Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsNursing Drug Study
Nursing Drug Study
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- UwordDocument43 pagesUwordkarl abiaad100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATENicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Fdar-Labor PainDocument5 pagesFdar-Labor PainNicole cuencos100% (1)
- Depression Case StudyDocument1 pageDepression Case StudyNicole cuencos100% (1)
- APPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Document3 pagesAPPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain Case StudyDocument7 pagesLabor Pain Case StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Case Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Document7 pagesCase Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Weigght Gain NCPDocument1 pageWeigght Gain NCPNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDocument3 pagesCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Spinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesSpinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityNicole cuencos50% (2)
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESDocument5 pagesDrug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Duavent Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Computation FormulasDocument1 pageComputation FormulasNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Document1 pageSignificance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- MEASLES PresentationDocument32 pagesMEASLES PresentationMobin Ur Rehman Khan0% (1)
- Opening: (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI) (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI)Document4 pagesOpening: (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI) (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI)Trisna meyanaNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Cardio SLE Mcqs With AnswersDocument37 pagesCardio SLE Mcqs With AnswersAsif Newaz100% (4)
- AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesAmoxicillinClarisse30No ratings yet
- Liver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument2 pagesLiver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsAdi Kurnia100% (1)
- Tuberculosis: Mariana Ngundju AwangDocument23 pagesTuberculosis: Mariana Ngundju AwangansyNo ratings yet
- Albendazol Tablet 400 MG Acyclovir Tablet 400 MGDocument4 pagesAlbendazol Tablet 400 MG Acyclovir Tablet 400 MGSharfina AbsharinaNo ratings yet
- H-Mole Pathophysiology in Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageH-Mole Pathophysiology in Schematic DiagramFaith Lumayog100% (2)
- Otitis Media: While The OMEDocument2 pagesOtitis Media: While The OMEKim EurelleNo ratings yet
- تجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Document6 pagesتجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Mohammed ShaddadNo ratings yet
- Antihelmintics DrugsDocument14 pagesAntihelmintics DrugsSalman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Riaphyllin Syrup Patient Information LeafletDocument1 pageRiaphyllin Syrup Patient Information Leafletpharmacia1.comNo ratings yet
- IST's - HPVDocument17 pagesIST's - HPVCaio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Related Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesDocument13 pagesRelated Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesMario BadayosNo ratings yet
- Naturopathy Treatments For 357 Diseases PDFDocument23 pagesNaturopathy Treatments For 357 Diseases PDFshilpi agarwalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Final 1Document47 pagesDrug Study Final 1Nik2No ratings yet
- Annual DOLE Report FormDocument7 pagesAnnual DOLE Report FormpnvtgaNo ratings yet
- Antiulcer DrugsDocument16 pagesAntiulcer DrugsJenNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument5 pagesPriceMubarak MHNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha DhakalDocument22 pagesFebrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha Dhakalsagar poudelNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Intussusception: Management OptionsDocument2 pagesRecurrent Intussusception: Management OptionsMuhammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- SMLE 2018 احدث اسئلة امتحان لأختبار الهيئه السعوديDocument441 pagesSMLE 2018 احدث اسئلة امتحان لأختبار الهيئه السعوديOman Edu100% (6)
- Case Presentation On Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument50 pagesCase Presentation On Diabetic KetoacidosisJoana Marie Gantuangco-MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Penguins Medicine August-SeptumberDocument215 pagesPenguins Medicine August-SeptumberKhattabNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Dengan Sikap Ibu Hamil Dalam Mengonsumsi Asam FolatDocument7 pagesPengetahuan Dengan Sikap Ibu Hamil Dalam Mengonsumsi Asam FolatMivtaNo ratings yet
- A Complete To HomeopathYDocument5 pagesA Complete To HomeopathYmukesh_singh_16No ratings yet
- Neuro Pharma PDFDocument258 pagesNeuro Pharma PDFNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- All About Vancomycin by SDocument2 pagesAll About Vancomycin by SSharan SahotaNo ratings yet
Nursing Drug Study
Nursing Drug Study
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesOriginal Title
NURSING DRUG STUDY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesNursing Drug Study
Nursing Drug Study
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
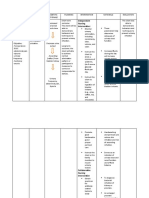
DRUG CLASSIFICATION/INDICATI MECHANIS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON M OF REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITI
ACTION FREQUENC ES
Y
Generic Acute bacterial worsening Binds to the Contraindicated in CNS: fatigue, -500 mg P.O. -Monitor patient
name: of COPD caused by 50S subunit patients headache, for superinfection.
AZITROMYCI Haemophilis influenza, bacteria hypersensitive to somnolence, Drug may cause
N Moraxella catarrhalis, or ribosomes, azithromycin, dizziness. overgrowth of non-
Streptocccus pnemoniae; blocking erythromycin, or CV: chest pain susceptible bacteria
Brand name: uncomplicated skin and protein other macrolide or palpitations or fungi.
AzaSite, skin-structure infections synthesis; ketolide antibiotics EENT: eye irritation -Monitor patient
Zithromax, caused by Staphylococcus bacteriostatic and in those with (ophthalmic) for CDAD, which
Zmax aureus, Sterptococcus or history of GI: abdominal pain, may range in
pyogens second-lined bactericidal, cholestatic jaundice anorexia, diarrhea, severity from mild
therapy for phyryngitis or depending on or hepatic nausea, vomiting, diarrhea to fatal
tonsillitis caused by concentration dysfunction from pseudomembranous colitis
S.pyogens prior use of colitis, dyspepsia, -Consider full risk
Community-acquired azithromycin flatulence, melena profile when
pneumonia caused by C. Don’t use oral drug Hepatic: cholestatic choosing
pneumoniae, H influenza, in patients with jaundice appropriate
M. pneumoniae, or S. pneumonia or in Skin: antibiotic therapy.
pneumoniae those with photosensitivity Alternative
Acute bacterial sinusitis moderate to severe reactions, rash pain macrolide or
caused by H. infdluenzae, illness or risk at injection site fluoroquinolone
M catarrhalis or S. factors (such as pruritus. class drugs also
pneumoniae cystic fibrosis, Other: angioedema have potential to
To prevent disseminated nosocomially cause QT-interval
Mycobacterium avium acquired infections, prolongation and
complex in patients with known or other significant
advanced HIV infection suspected adverse effects.
Bacterial conjunctivitis bacteremia; -Warn patient to
caused by coryneform hospitalized, seek immediate
group G, H. influenza elderly, or medical care for
Staphylococcus aureus, debilitated irregular heartbeat,
Streptococcus mitis group. patients; or shortness of
patients with breath, dizziness or
immunodeficiency fainting.
or functional
asplenia.
Elderly patients
may be at
increased risk for
drug associated QT-
interval effects.
DRUG CLASSIFIACATION/INDICATI MECHANISM CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION DOSE, NURSING
ON OF ACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILI
FREQUENC TIES
Y
Bespri Initial treatment of CV disorders eg, Thought to -Avoid use in patients with -GI disturbances eg, 75-100 mg Give the
n angina pectoris & MI. Prevention of produce severe hepatic impairment nausea, dyspepsia & medication on a
cerebrovascular disorders eg, analgesia and or history of active peptic vomiting. Urticaria & schedule rather
stroke. exert its anti- ulcer disease. other skin eruptions, than as needed.
inflammatory -use cautiously in patients angioedema, rhinitis &
effected by with GI lesions impaired severe/fatal paroxysmal -Monitor elderly
inhibiting renal function, bronchospasm & dyspnea. patients closely
prostaglandin hypoprothrombinemia, Increased bleeding time, because they may
and other vitamin K deficiency, decreased platelet be more
substances that thrombotic adhesiveness & susceptible to
sensitize pain thrombocytopenic purpura. hypoprothrombinemia aspirins toxic
receptors. Drug (large dose). May exhibit effects.
may relieve cross-sensitivity to other
fever through NSAIDs. Symptoms of -Monitor patient
central action in salicylism eg, dizziness, for
the tinnitus, deafness, hypersensitivity
hypothalamic sweating, nausea & reactions such as
heat-regulating vomiting, headache & anaphylaxis and
center. In low mental confusion; trauma.
doses, drug also
appears to
interfere with
clothing by
keeping a
platelet-
aggregating
substance from
forming.
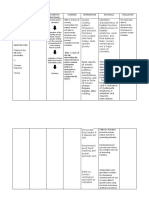
DRUG CLASSIFIACATION/INDICATI MECHANISM CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON OF ACTION N REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITIES
FREQUENC
Y
Provasc - Chronic stable angina, Inhibits calcium -contraindicated in CNS: Oral ; Monitor patient carefully.
vasospatic angina; to reduce ion influx patients hypersensitive headache, 500mg /tab Some patients, especially
Generic risk of hospitalization across cardiac to drug. fatigue, those with severe
name – because of angina; to reduce and smooth- -use cautiously in dizziness obstructive CAD, have
amlodipine risk of coronary muscle cells, patients receiving other CV: edema, developed increased
revascularization procedure dilates coronary peripheral vasodilators, flushing, frequency, duration or
in patients with recently arteries and especially those with palpitations severity of angina or acute
documented CAD by arterioles and GI: nausea, MI after inhibition of
severe aortic stenosis or
angiography and without HF decrease BP abdominal calcium channel blocker
hypertrophic
or with LVEF less than 40% and myocardial pain therapy or at time of
- Hypertension oxygen cardiomyopathy with Respiratory: dosage increase.
demand. outflow tract pulmonary
obstruction, and in edema,
patients with HF with dyspnea
reduced LVEF. Because Skin: prutish,
drug is metabolized by rash.
the liver, use cautiously
and reduce dosage in
patients with severe
hepatic diseases.
DRUG CLASSIFICATION/INDICATI MECHANISM OF CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON ACTION N REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILIT
FREQUENC IES
Y
Management of reversible To reduces Contraindicated in CNS: dizziness, Oral; -Safety and
Generic bronchospasm associated bronchospasm patients hypersensitive headache, pain Inhalation effectiveness of
Name: with obstructive airway through both to drug, atropine, or its CV: chest pain, Onset-5-15 intranasal use
Ipratropium diseases (eg, bronchial anticholinergic and derivatives. palpitation, minutes beyond 4 days in
asthma).
Salbutamol sympathomimetic hypertension patients with a
For patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary
mechanisms. Use cautiously in EENT: blurred common cold
Brand Simultaneous patients with angel vision, rhinitis, haven’t been
disease (COPD) on a
Name: administration of closure glaucoma, pharyngitis , established.
regular inhaled
DUAVENT both drugs produces prostatic hyperplasia or sinusitis, epistaxis
bronchodilator who
continue to have evidence a greater bladder-neck GI: dyspepsia, -if patient uses a
of bronchospasm and who bronchodilator effect obstruction nausea, GI facemask for a
require a second than when either distress, dry nebulizer, take
bronchodilator. drug is used alone at mouth, care to prevent
recommended constipation leakage around the
dosages. { GU: UTI mask because eye
Musculoskeletal: pain or temporary
back pain blurring of vision
Respiratory: URI, may occur.
bronchitis, - Warn patient
bronchospasm, that drug isn’t
cough dyspnea, effective for
increased sputum treating acute
Skin: rash episodes of
Other: flulike bronchospasm
symptoms, when rapid
hypersensitivity response is
reactions. needed.
-if more than 1
inhalation is
prescribed tell
patient to wait at
least 2 minutes
before repeating
procedure.
Teach patient to
use metered-dose
inhaler (MDI) or
oral nebulizer
correctly. Refer to
manufacturer’s
instructions for
use.
DRUG CLASSIFICATION/INDICATI MECHANIS CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON M OF N REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITI
ACTION FREQUENC ES
Y
Susceptible bacterial Inhibits cell- -Contraindicated in GI: pseudomembranous IV/IM; 1-2g
CEFRIOXONE septicemia, acute bacterial wall synthesis, patients hypersensitive colitis, diarrhea. Monitor patients
otitis media, lower promoting to drug or other Hematologic: for superinfection,
Brand name: respiratory tract, UTIs, osmotic cephalosporins. eosinophilia, diarrhea, and
Rocephin skin and skin structure, instability; -Use cautiously in thrombocytosis, anemia, and treat
bone and joint, pelvic usually patients hypersensitive leukopenia. appropriately.
inflammatory disease bactericidal to penicillin because of Skin: pain, induration,
(PID), intraabdominal
possibility with other tenderness at injections
infections, meningitis,
beta-lactum. site, rash.
uncomplicated gonorrhea.
Surgical prophylaxis. -may cause hemolytic Other: hypersensitivity
anemia, which can be reactions, serum
fatal. If anemia sickness, anaphylaxis.
develops during
therapy, stop drug until
cause is determined.
DRUG CLASSIFICATION/INDICATI MECHANIS CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON M OF N REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITI
ACTION FREQUENC ES
Y
Diamicron Non-insulin dependent Lowers blood Hypersensitivity Headache, intense Oral ½ tablet
diabetes (type 2), in glucose by hunger, nausea, for single Explain to
; cross sensitivity
association with dietary stimulating the vomiting, lassitude, dose
with other patient that this
measures and exercise, release of reduced awareness & 60-120 mg
when these measures insulin from sulfonylureas may slowed reactions, medication does
alone are not sufficient. the pancreas occur; depression, confusion, not cure diabetes
and increasing Unstable visual & speech and must be used
sensitivity to disorders, , dizziness,
diabetes, type 1 in conjunction
insulin at feeling of
receptor sites. diabetes mellitus, powerlessness, loss of with a prescribed
diabetic self-control, delirium, diet, exercise
ketoacidosis, convulsions, shallow regimen, to
respiration, bradycardia, prevent
diabetic coma or pre- drowsiness & loss of
coma; consciousness, possibly hypoglycemic
Severe hepatic resulting in coma & and
or renal impairment; lethal outcome; hyperglycemic
sweating, clammy skin, events.
Concurrent use
anxiety, tachycardia,
of oral/oromucosal Instruct
HTN, palpitations,
miconazole, alcohol angina pectoris & patient on proper
or alcohol- cardiac arrhythmia. GI technique for
containing disorders eg, abdominal home glucose
pain, nausea, vomiting,
medications, or monitoring.
indigestion, diarrhea &
systemic constipation (reduced Monitor closely
phenylbutazone; when taken w/ meal). during periods of
Skin reactions eg, rash
OB: Should not stress or illness
which may progress to
be used during widespread skin and health care
pregnancy, insulin is blistering or peeling, professional
preferred; redness, itching, hives, notified if
Lactation: Sho angioedema. Visual significant
disturbances
uld not be used changes occur.
during lactation, Review
insulin is perferred. signs of
hypoglycemia
and
hyperglycemia
with patient. If
hypoglycemia
occurs, advise
patient to drink a
glass of orange
juice or ingest 2–
3 tsp of sugar,
honey, or corn
syrup dissolved
in water or an
appropriate
number of
glucose tablets
and notify health
care
professional.
Encourage
patient to follow
prescribed diet,
medication, and
exercise regimen
to prevent
hypoglycemic or
hyperglycemic
episodes.
Concurrent
use of alcohol
may cause a
disulfiram-like
reaction
(abdominal
cramps, nausea,
flushing,
headaches, and
hypoglycemia).
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- UwordDocument43 pagesUwordkarl abiaad100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATENicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Fdar-Labor PainDocument5 pagesFdar-Labor PainNicole cuencos100% (1)
- Depression Case StudyDocument1 pageDepression Case StudyNicole cuencos100% (1)
- APPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Document3 pagesAPPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain Case StudyDocument7 pagesLabor Pain Case StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Case Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Document7 pagesCase Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Weigght Gain NCPDocument1 pageWeigght Gain NCPNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDocument3 pagesCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Spinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesSpinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityNicole cuencos50% (2)
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESDocument5 pagesDrug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Duavent Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Computation FormulasDocument1 pageComputation FormulasNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Document1 pageSignificance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- MEASLES PresentationDocument32 pagesMEASLES PresentationMobin Ur Rehman Khan0% (1)
- Opening: (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI) (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI)Document4 pagesOpening: (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI) (EN-ES-EI-AI-DI)Trisna meyanaNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Cardio SLE Mcqs With AnswersDocument37 pagesCardio SLE Mcqs With AnswersAsif Newaz100% (4)
- AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesAmoxicillinClarisse30No ratings yet
- Liver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument2 pagesLiver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsAdi Kurnia100% (1)
- Tuberculosis: Mariana Ngundju AwangDocument23 pagesTuberculosis: Mariana Ngundju AwangansyNo ratings yet
- Albendazol Tablet 400 MG Acyclovir Tablet 400 MGDocument4 pagesAlbendazol Tablet 400 MG Acyclovir Tablet 400 MGSharfina AbsharinaNo ratings yet
- H-Mole Pathophysiology in Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageH-Mole Pathophysiology in Schematic DiagramFaith Lumayog100% (2)
- Otitis Media: While The OMEDocument2 pagesOtitis Media: While The OMEKim EurelleNo ratings yet
- تجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Document6 pagesتجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Mohammed ShaddadNo ratings yet
- Antihelmintics DrugsDocument14 pagesAntihelmintics DrugsSalman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Riaphyllin Syrup Patient Information LeafletDocument1 pageRiaphyllin Syrup Patient Information Leafletpharmacia1.comNo ratings yet
- IST's - HPVDocument17 pagesIST's - HPVCaio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Related Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesDocument13 pagesRelated Teenshealth Links: Health Problems SeriesMario BadayosNo ratings yet
- Naturopathy Treatments For 357 Diseases PDFDocument23 pagesNaturopathy Treatments For 357 Diseases PDFshilpi agarwalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Final 1Document47 pagesDrug Study Final 1Nik2No ratings yet
- Annual DOLE Report FormDocument7 pagesAnnual DOLE Report FormpnvtgaNo ratings yet
- Antiulcer DrugsDocument16 pagesAntiulcer DrugsJenNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument5 pagesPriceMubarak MHNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha DhakalDocument22 pagesFebrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha Dhakalsagar poudelNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Intussusception: Management OptionsDocument2 pagesRecurrent Intussusception: Management OptionsMuhammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- SMLE 2018 احدث اسئلة امتحان لأختبار الهيئه السعوديDocument441 pagesSMLE 2018 احدث اسئلة امتحان لأختبار الهيئه السعوديOman Edu100% (6)
- Case Presentation On Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument50 pagesCase Presentation On Diabetic KetoacidosisJoana Marie Gantuangco-MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Penguins Medicine August-SeptumberDocument215 pagesPenguins Medicine August-SeptumberKhattabNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Dengan Sikap Ibu Hamil Dalam Mengonsumsi Asam FolatDocument7 pagesPengetahuan Dengan Sikap Ibu Hamil Dalam Mengonsumsi Asam FolatMivtaNo ratings yet
- A Complete To HomeopathYDocument5 pagesA Complete To HomeopathYmukesh_singh_16No ratings yet
- Neuro Pharma PDFDocument258 pagesNeuro Pharma PDFNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- All About Vancomycin by SDocument2 pagesAll About Vancomycin by SSharan SahotaNo ratings yet