Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology Flow Chart of Bronchiectasis
Pathophysiology Flow Chart of Bronchiectasis
Uploaded by
Esmareldah Henry Sirue100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
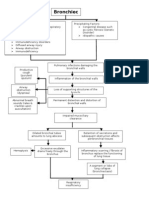
364 views2 pagesThe pulmonary infections associated with bronchiectasis damage the bronchial walls, causing them to become permanently distended and distorted. This impairs mucociliary clearance and causes thick sputum to obstruct the bronchi. In saccular bronchiectasis, each dilated peribronchial tube is like a lung abscess that freely drains pus into the bronchus. Over time, the retained secretions cause alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse while inflammatory scarring replaces functioning lung tissue, leading to respiratory insufficiency.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pathophysiology flow chart of Bronchiectasis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe pulmonary infections associated with bronchiectasis damage the bronchial walls, causing them to become permanently distended and distorted. This impairs mucociliary clearance and causes thick sputum to obstruct the bronchi. In saccular bronchiectasis, each dilated peribronchial tube is like a lung abscess that freely drains pus into the bronchus. Over time, the retained secretions cause alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse while inflammatory scarring replaces functioning lung tissue, leading to respiratory insufficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
364 views2 pagesPathophysiology Flow Chart of Bronchiectasis
Pathophysiology Flow Chart of Bronchiectasis
Uploaded by
Esmareldah Henry SirueThe pulmonary infections associated with bronchiectasis damage the bronchial walls, causing them to become permanently distended and distorted. This impairs mucociliary clearance and causes thick sputum to obstruct the bronchi. In saccular bronchiectasis, each dilated peribronchial tube is like a lung abscess that freely drains pus into the bronchus. Over time, the retained secretions cause alveoli distal to the obstruction to collapse while inflammatory scarring replaces functioning lung tissue, leading to respiratory insufficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
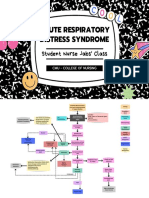
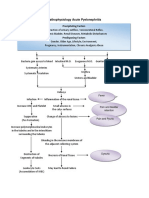
Pathophysiology flow chart of imbalance) and hypoxemia.
Bronchiectasis
The pulmonary infection associate with the
inflammatory process damages the bronchial
wall, causing a loss of its supporting
structure and result in thick sputum that
ultimately obstruct the bronchi. The walls
become permanently distended and
distorted, impairing mucociliary clearance.
In saccular bronchiectasis each dilated
peribronchial tubes amount to a lung
abscess, the excudate of which drains freely
to the bronchus. Bronchiectasis is usually
localized affecting a segment or lobe of the
lung, most frequently the lower lobes. The
retention of the secretions and subsequent
obstruction ultimately cause the alveoli
distal to the obstruction to collapse
(atelectasis). Inflammatory scarring or
fibrosis replaces functioning lung tissue. In
the time patient develops respiratory
insufficiency with reduced vital capacity
decreased ventilation and an increased ratio
of residual volume to lung capacity. There is
impairment in the match of ventilation to
perfusion (ventilation – perfusion
You might also like
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 pagesARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Causative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDocument21 pagesCausative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDon Chiaw Manongdo100% (1)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Pathophysiologyjordan aguilar67% (3)
- Review Test #1-Malinda SirueDocument2 pagesReview Test #1-Malinda SirueEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 RLE - MODULE-Disaster-NursingDocument15 pagesNCM 106 RLE - MODULE-Disaster-NursingEsmareldah Henry Sirue100% (2)
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology TBDocument2 pagesPathophysiology TBJhen DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoNo ratings yet
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument27 pagesAspiration PneumoniaReya Awali SuasoNo ratings yet
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Naso & Orogastric Tube Placement, Testing & FeedingDocument10 pagesNaso & Orogastric Tube Placement, Testing & FeedingYwagar Ywagar100% (1)
- Anatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaKevin Comahig100% (1)
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Pneumoniapallavi100% (2)
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument4 pagesConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Ambrolex Generic Name: Ambroxol HCL Indication: Acute andDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Ambrolex Generic Name: Ambroxol HCL Indication: Acute andianecunar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 pagesPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument4 pagesDengueKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology 3Document2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology 3billiam123No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- COPD PathophysioDocument1 pageCOPD Pathophysionanette flores dela cruzNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument15 pagesAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisJeanne Marie ValesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Tetanus PathoDocument3 pagesTetanus PathoElisha Gine AndalesNo ratings yet
- Return Demonstration: Urinary Catheterization Perineal CareDocument3 pagesReturn Demonstration: Urinary Catheterization Perineal CareDebbie beeNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophymharz_astilloNo ratings yet
- NebulizationDocument2 pagesNebulizationArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Pleural Effusion: Union Christian CollegeDocument8 pagesCase Study: Pleural Effusion: Union Christian CollegeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Generic (Trade Name) Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesGeneric (Trade Name) Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. Responsibilitiesliesel_12100% (1)
- Influenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesInfluenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaNo ratings yet
- Patho DengueDocument3 pagesPatho DengueLindy Shane BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyZandra Lyn AlundayNo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaNo ratings yet
- NCP AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP AirwayjlucandoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology m7 Post Task CaparasDocument3 pagesPharmacology m7 Post Task CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- Book Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument7 pagesBook Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDocument3 pagesJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963No ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PTBDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PTBChelsea AquinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of COPDoxidalaj100% (1)
- Signs and Symptoms of Neonatal PneumoniaDocument4 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Neonatal PneumoniaMäc LäntinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNo ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument22 pagesAspiration PneumoniaAya AlamsjahNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyBrunhild BangayanNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyKim Gonzales86% (7)
- Dr. ChintanDocument26 pagesDr. ChintanArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Respi PathophysioDocument31 pagesRespi PathophysioIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- CA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Document6 pagesCA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Laws Affecting Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesLaws Affecting Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesEsmareldah Henry Sirue100% (1)
- My Family-TreeDocument1 pageMy Family-TreeEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 Task 4: Pathophysiology For Cardiac Tamponade Using AlogorithmDocument2 pagesCase Scenario 1 Task 4: Pathophysiology For Cardiac Tamponade Using AlogorithmEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Colostomy - Care - Module 2Document5 pagesColostomy - Care - Module 2Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Tips To Increase Speed of AssessmentDocument6 pagesTips To Increase Speed of AssessmentEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Nursing Act of 2002Document11 pagesThe Philippine Nursing Act of 2002Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 Task 4: Pathophysiology For Cardiac Tamponade Using AlogorithmDocument1 pageCase Scenario 1 Task 4: Pathophysiology For Cardiac Tamponade Using AlogorithmEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Laws Affecting Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesLaws Affecting Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument7 pages13 Areas of AssessmentEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution SamplesDocument11 pagesFrequency Distribution SamplesEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Coteng' Faith Guira, Louella Joseph, Boikhuts o Lachica, JocelynDocument2 pagesCoteng' Faith Guira, Louella Joseph, Boikhuts o Lachica, JocelynEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet-1st Quiz - Malinda SirueDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheet-1st Quiz - Malinda SirueEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet - Quiz 3&4-Malinda SirueDocument1 pageAnswer Sheet - Quiz 3&4-Malinda SirueEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Drug StudyEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication: Action: Mechanism of Action Classificatio N Adverse Effects Contraindications: Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indication: Action: Mechanism of Action Classificatio N Adverse Effects Contraindications: Nursing ConsiderationsEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Keflex Capsules: Cephalexin, UspDocument9 pagesKeflex Capsules: Cephalexin, UspEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Kardex: College of Community Health and Allied Medical SciencesDocument1 pageKardex: College of Community Health and Allied Medical SciencesEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: HematologicDocument2 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: HematologicEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet