Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell (Biology) - c2
Cell (Biology) - c2
Uploaded by
piping stressOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell (Biology) - c2
Cell (Biology) - c2
Uploaded by
piping stressCopyright:
Available Formats
6/17/2020 Cell (biology) - Wikipedia
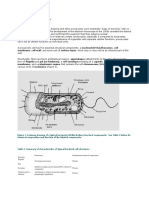
Cell wall
Many types of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cell wall. The cell wall acts to protect the cell
mechanically and chemically from its environment, and is an additional layer of protection to the cell
membrane. Different types of cell have cell walls made up of different materials; plant cell walls are
primarily made up of cellulose, fungi cell walls are made up of chitin and bacteria cell walls are made up
of peptidoglycan.
Prokaryotic
Capsule
A gelatinous capsule is present in some bacteria outside the cell membrane and cell wall. The capsule
may be polysaccharide as in pneumococci, meningococci or polypeptide as Bacillus anthracis or
hyaluronic acid as in streptococci. Capsules are not marked by normal staining protocols and can be
detected by India ink or methyl blue; which allows for higher contrast between the cells for
observation.[21]:87
Flagella
Flagella are organelles for cellular mobility. The bacterial flagellum stretches from cytoplasm through
the cell membrane(s) and extrudes through the cell wall. They are long and thick thread-like
appendages, protein in nature. A different type of flagellum is found in archaea and a different type is
found in eukaryotes.
Fimbriae
A fimbria (plural fimbriae also known as a pilus, plural pili) is a short, thin, hair-like filament found on
the surface of bacteria. Fimbriae are formed of a protein called pilin (antigenic) and are responsible for
the attachment of bacteria to specific receptors on human cells (cell adhesion). There are special types of
pili involved in bacterial conjugation.
Cellular processes
Replication
Cell division involves a single cell (called a mother cell) dividing into two daughter cells. This leads to
growth in multicellular organisms (the growth of tissue) and to procreation (vegetative reproduction) in
unicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, while eukaryotic cells usually undergo a
process of nuclear division, called mitosis, followed by division of the cell, called cytokinesis. A diploid
cell may also undergo meiosis to produce haploid cells, usually four. Haploid cells serve as gametes in
multicellular organisms, fusing to form new diploid cells.
DNA replication, or the process of duplicating a cell's genome,[4] always happens when a cell divides
through mitosis or binary fission. This occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology) 8/16
You might also like
- Case Study 1Document13 pagesCase Study 1JoseDavidSierraLugoNo ratings yet
- Schuessler Tissue Salts HandbookDocument52 pagesSchuessler Tissue Salts HandbookBashir Ahmed100% (3)
- Luise Hay Symptoms ListDocument12 pagesLuise Hay Symptoms Listmaviladin100% (2)
- Neurobiology of Mental Illness PDFDocument1,259 pagesNeurobiology of Mental Illness PDFqa100% (5)
- Chapter 4: Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument94 pagesChapter 4: Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Unit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument8 pagesUnit I Module 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsMirunalini GobinathNo ratings yet
- Bact Cell str2022Document9 pagesBact Cell str2022sajad abasewNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument15 pagesStructurefatimasanusimorikiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Microorganisms in Food and SpoilageDocument24 pagesModule 1 Microorganisms in Food and SpoilageSiddNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cytology Resonance PDFDocument79 pagesCell and Cytology Resonance PDFEkta Manglani100% (1)
- Presentation 2Document54 pagesPresentation 2hunter zoneNo ratings yet
- Cells Cell Membrane Over-Expansion Cell Plants Fungi Prokaryotic MycoplasmasDocument5 pagesCells Cell Membrane Over-Expansion Cell Plants Fungi Prokaryotic MycoplasmasbbhoeeNo ratings yet
- 8.Virology-Cell CultureDocument2 pages8.Virology-Cell CultureAbdus SubhanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Bacterial MorphologyDocument4 pages1.3 Bacterial MorphologyJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument23 pagesBacteriologyaleeshaNo ratings yet
- Medmicro Chapter 73Document9 pagesMedmicro Chapter 73kronamNo ratings yet
- CELL Study MaterialDocument12 pagesCELL Study MaterialShyamasree SenguptaNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument2 pagesBacteriaGrace Jane HannaNo ratings yet
- L2 Bacterial StructureDocument46 pagesL2 Bacterial StructureNarmathaa ThevarNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 8-MinDocument25 pagesCell The Unit of Life Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 8-MinAli WarisNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument8 pages11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsVansh Mehta100% (1)
- General Microbiology (Chapter 3)Document18 pagesGeneral Microbiology (Chapter 3)Ashraf OsmanNo ratings yet
- Composition and Function of CellDocument61 pagesComposition and Function of CellJeah Mae CastroNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSDocument10 pagesMicrobiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSEmily RaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- Prokaryotic Cells. BacteriaDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cells. BacteriaAndreea VrabieNo ratings yet
- Cuk Cell Biology 2020 (2nd Sem)Document10 pagesCuk Cell Biology 2020 (2nd Sem)Pokemon GoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4EDLE FAITH ANDREA CATABIANNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Biochem (Lesson 2)Document6 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Biochem (Lesson 2)janmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- 32 Bacterialcell 2009Document5 pages32 Bacterialcell 2009ariffdrNo ratings yet
- This Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideDocument8 pagesThis Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideZuzuNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - 1st - ChapterDocument21 pagesCell Biology - 1st - ChapternandhumangoNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesMicrobiologyOomar LeoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationDocument24 pagesEukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationVARIGALA SAI CHARAN GUPTANo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document56 pagesLecture 02bsmls-f18-017No ratings yet
- Biology Fiitjee Chennai CentreDocument27 pagesBiology Fiitjee Chennai CentreT SunderamalolanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaDocument4 pagesBacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaTLCRNo ratings yet
- Functions of Organelles in CellDocument23 pagesFunctions of Organelles in CellZahid ShehzarNo ratings yet
- Bacteria. 1st Sem. 2022Document60 pagesBacteria. 1st Sem. 2022PowerNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue CulturesDocument5 pagesCell and Tissue CulturesJessa Nicole ReteracionNo ratings yet
- GATE Sample Material - MicrobiologyDocument0 pagesGATE Sample Material - MicrobiologyAnkur BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument122 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsAdithya NanuvalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Part 1Document29 pagesCell Biology Part 1hafiz.umer.7169No ratings yet
- BIO 001 Real Slide First SemesterDocument44 pagesBIO 001 Real Slide First Semestermarkwelly367No ratings yet
- The Bacterial Cell: Classification and Morphology: Arthur C. Benignos Ii M.DDocument51 pagesThe Bacterial Cell: Classification and Morphology: Arthur C. Benignos Ii M.Dunno hiquianaNo ratings yet
- Activities With in CellDocument10 pagesActivities With in CellTiwaan02No ratings yet
- Proses Produksi BioindustriDocument28 pagesProses Produksi BioindustriAriiezma Selaludhamay D'hatiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Structure, Growth, and MetabolismDocument77 pagesBacterial Structure, Growth, and MetabolismNelle ReneiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Overview: 8: FungiDocument17 pagesChapter Overview: 8: FungiBianca ElbrechtNo ratings yet
- SGL 2 (Structure of Bacterial Cell)Document32 pagesSGL 2 (Structure of Bacterial Cell)rekanshwan5No ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1 BiologyDocument8 pagesAssigment 1 BiologyshimaabdollahpourNo ratings yet
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesmitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Procaryotic Cell ArchitectureDocument18 pagesProcaryotic Cell ArchitectureWindi Dawn SallevaNo ratings yet
- Structure & Functions of Prokaryotic Cell. Bacteriophages.: Lecturer: - Sergei V. RedkozubovDocument54 pagesStructure & Functions of Prokaryotic Cell. Bacteriophages.: Lecturer: - Sergei V. RedkozubovJustineNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 6th LectureDocument37 pagesBIO 001 6th LectureManuelNo ratings yet
- Functional AnatomyDocument38 pagesFunctional AnatomyFransiscaa HellenNo ratings yet
- Eubacteria - Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types, ExamplesDocument8 pagesEubacteria - Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types, ExamplesАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- PipingDocument6 pagesPipingpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Vernacular Literature - WikipediaDocument2 pagesVernacular Literature - Wikipediapiping stressNo ratings yet
- Propositional AttitudeDocument4 pagesPropositional Attitudepiping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 6Document1 pagePsychology - Article 6piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 11Document1 pagePsychology - Article 11piping stressNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument39 pagesMathematicspiping stressNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument42 pagesPhilosophypiping stressNo ratings yet
- KnowledgeDocument33 pagesKnowledgepiping stressNo ratings yet
- Justification (Epistemology)Document3 pagesJustification (Epistemology)piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 9Document1 pagePsychology - Article 9piping stressNo ratings yet
- ConfucianismDocument33 pagesConfucianismpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 3Document1 pagePsychology - Article 3piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 37 PDFDocument1 pagePsychology - Article 37 PDFpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 10Document1 pagePsychology - Article 10piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 8Document1 pagePsychology - Article 8piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 13Document1 pagePsychology - Article 13piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 4Document1 pagePsychology - Article 4piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 5Document1 pagePsychology - Article 5piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 7Document1 pagePsychology - Article 7piping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 2Document1 pagePsychology - Article 2piping stressNo ratings yet
- Configuration and Management: Push-Back Rack For Motorcycles, A LIFO Rack System For StorageDocument1 pageConfiguration and Management: Push-Back Rack For Motorcycles, A LIFO Rack System For Storagepiping stressNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Article 1Document1 pagePsychology - Article 1piping stressNo ratings yet
- Logistic 13 PDFDocument1 pageLogistic 13 PDFpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Logistic 14 PDFDocument1 pageLogistic 14 PDFpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Logistic 12 PDFDocument1 pageLogistic 12 PDFpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Logistics Automation: Horizontal Alliances Between Logistics Service ProvidersDocument1 pageLogistics Automation: Horizontal Alliances Between Logistics Service Providerspiping stressNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Management System and Control: Airline Logistic Network. Denver Works As A Hub in The NetworkDocument1 pageWarehouse Management System and Control: Airline Logistic Network. Denver Works As A Hub in The Networkpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Handling and Order ProcessingDocument1 pageHandling and Order Processingpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Nodes of A Distribution Network: A Forklift Stacking A Logistics Provider's Warehouse of Goods On PalletsDocument1 pageNodes of A Distribution Network: A Forklift Stacking A Logistics Provider's Warehouse of Goods On Palletspiping stressNo ratings yet
- Logistic 6Document1 pageLogistic 6piping stressNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nurhayu Ab RahmanDocument24 pagesDr. Nurhayu Ab RahmanHotaru ImaiNo ratings yet
- Appetite: SciencedirectDocument5 pagesAppetite: Sciencedirectanon_169914597No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: ISO 9001-2008 FM 70321Document3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: ISO 9001-2008 FM 70321miyomiyo5678No ratings yet
- A Culturally Competent Model of Care For African Americans: Josepha Campinha-BacoteDocument6 pagesA Culturally Competent Model of Care For African Americans: Josepha Campinha-BacoteEE KMNo ratings yet
- Herpangina StatPearls NCBIBookshelfDocument2 pagesHerpangina StatPearls NCBIBookshelfThaysa BarbosaNo ratings yet
- AD RealMind BiotechDocument4 pagesAD RealMind Biotechlinjinxian444No ratings yet
- Side EffectsDocument2 pagesSide EffectsFahad AlkenaniNo ratings yet
- Rabbit From Farm To TableDocument3 pagesRabbit From Farm To Tablekarthik kumar100% (1)
- AHSReport NHMS2017Document275 pagesAHSReport NHMS2017AmirOthmanNo ratings yet
- Sub0118.1 Australiasian Sleep AssociationDocument6 pagesSub0118.1 Australiasian Sleep Associationjorgezamora1168No ratings yet
- Borax Crystal DetoxificationDocument4 pagesBorax Crystal DetoxificationIan BersabalNo ratings yet
- Obesity ProjectDocument92 pagesObesity ProjectAjay Pal Natt100% (1)
- Hospice and Palliative Care in IndiaDocument9 pagesHospice and Palliative Care in IndiaArunpv001No ratings yet
- Vice and Drug EducationDocument20 pagesVice and Drug EducationKarl David CalaguiNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu On Thi Tuyen Sinh Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Du Dang Bai TapDocument117 pagesTai Lieu On Thi Tuyen Sinh Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Du Dang Bai TapLê Trung Kiên100% (1)
- AIIMS Jodhpur & RishikeshDocument30 pagesAIIMS Jodhpur & Rishikeshshubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia For Dental ChildDocument23 pagesLocal Anesthesia For Dental ChildDr. Abdulsalam Awas Dental CenterNo ratings yet
- Name: Subject: Date:: Surname 1Document3 pagesName: Subject: Date:: Surname 1mutua daveNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SOFADocument11 pagesJurnal SOFAMekar PalupiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusNo ratings yet
- Sahodaya English QP Set BDocument13 pagesSahodaya English QP Set BVK THE GAMER100% (2)
- Recent Advances in Contraception: Dr. Siddhartha Dutta Mamc, New DelhiDocument51 pagesRecent Advances in Contraception: Dr. Siddhartha Dutta Mamc, New DelhiJalajarani SelvaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fertilizers, Manure and Poluthene On The Rate of Elongfation of HypocotylDocument6 pagesEffects of Fertilizers, Manure and Poluthene On The Rate of Elongfation of Hypocotylmusic madissNo ratings yet
- Plant Micropropagation: Section (9) Lab (B) Number (50:60)Document14 pagesPlant Micropropagation: Section (9) Lab (B) Number (50:60)Nada SamiNo ratings yet
- Case MalariaDocument2 pagesCase MalariaRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Microbiologist PDFDocument9 pagesMicrobiologist PDFNiharikaNo ratings yet