Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dowel Bars at Joints / Jacketing Requirement R4
Dowel Bars at Joints / Jacketing Requirement R4
Uploaded by
Kumy engineeringOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dowel Bars at Joints / Jacketing Requirement R4
Dowel Bars at Joints / Jacketing Requirement R4
Uploaded by
Kumy engineeringCopyright:
Available Formats
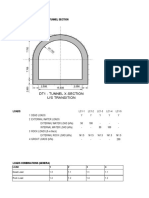
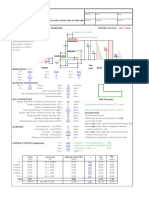
DOWEL BARS AT JOINTS / JACKETING REQUIREMENT R4
Width of the member (Initial) m 0.9 Axial load - Dead Ton 1653
Width of the member (Final after jacketing) m 1.3 Axial load - Lateral Ton 156
Thickness (Size along the shear force, ie critical direction) Initial m 0.9 Shear force - Dead Ton 40.0
Thickness (Size along the shear force ie, critical direction) Final after jacketing m 1.3 Shear force - Lateral Ton 24.0
Critical shear force (Assume 0.9D+1.5 Lateral) Ton 72.0
Critical Axial Load (Assume 0.9D-1.5 Lateral) Ton 1254 Coefficient of Friction ( µ ) 0.4
Beta (B) (A factor in the eqn of TauC) 2.90
Shear strength in concrete (Tau C) N/mm2 0.64 % Frictional force to be considered ( 100% means full friction) % 100
Shear Force capacity of the whole section Ton 72.3 Grade of Concrete N/mm2 25
Shear Force capacity of the initial section Ton 34.6 Grade of steel N/mm2 415
Shear Resistance due to Friction Ton 261.2 Rebar content % 1.0
Design Shear Force to be resisted by Shear Legs /dowel bars Ton 37.6 Rebar diameter for Shear legs mm 10
Total Area of Shear Legs /dowel bars mm2 1649 No. of legs in the critical direction Nos 4
Total No. of Legs for the dowel Nos 22 OR Spacing of legs along the member span from the c/s mm 400
1.0 Coefficient of Friction ( µ ): The PCA's Concrete Masonry Handbook, Appendix A, gives a precast concrete-to-concrete masonry friction coefficient of 0.4 with F.S of 2.
2.0 Increased Shear strength under Axial Compression is not considered in the calculation.
You might also like
- Examples 8.3 and 8.4Document12 pagesExamples 8.3 and 8.4itissa INGENIERIANo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1Document8 pagesChemistry 2 Practice Exam 1Ruby RichiezNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of FoundationsDocument3 pagesConceptual Design of FoundationsJames AswaNo ratings yet
- Load Capacity of Pile From Driving FormulaDocument9 pagesLoad Capacity of Pile From Driving Formuladaus_parisi0% (1)
- Rebar Chair Designr1Document3 pagesRebar Chair Designr1John Vincent MusngiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Restrained Pipe Length at TR-02 (Ch-14+426) - 1.2mDocument2 pagesCalculation of Restrained Pipe Length at TR-02 (Ch-14+426) - 1.2mSaifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Shear: Tank SupportDocument12 pagesConcrete Shear: Tank SupportfostbarrNo ratings yet
- Kopya NG PAES613-DesignofaDiversionDam PDFDocument57 pagesKopya NG PAES613-DesignofaDiversionDam PDFJohn Paulo PeridoNo ratings yet
- (Final Version) Multistory Frame Under Lateral LoadingDocument36 pages(Final Version) Multistory Frame Under Lateral LoadingHo Fai TangNo ratings yet
- Gorhar-Khairatunda: Subject: Estimation of VUP at KM 1+330 DataDocument17 pagesGorhar-Khairatunda: Subject: Estimation of VUP at KM 1+330 Datanandu523No ratings yet
- Load Combination 2Document4 pagesLoad Combination 2Espn SachinNo ratings yet
- Table of Pavement Design ValuesDocument12 pagesTable of Pavement Design ValuesCity AspireNo ratings yet
- SHEAR WALL REBAR Autosaved ExcelDocument10 pagesSHEAR WALL REBAR Autosaved ExcelSohagNo ratings yet
- 2007 - 01 Sewer Installation by Pipejacking in The Urban Areas of Hong Kong Part IDocument14 pages2007 - 01 Sewer Installation by Pipejacking in The Urban Areas of Hong Kong Part IAldro SopiohNo ratings yet
- 24-04 - 1200-1330 - Ejercicio Geotextile Reinforced Embankment With Consolidation (PLAXIS)Document16 pages24-04 - 1200-1330 - Ejercicio Geotextile Reinforced Embankment With Consolidation (PLAXIS)Andres Flores BaezNo ratings yet
- EsalcalcDocument28 pagesEsalcalcRaul Zapana ZelaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LevelDocument4 pages1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LeveldsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- HansenDocument76 pagesHansenJuan Manuel Velazquez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Strength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityDocument4 pagesStrength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityAlma M. LaraNo ratings yet
- HDB Requirements For A&a Work On HDB PremisesDocument16 pagesHDB Requirements For A&a Work On HDB PremiseschemicalbreadNo ratings yet
- Checking Bearing CapacityDocument1 pageChecking Bearing CapacityAmir SyamNo ratings yet
- ME328 Introduction to Design Cylinder Stresses: ldr + 2σ lr − 2l (σ dr term because it's theDocument3 pagesME328 Introduction to Design Cylinder Stresses: ldr + 2σ lr − 2l (σ dr term because it's theAndri IndriawanNo ratings yet
- EqualAngle PDFDocument2 pagesEqualAngle PDFGalih PutraNo ratings yet
- Project Area Sub Area Plant/Unit Code Se-Spml (JV) RevDocument13 pagesProject Area Sub Area Plant/Unit Code Se-Spml (JV) RevBanwari Lal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Elastic Modulus and Strength of ConcreteDocument24 pagesElastic Modulus and Strength of ConcreteChatchai ManathamsombatNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LevelDocument4 pages1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LeveldsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- CorbelDocument12 pagesCorbelSri Datta Kiran Kuchibhatla67% (3)
- Crux Prestressing Pvt. LTD.: Pile DataDocument5 pagesCrux Prestressing Pvt. LTD.: Pile DataIlmtalabNo ratings yet
- Irc 58 2002Document40 pagesIrc 58 2002Hari Prasad Paruchuri100% (1)
- Design Guideline To Improve The Appearance of Noise Walls in NSWDocument38 pagesDesign Guideline To Improve The Appearance of Noise Walls in NSWdnbnms nda,mfsdnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Bearings & Expansion Joints: WSDOT Bridge Design Manual M 23-50.06 Page 9-I July 2011Document34 pagesChapter 9 Bearings & Expansion Joints: WSDOT Bridge Design Manual M 23-50.06 Page 9-I July 2011Eddie Chan100% (1)
- Bearing CapacityDocument7 pagesBearing CapacityLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2395 CH 15Document19 pages2395 CH 15abdülkadir cebeciNo ratings yet
- Beggs Deformeter CalculationsDocument5 pagesBeggs Deformeter CalculationsCivil EngineerNo ratings yet
- Analysis On The Causes of Cracks in BridgesDocument14 pagesAnalysis On The Causes of Cracks in BridgesNguyễn Văn MinhNo ratings yet
- SECTION 13 RAILINGS Table A13.2-1 Design PDFDocument2 pagesSECTION 13 RAILINGS Table A13.2-1 Design PDFabdulazeez88No ratings yet
- SSE Retaining - Wall - ACI Sheet v1.02Document1 pageSSE Retaining - Wall - ACI Sheet v1.02SES DESIGNNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Steel Tube Concrete Column With Steel Tube Concrete Composite ColumnDocument9 pagesComparison of Steel Tube Concrete Column With Steel Tube Concrete Composite ColumngetNo ratings yet
- ACI-Beam LedgeDocument7 pagesACI-Beam Ledgeja'far baderNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Steel PlateDocument2 pagesCalculation of Steel PlateChan Kin CheungNo ratings yet
- 8 - Design of Rigid PavementsDocument32 pages8 - Design of Rigid PavementsBAMS100% (1)
- DN400Document32 pagesDN400ersivarajNo ratings yet
- Properties of Vertical CurvesDocument9 pagesProperties of Vertical CurvesJayanth MysoreNo ratings yet
- Buckling Consideration in Pile Design ISFOG 2005Document9 pagesBuckling Consideration in Pile Design ISFOG 2005111111No ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design Different Grades of ConcreteDocument1 pageConcrete Mix Design Different Grades of ConcreteHarshwardhan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Pile StirrupDocument1 pagePile Stirrupbuffyto5377No ratings yet
- Sensing and Monitoring in Tunnels Testing and Monitoring Methods For The Assessment of TunnelsDocument21 pagesSensing and Monitoring in Tunnels Testing and Monitoring Methods For The Assessment of Tunnelsjyotish pandeyNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pavement Design Details and Construction Practices Companion WorkbookDocument13 pagesConcrete Pavement Design Details and Construction Practices Companion Workbookrobert_salas_14No ratings yet
- Excavation Induced Building DamageDocument5 pagesExcavation Induced Building DamageMarco Dos Santos NevesNo ratings yet
- Sample Portal AnalysisDocument63 pagesSample Portal Analysisacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Design of Fire Brick Wall FootingDocument4 pagesDesign of Fire Brick Wall FootingSATISH GAIKWADNo ratings yet
- Design PDFDocument260 pagesDesign PDFPrf El-SakhawyNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument1 pageRetaining Wall Design// Library SSECNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Structures through Unified FormulationFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis of Structures through Unified FormulationNo ratings yet
- Solid Slab Prestressed PDFDocument11 pagesSolid Slab Prestressed PDFAbu BiduNo ratings yet
- Power Calculations PPDocument3 pagesPower Calculations PPbashok20No ratings yet
- Cantilever 1111Document36 pagesCantilever 1111Gaurav GhaiNo ratings yet
- Design Excel SheetDocument17 pagesDesign Excel SheetbuntyNo ratings yet
- Continous Composite Beam13Document27 pagesContinous Composite Beam13Matthew ChinNo ratings yet
- Beam Design For Moment, Shear & TorsionDocument6 pagesBeam Design For Moment, Shear & Torsionsidiq7No ratings yet
- Flat Slab Punching Shear Check R2Document9 pagesFlat Slab Punching Shear Check R2Kumy engineeringNo ratings yet
- Slab Design Oneway R2Document3 pagesSlab Design Oneway R2Kumy engineeringNo ratings yet
- Typ. Plan of Beam and Slab Cuplock at 1.2M C/C: LOAD/SQ.M 2.375 T 2.375 X 1.2 X 1.2 3.42 T/VERTICALDocument1 pageTyp. Plan of Beam and Slab Cuplock at 1.2M C/C: LOAD/SQ.M 2.375 T 2.375 X 1.2 X 1.2 3.42 T/VERTICALKumy engineeringNo ratings yet
- Hoarding Structure (Wind Forces)Document1 pageHoarding Structure (Wind Forces)Kumy engineeringNo ratings yet
- Basic GC PresentaionDocument31 pagesBasic GC PresentaionShrikrishna GadkarNo ratings yet
- Tacometro DT 2268Document2 pagesTacometro DT 2268WilliamNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology: (PEC-CH311)Document17 pagesMembrane Technology: (PEC-CH311)Abhinandan GayakiNo ratings yet
- 181309-180505-Multi Component Distillation (Department Elective-II)Document2 pages181309-180505-Multi Component Distillation (Department Elective-II)Aniruddh ModiNo ratings yet
- Transport Series: CycloblowerDocument8 pagesTransport Series: CycloblowerCarlos LopezNo ratings yet
- Cooling System For Electronics in Computer System-An OverviewDocument4 pagesCooling System For Electronics in Computer System-An OverviewAzhariArdyNo ratings yet
- 2021-07 Ecp-05-2021 AhuDocument92 pages2021-07 Ecp-05-2021 AhuBulboaca BogdanNo ratings yet
- Fluoropolymer Tubing (MS 02 196)Document2 pagesFluoropolymer Tubing (MS 02 196)herysyam1980No ratings yet
- Wmo Standards & Best Practices: World Meteorological OrganizationDocument32 pagesWmo Standards & Best Practices: World Meteorological OrganizationCyclone warning centre VisakhapatnamNo ratings yet
- ElectretsDocument7 pagesElectretsandreaNo ratings yet
- Ovalle, Lenn y McCain.-Tools To Manage Gas - Condensate Reservoirs Novel Fluid-Property CorrelationsDocument8 pagesOvalle, Lenn y McCain.-Tools To Manage Gas - Condensate Reservoirs Novel Fluid-Property Correlationssergio floresNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Internal FlowsDocument31 pagesChapter7 Internal FlowsMithun PNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Science - 4TH QuarterDocument8 pagesActivity Sheets in Science - 4TH QuarterMa Fatima AbacanNo ratings yet
- CompressorsDocument10 pagesCompressorsjagdishhpatilNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Turbine GBS Feng.14.00007 PDFDocument9 pagesOffshore Wind Turbine GBS Feng.14.00007 PDFFunky DopeNo ratings yet
- F&G Mapping Using Detect 3D: A Study On Software Working, Advantages & ComparisonDocument24 pagesF&G Mapping Using Detect 3D: A Study On Software Working, Advantages & ComparisonTania NoorNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of R.C. Frame Building With Shear Wall: Nitin Choudhary Prof. Mahendra WadiaDocument5 pagesPushover Analysis of R.C. Frame Building With Shear Wall: Nitin Choudhary Prof. Mahendra Wadiabadr amNo ratings yet
- CEC2017 After Revision Final VersionDocument9 pagesCEC2017 After Revision Final VersionAli GhavamiNo ratings yet
- B6401 JarDocument1 pageB6401 JarStella KazanciNo ratings yet
- DSM-0210.2 NiCrMo SelfSealingDocument4 pagesDSM-0210.2 NiCrMo SelfSealingApichitNo ratings yet
- Ballast Pump, Sea Water PumpDocument4 pagesBallast Pump, Sea Water PumpKarina Puteri WardaniNo ratings yet
- Recovery Boiler: Esa VakkilainenDocument20 pagesRecovery Boiler: Esa Vakkilainenmarcus vinicius silva de souzaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Mod1 - Electronic Structure of Matter - VerFinalDocument34 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Mod1 - Electronic Structure of Matter - VerFinalMARIA LOURDES MENDOZA90% (39)
- Fluid Engineering - Flow in PipesDocument6 pagesFluid Engineering - Flow in PipesSherif Abdel Hamid FakhryNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Parts of An Electrochemical Cell and Their Functions. Electrode Half Reactions For Cathodes and AnodesDocument12 pagesObjectives: Parts of An Electrochemical Cell and Their Functions. Electrode Half Reactions For Cathodes and AnodesJanaNo ratings yet
- Teco 26 ReviewerDocument143 pagesTeco 26 ReviewerRose Marie BaylonNo ratings yet
- AquaGen En0411Document2 pagesAquaGen En0411Mustapha ElecNo ratings yet
- Fad Api 579 PDFDocument11 pagesFad Api 579 PDFMalik BetaNo ratings yet
- 4 Effect of Acceleration On Static FluidDocument15 pages4 Effect of Acceleration On Static FluidNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet