Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(A) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con-Nected by Point-To-Point Wired Links (B) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con - Nected by A Wired Bus
(A) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con-Nected by Point-To-Point Wired Links (B) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con - Nected by A Wired Bus
Uploaded by
de veronOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(A) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con-Nected by Point-To-Point Wired Links (B) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con - Nected by A Wired Bus
(A) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con-Nected by Point-To-Point Wired Links (B) A Collection of Eight Nodes Con - Nected by A Wired Bus
Uploaded by
de veronCopyright:
Available Formats
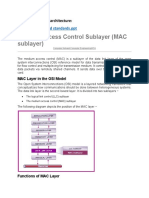
(a) A collection of eight nodes con- (b) A collection of eight nodes con-
nected by point-to-point wired links nected by a wired bus
Figure 1.6: Illustration of the point-to-point link and multiple access bus topologies
dependent but in general an address can be thought of as a string of bits which uniquely identify
a node. In many systems, the manufacturer assigns this address to a node.
The second and more important issue is that of sharing the channel access among the source-
destination pairs or channel allocation. A collision occurs when two nodes send information at
the same time onto the bus. The received signal at all the other nodes will be a superposition
of the transmitted signals and cannot be demodulated correctly at their respective receivers.
Distributed algorithms called medium access control (MAC) protocols are used to avoid or recover
from collisions in multiple access channels. For this reason, the addresses described in the
previous paragraph are called MAC addresses. MAC protocols require the cooperation of all the
nodes sharing the multiple access channel and run in a distributed fashion on all of them.
Some MAC protocols are based on the principle of random access which works well if the sources
send information infrequently. In this approach, a source node sends information whenever it
needs to and hopes for no collisions. When collisions occur, the source node knows that there
are other nodes competing to access the channel. All the source nodes involved in the collision
then time their retransmissions carefully in order to minimize the chances of future collisions.
An improvement over the pure random access MAC protocols is carrier sense multiple access
(CSMA). In this scheme, the source node senses the channel to check if a transmission is ongoing
and transmits only if the channel is idle. This scheme does not necessarily mean that the
transmitted signal needs to have a carrier. It is used in baseband systems as well and the
terminology is because it was developed initially for narrowband systems.
Random access MAC protocols do not perform well if the collisions are frequent, that is when
the source nodes want to send information frequently. In this case, MAC protocols based on
scheduling or reservation are used. Such MAC protocols are also called conflict-free protocols
because they ensure that a transmission is always successful by preventing interference from
other transmissions. Time division multiple access (TDMA) is a MAC protocol where the
time axis is divided into slots and each slot is allotted to a source node for transmission. In
frequency division multiple access (FDMA), the frequency bandwidth is divided into smaller
bands which are then allocated to the source nodes. The assignment of time slots or frequency
bands can be static or dynamic. There are also other reservation-based MAC protocols suitable
for wireless channels where the source and destination nodes exchange control messages before
actual information transmission. These control messages are received by all the nodes in the
transmission range who then refrain from transmitting until the source-destination pair has
You might also like
- Manual Usuario HP 15-AN051DXDocument142 pagesManual Usuario HP 15-AN051DXDiseño CincoupNo ratings yet
- Routing ProtocolsDocument6 pagesRouting Protocolssmskdevil008No ratings yet
- Chapter6MAC LayerDocument35 pagesChapter6MAC LayerMd NehalNo ratings yet
- WSN Unit-3Document89 pagesWSN Unit-3mr8566No ratings yet
- Csma CaDocument4 pagesCsma Cakurib38No ratings yet
- CR ECE Unit 4Document88 pagesCR ECE Unit 4deepas dineshNo ratings yet
