Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anesthetic Complications
Anesthetic Complications
Uploaded by
Isabel CastilloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anesthetic Complications
Anesthetic Complications
Uploaded by
Isabel CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
ANESTHESIOLOGY
ANESTHETIC COMPLICATIONS EXIMIUS
AA Dr. Romina Alexis Pinson-Sulit June ata 2020 2021
Anesthetic Complications It is often impossible to assign the responsibility for a poor outcome
Frequently asked questions: to the patient’s inherent disease, the surgical procedure, or the
Will I lose my memory after general anesthesia? anesthetic management.
Is there a chance I won’t wake up after general anesthesia?
Will I be paralyzed after spinal anesthesia?
Will I DIE?
E.g. Michael Jackson
Propofol Addiction (fast administration of propofol
may lead to apnea) Cardiac arrest
E.g. Business woman year 2017
Prolonged plastic surgery (7pm to 3 am) under general
anesthesia @ 2am hemodynamics crashed not
managed cardiac arrest
Complications related to the delivery of anesthesia care are
inevitable.
Anesthetic mishaps can be categorized as preventable or
unpreventable. General Anesthesia
When complications do occur, appropriate evaluation, Most common complications
management, and documentation are critical in minimizing or Difficult airway
eliminating negative outcomes.
Airway injury – during intubation/ laryngoscopy
Hypoxia/hypoxemia
o During anesthetic induction and you don’t give enough
oxygen initially to the patient prior administration of
propofol/ muscle relaxant patient can go to hypoxia (99
60%) desaturation and blood will not have oxygen
hypoxemia
Corneal abrasion: Most common complication of G.A.
o Because GA gases have inherent properties to dry the
eyes that’s why we tape the eyes before administration.
Intraoperative awareness
o Evidence of awareness under GA was found to be
0.2-0.4%
o 20% were for awake paralysis
o Recall- more likely in women and when anesthesia relying
on opioids and muscle relaxants without volatile
anesthetic was used.
o Seen during Cardiac operations e.g. CABG
o Bitetral index monitor: Monitors if patient is awake
Score of 40- sleeping
Score of 60- patulog palang
Score of 80- fully awake
Ranked low in the law suit due to complications, why?
In the past 30 years, the mortality rate attributable
primarily to anesthesia appears to have dropped.
Increased monitoring and awareness of anesthesiologist.
From 1-2: 3,000 anesthetic experiences to a current
rate of 1-2: 20,000 experiences.
This decline may be due to:
1. New monitoring equipment
New machines, better gases
Video laryngoscope: gives high success for intubation
Ultrasound
2. Knowledge of anesthetic physiology and pharmacology
3. Improved surgical and medical care
TRANSCRIBERS Group 3 EDITOR besm
1of 2
EXIMIUS
ANESTHETIC COMPLICATIONS 2021
0000
Spinal Anesthesia
Other preventable complications:
Allergic reactions: preservatives (PABA)
Local anesthetics
Neuromuscular blockers
NSAIDS
Propofol
Peripheral Nerve injury: put pads under bony prominences
Due to patient positioning
o Most common PNI: common peroneal
nerve: lithotomy position.
Sudden Cardiac arrest Regional technique
During an otherwise routine administration of spinal anesthetic Hemodynamic instability
is an uncommon but catastrophic complication o Give fluid and pressors so when blood vessels dilate
Sympathetic blockade (dilate vessels) increased vagal tone there will still be a source for cardiac output.
decreased cardiac output bradycardia hypotension then
cardiac arrest
Management
LAST: Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity
- MC complication of Spinal Anesthesia
- Bupivacane
TRANSCRIBERS Group 3 EDITOR : besm 2of2
You might also like
- SGD Cases: MYASTHENIC CRISIS (+ Tensilon Test)Document1 pageSGD Cases: MYASTHENIC CRISIS (+ Tensilon Test)Kim Ramos100% (1)
- AHA-PALS 2010: Pediatric Chain of SurvivalDocument10 pagesAHA-PALS 2010: Pediatric Chain of SurvivalIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- ToxicologyDocument8 pagesToxicologysarguss14100% (3)
- Anesthesia in Ophthal Mic SurgeryDocument98 pagesAnesthesia in Ophthal Mic SurgeryT Z BenNo ratings yet
- Depth of Anaesthesia Monitoring: What's Available, What's Validated and What's Next?Document10 pagesDepth of Anaesthesia Monitoring: What's Available, What's Validated and What's Next?drardigustian2986No ratings yet
- Uncommon Complications of Spinal Anaesthesia - AnesthesiaworldDocument14 pagesUncommon Complications of Spinal Anaesthesia - AnesthesiaworldAida TantriNo ratings yet
- General Anaesthesia: Welcome ToDocument21 pagesGeneral Anaesthesia: Welcome Toفرسان الدعوةNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia in Surgical PTS 1Document41 pagesAnesthesia in Surgical PTS 1Minale MenberuNo ratings yet
- Anestesia Ocular 2018 PDFDocument4 pagesAnestesia Ocular 2018 PDFChristian Andres Cruz PerezNo ratings yet
- 6 Regional AnaesthesiaDocument12 pages6 Regional AnaesthesiasaniaaNo ratings yet
- Epidural ManagementDocument8 pagesEpidural ManagementSteve McLarenNo ratings yet
- Temporary Blindness After Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument2 pagesTemporary Blindness After Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockIbramanto WarganegaraNo ratings yet
- Sleep EndosDocument7 pagesSleep EndosNicolás HenaoNo ratings yet
- 2.3 General AnesthesiaDocument8 pages2.3 General AnesthesiaLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- 02-AirwayManage 2021Document26 pages02-AirwayManage 2021Kajanthan SatkunarajahNo ratings yet
- Regional Anaesthesia: (Spinal or Epidural) For Caesarean SectionDocument2 pagesRegional Anaesthesia: (Spinal or Epidural) For Caesarean Sectionida wahyuni mapsanNo ratings yet
- General Anesthesi A: Nicyela Jillien Harlendea (406182061) Pembimbing: Dr. Budi Wahono, Sp. AnDocument31 pagesGeneral Anesthesi A: Nicyela Jillien Harlendea (406182061) Pembimbing: Dr. Budi Wahono, Sp. AnNicyela JillienNo ratings yet
- Nervio AlveolarDocument3 pagesNervio AlveolarLuis GustavoNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia PlainDocument39 pagesAnesthesia PlainMIKAELA DAVIDNo ratings yet
- AnaesthesiaDocument3 pagesAnaesthesiaJoan nakijjobaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative MGMT of Osa and OhsDocument10 pagesPerioperative MGMT of Osa and OhsdullzineaaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Low Dose Hyperbaric Bupivacine With Fentanyl and Hyperbaric Bupivacaine in Spinal Anaesthesia For Below Umbilical SurgeriesDocument1 pageA Comparative Study of Low Dose Hyperbaric Bupivacine With Fentanyl and Hyperbaric Bupivacaine in Spinal Anaesthesia For Below Umbilical SurgeriesTahirNo ratings yet
- Heavy Bupivacaine 0.5% or Plain Bupivacaine 0.5% Is TheDocument4 pagesHeavy Bupivacaine 0.5% or Plain Bupivacaine 0.5% Is TheRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada Fraktur MandibulaDocument11 pagesAnestesi Pada Fraktur MandibulaCredo AriefNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument54 pagesAnesthesiaNURDINI BINTI ZAMRI MoeNo ratings yet
- RaVoR™ - Bipolar Radiofrequency Volume Reduction (RaVoR™) of The Inferior Turbinates - M. SarteDocument2 pagesRaVoR™ - Bipolar Radiofrequency Volume Reduction (RaVoR™) of The Inferior Turbinates - M. Sartediana mistraNo ratings yet
- Paper 65Document1 pagePaper 65abdul hamidNo ratings yet
- 2 LaDocument233 pages2 LaSudeep DkNo ratings yet
- Non-Operating Room Anesthesia: April 2017Document26 pagesNon-Operating Room Anesthesia: April 2017Eolia EffendiNo ratings yet
- Fisiologia de Los Opioides Epidurales e IntratectalesDocument13 pagesFisiologia de Los Opioides Epidurales e Intratectalessanjuandediosanestesia100% (5)
- Tehnici de AnestezieDocument18 pagesTehnici de AnestezieMacsuta VladNo ratings yet
- Tugas Jurnal The Principles of Anesthesia - Nurul Rahmadiani Ukfah-70700119022Document5 pagesTugas Jurnal The Principles of Anesthesia - Nurul Rahmadiani Ukfah-70700119022Nurul Rahmadiani UkfahNo ratings yet
- E044168 FullDocument7 pagesE044168 FulldrmelinjoeNo ratings yet
- Neuroanesthesia and Outcomes: Evidence, Opinions, and Speculations On Clinically Relevant TopicsDocument7 pagesNeuroanesthesia and Outcomes: Evidence, Opinions, and Speculations On Clinically Relevant TopicsenriquegarciagalianaNo ratings yet
- 201426112556-Ultrasom Musculoesq.Document5 pages201426112556-Ultrasom Musculoesq.Antero Marques CardosoNo ratings yet
- 4 Pharma General AnestheticsDocument10 pages4 Pharma General AnestheticsisahNo ratings yet
- Premedication and Other Prophylactic MeasuresDocument39 pagesPremedication and Other Prophylactic Measuresanugerah_buang3842No ratings yet
- Drug Study On AnestheticsDocument9 pagesDrug Study On AnestheticsKalvinArtRazalanCelebradosNo ratings yet
- Ankle Nerve Block 2Document7 pagesAnkle Nerve Block 2JAVIERBURGOS1No ratings yet
- Right Open Nephrectomy Under Combined Spinal and Peridural Operative Anesthesia and Analgesia (CSE) : A New Anesthetic Approach in Abdominal SurgeryDocument2 pagesRight Open Nephrectomy Under Combined Spinal and Peridural Operative Anesthesia and Analgesia (CSE) : A New Anesthetic Approach in Abdominal SurgeryPablo Segales BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Regional AnesthesiaDocument6 pages2.4 Regional AnesthesiaLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- (JM) Myofascial Pain Syndrome of The Occipitofrontalis Muscle and Its Ophthalmological ImplicationsDocument3 pages(JM) Myofascial Pain Syndrome of The Occipitofrontalis Muscle and Its Ophthalmological Implicationschiendy.yNo ratings yet
- Art Profe Julian 1Document9 pagesArt Profe Julian 1Julian LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Influenza Della Condotta Anestesiologica Sullo Stato Mentale Di Soggetti AnzianiDocument7 pagesInfluenza Della Condotta Anestesiologica Sullo Stato Mentale Di Soggetti AnzianiMatteo BrambatiNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Exam TipsDocument9 pagesLocal Anesthesia Exam TipsshadapaaakNo ratings yet
- E59 s53 Anesthetic Management of A Patient With Sleep Paralysis FileDocument3 pagesE59 s53 Anesthetic Management of A Patient With Sleep Paralysis FileMacaela HardingNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Sedation and Analgesia in The Interventional Radiology DepartmentDocument10 pagesSedation and Analgesia in The Interventional Radiology DepartmentAhmed ElshewiNo ratings yet
- Anes - Intraoperative ManagementDocument10 pagesAnes - Intraoperative ManagementSGD5Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Croup Summary PDFDocument2 pagesCroup Summary PDFnurfitriaNo ratings yet
- Onset Positions in Induction of Anesthesia Spinal Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Respiratory Complications Respiratory ObstructionDocument7 pagesOnset Positions in Induction of Anesthesia Spinal Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Respiratory Complications Respiratory ObstructionArvin Ian Penaflor50% (2)
- TX Farmacologico NvpoDocument14 pagesTX Farmacologico NvpoKrish RendonNo ratings yet
- (OB) 2B - Obstetrical Anesthesia (By Dr. Bretta Lucion)Document3 pages(OB) 2B - Obstetrical Anesthesia (By Dr. Bretta Lucion)CleoGomezNo ratings yet
- The Anaesthesiologist and The Surgical ICU Patient: EditorialDocument2 pagesThe Anaesthesiologist and The Surgical ICU Patient: EditorialFIA SlotNo ratings yet
- Case Report Renal Cystectomy With TMJ AnkylosisDocument1 pageCase Report Renal Cystectomy With TMJ AnkylosisLollapallooza 23No ratings yet
- 2018-Fusco-Could The Combination of PENG Block and LIA Be A Useful Analgesic Strategy in The Treatment of Postoperative Pain For Hip ReplacementDocument1 page2018-Fusco-Could The Combination of PENG Block and LIA Be A Useful Analgesic Strategy in The Treatment of Postoperative Pain For Hip ReplacementDr LAUMONERIENo ratings yet
- 3 Ncp'sDocument3 pages3 Ncp'sJohn Michael EstevesNo ratings yet
- AAOS Paperchapter With Jupiter and AmadioDocument11 pagesAAOS Paperchapter With Jupiter and AmadioreyNo ratings yet
- Modern Anaesthesia:: A Concise Guide to the Study and Practice of Anaesthesia.From EverandModern Anaesthesia:: A Concise Guide to the Study and Practice of Anaesthesia.No ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurogenic Oropharyngeal DysphagiaFrom EverandDiagnosis and Treatment of Neurogenic Oropharyngeal DysphagiaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - CNSDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - CNSIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ok Ok Notes PediaDocument10 pagesOk Ok Notes PediaIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableDocument4 pagesSURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument6 pagesDermatology - Exanthematous Viral DiseasesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Implantataion Placental Development and AbnormalitiesDocument62 pagesImplantataion Placental Development and AbnormalitiesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - Skin NeoplasmsDocument12 pagesDermatology - Skin NeoplasmsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankDocument4 pagesAcute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY - Cuteneous Candidiasis, PityrosporumDocument4 pagesDERMATOLOGY - Cuteneous Candidiasis, PityrosporumIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument60 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOGENESIS and Fetal DevtDocument50 pagesEMBRYOGENESIS and Fetal DevtIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Medicine: Early AdolescenceDocument2 pagesAdolescent Medicine: Early AdolescenceIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDiseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Document13 pagesPediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Isabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pedia Pre School NewsDocument3 pagesPedia Pre School NewsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: TranscribersDocument6 pagesPneumonia: TranscribersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseDocument4 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Disease of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesApproach To The Patient With Disease of The Respiratory SystemIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument3 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument4 pagesAsthmaIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Interatitial Lung DiseaseDocument2 pagesInteratitial Lung DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mesenteric Vascular Insufficiency: ClassificationDocument2 pagesMesenteric Vascular Insufficiency: ClassificationIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pack-Years of Cigarette Smoking Is The Most HighlyDocument5 pagesPack-Years of Cigarette Smoking Is The Most HighlyIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesAcute and Chronic PancreatitisIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
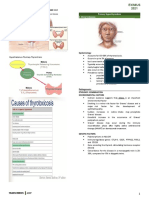
- Causes of HypothyroidismDocument6 pagesCauses of HypothyroidismIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism: EpidemiologyDocument8 pagesHyperthyroidism: EpidemiologyIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anorectal Disease and Common Anorectal DisordersDocument2 pagesAnorectal Disease and Common Anorectal DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Esophagus.Document3 pagesDiseases of Esophagus.Isabel Castillo100% (2)
- Rehabilitation After Total LaryngectomyDocument7 pagesRehabilitation After Total LaryngectomyAnois Llivar100% (1)
- The Future Doctors Academy Orthopedic CourseDocument77 pagesThe Future Doctors Academy Orthopedic CourseAnton ScheepersNo ratings yet
- Intimacy and Sexuality After Treatment For Gynecologic CancerDocument37 pagesIntimacy and Sexuality After Treatment For Gynecologic CancerCarleone PrimaNo ratings yet
- Principles For Vertical Ridge Augmentation in The Atrophic Posterior Mandible - A Technical Review - Urban2017Document8 pagesPrinciples For Vertical Ridge Augmentation in The Atrophic Posterior Mandible - A Technical Review - Urban2017Claudio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Sign of Canal ParesisDocument3 pagesA Clinical Sign of Canal ParesisMadelinePérezNo ratings yet
- Repair of Umbilical and Epigastric Hernias 2013 PDFDocument33 pagesRepair of Umbilical and Epigastric Hernias 2013 PDFalemago90No ratings yet
- SciTech Writing II Basic StructureDocument4 pagesSciTech Writing II Basic Structureangelie.babasNo ratings yet
- January 2018 1516198794 146 PDFDocument1 pageJanuary 2018 1516198794 146 PDFGaby ZapataNo ratings yet
- Spinal Stenosis 3Document8 pagesSpinal Stenosis 3hunter_axl01No ratings yet
- 6 Cutaneous Amalgam Tattoo in A Dental ProfessionalDocument2 pages6 Cutaneous Amalgam Tattoo in A Dental ProfessionalleilyanisariNo ratings yet
- Effect of Visceral Adipose Tissue On The AccuracyDocument8 pagesEffect of Visceral Adipose Tissue On The AccuracyMaria GoretiNo ratings yet
- New Case StudyDocument26 pagesNew Case Studyfaisal saifNo ratings yet
- Medical Tourism in India Strengths and WeaknessesDocument4 pagesMedical Tourism in India Strengths and Weaknessesjimmy3229No ratings yet
- 5.4 Treatment of Early (Stage I and II) Head and Neck Cancer - The Larynx - UpToDateDocument33 pages5.4 Treatment of Early (Stage I and II) Head and Neck Cancer - The Larynx - UpToDateMarco GornattiNo ratings yet
- Adverse Event Report Form 2 PDFDocument4 pagesAdverse Event Report Form 2 PDFtosadeliNo ratings yet
- Urine-Catherther-Insertion-And-Removal DocsDocument6 pagesUrine-Catherther-Insertion-And-Removal DocssrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Discomfort and Pain Pada Laser HemorrhoidoplastyDocument7 pagesPostoperative Discomfort and Pain Pada Laser HemorrhoidoplastyRatu AstridNo ratings yet
- Lower-Limb Orthotics: Melvin Stills, C - ODocument10 pagesLower-Limb Orthotics: Melvin Stills, C - OCalugareanu MadalinaNo ratings yet
- AppoloDocument2 pagesAppoloRishabh Madhu SharanNo ratings yet
- Brochure Iolmaster 700 ModfDocument11 pagesBrochure Iolmaster 700 ModfTT XNo ratings yet
- Tympanoplasty - Surgical Repair of The Perforated EardrumDocument1 pageTympanoplasty - Surgical Repair of The Perforated EardrumMelly Selvia ANo ratings yet
- Nurse Duties and Medical Equipment in OperatingDocument10 pagesNurse Duties and Medical Equipment in OperatingFita DinarNo ratings yet
- Principles, Concepts, and Practices in Prosthodontics-1989Document22 pagesPrinciples, Concepts, and Practices in Prosthodontics-1989ayush srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Paul Barash EtDocument994 pagesPaul Barash EtJaylive Anzia100% (4)
- Mcgraw-Hill Companies, IncDocument2 pagesMcgraw-Hill Companies, IncLu LubNaNo ratings yet
- MastectomyDocument6 pagesMastectomyJustinAlmedaNo ratings yet
- SOAL OSTEOSYNTHESIS-halaman-1-7,11-18-dikonversiDocument16 pagesSOAL OSTEOSYNTHESIS-halaman-1-7,11-18-dikonversiFajriRoziKamarisNo ratings yet
- Lunotriquetral CoalitionDocument3 pagesLunotriquetral Coalitionsuribabu963No ratings yet
- I HFGDocument31 pagesI HFGmarcelo.lacknerNo ratings yet
- Case Study 39-Year-Old Women Diagnosed As Solitary Rectal Ulcer SyndromeDocument5 pagesCase Study 39-Year-Old Women Diagnosed As Solitary Rectal Ulcer SyndromeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet