Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Saraba Sa3
Saraba Sa3
Uploaded by
Stanley ArabaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CNOR Cram Sheet (2024)Document9 pagesCNOR Cram Sheet (2024)Aaron LanniNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis NCPXhla Ng78% (18)
- Critical Care NotesDocument18 pagesCritical Care NotesjulieNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument11 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDemiar Madlansacay QuintoNo ratings yet
- Shock: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPDocument38 pagesShock: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPPatrick KosgeiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Mat 2 Case Pres PDFDocument14 pagesNCP For Mat 2 Case Pres PDFJuliane Ryne RosasNo ratings yet
- 4 - Hemorrhagic ShockDocument114 pages4 - Hemorrhagic ShockclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- FE Enrichment 2024Document4 pagesFE Enrichment 2024tarahggggNo ratings yet
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNo ratings yet
- HEMORRHOIDSDocument24 pagesHEMORRHOIDSNARUTONo ratings yet
- NCP - Delivery RoomDocument8 pagesNCP - Delivery RoomAUBREY MARIE . GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy-1Document67 pagesFluid Therapy-1Abdul MaalikNo ratings yet
- Null 7Document21 pagesNull 7Muneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy - : ALGORITHM 1. Assessment of Overall Fluid StatusDocument13 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy - : ALGORITHM 1. Assessment of Overall Fluid Statusfernin96No ratings yet
- Shock OverviewDocument6 pagesShock OverviewKrys Segarra GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Administration: B260 Foundations of NursingDocument59 pagesIntravenous Fluid Administration: B260 Foundations of NursingAli ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage 131223001506 Phpapp02Document24 pagesHemorrhage 131223001506 Phpapp02sekharurlaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric ShockDocument65 pagesObstetric Shockkqz39931No ratings yet
- Upper GI Bleed by Wajid MunirDocument49 pagesUpper GI Bleed by Wajid MunirAtifNo ratings yet
- Intake and Output HandoutDocument3 pagesIntake and Output HandoutLevi AckerManNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument26 pagesShockdaisy100% (1)
- Module 1 (Lesson 2)Document11 pagesModule 1 (Lesson 2)Jovencio Jr. Milo MilanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Fulfilling Fluid and Electrolyte NeedsDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts of Fulfilling Fluid and Electrolyte NeedsHarum BulanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- NCP-Drug-Study KDocument2 pagesNCP-Drug-Study KKyla Mae ZabalaNo ratings yet
- NCM109 Midterm All Notes 1 3Document36 pagesNCM109 Midterm All Notes 1 3Maria JuanilloNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapies in Critical CareDocument46 pagesRenal Replacement Therapies in Critical CareLe ThyNo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony: Group 3Document23 pagesUterine Atony: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemia and Hemorrhage: Clinical Manifestations of HypovolemiaDocument6 pagesHypovolemia and Hemorrhage: Clinical Manifestations of HypovolemiajbNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Final NCP1 2Document2 pagesFinal NCP1 2hahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Analisa Cairan Tubuh SinghDocument60 pagesAnalisa Cairan Tubuh SinghPrabJot SinGhNo ratings yet
- Blood Transuation AssignmentDocument6 pagesBlood Transuation AssignmentvimajavNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesNcp-Liver CirrhosisNorbelisa Tabo-ac CadungganNo ratings yet
- Course - Subject-Unit / Topic - Title - Prepared byDocument39 pagesCourse - Subject-Unit / Topic - Title - Prepared byEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Review On Peripheral IV FluidsDocument37 pagesReview On Peripheral IV FluidsWoot RootNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Fluids and Electrolytes Acid Base Balance and Renal DisordersDocument72 pagesLECTURE Fluids and Electrolytes Acid Base Balance and Renal DisordersAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingNo ratings yet
- Haemorrhagic Shock: Kareena (Grp:45)Document33 pagesHaemorrhagic Shock: Kareena (Grp:45)ShivamNo ratings yet
- SHOCK HandoutsDocument4 pagesSHOCK Handoutslucero.ja39No ratings yet
- NCP DennielleDocument3 pagesNCP DennielleSkynet DivineNo ratings yet
- HemorrhageDocument24 pagesHemorrhageRiry AmbarsaryNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid Compartments 0Document15 pagesBody Fluid Compartments 0Abdo MohdyNo ratings yet
- NCP CP2Document4 pagesNCP CP2Abbeygale GalanNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument36 pagesHypovolemic ShockRia CintyaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever - Ang Ban HongDocument46 pagesDengue Fever - Ang Ban HongSharimanfadhly YahayaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 AlllllDocument285 pagesLec 11 Alllllaryam0012122No ratings yet
- CPG DengueDocument35 pagesCPG DengueSharimanfadhly YahayaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Dan Prinsip Resusitasi Cairan Pada SyokDocument28 pagesKonsep Dasar Dan Prinsip Resusitasi Cairan Pada SyokraraNo ratings yet
- From SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Document1 pageFrom SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Andrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument23 pagesShocknistobdhoraat3No ratings yet
- 5 IV Therapy TransesDocument9 pages5 IV Therapy TransesKeana Dacayana100% (1)
- HTNDocument46 pagesHTNAbdulqader Al-MasoumiNo ratings yet
- New PDF SeminarDocument44 pagesNew PDF SeminarElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNo ratings yet
Saraba Sa3
Saraba Sa3
Uploaded by
Stanley ArabaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Saraba Sa3
Saraba Sa3
Uploaded by
Stanley ArabaCopyright:
Available Formats
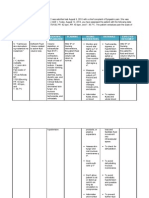
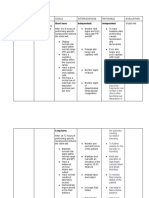
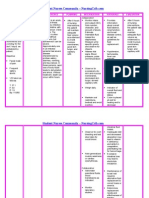
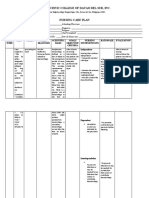
The “shocking” tale of the life-threatening condition!
MANAGEMENT
ASSESSMENT • Assess respiratory rate and
rhythm
The symptoms a patient
ETIOLOGY experiences depends on the
• Monitor the patients urine
output. It is a sign of
Hypovolemic shock is the severity of fluid or blood loss.
inadequate renal perfusion
result of significant blood or • Class I: 15% fluid vol. loss
• Slight anxiety • Administer IV fluids as
fluid loss from
• Class II: 15-30% fluid vol. ordered. Crystalloid solutions
• Blunt trauma
• Increased HR, RR should be used for electrolyte
• Large lesions
• Flat jugular veins balance. It is the first-line
• Severe vomiting • Pale & cool skin choice for fluid resuscitation
• Ruptured spleen • Class III: 30-40% fluid vol. • Apply pressure to the bleeding
Because of this, not enough • Decreased BP
site
oxygen can get to your • Confusion
• Oliguria • Administer blood products as
organs and tissues.
• Class IV: 40%+ fluid vol. ordered
• Cyanotic • Assess the patient’s anxiety
• No urine output level
• Organ failure
You might also like
- CNOR Cram Sheet (2024)Document9 pagesCNOR Cram Sheet (2024)Aaron LanniNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis NCPXhla Ng78% (18)
- Critical Care NotesDocument18 pagesCritical Care NotesjulieNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument11 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalancesDemiar Madlansacay QuintoNo ratings yet
- Shock: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPDocument38 pagesShock: Mazen Kherallah, MD, FCCPPatrick KosgeiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Mat 2 Case Pres PDFDocument14 pagesNCP For Mat 2 Case Pres PDFJuliane Ryne RosasNo ratings yet
- 4 - Hemorrhagic ShockDocument114 pages4 - Hemorrhagic ShockclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- FE Enrichment 2024Document4 pagesFE Enrichment 2024tarahggggNo ratings yet
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNo ratings yet
- HEMORRHOIDSDocument24 pagesHEMORRHOIDSNARUTONo ratings yet
- NCP - Delivery RoomDocument8 pagesNCP - Delivery RoomAUBREY MARIE . GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy-1Document67 pagesFluid Therapy-1Abdul MaalikNo ratings yet
- Null 7Document21 pagesNull 7Muneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy - : ALGORITHM 1. Assessment of Overall Fluid StatusDocument13 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy - : ALGORITHM 1. Assessment of Overall Fluid Statusfernin96No ratings yet
- Shock OverviewDocument6 pagesShock OverviewKrys Segarra GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Administration: B260 Foundations of NursingDocument59 pagesIntravenous Fluid Administration: B260 Foundations of NursingAli ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage 131223001506 Phpapp02Document24 pagesHemorrhage 131223001506 Phpapp02sekharurlaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric ShockDocument65 pagesObstetric Shockkqz39931No ratings yet
- Upper GI Bleed by Wajid MunirDocument49 pagesUpper GI Bleed by Wajid MunirAtifNo ratings yet
- Intake and Output HandoutDocument3 pagesIntake and Output HandoutLevi AckerManNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument26 pagesShockdaisy100% (1)
- Module 1 (Lesson 2)Document11 pagesModule 1 (Lesson 2)Jovencio Jr. Milo MilanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Fulfilling Fluid and Electrolyte NeedsDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts of Fulfilling Fluid and Electrolyte NeedsHarum BulanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- NCP-Drug-Study KDocument2 pagesNCP-Drug-Study KKyla Mae ZabalaNo ratings yet
- NCM109 Midterm All Notes 1 3Document36 pagesNCM109 Midterm All Notes 1 3Maria JuanilloNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapies in Critical CareDocument46 pagesRenal Replacement Therapies in Critical CareLe ThyNo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony: Group 3Document23 pagesUterine Atony: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemia and Hemorrhage: Clinical Manifestations of HypovolemiaDocument6 pagesHypovolemia and Hemorrhage: Clinical Manifestations of HypovolemiajbNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Final NCP1 2Document2 pagesFinal NCP1 2hahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Analisa Cairan Tubuh SinghDocument60 pagesAnalisa Cairan Tubuh SinghPrabJot SinGhNo ratings yet
- Blood Transuation AssignmentDocument6 pagesBlood Transuation AssignmentvimajavNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesNcp-Liver CirrhosisNorbelisa Tabo-ac CadungganNo ratings yet
- Course - Subject-Unit / Topic - Title - Prepared byDocument39 pagesCourse - Subject-Unit / Topic - Title - Prepared byEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Review On Peripheral IV FluidsDocument37 pagesReview On Peripheral IV FluidsWoot RootNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Fluids and Electrolytes Acid Base Balance and Renal DisordersDocument72 pagesLECTURE Fluids and Electrolytes Acid Base Balance and Renal DisordersAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingNo ratings yet
- Haemorrhagic Shock: Kareena (Grp:45)Document33 pagesHaemorrhagic Shock: Kareena (Grp:45)ShivamNo ratings yet
- SHOCK HandoutsDocument4 pagesSHOCK Handoutslucero.ja39No ratings yet
- NCP DennielleDocument3 pagesNCP DennielleSkynet DivineNo ratings yet
- HemorrhageDocument24 pagesHemorrhageRiry AmbarsaryNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid Compartments 0Document15 pagesBody Fluid Compartments 0Abdo MohdyNo ratings yet
- NCP CP2Document4 pagesNCP CP2Abbeygale GalanNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument36 pagesHypovolemic ShockRia CintyaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever - Ang Ban HongDocument46 pagesDengue Fever - Ang Ban HongSharimanfadhly YahayaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 AlllllDocument285 pagesLec 11 Alllllaryam0012122No ratings yet
- CPG DengueDocument35 pagesCPG DengueSharimanfadhly YahayaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Dan Prinsip Resusitasi Cairan Pada SyokDocument28 pagesKonsep Dasar Dan Prinsip Resusitasi Cairan Pada SyokraraNo ratings yet
- From SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Document1 pageFrom SIRS To Septic Shock (2022!01!22 00-25-28 UTC)Andrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument23 pagesShocknistobdhoraat3No ratings yet
- 5 IV Therapy TransesDocument9 pages5 IV Therapy TransesKeana Dacayana100% (1)
- HTNDocument46 pagesHTNAbdulqader Al-MasoumiNo ratings yet
- New PDF SeminarDocument44 pagesNew PDF SeminarElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNo ratings yet