- A Multichannel CSMA MAC Protocol For Multihop Wireless NetworksDocument5 pagesA Multichannel CSMA MAC Protocol For Multihop Wireless Networksashish88bhardwaj_314No ratings yet
- VJJVJVJDocument7 pagesVJJVJVJAnirudh KawNo ratings yet
- CN - CHPT 5Document7 pagesCN - CHPT 5Deepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- WSN Unit 3Document90 pagesWSN Unit 3kd2176No ratings yet
- Wireless MAC Protocols1Document21 pagesWireless MAC Protocols1mldc14No ratings yet
- CN Unit-IIIDocument14 pagesCN Unit-IIIAb VNo ratings yet
- 3.1 MAC ProtocolDocument48 pages3.1 MAC ProtocolVENKATA SAI KRISHNA YAGANTINo ratings yet
- Addressing Mechanism: Access ControllerDocument3 pagesAddressing Mechanism: Access ControllerPinky JudgeNo ratings yet
- InTech-An Overview of Dsa Via MultiDocument17 pagesInTech-An Overview of Dsa Via MultiC.V. VickNNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report Format-2 PDFDocument7 pagesMinor Project Report Format-2 PDFSohil KhanNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report Format-2 PDFDocument7 pagesMinor Project Report Format-2 PDFSohil KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 NotesDocument30 pagesUnit-3 NotesMOGILIPURI KEERTHINo ratings yet
- Aloha For ClassDocument23 pagesAloha For ClassetasureshNo ratings yet
- What Is A MAC Address?Document20 pagesWhat Is A MAC Address?peeyushNo ratings yet
- 02 Models and Ethernet FramingDocument3 pages02 Models and Ethernet FramingKai BaguioNo ratings yet
- RAVIKANT Paper 1 SuveyDocument8 pagesRAVIKANT Paper 1 SuveyDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument18 pagesUnit 3 - Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inROHIT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Lan Standards and ArchitectureDocument34 pagesLan Standards and ArchitectureNawal K SahNo ratings yet
- A Multichannel CSMA MAC Protocol With Receiver-Based Channel Selection For Multihop Wireless NetworksDocument8 pagesA Multichannel CSMA MAC Protocol With Receiver-Based Channel Selection For Multihop Wireless NetworksSatish NaiduNo ratings yet
- L-CSMA: A MAC Protocol For Multihop Linear Wireless (Sensor) NetworksDocument15 pagesL-CSMA: A MAC Protocol For Multihop Linear Wireless (Sensor) NetworkscarieanilNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 WholeDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Wholepriya nmNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 Mac CsmaDocument12 pagesLecture06 Mac CsmaDr. Pallabi SaikiaNo ratings yet
- CS 602 Computer Network Unit 3Document22 pagesCS 602 Computer Network Unit 3NeEmMaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three 3. Developing A Cost Effective Strategy For Wireless CommunicationDocument9 pagesChapter Three 3. Developing A Cost Effective Strategy For Wireless CommunicationMehari TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Csma OfdmDocument35 pagesCsma OfdmDARRYL IVAN BODOLLONo ratings yet
- Introducing SOFT MAC: Ghassan M. Abdalla, Mosa Ali Abu-Rgheff and Sidi-Mohammed SenouciDocument10 pagesIntroducing SOFT MAC: Ghassan M. Abdalla, Mosa Ali Abu-Rgheff and Sidi-Mohammed SenouciUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Network Layer 1 Lec 12Document26 pagesNetwork Layer 1 Lec 12سهيل خليفةNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Part 2 Notes Sem5 Communication NetworkDocument17 pagesUnit2 Part 2 Notes Sem5 Communication Network054 Jaiganesh MNo ratings yet
- A Survey and Qualitative Analysis of MacDocument26 pagesA Survey and Qualitative Analysis of MacArjun BediNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Mac Protocols For Wireless Multimedia Networks.Document18 pagesA Survey On Mac Protocols For Wireless Multimedia Networks.ijcsesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document12 pagesUnit 2PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid MAC Protocol For Wireless Sensor Network: Minsheng Tan Liang TangDocument5 pagesA Hybrid MAC Protocol For Wireless Sensor Network: Minsheng Tan Liang TangZaineb AlaniNo ratings yet
- CS6003 ASN ConceptsDocument15 pagesCS6003 ASN ConceptsVijayaprabaNo ratings yet
- Dbtma: Multiple Access With Collision Avoidance (MACA) Is A SlottedDocument19 pagesDbtma: Multiple Access With Collision Avoidance (MACA) Is A SlottedPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- C-OFDMA: Improved Throughput For Next Generation WLAN Systems Based On Ofdma and Csma/CaDocument6 pagesC-OFDMA: Improved Throughput For Next Generation WLAN Systems Based On Ofdma and Csma/CafakeNo ratings yet
- Module2 2Document27 pagesModule2 2Anurag DavesarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing (Iv B.Tech, It) (Wireless) Medium Access Control: Motivation For A Specialized MAC (Hidden and Exposed Terminals, Near and Far Terminals), SDMA, FDMA, TDMA, CDMADocument13 pagesMobile Computing (Iv B.Tech, It) (Wireless) Medium Access Control: Motivation For A Specialized MAC (Hidden and Exposed Terminals, Near and Far Terminals), SDMA, FDMA, TDMA, CDMAVenugopal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Directional Mac With Deafness Solution For Ad Hoc NetworkDocument6 pagesDirectional Mac With Deafness Solution For Ad Hoc Networkashish chaturvediNo ratings yet
- COmputer Commmunication and NetworkDocument51 pagesCOmputer Commmunication and NetworkJyoti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- A Set of Network Standards Developed by The IEEE. They IncludeDocument19 pagesA Set of Network Standards Developed by The IEEE. They IncludeYogendra RajavatNo ratings yet
- Report On CSMADocument12 pagesReport On CSMAUtkarsh HathiNo ratings yet
- Routing&Switching NotesDocument66 pagesRouting&Switching NotesMalxy55 DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3Getaneh AwokeNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 The Link Layer and Local Area NetworksDocument8 pagesUnit-5 The Link Layer and Local Area NetworkswaleedNo ratings yet
- Lec4 WWW Cs Sjtu Edu CNDocument134 pagesLec4 WWW Cs Sjtu Edu CNAUSTIN ALTONNo ratings yet
- Contention Based ProtocolsDocument8 pagesContention Based ProtocolsKarna NiLa100% (1)
- Dynamic Channel Allocation in Lans and MansDocument9 pagesDynamic Channel Allocation in Lans and MansJing DelfinoNo ratings yet
- Random Access Career Sense Protocol A Comparative Analysis of Non Persistent and 1 Persistent CSMADocument5 pagesRandom Access Career Sense Protocol A Comparative Analysis of Non Persistent and 1 Persistent CSMAEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Developing - A - Cost - Effective - Strategy - For - Wireless - CommunicationDocument9 pagesChapter 3 - Developing - A - Cost - Effective - Strategy - For - Wireless - CommunicationOz GNo ratings yet
- Ad Hoc PPTDocument85 pagesAd Hoc PPTPavan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- A Survey On TDMA-based MAC Protocols For Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument12 pagesA Survey On TDMA-based MAC Protocols For Wireless Sensor NetworkkeliliNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System For MAC LayerDocument6 pagesIntrusion Detection System For MAC LayerDeep ShahNo ratings yet
- Data Link ProtocolDocument7 pagesData Link ProtocolDarmoni LaishramNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 SGDocument16 pagesChapter05 SGAnis KhalafNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure CDP and LLDP: (Instructor Version)Document20 pagesLab - Configure CDP and LLDP: (Instructor Version)de veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled4 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled4 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations: (Instructor Version - Optional Lab)Document17 pagesLab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations: (Instructor Version - Optional Lab)de veronNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1 Cyclic Redundancy CheckDocument1 page4.2.1 Cyclic Redundancy Checkde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled7 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled7 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer: 4.1 FramingDocument1 pageData Link Layer: 4.1 Framingde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled13 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled13 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Error ControlDocument1 page4.2 Error Controlde veronNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer: 3.1 Baseband CommunicationDocument1 pagePhysical Layer: 3.1 Baseband Communicationde veronNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Spread Spectrum CommunicationDocument1 page3.3 Spread Spectrum Communicationde veronNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Narrowband CommunicationDocument1 page3.2 Narrowband Communicationde veronNo ratings yet
- 2.2 The TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument1 page2.2 The TCP/IP Reference Modelde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled13 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled13 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- 2.3 A Hybrid Reference ModelDocument1 page2.3 A Hybrid Reference Modelde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled5 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled5 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- 2.2 The TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument1 page2.2 The TCP/IP Reference Modelde veronNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The OSI Reference ModelDocument1 page2.1 The OSI Reference Modelde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled7 PDFDocument1 pageUntitled7 PDFde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled 6Document1 pageUntitled 6de veronNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The OSI Reference ModelDocument1 page2.1 The OSI Reference Modelde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled 3Document1 pageUntitled 3de veronNo ratings yet
- 1.2.5 Flow and Congestion ControlDocument1 page1.2.5 Flow and Congestion Controlde veronNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer: 3.1 Baseband CommunicationDocument1 pagePhysical Layer: 3.1 Baseband Communicationde veronNo ratings yet
- 1.2.3 Multiple Access ChannelsDocument1 page1.2.3 Multiple Access Channelsde veronNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document1 pageUntitled 2de veronNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Communication Network?Document1 page1.1 What Is A Communication Network?de veronNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Issues in Communication Network DesignDocument1 page1.2 Issues in Communication Network Designde veronNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2 Reliable Communication: Transmitter ReceiverDocument1 page1.2.2 Reliable Communication: Transmitter Receiverde veronNo ratings yet
- S TR Lightning (Rev.0 2009)Document8 pagesS TR Lightning (Rev.0 2009)Abhinav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Tomasi PDFDocument159 pagesTomasi PDFmiel_garrido82% (11)
- 06.Pdf GRB200Document42 pages06.Pdf GRB200tuantz206No ratings yet
- OpenBTS P2.8 Users' Manual Doc. Rev. 3 (OpenBTS)Document58 pagesOpenBTS P2.8 Users' Manual Doc. Rev. 3 (OpenBTS)QuantDev-M100% (1)
- 214 Lab 4 ManualDocument14 pages214 Lab 4 ManualAllie JuneNo ratings yet
- W9NK90ZDocument16 pagesW9NK90ZmecanicoloocianniNo ratings yet
- PCBA Checklist 2024Document28 pagesPCBA Checklist 2024fisher.grubb9944No ratings yet
- SR-001MK2: Electrostatic Audio ProductsDocument1 pageSR-001MK2: Electrostatic Audio ProductsZondaNo ratings yet
- Led TV: Owner'S ManualDocument50 pagesLed TV: Owner'S Manualind3digNo ratings yet
- Radio Access Network Planning Guidelines v2Document111 pagesRadio Access Network Planning Guidelines v2Karim Mohamed100% (1)
- 01 Computer Communication and Networks V PDFDocument30 pages01 Computer Communication and Networks V PDFkartikNo ratings yet
- Buffer AmplifierDocument9 pagesBuffer AmplifierDicky D.M.No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Inverter 5kVA SetecDocument10 pagesData Sheet Inverter 5kVA SetecFadkhuli Sholih FahmiNo ratings yet
- NPT Atp Document r3Document19 pagesNPT Atp Document r3satyvan2003No ratings yet
- Summer Training Report in Central Electronics LTDDocument20 pagesSummer Training Report in Central Electronics LTDMahendra Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Power Control LTE Radio Parameters RL50Document36 pagesPower Control LTE Radio Parameters RL50GuillermoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument122 pagesUntitledMax LorenNo ratings yet
- Touchscreen Technology PPT by Pavan Kumar M.T.Document24 pagesTouchscreen Technology PPT by Pavan Kumar M.T.pavankumarmt91% (11)
- Varistores E3Document214 pagesVaristores E3Doris Elizabeth Rolón de EitzenNo ratings yet
- Touch Voltage - Ground Current (1.1.19)Document2 pagesTouch Voltage - Ground Current (1.1.19)jiguparmar1516No ratings yet
- 1117Z Reg de V FijoDocument4 pages1117Z Reg de V Fijojavier venturaNo ratings yet
- Ma Nu Ale Microbe Tam 02 EngDocument39 pagesMa Nu Ale Microbe Tam 02 EngNevenko Arlov100% (3)
- Icp N70Document6 pagesIcp N70saul camposNo ratings yet
- Manual Vas5051 310 GBDocument248 pagesManual Vas5051 310 GBJean-Baptiste BulliardNo ratings yet
- Net-Analyser Na96 and Na96+: General InformationDocument31 pagesNet-Analyser Na96 and Na96+: General Informationb400013No ratings yet
- Protection Schemes For Alternator & GeneratorDocument3 pagesProtection Schemes For Alternator & GeneratorSaikumar NemalikantiNo ratings yet
- SGM911Document2 pagesSGM911yu3zaNo ratings yet
- EasyPact EZC - EZC400N3320NDocument6 pagesEasyPact EZC - EZC400N3320NHardi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Lec2 - Programmable Logic Controller PLCDocument11 pagesLec2 - Programmable Logic Controller PLCSaif AlabdullahNo ratings yet