Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPv4 Is 32-Bit-WPS Office
IPv4 Is 32-Bit-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Yawar ArslanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IPv4 Is 32-Bit-WPS Office
IPv4 Is 32-Bit-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Yawar ArslanCopyright:
Available Formats
IPv4 is 32-Bit IP address whereas IPv6 is a 128-Bit IP address.
IPv4 is a numeric addressing method whereas IPv6 is an alphanumeric addressing method.
IPv4 binary bits are separated by a dot(.) whereas IPv6 binary bits are separated by a colon(:).
IPv4 offers 12 header fields whereas IPv6 offers 8 header fields.
IPv4 supports broadcast whereas IPv6 doesn’t support broadcast.
IPv4 has checksum fields while IPv6 doesn’t have checksum fields
IPv4 supports VLSM (Virtual Length Subnet Mask) whereas IPv6 doesn’t support VLSM.
IPv4 uses ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to map to MAC address whereas IPv6 uses NDP (Neighbour
Discovery Protocol) to map to MAC address.
Features of IPv4
Connectionless Protocol
Allow creating a simple virtual communication layer over diversified devices
It requires less memory, and ease of remembering addresses
Already supported protocol by millions of devices
Offers video libraries and conferences
Features of IPv6
Hierarchical addressing and routing infrastructure
Stateful and Stateless configuration
Support for quality of service (QoS)
An ideal protocol for neighboring node interaction
Definition - What does Broadband Remote Access Server (B-RAS) mean?
A broadband remote access server (B-RAS) is a specialized server based at an Internet service provider
(ISP) network that facilitates the convergence of multiple Internet traffic sources. These sources include
cable, DSL, Ethernet or broadband wireless. B-RAS converges them into a single network that routes
traffic to and from digital subscriber line access multiplexers.
You might also like
- IPv4 Vs IPv6Document8 pagesIPv4 Vs IPv6sotiatNo ratings yet
- IPV6Document26 pagesIPV6RmkumarsNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument33 pagesIP AddressVikas JatNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Vs IPv6 - What's The DifferenceDocument6 pagesIPv4 Vs IPv6 - What's The DifferenceKeep learningNo ratings yet
- IPv6 PDFDocument155 pagesIPv6 PDFharikrishna242424No ratings yet
- Hari Krishna Raju Kanekal Nomus Comm-SystemsDocument155 pagesHari Krishna Raju Kanekal Nomus Comm-Systemsharikrishna242424No ratings yet
- Plan 7Document48 pagesPlan 7Zain Alabeeden AlarejiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4b IPv6 FeaturesDocument18 pagesChapter 4b IPv6 Featuresbettelly84No ratings yet
- Ip V 6: - Ipng Short For Internet Protocol Next Generation, A New Version of The Internet Protocol (Ip)Document7 pagesIp V 6: - Ipng Short For Internet Protocol Next Generation, A New Version of The Internet Protocol (Ip)karthikaNo ratings yet
- IPv6 SlideDocument35 pagesIPv6 SlideChantich CharmtongNo ratings yet
- LectureNote 01-2 IPv6AddressesDocument30 pagesLectureNote 01-2 IPv6AddressesKelemework DagneNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument3 pagesSolvePiyush PatilNo ratings yet
- Acn CH2 Next Generation Ip11 PDFDocument10 pagesAcn CH2 Next Generation Ip11 PDFRavi RathodNo ratings yet
- WIA1005 Network Technology FoundationDocument35 pagesWIA1005 Network Technology FoundationAina NajihahNo ratings yet
- IPv 6Document34 pagesIPv 6Ruben BermudezNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Ipv4 & Ipv6Document34 pagesA Seminar On Ipv4 & Ipv6Deepak RathoreNo ratings yet
- 22is504 23-24 LM12Document31 pages22is504 23-24 LM12SRIRAM SNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Muhammad Areeb ShahidDocument4 pagesAssignment 1: Muhammad Areeb ShahidAreeb ShahidNo ratings yet
- Digital Network - Lecturer3Document32 pagesDigital Network - Lecturer3sammydtechNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Addressing: Yashvant Singh Centre For Excellence in Telecom Technology and ManagementDocument45 pagesIpv6 Addressing: Yashvant Singh Centre For Excellence in Telecom Technology and ManagementRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolsDocument14 pagesInternet ProtocolsShivani ThakurNo ratings yet
- IPV6Document46 pagesIPV6ShubhamSetiaNo ratings yet
- Address Resolution ProtocolDocument5 pagesAddress Resolution ProtocolTushar VermaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6Document5 pagesDifference Between IPv4 and IPv6Ardit Mezini100% (1)
- IPv 6Document29 pagesIPv 6meriem hasNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 (Network Layer) - Part II DDocument75 pagesUnit - 4 (Network Layer) - Part II Dnikshithcharan11No ratings yet
- Comparison Between Internet Protocol Version 4 and 6Document9 pagesComparison Between Internet Protocol Version 4 and 6كمال الطويرNo ratings yet
- Ipv 6Document39 pagesIpv 6DEEPALI BAGULNo ratings yet
- What'S The Difference Between Ipv4 and Ipv6?: Electronic DesignDocument6 pagesWhat'S The Difference Between Ipv4 and Ipv6?: Electronic DesignRoshan RajuNo ratings yet
- Omnisecu IPv6Document23 pagesOmnisecu IPv6harmansagguNo ratings yet
- Security Aspects & Performance Analysis of Mobile & IP Networks - Chapter 3Document13 pagesSecurity Aspects & Performance Analysis of Mobile & IP Networks - Chapter 3RahulNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Adressing: in This Section, We ExamineDocument5 pagesIpv6 Adressing: in This Section, We ExaminePreethin BabuNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Introduction On Mikrotik: - SpeakerDocument27 pagesIpv6 Introduction On Mikrotik: - SpeakerEric MUHIMUZINo ratings yet
- IPV6 - Security and ImplementationDocument68 pagesIPV6 - Security and Implementationavijoshi4No ratings yet
- Ipv4 & Ipv6: Hanar Ahmed Sako Dlshad Gashaw OmarDocument18 pagesIpv4 & Ipv6: Hanar Ahmed Sako Dlshad Gashaw OmarHanar AhmedNo ratings yet
- IP Address: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesIP Address: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnonymous yDM6SRNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 vs. Ipv6: Anne-Marie Ethier Andrei IoticiDocument21 pagesIpv4 vs. Ipv6: Anne-Marie Ethier Andrei Ioticilbillings1No ratings yet
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2SelormNo ratings yet
- Ip AddressDocument23 pagesIp AddressShubham JoshiNo ratings yet
- CN GD Doc: Topic: Ipv6Document3 pagesCN GD Doc: Topic: Ipv6ross gellerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Implementing Ipv6: Windows Platform - CH 8Document19 pagesChapter 8: Implementing Ipv6: Windows Platform - CH 8aya ghouryNo ratings yet
- Design of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationDocument5 pagesDesign of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationsaravananaecNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Technology Overview Tutorial Part II Rev1Document70 pagesIPv6 Technology Overview Tutorial Part II Rev1Manju DevarajNo ratings yet
- 12 Advanced TCPIP ConfigurationDocument10 pages12 Advanced TCPIP ConfigurationChis LebroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: IPv6 FundamentalsDocument35 pagesLesson 3: IPv6 FundamentalsMahmmoud MahdiNo ratings yet
- CN-Unit 4Document44 pagesCN-Unit 4panimalar123No ratings yet
- Title: Internet Protocol Version 6 Ipv6 1Document6 pagesTitle: Internet Protocol Version 6 Ipv6 1rahmatullah KhairiNo ratings yet
- IPV6Document47 pagesIPV6Bass Lin3No ratings yet
- IPv6 AddressDocument16 pagesIPv6 Addressjim1234uNo ratings yet
- Module 12: Ipv6 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)Document52 pagesModule 12: Ipv6 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)thanh vienNo ratings yet
- IPv6 - OverviewDocument37 pagesIPv6 - OverviewPathum PramodyaNo ratings yet
- Compared Between Ipv6 and With Ipv4Differences andDocument9 pagesCompared Between Ipv6 and With Ipv4Differences andowloabi ridwanNo ratings yet
- Compared Between Ipv6 and With Ipv4Differences andDocument9 pagesCompared Between Ipv6 and With Ipv4Differences andowloabi ridwanNo ratings yet
- BSCI30S08 IPv6Document73 pagesBSCI30S08 IPv6Fabio QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Ipv6: Jaringankomputer2 Lab. Komunikasidigital Gedungd4 LT 1 Gedungd4 Lt. 1 Eepis-ItsDocument29 pagesIpv6 Ipv6: Jaringankomputer2 Lab. Komunikasidigital Gedungd4 LT 1 Gedungd4 Lt. 1 Eepis-ItsfrendianaNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 and SubnettingDocument21 pagesIpv6 and SubnettingdurgeshNo ratings yet
- IPv6 ADRESSINGDocument35 pagesIPv6 ADRESSINGADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- BSCI30S08 IPv6Document73 pagesBSCI30S08 IPv6Amine TellibiNo ratings yet
- CCNA Certification All-in-One For DummiesFrom EverandCCNA Certification All-in-One For DummiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
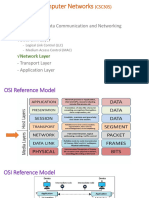
- Network Models Tcp/IpDocument23 pagesNetwork Models Tcp/IpYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Apr PDFDocument1 pageApr PDFYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
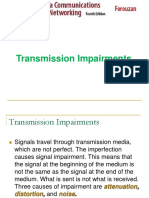
- Transmission ImpairmentsDocument19 pagesTransmission ImpairmentsYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- What Is NGN-WPS OfficeDocument17 pagesWhat Is NGN-WPS OfficeYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Apr 2020 PDFDocument1 pageApr 2020 PDFYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- New Resume 001Document1 pageNew Resume 001Yawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Active Filters 1Document1 pageApplications of Active Filters 1Yawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Apr 2020Document1 pageApr 2020Yawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- JFET Note StudentDocument75 pagesJFET Note StudentYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- JFET Note StudentDocument75 pagesJFET Note StudentYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Low Pass FLTRDocument7 pagesLow Pass FLTRYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Passive Filters I: Dr. Mohamed Refky AminDocument27 pagesPassive Filters I: Dr. Mohamed Refky AminYawar ArslanNo ratings yet