Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Civn3011 2013 PDF
Civn3011 2013 PDF
Uploaded by
Thabiso Motalingoane0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pagesOriginal Title
CIVN3011 2013.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pagesCivn3011 2013 PDF
Civn3011 2013 PDF
Uploaded by
Thabiso MotalingoaneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 8
81350
Shes jens! 2013
EXAMS OFFICE
CB 2286 USE ONLY
University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
Course or topic No(s)
Course or topic name(s)
Paper Number & title
Examination/Fest* to be held during
month(s) of (“delete 2s applicable)
‘Year of Study (Avts & Science leave blank)
Degree/Diplomas for which
This course is prescribed
(Se (Eng) shoud inaate which ranch)
Faculty/ies presenting candidates
Internal examiner(s) and
‘Telephone extension number(s)
External examiner(s)
Special materials required
(graphimusictdrawing paper, maps,
sagrams, tables, computer cards, etc.)
Time allowance
Instructions to candidates
(Examiners may wish to use this space
to indicate, inter alia, the contribution
made by this examination or test towards
the year mark, if appropriate)
CIVN 3011
Reinforced Conerete Design
May 2013
BSc (Eng) Civil
Engineering and the Built Environment
Prof M. Gohnert x7-7125
Dr. du Plessis
(Open Book Exam
Course [CIVN 3011
(3 Hours
No(s) Hours
Answer ALL questions
Internal Examiners or Heads of Department are requested
to sign the declaration overleaf
The University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
School of Civil and Environmental Engineering
CIVN 3011 — Reinforced Concrete Design 5 Pages
Question 1 [25]
Answer the multiple choice questions on the electronic marking sheet
1. | Shear stresses—what answer is most correct? :
a. The theoretical shear crack will form at an angle of 45°
b. Actual shear cracks generally occurs at an angle of 30°
c. For the case of a UDL, the maximum shear stress occurs near the support and at
the neutral axis.
4. A shear crack is actually a tension crack, where the tension forces act 90° to the
angle of the crack,
Alll of the above,
2. Wind loading—what answer is most correct?
1. A double pitched roof will always have suetions on both sides of the roof (no
positive pressures).
Roof uplift is rarely a problem with conerete flat roofs.
c. Itis only necessary to check the effects of wind pressure on the long side of
buildings,
‘The maximum wind pressures on a roof will occur near the centre of the roof.
None of the above.
=
ee
3. The load combination 0.9DL + 1.3WL is a valid load combination and is an
overturning case.
a. True
b. False
4. Secondary steel is referring to:
a. Steel placed 90° to the main reinforcement and is used in one-way slabs.
Helps resists point loads on slabs.
Creep reinforcement
Shrinkage reinforcement.
All of the above
eaos
10.
ne
12
‘The expression —Vb/3 is the approximate drop in bending moment at the first interior
support of an end-span.
a. True
b. False
What answer is most correct concerning shrinkage cracks in slabs?
The crack is jagged and irregular.
‘The crack is always near the centre and located on the bottom of the slab.
Characteristically, the crack passes completely through the slabs.
Shrinkage crack only occur at a construction joint.
Shrinkage cracks are generally not a problem in conerete members.
oP
eae
.. At coffered slab is identified by ribs running in one direction.
a, True
b. False
A one-way slab is characterized by curvature in one direction, supports opposite
and/or the ratio of the long dimension to the short dimension is greater than 3.
a, True
b. False
Columns—what is the most correct answer?
a, The PA effect only occurs in slender columns that are unbraced.
b, Ifthe term “k” is greater than one, it means that the column may need compression
steel.
c. The column moments Mp are the maximum moments located at mid-height.
4, Columns act more like a beam if k= M/Mbai> 1.0
e. None of the above.
In the expression S, < 125s (see shear reinforcement of columns), the subscript $B
means shear bar?
a, True
b. False
The intension of a raft foundation is to float the structure?
a, True
b. False
Steel is generally not used in strip foundations. However, if steel is placed in a strip
foundation, it should be placed along the length of the foundation.
a. True
b. False
13. In a two-way rectangular slab, bottom most steel should be placed in the long
direction.
a. True
b. False
14, Figure 10 in the code approximates the location of zero shears in addition to
describing the distribution load to beams.
a. True
b. False
15. Slab design—what answer is NOT correct?
a. & two-way slab may be solid or have ribs in two directions.
b. A flat slab is a slab system without beams.
¢. A solid slab is designed like a beam, assuming the beam to be 1000 mm wide.
d. Ribbed slabs are only used where the span is long or loads are heavy.
e
. The negative moments along a discontinuous edge are reduced to the moments at
the face of the support.
16. An under-reinforced beam means:
a, The beam does not have sufficient steel.
The steel will yield prior to the failure of the concrete,
The term refers to the bottom steel.
The main steel is less than 0.13%
None of the above.
paos
17. Maximum steel requirements ensures:
‘The maximum bending stress is resisted,
The concrete doesn’t fail in compression before yielding of the steel,
‘The steel doesn’t fail in tension before the concrete fails in compression.
‘That the optimum area of steel is used,
None of the above.
oP
pao
18. A bar may be extended by simply overlapping the bar with another bar and ensuring
that the lap is the appropriate anchorage length.
a. True
b. False
19. Pairs of bars placed one above the other is a better orientation than placed side by side,
a, True
b. False
20.
21.
22.
23.
24,
25.
Redistribution of moments—what statement is NOT correct?
a, Redistribution is only applicable in continuous beams (two or more spans).
b. Redistribution allows the reduction of a negative moment.
c. The magnitude of the reduced negative moments is distributed to the positive
moments of adjacent spans.
4. Redistribution of moments is a practice to even the distribution of top steel.
For the case of no redistribution, the maximum spacing of the bars is 170 mm.
. The weight of the foundation, soil and surface bed must be included when calculating
the flexural steel in spread footings?
a, True
b. False
Top steel in spread footings serves what purpose?
a, To resist the effects of sliding,
Bending moments in the foundation caused by an uplift force.
To resist punching shear.
Only used as fixing steel.
‘None of the above
eaes
When modelling a structure, using a structural analysis package, what statement is
NOT true?
a. When modelling pinned supports of a single span beam, one end should be pinned
(preventing X and Y translations) and the other end on rollers (only Y translations
are prevented).
b. The accuracy of a frame analysis is dependent on the number of elements (nodes)
along the length of the member.
¢. Nodes are placed where the member size or direction changes and where
deflections and internal forces are required.
d. Finite elements provides an approximate solution, but the solution improves
proportional to the number of elements.
e. Structural elements are modelled as lines and located at the centroid of the
member.
Cross bracing and “K” bracing are commonly applied to concrete structures to resist
lateral forces from wind.
a, True
b. False
Movement joints are placed in concrete structures only in earthquake zones.
a, True
b. False
Question 2 75}
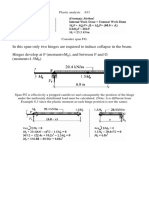
A. 3000 mm wide slab is support by a single beam, measuring 700 x 400 mm. The
slab is tapered, with a thickness of 200 mm at the edge and increasing to 300 mm at
the beam support. The beam is supported at four points, which are simply supports.
‘Assume that the support width is 300 mm. The live load is 3 kN/m?. Design the
beam and the slab (do not use "T” beam theory).
fou = 40 MPa
Cover = 25 mm
Fire resistance = 0.5 hrs
ke 5000 ale 5500 5000 >|
Elevation
200
300 a “Fso0 | 700
fea] 400
Cross-Section
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Modal Analysis of MDOF Unforced Undamped Systems: ASEN 3112 - StructuresDocument13 pagesModal Analysis of MDOF Unforced Undamped Systems: ASEN 3112 - StructuresThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis-ProblmsDocument32 pagesPlastic Analysis-ProblmsThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- Mode Superposition ExampleDocument10 pagesMode Superposition ExampleThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- Example - Transformed Sections Fig. 1: A y A yDocument1 pageExample - Transformed Sections Fig. 1: A y A yThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- CIVN3004Document6 pagesCIVN3004Thabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- CIVN3001-FINAL REPORT ... MDocument20 pagesCIVN3001-FINAL REPORT ... MThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- CIVN3004 - 2011 TestDocument2 pagesCIVN3004 - 2011 TestThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- CIVN3011Document6 pagesCIVN3011Thabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- Civn3011 2011 PDFDocument2 pagesCivn3011 2011 PDFThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- Civn3011 2008 PDFDocument3 pagesCivn3011 2008 PDFThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet