Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04
Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04
Uploaded by
Gurnaj Singh MannOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04
Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04
Uploaded by
Gurnaj Singh MannCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Ch—04 Moving Charges and Magnetism
Daily Practice Problem 04
Q1. A charged particle of mass 5 mg and Q5. A particle with charge -5.60 nC is
charge q = +2 𝜇𝜇 C has velocity 𝑣𝑣⃗ = moving in a uniform magnetic field 𝐵𝐵 �⃗ =
2𝚤𝚤̂ — 3 𝚥𝚥̂ + 4𝑘𝑘�. Find out the magnetic force − (1.25 𝑇𝑇)𝑘𝑘�. The magnetic force on the
on the charged particle and its acceleration particle is measured to be 𝐹𝐹⃗ = −(3.36 ×
�⃗ = 3𝚥𝚥̂ −
at this instant due to magnetic field 𝐵𝐵 10−7 𝑁𝑁)𝚤𝚤̂ + (7.42 × 10−7 𝑁𝑁)𝚥𝚥̂.
2𝑘𝑘� . 𝑣𝑣⃗ and 𝐵𝐵
�⃗ are in m s-1 and Wb m-2,
a. Calculate all components of velocity of
respectively.
the particle from this information.
b. Calculate the scalar product 𝑣𝑣⃗ . 𝐹𝐹⃗ . What is
the angle between v and F?
Q2. A charged particle has acceleration 𝑎𝑎⃗ =
�⃗ = −3𝚤𝚤̂ + 2𝚥𝚥̂ −
2𝚤𝚤̂ + 𝑥𝑥𝚥𝚥̂ in a magnetic field 𝐵𝐵
4𝑘𝑘�, Find the values of x.
Q6. An electron is moving at 106 ms-1 in a
direction parallel to a current of 5 A, flowing
through an infinitely long straight wire,
separated by a perpendicular distance of 10
Q3. When a proton has a velocity 𝑣𝑣⃗ = cm in air. Calculate the magnitude of the
(2𝚤𝚤̂ + 3𝚥𝚥̂) × 106 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1 , it experiences a force experienced by the electron.
force 𝐹𝐹⃗ = −(1.28 × 10−13 𝑘𝑘) N. When its
velocity is along the z-axis, it experiences a
force along the x-axis. What is the magnetic
field?
Q7. A positive charge of 1.5 𝜇𝜇C is moving
with a speed of 2 x 106ms-1 along the positive
�⃗ = (0.2 𝚥𝚥̂ + 0.4 𝑘𝑘� )
X-axis. A magnetic field, 𝐵𝐵
tesla acts in space. Find the magnetic force
Q4. A charge 𝑞𝑞 = −4 𝜇𝜇𝜇𝜇 has an acting on the charge.
instantaneous velocity 𝑣𝑣⃗ = (2𝚤𝚤̂ − 3 𝚥𝚥̂ +
� 6
𝑘𝑘 ) 𝑥𝑥 10 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1
in a uniform magnetic field
𝐵𝐵 = �2𝚤𝚤̂ + 5𝚥𝚥̂ − 3𝑘𝑘� � × 10−2 𝑇𝑇. What is the
�⃗
force on the charge?
Moving Charges and Magnetism 2
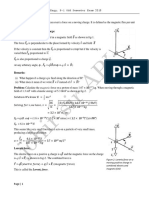
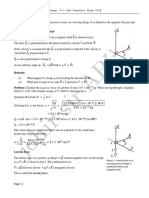
Q8. A long straight wire AB carries a current path. The magnitude of the total work done
of 4 𝐴𝐴. A proton P travels is
at 4 x 106 m /s, parallel to
a. (0.35) q b. (0.15) q
the wire, 0.2 m from it and
in a direction opposite to
c. (2.5) q d. 5 q
the current as shown in
Fig. Calculate the force
which the magnetic field
of current exerts on the proton. Also specify
the direction of the force.
Q11. An ionized gas contains both positive
and negative ions. If it is subjected
simultaneously to an electric field along the
+x-direction and a magnetic field along the
Q9. An electron is moving through a uniform +z-direction, then
magnetic field given by 𝐵𝐵 �⃗ = 𝐵𝐵𝑥𝑥 𝚤𝚤̂ + (3.0𝐵𝐵𝑥𝑥 )𝚥𝚥̂
a. positive ions deflect towards +y-direction
At a particular instant, the electron has and negative ions towards -y-direction
velocity 𝑣𝑣⃗ = (2.0𝚤𝚤̂ + 4.0𝚥𝚥̂) m/s and the
magnetic force acting on it is b. all ions deflect towards +y-direction
(6.4 𝑥𝑥 10−19 𝑁𝑁)𝑘𝑘� . 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 𝐵𝐵𝑥𝑥 c. all ions deflect towards -y-direction
d. positive ions deflect towards -y-direction
and negative ions towards -y-direction
Q10. A particle of mass 𝑚𝑚 and charge 𝑞𝑞 is in
an electric and magnetic field is given by
𝐸𝐸�⃗ = 2𝚤𝚤̂ + 3𝚥𝚥̂ , 𝐵𝐵 = 4𝚥𝚥̂ + 6𝑘𝑘�
The charged particle is shifted from the origin
to the point 𝑃𝑃(𝑥𝑥 = 1, 𝑦𝑦 = 1) along a straight
Moving Charges and Magnetism 3
ANSWERS
1. 2 × 10−6 �−6𝚤𝚤̂ + 4𝚥𝚥̂ + 6𝑘𝑘� �𝑁𝑁; 6. 1.6 × 10−18 𝑁𝑁
0.8�−3𝚤𝚤̂ + 2𝚥𝚥̂ + 3𝑘𝑘� �𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −2
7. �0.6𝑘𝑘� − 1.2𝚥𝚥̂�𝑁𝑁
2. 3
8. 2.56 × 10−18 𝑁𝑁
3. −(0.4𝚥𝚥̂)𝑇𝑇
9. -2.0 T
4. −16�𝚤𝚤̂ + 2𝚥𝚥̂ + 4𝑘𝑘�� × 10−2 𝑁𝑁
10. d
5. a. 𝑣𝑣𝑥𝑥 = −106 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1 ; 𝑣𝑣𝑦𝑦 = −48 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1 11. c
b. 𝑣𝑣⃗ . 𝐹𝐹⃗ = 0; 90°
You might also like
- Grade Xii Book IIDocument137 pagesGrade Xii Book IIEdwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Magnetic Field FULL 2Document27 pagesChapter 20 Magnetic Field FULL 2froyo1119No ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces and Fields: (Chapter 12)Document48 pagesMagnetic Forces and Fields: (Chapter 12)Allan Gabriel LariosaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4Document34 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4Infamous LegendsNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance DPP-04 Lec-7 @physicswallahlakshyavideos PhysicswallahlakshyavideosDocument3 pagesElectrostatic Potential & Capacitance DPP-04 Lec-7 @physicswallahlakshyavideos Physicswallahlakshyavideosasiffatmi123No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field - Force - Moving Charge in Magnetic Field, Helical PathDocument4 pagesMagnetic Field - Force - Moving Charge in Magnetic Field, Helical PathManas DasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldsDocument48 pagesMagnetic Fieldsdayana hanis hassanNo ratings yet
- Atomic SanjuDocument42 pagesAtomic Sanjusaptarshi bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Due To Electric Current Important Points by A.M.KharcheDocument43 pagesDue To Electric Current Important Points by A.M.KharcheZainNo ratings yet
- AEMT Assignment1 2023Document2 pagesAEMT Assignment1 2023Sujay SNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument20 pagesMagnetismyd kmNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument15 pagesMagnetic FieldShiu Ping WongNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and Magnetism-Ii Puc PDFDocument23 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetism-Ii Puc PDFAnsha NasarNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Magnetic Fields and Lines - University Physics Volume 2 - OpenStaxDocument7 pages11.2 Magnetic Fields and Lines - University Physics Volume 2 - OpenStaxksmida2022No ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12 General Physics 2Document5 pagesScience, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12 General Physics 2riza amoresNo ratings yet
- AYJR 2024 (Advanced) - Paper 1 - Provisional Answer KeysDocument27 pagesAYJR 2024 (Advanced) - Paper 1 - Provisional Answer KeysSano ManjiroNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges & Fields DPP 7Document3 pagesElectric Charges & Fields DPP 7kijetNo ratings yet
- 6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsDocument5 pages6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsAyush GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ep23btech11028No ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument7 pagesMagnetism and MatterROHANNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Lecture NotesDocument50 pagesKinematics Lecture NotesThanh ChươngNo ratings yet
- Physics 222 - Test 1 - Spring 2010Document2 pagesPhysics 222 - Test 1 - Spring 2010eltytanNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XII Physics - Chap-4 (Moving Charges & Magnetism)Document23 pagesCBSE-XII Physics - Chap-4 (Moving Charges & Magnetism)amankumaryadav6205No ratings yet
- (Merge) HW5 Answer Copy - 20231019 - 193322Document12 pages(Merge) HW5 Answer Copy - 20231019 - 193322shakib33001No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument28 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current11thA -13-DarshilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MagnetismDocument1 pageAssignment 1 MagnetismShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument6 pagesMagnetismRM MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Motion of A Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Fields 2Document12 pagesMotion of A Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Fields 2Dinesh KatochNo ratings yet
- MFDECDocument21 pagesMFDECTanmay TingreNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Home WorkDocument2 pagesMagnetism Home Workkaushik247No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Steady Electric and Magnetic FieldsDocument32 pagesModule 2 - Steady Electric and Magnetic FieldsBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Attendance Quiz Format Sheet of Yellow Pad Sized PaperDocument45 pagesAttendance Quiz Format Sheet of Yellow Pad Sized PaperByron BanzonNo ratings yet
- Moving Charge MagnetismDocument23 pagesMoving Charge Magnetismtamana99bNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Magnetic Field (With Answers)Document40 pagesChapter 8 - Magnetic Field (With Answers)ngu lonNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and ForceDocument14 pagesMagnetic Field and ForceCamille SalasNo ratings yet
- Phy CHP 4 NotesDocument30 pagesPhy CHP 4 Notesayaan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems - Chap29Document8 pagesSolved Problems - Chap29dream100% (4)
- Magnetic Force On A Moving ChargeDocument6 pagesMagnetic Force On A Moving ChargeJohurul IslamNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 17 18 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4Document32 pagesCLS Aipmt 17 18 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 4nishat anjum57% (21)
- Basic Electrical by Jahir Sir 1Document7 pagesBasic Electrical by Jahir Sir 1Sakib ruNo ratings yet
- 4 MCDocument21 pages4 MCphysicskn92No ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetic Force On Charge or CurrentDocument5 pagesSubjective Questions: Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetic Force On Charge or CurrentrgNo ratings yet
- 4 Unit-2Document21 pages4 Unit-2hopefulantonelliNo ratings yet
- Physics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2012Document2 pagesPhysics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2012eltytanNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument54 pagesProblem SetXyNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesDaily Practice ProblemsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Document8 pagesProblem Set 6: Solutions: U A Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / Leclair Fall 2008Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six-Magnetic FieldDocument31 pagesChapter Six-Magnetic FieldktanvirkNo ratings yet
- 6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsDocument5 pages6 April Evening Shift - 2 PhysicsSHAKTI SWARUP SAHOONo ratings yet
- Muma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFDocument8 pagesMuma - Mulenga 1586370412 A PDFBethelNo ratings yet
- Electro Static Force TestDocument3 pagesElectro Static Force Testshyamsrikant2No ratings yet
- KD4010 - EM - Seminar - 5 - ProblemsDocument2 pagesKD4010 - EM - Seminar - 5 - Problemsmohamed redaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 8 NotesEdward William ElgarNo ratings yet
- 19 Moving Charges and Magnetism: SolutionsDocument32 pages19 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Solutionssunaarvind1922No ratings yet
- Chapter Four NOTES1 2021syllabusDocument33 pagesChapter Four NOTES1 2021syllabusGopika GNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Mysterious World of Fundamental Particles: Cosmic BeginningsFrom EverandThe Mysterious World of Fundamental Particles: Cosmic BeginningsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Ch-02 Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance: Lect-01Document20 pagesCh-02 Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance: Lect-01Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 04Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 02Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 02Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 02Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 02Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Chapter09 - Hydrocarbons PDFDocument51 pagesChapter09 - Hydrocarbons PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument32 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's School: STD - Vii EnglishDocument2 pagesSt. Xavier's School: STD - Vii EnglishGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument22 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument36 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument47 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Chapter04 - Nomenclature PDFDocument45 pagesChapter04 - Nomenclature PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Chapter03 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument73 pagesChapter03 - Chemical Bonding PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument38 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFGurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument29 pagesSeminarAkash shindeNo ratings yet
- Milling MachinesDocument39 pagesMilling MachinesSahil Sheth0% (1)
- P1NN Gallardo - Pinal - ErikaDocument17 pagesP1NN Gallardo - Pinal - ErikaOnda ElectromagnéticaNo ratings yet
- Nursing School Study Checklist PDFDocument8 pagesNursing School Study Checklist PDFDeannaNo ratings yet
- Proposal Lab 5Document4 pagesProposal Lab 5darkzainiNo ratings yet
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- Ingeteam Catalogo Cms Mayo2019 Eng MailDocument7 pagesIngeteam Catalogo Cms Mayo2019 Eng MailChrist Rodney MAKANANo ratings yet
- Tabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDocument49 pagesTabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDesenvolvimento MHNo ratings yet
- Product 043 UMDocument31 pagesProduct 043 UMPankaj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual TTI TCB-771 ENGDocument13 pagesService Manual TTI TCB-771 ENGAdam100% (1)
- Research Article: ISSN: 0975-833XDocument5 pagesResearch Article: ISSN: 0975-833XAdeep MathurNo ratings yet
- 320DLRR GMX ELE SchematicDocument14 pages320DLRR GMX ELE Schematicthaw3tar3minNo ratings yet
- NK 3 Final With DataDocument20 pagesNK 3 Final With DataАлексейNo ratings yet
- Direction: Show Your Clear and Complete Solution To The Following Reliability Tests by Completing The Attached Tables. I. Test Retest MethodDocument8 pagesDirection: Show Your Clear and Complete Solution To The Following Reliability Tests by Completing The Attached Tables. I. Test Retest MethodJan Aries ManiponNo ratings yet
- Resume - Soumya Prasad SenguptaDocument2 pagesResume - Soumya Prasad Senguptagcgary87No ratings yet
- 1385 PDFDocument70 pages1385 PDFEdmund ZinNo ratings yet
- Floating Boat Library-Mini Project-1Document37 pagesFloating Boat Library-Mini Project-1parmayadav56789No ratings yet
- En SATURNevo ZGS.10.20 User Manual 13Document1 pageEn SATURNevo ZGS.10.20 User Manual 13emadsafy20002239No ratings yet
- Mbm-Italien EnuDocument285 pagesMbm-Italien EnuRadwan AL TrougNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Resonator - Ceralock - 312547Document43 pagesCeramic Resonator - Ceralock - 312547wayan.wandira8122No ratings yet
- CA Level 1Document43 pagesCA Level 1Cikya ComelNo ratings yet
- Sensor Manual 1Document11 pagesSensor Manual 1Tame PcAddictNo ratings yet
- File DisksDocument22 pagesFile DisksAlana PetersonNo ratings yet
- ADT Service ManualDocument152 pagesADT Service ManualZakhele MpofuNo ratings yet
- C.S. Sharma and Kamlesh Purohit - Theory of Mechanisms and Machines-PHI Learning Private Limited (2006)Document723 pagesC.S. Sharma and Kamlesh Purohit - Theory of Mechanisms and Machines-PHI Learning Private Limited (2006)tp coephNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2020) - 3Document2 pagesPractice Test (2020) - 3Duy HảiNo ratings yet
- Indiana University PressDocument33 pagesIndiana University Pressrenato lopesNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Event Driven ProgrammingDocument22 pagesUnit 5 - Event Driven ProgrammingdharanyaNo ratings yet
- Gosat Gs 7055 Hdi FirmwareDocument3 pagesGosat Gs 7055 Hdi FirmwareAntoinetteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6گل میوہNo ratings yet