Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Chambel7
Bio Chambel7
Uploaded by
M Hanif0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageTermination of translation occurs when a stop codon in the mRNA reaches the A site of the ribosome. A release factor binds to the stop codon and causes the addition of a water molecule instead of an amino acid, breaking the bond between the polypeptide and tRNA in the P site and releasing the completed polypeptide. The translation assembly then comes apart through a multi-step process requiring the hydrolysis of two more GTP molecules.
Original Description:
Original Title
bio chambel7.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTermination of translation occurs when a stop codon in the mRNA reaches the A site of the ribosome. A release factor binds to the stop codon and causes the addition of a water molecule instead of an amino acid, breaking the bond between the polypeptide and tRNA in the P site and releasing the completed polypeptide. The translation assembly then comes apart through a multi-step process requiring the hydrolysis of two more GTP molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBio Chambel7
Bio Chambel7
Uploaded by
M HanifTermination of translation occurs when a stop codon in the mRNA reaches the A site of the ribosome. A release factor binds to the stop codon and causes the addition of a water molecule instead of an amino acid, breaking the bond between the polypeptide and tRNA in the P site and releasing the completed polypeptide. The translation assembly then comes apart through a multi-step process requiring the hydrolysis of two more GTP molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
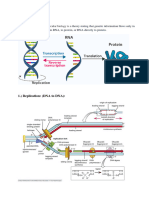
Termination of Translation
The final stage of translation is termination (Figure 17.20).
Elongation continues until a stop codon in the mRNA
reaches the A site of the ribosome. The nucleotide base
triplets UAG, UAA, and UGA do not code for amino acids
but instead act as signals to stop translation. A release factor, a protein shaped like an aminoacyl tRNA,
binds directly
to the stop codon in the A site. The release factor causes
the addition of a water molecule instead of an amino acid to
the polypeptide chain. (There are plenty of water molecules
available in the aqueous cellular environment.) This reaction
breaks (hydrolyzes) the bond between the completed polypeptide and the tRNA in the P site, releasing the
polypeptide
through the exit tunnel of the ribosome’s large subunit. The
remainder of the translation assembly then comes apart in
a multistep process, aided by other protein factors. Breakdown of the translation assembly requires the
hydrolysis of
two more GTP molecules
You might also like
- Building A PolypeptideDocument2 pagesBuilding A PolypeptideDiana RomeroNo ratings yet
- Translation: The Last Stage of Central DogmaDocument10 pagesTranslation: The Last Stage of Central DogmaChandu Kishore KalloniNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral DogmaGunaalNo ratings yet
- Translation (Biology)Document22 pagesTranslation (Biology)Manoj JoshiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Revision PosterDocument1 pageProtein Synthesis Revision PosterShonaWNo ratings yet
- The Translation: Translation Is A Process by Which The Genetic Code Contained Within An mRNADocument5 pagesThe Translation: Translation Is A Process by Which The Genetic Code Contained Within An mRNAShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Protien Synthesis Elongation & TerminationDocument14 pagesProtien Synthesis Elongation & TerminationvesascNo ratings yet
- Translation: The Synthesis of Polypeptides Using Mrna TemplatesDocument4 pagesTranslation: The Synthesis of Polypeptides Using Mrna TemplatesMudjaijah draNo ratings yet
- Translation AnoverviewDocument32 pagesTranslation AnoverviewshitalchandrasitNo ratings yet
- 10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationDocument4 pages10.06 Prokaryotic TranslationWidya NingsiNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation - Dr. Mohammed OsmanDocument43 pagesDNA Translation - Dr. Mohammed Osmanمعتز محمدNo ratings yet
- Physio Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesPhysio Protein SynthesisM.TAYYAB KHANNo ratings yet
- The Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesThe Birth and Death of Proteins: Some Key ConceptsLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document4 pagesBiochemistry 1Beatriz SilvaNo ratings yet
- Translation in ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesTranslation in ProkaryotesAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Translation-An Overview: Professor (DR.) Namrata Chhabra Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes WWW - Namrata.coDocument32 pagesTranslation-An Overview: Professor (DR.) Namrata Chhabra Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes WWW - Namrata.coDurga Charan PradhanNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument6 pagesTranslationapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Answer q5Document4 pagesAnswer q5muhammad khurram maqsoodNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Translation) - Mechanism and Control in Pro - and Eukaryotes.-3Document9 pagesProtein Synthesis (Translation) - Mechanism and Control in Pro - and Eukaryotes.-3carlottabovi28No ratings yet
- DNA Translation - Phases - TeachMePhysiologyDocument3 pagesDNA Translation - Phases - TeachMePhysiologyTasmia YounasNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationtshahriyarNo ratings yet
- Microm 410 Midterm 2 GlossaryDocument8 pagesMicrom 410 Midterm 2 GlossaryNatalie ChenNo ratings yet
- Genetics Final ReviewDocument3 pagesGenetics Final ReviewĐức Huy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- GEB 201 Ahmed Julker Nine 2020-1!77!042Document9 pagesGEB 201 Ahmed Julker Nine 2020-1!77!0422020-1-77-042No ratings yet
- LECTURE 12 TranslationDocument17 pagesLECTURE 12 TranslationAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument90 pagesTranslationspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Vocabulary 2Document4 pagesVocabulary 2AMALIA S APONTE-COLONNo ratings yet
- 13 Miller Chap 4b LectureDocument21 pages13 Miller Chap 4b LectureGerone Tolentino AtienzaNo ratings yet
- TDNº3 Part2Document3 pagesTDNº3 Part2selmi bouzidNo ratings yet
- 251 13 Exam3 KeyDocument8 pages251 13 Exam3 KeyAarati SriramNo ratings yet
- Translation Bio Ch6Document12 pagesTranslation Bio Ch6Hordit LyngdohNo ratings yet
- Advanced Chemistryprize2009 PDFDocument24 pagesAdvanced Chemistryprize2009 PDFJeremy GordonNo ratings yet
- Translation and Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument51 pagesTranslation and Regulation of Gene ExpressionP. Jacksen Sam PaulNo ratings yet
- Polar Glutamine, Asparagine Serine, Threonine Tyrosine CysteineDocument2 pagesPolar Glutamine, Asparagine Serine, Threonine Tyrosine CysteineSteven XuNo ratings yet
- From Dna To ProteinDocument6 pagesFrom Dna To ProteinMadona BadoevNo ratings yet
- 24.2 Genes: Gene (Diagram Packages P3 D1-2)Document6 pages24.2 Genes: Gene (Diagram Packages P3 D1-2)kw2533No ratings yet
- Module 10Document7 pagesModule 10Sri Harsha BairisettyNo ratings yet
- RNA TranslationDocument9 pagesRNA TranslationRhio SumayloNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument2 pagesTranslationRandom StuffNo ratings yet
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocument20 pagesPost Transcriptional ModificationZain YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Post-Transcriptional ModificationDocument20 pagesPost-Transcriptional ModificationZain YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Sharma XII - A Biology Investigatory Project - TranslationDocument24 pagesUtkarsh Sharma XII - A Biology Investigatory Project - TranslationUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Short Notes FinalDocument5 pagesBio Short Notes FinalMUHAMMAD HAFIZ FAZRISHAH BIN JEFFRY KIMNo ratings yet
- TRANSLATIONDocument12 pagesTRANSLATIONNEET STUDIESNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021925822009528 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0021925822009528 MainDhea Rahmanda putriNo ratings yet
- DNA TranslationDocument38 pagesDNA TranslationFarlogy100% (1)
- Ekspresi Gen PDFDocument36 pagesEkspresi Gen PDFainulavidaNo ratings yet
- TRANSLATION - PicsDocument62 pagesTRANSLATION - PicsJisna JaisonNo ratings yet
- TRANSLATIONDocument3 pagesTRANSLATIONSwayam Sampurna MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Transcription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalDocument4 pagesTranscription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalAnand RajNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Eukaryotic TranscriptionDocument10 pagesUNIT 7 Eukaryotic TranscriptionSarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein BiosynthesisOlusola OtasanyaNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein BiosynthesisMyrrh Tagurigan TrainNo ratings yet
- Empty McqsDocument7 pagesEmpty Mcqsmalik sahbNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 7. Molecular Basis of Heredity Gene Action Transcription and TranslationDocument5 pagesEXERCISE 7. Molecular Basis of Heredity Gene Action Transcription and TranslationMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Draft 1Document11 pagesDraft 1Afiah LutfiNo ratings yet
- Translation 1Document68 pagesTranslation 1Disha GuptaNo ratings yet
- TRANSLATIONDocument19 pagesTRANSLATIONUsha SuthersonNo ratings yet
- Temperature-Responsive Polymers: Chemistry, Properties, and ApplicationsFrom EverandTemperature-Responsive Polymers: Chemistry, Properties, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Hydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandHydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisNo ratings yet
- Microscopy: Microscope (LM), Visible Light Is Passed Through The Specimen and ThenDocument1 pageMicroscopy: Microscope (LM), Visible Light Is Passed Through The Specimen and ThenM HanifNo ratings yet
- Chambel Note4Document1 pageChambel Note4M HanifNo ratings yet
- Rising Atmospheric CO Levels: Greenhouse Effect, The Average Air Temperature at Earth'sDocument1 pageRising Atmospheric CO Levels: Greenhouse Effect, The Average Air Temperature at Earth'sM HanifNo ratings yet
- Bio Chambel4Document1 pageBio Chambel4M HanifNo ratings yet
- Bio Chambel4Document1 pageBio Chambel4M HanifNo ratings yet
- Iplant Systems Biology (Ipsb) : An International Network Hub in The Plant CommunityDocument4 pagesIplant Systems Biology (Ipsb) : An International Network Hub in The Plant CommunityM HanifNo ratings yet
- Chambel Note 2Document1 pageChambel Note 2M HanifNo ratings yet
- Bio Palson11Document1 pageBio Palson11M HanifNo ratings yet
- Constraining Behaviors Because of Dual Causality, Mathematical Model-Building inDocument1 pageConstraining Behaviors Because of Dual Causality, Mathematical Model-Building inM HanifNo ratings yet
- Vacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments: Vacuoles Are Large Vesicles Derived From The EndoplasmicDocument1 pageVacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments: Vacuoles Are Large Vesicles Derived From The EndoplasmicM HanifNo ratings yet
- Bio Chambel8Document1 pageBio Chambel8M HanifNo ratings yet
- Acidification: A Threat To Water Quality: (Figure 3.11)Document1 pageAcidification: A Threat To Water Quality: (Figure 3.11)M HanifNo ratings yet
- Elongation of The RNA Strand: (Figure 17.9)Document1 pageElongation of The RNA Strand: (Figure 17.9)M HanifNo ratings yet
- The Products of Gene Expression: A Developing StoryDocument1 pageThe Products of Gene Expression: A Developing StoryM HanifNo ratings yet
- Half A Billion Years of BackbonesDocument1 pageHalf A Billion Years of BackbonesM HanifNo ratings yet
- The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory: Reticulum Is Latin For "Little Net.") The ER Consists of ADocument1 pageThe Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory: Reticulum Is Latin For "Little Net.") The ER Consists of AM HanifNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisM HanifNo ratings yet
- EchinodermsDocument1 pageEchinodermsM HanifNo ratings yet
- A Chemical Connection To Biology: (Figure 2.1)Document1 pageA Chemical Connection To Biology: (Figure 2.1)M HanifNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts ChangeDocument1 pageMitochondria and Chloroplasts ChangeM HanifNo ratings yet
- Scribd2 PDFDocument1 pageScribd2 PDFM HanifNo ratings yet