogramDocument2 pagesLabChart Spike HistogrammanuelNo ratings yet
- Attitudes Based On Low EffortsDocument2 pagesAttitudes Based On Low EffortsfreeNo ratings yet
- Study Tips For People With ADHDDocument12 pagesStudy Tips For People With ADHDGuita YasseriNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology - Biological ApproachDocument19 pagesIB Psychology - Biological ApproachNayeli NARANJO TOAPANTA (11M)No ratings yet
- Dement - Kleitman (1957) Sleep and DreamingDocument5 pagesDement - Kleitman (1957) Sleep and Dreamingvanessa claraNo ratings yet
- Reduced Perceptual Narrowing in Synesthesia: A B C D e FDocument8 pagesReduced Perceptual Narrowing in Synesthesia: A B C D e FAbraham DaltonNo ratings yet
- Post Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument7 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disordersomebody_maNo ratings yet
- How To Overcome Your Fear of Public Speaking DR Aziz PDFDocument25 pagesHow To Overcome Your Fear of Public Speaking DR Aziz PDFLefterisNo ratings yet
- Module 3-HUMANITIES Art AppreciationDocument3 pagesModule 3-HUMANITIES Art AppreciationKentoy Galagate GoleNo ratings yet
- Robotics QAME FormsDocument42 pagesRobotics QAME FormsAlbert Corsame UmbacNo ratings yet
- Free Personality Test - SAPA-Project - Your Customized ReportDocument12 pagesFree Personality Test - SAPA-Project - Your Customized ReportKaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument7 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMERCEDITA S. TOJINONo ratings yet
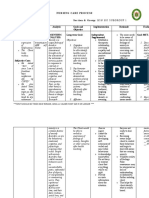
- Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationKyla Castro100% (1)
- Outline Social WellnessDocument11 pagesOutline Social WellnessRodel CruzNo ratings yet
- A Study to Assess the Knowledge of Primary School Teachers Regarding Behavioural Problems and their Prevention among School Going Children in Selected Government Primary Schools at Bagalkot with a View to Develop an Information BookletDocument25 pagesA Study to Assess the Knowledge of Primary School Teachers Regarding Behavioural Problems and their Prevention among School Going Children in Selected Government Primary Schools at Bagalkot with a View to Develop an Information BookletAnonymous izrFWiQ100% (3)
- Barth BulimiaDocument13 pagesBarth BulimiaFernando Mišel PessoaNo ratings yet
- English TestingDocument3 pagesEnglish TestingFaozzan Affandi100% (2)
- 6 Ways Educators Can Prevent Bullying in SchoolsDocument4 pages6 Ways Educators Can Prevent Bullying in SchoolsJhay-are PogoyNo ratings yet
- Why Should Language Teachers Be Interested in PsycholinguisticsDocument6 pagesWhy Should Language Teachers Be Interested in PsycholinguisticsMeizen Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Students' Perception About Improving English Listening Skills Using Movies Among The Vocational High School StudentsDocument11 pagesStudents' Perception About Improving English Listening Skills Using Movies Among The Vocational High School StudentsMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Article HARRY SULLIVAN'S THEORY OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONS IN CHARACTERIZING Nora Personality in Henrik Isben's A Doll's House PDFDocument9 pagesArticle HARRY SULLIVAN'S THEORY OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONS IN CHARACTERIZING Nora Personality in Henrik Isben's A Doll's House PDFAnonymous 1d1iD8vNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 (Theoretical Framework & Conceptual Framework)Document3 pagesCHAPTER1 (Theoretical Framework & Conceptual Framework)Abegail ContenedoNo ratings yet
- Albirex Niigata Singapore: Top Team Players IdpDocument11 pagesAlbirex Niigata Singapore: Top Team Players IdpAiman HakimNo ratings yet