Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharma
Pharma
Uploaded by
Patrick MangilinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharma
Pharma
Uploaded by
Patrick MangilinCopyright:
Available Formats
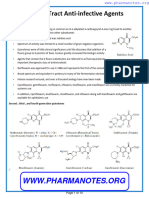
•
Norfloxacin is used to treat UTIs and
Fluoroquinolones
prostatitis
Structurally similar synthetic antibacterial
• Ofloxacin is used to treat selected sexually
drugs.
transmitted diseases, lower respiratory tract
They're primarily administered to treat
infection, skin infections and prostatitis.
UTIs, upper respiratory tract infections,
Gatifloxacin is use to treat condition like
pneumonia and gonorrhoea.
respiratory tract infections, soft tissue
- medicines that kill bacteria or prevent their
infections, UTI.
growth .
Sparfloxacin is indicated in condition like acne,
bacterial infections, bronchitis, pneumonia
Examples of fluoroquinolones:
tonsillitis.
• Cifrofloxacin
• Gemifloxacin
Adverse Reactions
• Levofloxacin
- Fluoriquinolones are well tolerated by most
• Moxifloxacin
patients, but some adverse effects may occur,
• Norfloxacin
including:
• Ofloxacin
• Dizziness
•gatifloxacin
• Nausea and vomiting
•sparfloxacin
• Diarrhea
• Abdominal pain.
Pharmacokinetic
After oral administration, fluoroquinolones
Nursing considerations
are absorbed well. They aren’t highly
Assessment
protein bound, minimally metabolized in the
· History: Allergy to fluoroquinolones, renal
liver, and are excreted primarily in the
dysfunction, seizures, lactation, pregnancy
urine.
· Physical: Skin color, lesions; T;
Pharmacodynamics
orientation, reflexes, affect; mucous
Bacteriostatic
membranes, bowel sounds; renal and liver
Fluoroquinolones interrupt DNA synthesis
function tests; blood glucose (diabetics)
during bacterial replication by inhibiting
DNA gyrase, an essential enzyme of
Interventions
replicating DNA. As a result, the bacteria
· Arrange for culture and sensitivity tests
can’t reproduce.
before beginning therapy.
· Continue therapy as indicated for
Pharmacotherapeutics
condition being treated.
- Fluoroquinolones can be used to treat a wide
· Administer oral drug 1 hr before or 2 hr
variety of UTIs.
after meals with a glass of water; separate oral
• Ciprofloxacin is used to treat lower
drug from other cation administration, including
respiratory tract infections, infectious diarrhea
antacids, by at least 2 hr.
and skin, bone and joint infection.
· Ensure that patient is well hydrated
• Gemifloxacin is used to treat bronchitis,
during course of therapy.
community acquired pneumonia, UTIs, and
· WARNING: Discontinue drug at any sign
gynaecologic infections.
of hypersensitivity (rash, photophobia) or at
• Levofloxacin is indicated for treatment of
complaint of tendon pain, inflammation, or
lower respiratory tract infections, skin
rupture.
infections and UTIs.
· Monitor clinical response; if no
• Moxifloxacin is used to treat bacterial
improvement is seen or a relapse occurs, repeat
sinusitis and mild to moderate community
culture and sensitivity test.
acquired pneumonia.
(pseudomembranous colitis), especially that due to the
exhibit concentration-dependent bactericidal activity by inhibiting
hypervirulent C. difficileribotype 027.
the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase, enzymes essential
Diarrhea, leukopenia, anemia, and photosensitivity are
for bacterial DNA replication. Fluoroquinolones are divided into 2
groups, based on antimicrobial spectrum and pharmacology: uncommon. Rash is uncommon unless gemifloxacin is used for > 1
Fluoroquinolone use for pneumon Older
wk and is more likely to develop in women < 40. Nephrotoxicity is
group: Ciprofloxacin
, norfloxacin rare.
, andofloxacin
Newer group: Gemifloxacin
, levofloxacin Fluoroquinolones interfere with bacterial DNA metabolism by
andmoxifloxacin the inhibition of two enzymes, Topoisomerase II (syn. DNA
Some newer fluoroquinolones have been withdrawn because gyrase) and Topoisomerase IV. In Gram-negative organisms
of toxicity; they include trovafloxacin (because of severe
hepatic toxicity) and gatifloxacin DNA gyrase is the primary target, whereas in Gram-positive
(because of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia). bacteria Topoisomerase IV was recently found to be most
affected.
ia is increasing, and with it so is bacterial resistance to
fluoroquinolones. The function of DNA gyrase is to introduce supercoils into
the linear DNA double helix, which results in the highly
Pharmacology
condensed 3-dimensional structure of the DNA usually
Oral absorption is diminished by coadministration of cations present inside the cell. The function of Topoisomerase IV still
(aluminum, Mg, Ca, zinc, and iron preparations). After oral and is barely understood.
parenteral administration, fluoroquinolones are widely distributed Models to explain the activity of quinolones at the target site
only exist for DNA gyrase: During the supercoiling process,
in most extracellular and intracellular fluids and are concentrated
both DNA strands are cleaved by DNA gyrase at 4 base pair
in the prostate, lungs, and bile. staggered sites, forming a "quinolone binding pocket".
Most fluoroquinolones are metabolized in the liver and excreted
Two quinolone molecules self-assemble inside the pocket in
in urine, reaching high levels in urine. Moxifloxacin is eliminated dimer structure and attach to the gyrase-DNA complex
primarily in bile. electrostatically, which stabilizes the intermediate stage of
Fluoroquinolones have traditionally been considered to be this reaction step.
contraindicated in children because they may cause cartilage
lesions if growth plates are open. However, some experts, who Permanent gaps in the DNA strands induce synthesis of
challenge this view because evidence is weak, have recommended repair enzymes (exonucleases), initiating uncoordinated
prescribing fluoroquinolones as a 2nd-line antibiotic and repair processes, which results in irreversible damage to the
restricting use to a few specific situations, including P. DNA and, finally, cell death.
aeruginosa infections in patients with cystic fibrosis, prophylaxis
and treatment of bacterial infections in immunocompromised
patients, life-threatening multiresistant bacterial infections in
neonates and infants, and Salmonella or Shigella GI tract
infections.
Upper GI adverse effects occur in about 5% of patients
because of direct GI irritation and CNS effects.
CNS adverse effects (eg, mild headache, drowsiness,
insomnia, dizziness, mood alteration) occur in < 5%. NSAIDs
may enhance the CNS stimulatory effects of
fluoroquinolones. Seizures are rare, but fluoroquinolones
should not be used in patients with CNS disorders.
Tendinopathy, including rupture of the Achilles
tendon, may occur even after short-term use of
fluoroquinolones.
QT-interval prolongation can occur, potentially leading
to ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
Fluoroquinolone use has been strongly associated
with Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea
You might also like
- Black Medicine I - The Dark Art of Death - N. Mashiro - DiOS PDFDocument48 pagesBlack Medicine I - The Dark Art of Death - N. Mashiro - DiOS PDFJoe Castor67% (6)
- Pharmaceutics Exam 2 - This SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Exam 2 - This Semesterapi-372361290% (21)
- 24 05 2021 Floroquinolones DR - Syeda ZainDocument46 pages24 05 2021 Floroquinolones DR - Syeda ZaintehreemNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Nucleic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsDocument21 pagesQuinolones: Nucleic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsShahid Iqbal100% (1)
- Fluoroquinolones: QuinolonesDocument7 pagesFluoroquinolones: QuinolonesGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyDocument37 pagesQuinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Flu Oro Quino L OnesDocument28 pagesFlu Oro Quino L Onesbushe_yhane23No ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones by Yasir Irafat GRP 11Document21 pagesFluoroquinolones by Yasir Irafat GRP 11Yasir IrafatNo ratings yet
- Neofloxin: (Ciprofloxacin IV Infusion)Document1 pageNeofloxin: (Ciprofloxacin IV Infusion)SharifulNo ratings yet
- Quinolone: Quinolone, Folic Acid Antagonists and Urinary Tract AntisepticsDocument9 pagesQuinolone: Quinolone, Folic Acid Antagonists and Urinary Tract AntisepticsNirav ValandNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacinramNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Anti-Infective AgentsDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Anti-Infective Agentsjinikrishna15No ratings yet
- Anti InfectivesDocument145 pagesAnti Infectivescharles babasaNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Submitted by Jithin GDocument12 pagesQuinolones: Submitted by Jithin GJithin GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Anti Infective AgentsDocument26 pagesUrinary Tract Anti Infective Agentspallavi DiwareNo ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin) : Mechanism of ActionDocument15 pagesFluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin) : Mechanism of ActionAhad SheikhNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Anti-Infectives and Anti-Inflammatory: Ncm106 - Pharmacology 2 Semester, AY 2020-2021Document34 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Anti-Infectives and Anti-Inflammatory: Ncm106 - Pharmacology 2 Semester, AY 2020-2021imnas100% (1)
- PRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EDocument31 pagesPRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- SESSION 6 - QuinolonesDocument15 pagesSESSION 6 - QuinolonesBruno NjawikeNo ratings yet
- Drugs & Inhibitors of DNA Replication: Aashutosh Nama M.SC Microbiology Sem - 1 Dr. B Lal Institute of BiotechnologyDocument22 pagesDrugs & Inhibitors of DNA Replication: Aashutosh Nama M.SC Microbiology Sem - 1 Dr. B Lal Institute of Biotechnologyaashutosh namaNo ratings yet
- QUINOLONESDocument23 pagesQUINOLONESKasturiRangan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- MoxigetDocument2 pagesMoxigetStar WalkerNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument24 pagesAntibacterial Agentsمصطفى أحمدNo ratings yet
- BY: Sonali Kanade Kaushik.N.Kuche Rucha.J.Kadmane Diksha KanojiyaDocument37 pagesBY: Sonali Kanade Kaushik.N.Kuche Rucha.J.Kadmane Diksha KanojiyaRaman KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim and FlouroquinolonesDocument24 pagesLecture 15 Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim and FlouroquinoloneshamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Antifungals Student'sDocument34 pagesAntifungals Student'sapril jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument42 pagesAntifungal AgentsOluwatobi AyomideNo ratings yet
- Inhibicion de AcidosDocument24 pagesInhibicion de AcidosItzel JuNo ratings yet
- Drug Use in LeprosyDocument23 pagesDrug Use in LeprosyIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- Tetracyclines: Mechanism of ActionDocument16 pagesTetracyclines: Mechanism of Actionammar amerNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Prof. Anuradha NischalDocument42 pagesQuinolones: Prof. Anuradha Nischalsekprodi profesifkyarsiNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Shaista Gul CMS#17303 SAP#6444Document33 pagesQuinolones: Shaista Gul CMS#17303 SAP#6444Javeria AjazNo ratings yet
- Voloxal TabletsDocument9 pagesVoloxal Tabletselcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- DR - Vijay Nagdev H.O. Medical Unit-IDocument24 pagesDR - Vijay Nagdev H.O. Medical Unit-IVijai KumarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihDocument29 pagesAntibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihPutri Sari SeptirianiNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument24 pagesAntibioticsAlba GonzálezNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument4 pagesLevofloxacinWaseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-AntibacterialDocument6 pagesDrug Study-AntibacterialKyla Marie NabongNo ratings yet
- 6 QuinolonesDocument15 pages6 Quinolonesnusaiba.alobaidyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Rle Final 1Document18 pagesDrug Study Rle Final 1YBH Construction SupplyNo ratings yet
- OFKA (Ofloxacin) Ofloxacin: Mechanism of ActionDocument4 pagesOFKA (Ofloxacin) Ofloxacin: Mechanism of Actiondhwanit31No ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument22 pagesPharmacologyhazel mrytleNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: Dewi Selvina R & Instiaty Department of Pharmacology FmuiDocument37 pagesAntifungal Agents: Dewi Selvina R & Instiaty Department of Pharmacology Fmuisalsa2506No ratings yet
- AntifungalDocument41 pagesAntifungalDeribe BekeleNo ratings yet
- Amphoterici N: Drug Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionDocument4 pagesAmphoterici N: Drug Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Antibiotics: Fluoroquinolone - Chloramphenicol - TetracycllineDocument40 pagesPharmacology Antibiotics: Fluoroquinolone - Chloramphenicol - TetracycllinemluthfidunandNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Document84 pagesFarmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Alex FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Antimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIDocument86 pagesAntimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIKresna Denta ElygioNo ratings yet
- AnuragDocument15 pagesAnuragManoj SisodiaNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument15 pagesLevofloxacinsonal aranhaNo ratings yet
- 12.1. Fluoroquinolone, Chloraphenicol & TetracyclineDocument40 pages12.1. Fluoroquinolone, Chloraphenicol & TetracyclinenugrahaaryaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy: Antifungal & AntiviralDocument7 pagesClinical Pharmacy: Antifungal & Antiviralوقت بدل ضايعNo ratings yet
- MoxifloxacinDocument3 pagesMoxifloxacinWaseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- SULFONAMIDES and FluroquinolonesDocument23 pagesSULFONAMIDES and FluroquinolonesRabi ShahNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinaraNo ratings yet
- Anthelmentics Version 2Document21 pagesAnthelmentics Version 2N Gv FcNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-Ruchita V Bhavsar 1 Sem M.Pharm Guided By: - Mr. Samaresh Pal Roy HOD of Pharmacology, SDPC, KimDocument42 pagesPrepared By:-Ruchita V Bhavsar 1 Sem M.Pharm Guided By: - Mr. Samaresh Pal Roy HOD of Pharmacology, SDPC, KimHenry DanielNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyecasantos595No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Furazolidone, Nalidixic Acidnorfloxacin, DapsoneDocument18 pagesUnit 3: Furazolidone, Nalidixic Acidnorfloxacin, DapsoneIshaani GargNo ratings yet
- H FloroquinolonesDocument10 pagesH Floroquinoloneshisto anatomyNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Play Therapy: Activity PlanDocument3 pagesPlay Therapy: Activity PlanPatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Inference Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Inference Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale EvaluationPatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- EuniceDocument4 pagesEunicePatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- Management: Minor BurnsDocument3 pagesManagement: Minor BurnsPatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper in Rizal: Eunice Valerie P. LazoDocument1 pageReaction Paper in Rizal: Eunice Valerie P. LazoPatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- C Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As Existence, KnowledgeDocument2 pagesC Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As Existence, KnowledgePatrick MangilinNo ratings yet
- Primary ComplexDocument24 pagesPrimary ComplexEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- ParanoiaDocument3 pagesParanoiatrinigalNo ratings yet
- GP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Document5 pagesGP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Lisa NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- Behavioral and Pharmacologic Therapies For Chronic Insomnia in Adults - UpToDateDocument45 pagesBehavioral and Pharmacologic Therapies For Chronic Insomnia in Adults - UpToDateJessica ChavesNo ratings yet
- Research Title (FTF) - RRL 2Document3 pagesResearch Title (FTF) - RRL 2Ueyni 24No ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug Studyjuan carlosNo ratings yet
- PMQA Lec Topic 1 2Document10 pagesPMQA Lec Topic 1 2armand bayoranNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AssignmentDocument6 pagesPharmacology AssignmentMaria MushtaqueNo ratings yet
- Wa0021.Document11 pagesWa0021.andini putri sabihiNo ratings yet
- Telaleaf Health Inc. and Vayamed A Division of Sanity Group Launch Exclusive PartnershipDocument3 pagesTelaleaf Health Inc. and Vayamed A Division of Sanity Group Launch Exclusive PartnershipPR.comNo ratings yet
- Poppy & Alkaloid Affairs: Turkish Grain BoardDocument24 pagesPoppy & Alkaloid Affairs: Turkish Grain BoardAura UrregoNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal DrugsDocument6 pagesAnti Fungal Drugsbilal ahmadNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionDocument13 pagesUrinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionTarek AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pharma Drug SufficesDocument3 pagesPharma Drug SufficesJillian GayleNo ratings yet
- PSB 368Document6 pagesPSB 368Miguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Key Drugs Mnemonics Study Tips Pebc Osce ResourcesDocument18 pagesKey Drugs Mnemonics Study Tips Pebc Osce Resourcesvishpinder sharma100% (1)
- All Category Name DescDocument286 pagesAll Category Name DescWeb SpringNo ratings yet
- Chloramphenicol: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept.: PharmacologyDocument17 pagesChloramphenicol: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept.: PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Culture Aerobic: Final Laboratory ReportDocument3 pagesCulture Aerobic: Final Laboratory Reportdr.diagnostics.labNo ratings yet
- Test 6 - Pharmacology & AnesthesiologyDocument5 pagesTest 6 - Pharmacology & Anesthesiologydr.jah9No ratings yet
- Glaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDocument8 pagesGlaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDr.Jibachha Sah,Vet.physician,author, & motivatorNo ratings yet
- Wipha Ready 02 Agustus 2021Document23 pagesWipha Ready 02 Agustus 2021priska valiniaNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument20 pagesAnalgesicsPamela Ria HensonNo ratings yet
- The Use of Vancomycin With Its Therapeutic and Adverse Effects: A ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Use of Vancomycin With Its Therapeutic and Adverse Effects: A Reviewdea yuniarNo ratings yet
- The Pharmacology of Inhaled Anesthetics - Eger, Edmond I., 1930 - Eisenkraft, James B Weiskopf, - 2002 - (S.L.) - Edmond I Eger - Anna's ArchiveDocument360 pagesThe Pharmacology of Inhaled Anesthetics - Eger, Edmond I., 1930 - Eisenkraft, James B Weiskopf, - 2002 - (S.L.) - Edmond I Eger - Anna's ArchiveBhrahmadhathan U M TNo ratings yet
- Standardization and Comparative Study of Guduchi Churna, Guduchi Ghan Vati and Guduchi SatwaDocument11 pagesStandardization and Comparative Study of Guduchi Churna, Guduchi Ghan Vati and Guduchi SatwaAnonymous pqtS3tcu1No ratings yet
- FentanylDocument11 pagesFentanylJereel Hope BaconNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Jonathan R. Dela Cruz BSN - Iii - IiiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Jonathan R. Dela Cruz BSN - Iii - IiiThan Ramile Dela CruzNo ratings yet