Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factorization PDF
Factorization PDF
Uploaded by
Mana GargiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factorization PDF
Factorization PDF
Uploaded by
Mana GargiCopyright:
Available Formats
QA – Factorization
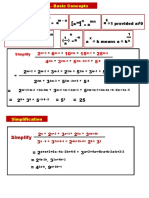
FACTORIZATION OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION
When factorizing quadratic equations, there is generally nothing that is common in every
term. In this case, we cannot pull a constant value out and rewrite the problem.
The final representation of the equation has to be in the form, (x + a) x (x + b). The trick is
knowing how to find a and b.
2 step process
y2 + 4y – 12=0
Step 1: Start with the constant term. In this particular case, the constant term is -12.
Factorize -12 into groups. Each group is a set of two numbers that when multiplied together
will give -12. With the number -12, these can be the following groups:
{-1,12}, {-2,6}, (-3,4), {1.-12}, {2,-6}, {3,-4}
Now you have six different groups.
Step 2: The next step is to find out the coefficient of the ly' term and the number to be
multiplied by ly' in the quadratic equation. In this case, that number is 4. Now, we have to
find out which one of the group will give us 4, when the two numbers of each group are
added together.
If you add -1 and 12, you get 11. This is not correct, So, try again.
If you add -2 and 6, then you get 4. This is the required group.
The numbers that you choose in the group (in this case -2 and 6) will be the a and the
b that we have been looking for. Which one you chose for a and which you chose for b does
not matter. I will just use a = -2 and b = 6,
[y + (2)] x (y + 6)
= (y – 2) (y + 6)
Therefore +bx+c=0⟹ (x – ) = 0, where are the roots of
quardratic equation.
Solved Examples:
1) The length of a rectangle is 7 cm more than it width. The area is 60 Find the
dimensions of the rectangle.
SOLUTION: Let width of the rectancle = x
Length of the rectangle = (x + 7) cm.
Area of rectangle = (x + 7) x x
⟹ (x + 7) (x) = 60
⟹ + 7x - 60 = 0
⟹ (x + 12) (x - 5) = 0
⟹ x = 12 and x = 5
Since width can never be negative, therefore x =5 cm at x+7 = 12 cm are the required
values.
Proprietary and Confidential ABS Classes 1
QA – Factorization
i.e., Lengh = 12 cm andwidth = 5
2) A passenger train takes 2 hours less for a journey 300 km if its speed is increased by
5km/hr from its usual speed. Find the usual speed of the train.
SOLUTION: Let the usual speed of the train be x km/hr
Usual time = = hour
If the speed is increased by 5 km/hr i.e., (x + 5) km/hr,
the time = - =2
⟹ 2x(x+5) = 1500
⟹ 0
⟹ x = 25 or x = - 30
Speed = 25 km/hr (x = - 30 is inadmissible)
3) A two digit number is such that the product of digits is 12. When 36 is added to the
number, its digits are reveres. Find the number.
SOLUTION Let the number be 10x + y
xy = 12 ⟹ y =
the number is 10x +
And the number with digits reversed is
10y + x = 10 ( )- x = +x
( ) + 36 = +x
⟹ 10x – x + - + 36 =0
⟹ 9x + (12 – 120) + 36 = 0
⟹ 9x - + 36 = 0
⟹ + 36x – 108 = 0
x = 2 or x = - 6
y= = = 6 (x = - 6 is inadmissible)
Hence, the number is 10x +y = 10 x 2 + 6 = 20 + 6 = 26
Proprietary and Confidential ABS Classes 2
You might also like
- Exercise Sheet 6: Theoretical Computer Science (Bridging Course)Document3 pagesExercise Sheet 6: Theoretical Computer Science (Bridging Course)madhavNo ratings yet
- 3260 ITouch User ManualDocument2 pages3260 ITouch User Manualenrique_ballestero_150% (2)
- Factorization of A Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesFactorization of A Quadratic EquationAnu AmruthNo ratings yet
- Selina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 6Document20 pagesSelina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 6Soureesh MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 9 Math PolynomialsDocument9 pages9 Math PolynomialsgocebuseskiNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesLinear EquationsDhiman DeyNo ratings yet
- The Binomial Theorem: Examples: X X N C C C C C C CDocument3 pagesThe Binomial Theorem: Examples: X X N C C C C C C CMarc Harold ChuaNo ratings yet
- 9 Math PolynomialsDocument9 pages9 Math PolynomialsAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- 10 Math Imp ch4 2Document20 pages10 Math Imp ch4 2crazy about readingNo ratings yet
- SAT ACT EquationsDocument18 pagesSAT ACT EquationsYb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document30 pagesAlgebra 2Cuthbert YedwaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesQuadratic EquationsLeo Jade AbiertasNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Maths - Quadratic EquationsDocument24 pagesClass 10 - Maths - Quadratic EquationsJamima HazarikaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 PDFDocument19 pagesCH 6 PDFMridula PriyaNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Latihan Ujian Sekolah 1 27 Januari 2021 OkDocument16 pagesPembahasan Latihan Ujian Sekolah 1 27 Januari 2021 OkMahardhikaNo ratings yet
- Sanam MathDocument13 pagesSanam MathAbrar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document7 pagesWorksheet 1Salsabila FitriNo ratings yet
- Problem 1:: SolutionDocument10 pagesProblem 1:: SolutionKristhel Pecolados RombaoaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations PDFDocument75 pagesRD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations PDFradha raman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersDocument12 pagesPolynomials Class 9 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2 With Solutions AnswersElina RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Number Systems Assignment 1Document5 pagesClass 10 Number Systems Assignment 1manojmathewNo ratings yet
- Solution 831896Document3 pagesSolution 831896Deepak SalwaniNo ratings yet
- 4.quadratic EquationsDocument40 pages4.quadratic EquationsMp SunilNo ratings yet
- The Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesThe Binomial TheoremMarc Harold ChuaNo ratings yet
- Polynomials: 1.1. DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPolynomials: 1.1. DefinitionsGieze AbabaNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Equations Reducible To Quadratic Form: QA - ConversionDocument4 pagesSolutions of Equations Reducible To Quadratic Form: QA - ConversionMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations CWDocument18 pagesQuadratic Equations CWshairyaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in One VariableDocument13 pagesLinear Equations in One VariableLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 4 - Quadratic EquationsDocument27 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 4 - Quadratic EquationsraviskskskNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Quadraticequations PDFDocument18 pagesChapter2 Quadraticequations PDFcm6699No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument15 pagesQuadratic EquationsVarunNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Important Questions 2024-25Document54 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Important Questions 2024-25prithvivasan0912No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.2Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.2NINJA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5KC BeltranNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFDocument13 pagesGrade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFSaurabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Final Lli 2 PDFDocument606 pagesFinal Lli 2 PDFRabeya Arefin TonniNo ratings yet
- Questions For The Regional MAth COmDocument17 pagesQuestions For The Regional MAth COmHannah Mae Pablo CorpuzNo ratings yet
- LR 8 Sec A202116016Document11 pagesLR 8 Sec A202116016Disha ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6-3Document28 pagesLesson 6-39pjb8mb8b2No ratings yet
- Algebra Revision Assignment 1Document5 pagesAlgebra Revision Assignment 1Deepak KanchanNo ratings yet
- FawaffwDocument11 pagesFawaffwJanaki KaushaniNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument42 pagesDerivativesDezalene CierteNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations Capter2Document12 pagesTheory of Equations Capter2Immanuel SNo ratings yet
- Cmi Sample Problems & Solutions: WWW - Ctanujit.inDocument12 pagesCmi Sample Problems & Solutions: WWW - Ctanujit.inaanbalanNo ratings yet
- Iq-Linear EquationsDocument114 pagesIq-Linear Equationsapi-452872929No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Completing The SquareDocument9 pagesQuadratic Equations: Completing The SquareSarah Ossama MaharemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document8 pagesLecture 12noman khanNo ratings yet
- 6.sũnyam SāmyasamuccayeDocument10 pages6.sũnyam SāmyasamuccayeshuklahouseNo ratings yet
- Problem On Numbers PDFDocument9 pagesProblem On Numbers PDFImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Agebra Revision Assignment 1Document5 pagesAgebra Revision Assignment 1darling deanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algeb ProjectDocument17 pagesAdvanced Algeb ProjectdiomNo ratings yet
- MPE1 Practice SolutionsDocument4 pagesMPE1 Practice SolutionsEsteban EroNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-3 Level-1 Chapter-9 PDFDocument28 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-3 Level-1 Chapter-9 PDFmaihar patelNo ratings yet
- Math 10.3Document14 pagesMath 10.3bea sailNo ratings yet
- Actual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Document15 pagesActual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Avdesh KothariNo ratings yet
- 4 (B) - PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (P - 1,2,3) - SOLUTIONSDocument38 pages4 (B) - PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (P - 1,2,3) - SOLUTIONSnittala.akshitaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 2Document8 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 2EktaNo ratings yet
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables: Key PointsDocument27 pagesPair of Linear Equations in Two Variables: Key PointsMeghana SriNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- One-Word Substitutes: Part 4: Sr. No. Phrase WordDocument18 pagesOne-Word Substitutes: Part 4: Sr. No. Phrase WordMana GargiNo ratings yet
- One-Word Substitutes: Part 3: Sr. No. Phrase WordDocument19 pagesOne-Word Substitutes: Part 3: Sr. No. Phrase WordMana GargiNo ratings yet
- One-Word Substitutes: Part-1: Sr. No. Phrase WordDocument15 pagesOne-Word Substitutes: Part-1: Sr. No. Phrase WordMana GargiNo ratings yet
- QA-01 %1 Vedi MathsDocument2 pagesQA-01 %1 Vedi MathsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Theory @clatimpstuffDocument48 pagesReading Comprehension Theory @clatimpstuffMana GargiNo ratings yet
- e-Prac-CAT-02 - TestDocument46 pagese-Prac-CAT-02 - TestMana GargiNo ratings yet
- e-Prac-CAT-03 - TestDocument45 pagese-Prac-CAT-03 - TestMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Additional Mock Cat Varc Test-1 (Wiley Cat Varc Book)Document11 pagesAdditional Mock Cat Varc Test-1 (Wiley Cat Varc Book)Mana GargiNo ratings yet
- e-Prac-CAT-01 - TestDocument39 pagese-Prac-CAT-01 - TestMana GargiNo ratings yet
- QAS04 - SolutionsDocument5 pagesQAS04 - SolutionsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- QAS05 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesQAS05 - SolutionsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- QAS01 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesQAS01 - SolutionsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- QA Concept 8 - Indices & Surds Session 1Document25 pagesQA Concept 8 - Indices & Surds Session 1Mana GargiNo ratings yet
- Word-Builders-Roots, Prefixes and SuffixesDocument16 pagesWord-Builders-Roots, Prefixes and SuffixesMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionDocument75 pagesEmbedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionSambasivaNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Monitor: Portable DesignDocument2 pagesVital Signs Monitor: Portable DesignharoldNo ratings yet
- Overview of Troubleshooting: Jason ZhangDocument49 pagesOverview of Troubleshooting: Jason ZhangMarco SánchezNo ratings yet
- 2605 Ds 31611 PDFDocument4 pages2605 Ds 31611 PDFNarcis PatrascuNo ratings yet
- Self-Organizing Map and Cellular Automata CombinedDocument8 pagesSelf-Organizing Map and Cellular Automata CombinedMarco Antonio Reséndiz DíazNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control Using MATLABDocument11 pagesModel Predictive Control Using MATLABAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Mod Menu Crash 2023 11 19-09 41 10Document2 pagesMod Menu Crash 2023 11 19-09 41 10РАВАНNo ratings yet
- Non-Government Teachers' Registration & Certification Authority (NTRCA)Document1 pageNon-Government Teachers' Registration & Certification Authority (NTRCA)SRN PUBG GAMMERNo ratings yet
- Velayutham RS 2023Document5 pagesVelayutham RS 2023dimasdudut channelNo ratings yet
- H-RCA: 802.11 Collision-Aware Rate Control: K. D. Huang, K. R. Duffy and D. MaloneDocument14 pagesH-RCA: 802.11 Collision-Aware Rate Control: K. D. Huang, K. R. Duffy and D. MaloneFavour AdenugbaNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Fundamental Accounting Principles 22nd Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument11 pagesInstant Download Fundamental Accounting Principles 22nd Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterpedrusticaltd1a100% (12)
- Basic Techniques of Detailed Capacity Planning ProcessDocument68 pagesBasic Techniques of Detailed Capacity Planning ProcesspatriciodanitzNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tpms DeviceDocument12 pagesProject Report On Tpms DeviceVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CMG's Modelling WorkflowsDocument96 pagesIntroduction To CMG's Modelling WorkflowsluisleftNo ratings yet
- Network SecurityDocument66 pagesNetwork SecurityTariqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs and ManagementDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs and ManagementKaye ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Alumni Details-RenounedDocument7 pagesAlumni Details-Renounedbhuvans80_mNo ratings yet
- CK 4100 (Data Logger)Document20 pagesCK 4100 (Data Logger)Giorgi KurtsikidzeNo ratings yet
- LG 32LJ610V, 32LJ622V Chassis LD75HDocument62 pagesLG 32LJ610V, 32LJ622V Chassis LD75Hmanuel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Blockchains: Architecture, Design and Use CasesDocument26 pagesBlockchains: Architecture, Design and Use Caseseira kNo ratings yet
- Convert PS3 Demo To RetailDocument2 pagesConvert PS3 Demo To RetailMarcus MasonNo ratings yet
- History of Website & InternetDocument10 pagesHistory of Website & Internet• Kɪɴɢ JᴀʏNo ratings yet
- M3SD K003 Gen Hyd01 F DTL 0003 1Document1 pageM3SD K003 Gen Hyd01 F DTL 0003 1Shreyas ChawaleNo ratings yet
- lastUIException 63806137181Document7 pageslastUIException 63806137181AgaathaaNo ratings yet
- FullStackCafe - Disgn PaterinDocument9 pagesFullStackCafe - Disgn PaterinMousa Nabil Al-KaloutiNo ratings yet
- STP-07-Quality Management InspectionDocument42 pagesSTP-07-Quality Management InspectionraghuNo ratings yet
- Ninacor SlidesCarnivalDocument27 pagesNinacor SlidesCarnivalDianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nayatel TransmissionDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Nayatel TransmissionmaryamNo ratings yet