Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
Uploaded by
Harish DCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 29 - Test: (60 Minutes)Document3 pagesChapter 29 - Test: (60 Minutes)Minh ThanhNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2018 Chemistry Set 1Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2018 Chemistry Set 1Saran.kNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 1Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 1Jenish DadhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination 2018 Marking Scheme - ChemistryDocument6 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination 2018 Marking Scheme - ChemistryNipun JainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5NitilNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme N-Set-2 2016Document7 pagesMarking Scheme N-Set-2 2016Suraj TankNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry MS PDFMeeralekshmi RNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 3Document26 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 3Sucharita GraceNo ratings yet
- Scoring Key Sample Paper (Chemistry) Class Xii Q.No Answers MarksDocument8 pagesScoring Key Sample Paper (Chemistry) Class Xii Q.No Answers MarksShubhanshu RaiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2015 Chemistry Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2015 Chemistry Set 1SA EEDNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerDocument10 pages12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerAlagu MurugesanNo ratings yet
- MS Chemistry Blind 2018Document5 pagesMS Chemistry Blind 2018AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry MS PDFArun PravinNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2014 Delhi Set 2 AnswerDocument8 pages12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2014 Delhi Set 2 AnswerKhushi JhaNo ratings yet
- Act Thrissur +1 Chem KeyDocument6 pagesAct Thrissur +1 Chem KeyYADUKRISHNAN K NAIRNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22sydneymazuba2024No ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSPankaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chem Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesChem Marking SchemeForzen flamesNo ratings yet
- Set 2 MSDocument7 pagesSet 2 MSsanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSNafeesNo ratings yet
- Che Ans 1Document9 pagesChe Ans 1Aditi KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination 2017 Marking Scheme - ChemistryDocument15 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination 2017 Marking Scheme - ChemistryBinayak SahuNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Chemistry - 2014Document7 pagesMarking Scheme: Chemistry - 2014Nidhi PrasadNo ratings yet
- 1993 Free Response Answers: Return To Questions Return To Additional Materials MenuDocument10 pages1993 Free Response Answers: Return To Questions Return To Additional Materials MenuNightNo ratings yet
- Case Marking Scheme 2016Document8 pagesCase Marking Scheme 2016Aditi KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- ( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument67 pages( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6Document54 pagesChemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6reneeyeung001No ratings yet
- G12 Exam Sept 2022 P2 MEMODocument4 pagesG12 Exam Sept 2022 P2 MEMOmichaelNo ratings yet
- MARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ADocument5 pagesMARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ASyed ShammazNo ratings yet
- 2018 Mark Scheme Final VersionDocument13 pages2018 Mark Scheme Final VersionJackieWilsonNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - 2017 Chemistry (043) / Class Xii Chemistry 56 (B)Document5 pagesMarking Scheme - 2017 Chemistry (043) / Class Xii Chemistry 56 (B)GreatNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Qualitative Chemistry ADocument67 pagesCHM1 Qualitative Chemistry AGM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- GgasfjofwojfosDocument68 pagesGgasfjofwojfosG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- A-Level Ap1 Paper 1 MsDocument9 pagesA-Level Ap1 Paper 1 MsumerNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Transition Metals General Properties MSDocument11 pages2.1 Transition Metals General Properties MSJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument67 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Chemistry-MS 22-23Document14 pagesCLASS XII Chemistry-MS 22-23Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSSatyam YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS Term2Document6 pagesChemistry MS Term2Divya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument7 pagesChemistry MSaneeshNo ratings yet
- N. B. An Energy Diagram Scores 0 MarksDocument65 pagesN. B. An Energy Diagram Scores 0 MarksG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 11-Chemistry UT-1 MS (2023-24)Document2 pages11-Chemistry UT-1 MS (2023-24)AnantNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Negative)Document66 pagesMathematical Negative)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- MS Chemistry Class XIDocument6 pagesMS Chemistry Class XIattitudes933No ratings yet
- UuydghdgdgtertstrwtDocument66 pagesUuydghdgdgtertstrwtG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Section A: 2018 Y6 H2 Chemistry Term 2 Common Test - Suggested SolutionsDocument18 pagesSection A: 2018 Y6 H2 Chemistry Term 2 Common Test - Suggested SolutionsImagreenbucklegirl SGNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JEE Solutions 2022Document17 pagesChemistry JEE Solutions 2022himesh himeshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2011: Expected Answers/Value PointsDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2011: Expected Answers/Value PointsYashika PuriNo ratings yet
- Correct Cycle in Any Possible Answers 0. 11, 0.110, 0.1111 (CL In) OCIDocument66 pagesCorrect Cycle in Any Possible Answers 0. 11, 0.110, 0.1111 (CL In) OCIG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (043) Marking Scheme 2016: Values PointsDocument8 pagesChemistry (043) Marking Scheme 2016: Values PointstarunNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Paper-1Document8 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Paper-1rahulNo ratings yet
- Error Is Mathematical Negative)Document65 pagesError Is Mathematical Negative)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument47 pagesComputerHarish DNo ratings yet
- 2020 Solution PDFDocument9 pages2020 Solution PDFHarish DNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2019Document6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2019Harish DNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument47 pagesComputer NotesHarish DNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Vector Algebra - QuestionsDocument7 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Vector Algebra - QuestionsHarish DNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Koordinasi Relay Ocr PDFDocument2 pagesContoh Soal Koordinasi Relay Ocr PDFEdi CarnediNo ratings yet
- WorkShop Supervisor Management NotesDocument10 pagesWorkShop Supervisor Management NotesWeyih ReganNo ratings yet
- What Causes HallucinationsDocument2 pagesWhat Causes Hallucinationslook at meNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Document26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Released FOR Manufacturing: 2509 ANTAMINA PERU SMC 100/14400 Truck Bridge Assembly Truck Bridge Steel Structure - RightDocument1 pageReleased FOR Manufacturing: 2509 ANTAMINA PERU SMC 100/14400 Truck Bridge Assembly Truck Bridge Steel Structure - RightCarlos ParedesNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems DE-40 EE - Semester 4 Spring 2020: Lab Report # 06Document21 pagesSignals and Systems DE-40 EE - Semester 4 Spring 2020: Lab Report # 06Muhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- 50 Milisimal PotencyDocument8 pages50 Milisimal PotencyDr. Surendra Singh100% (3)
- Offset Flail Mowers: OFM3678, OFM3690 & OFM3698Document38 pagesOffset Flail Mowers: OFM3678, OFM3690 & OFM3698gomezcabellojosemanuelNo ratings yet
- Lipke-Perry, Tracy D. Integrating Piano Technique, Physiology, and Motor Learning - Strategies For Performing The Chopin EtudesDocument206 pagesLipke-Perry, Tracy D. Integrating Piano Technique, Physiology, and Motor Learning - Strategies For Performing The Chopin EtudesNoMoPoMo576No ratings yet
- DimpuDocument27 pagesDimpuDippu SihombingNo ratings yet
- Formulation - of - Corrosion - Inhibitors-Yun Chen and Wenzhong Yang 23 PAGESDocument23 pagesFormulation - of - Corrosion - Inhibitors-Yun Chen and Wenzhong Yang 23 PAGESChoice Organo100% (4)
- Gregory, D. Imagery and Possibility 2020Document19 pagesGregory, D. Imagery and Possibility 2020IdrilNo ratings yet
- BEVAE-181 Sample PPR 2Document4 pagesBEVAE-181 Sample PPR 2saketsharmaytNo ratings yet
- Cloze Passage For SMP Kls 3Document7 pagesCloze Passage For SMP Kls 3DibaPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Dell Service ManualDocument220 pagesDell Service ManualYeik ThaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Fundamentals - Rían DorisDocument7 pagesSleep Fundamentals - Rían Dorisseristudies007No ratings yet
- ProposalDocument1 pageProposalrahim bakhshNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument32 pagesProjectFavour NwachukwuNo ratings yet
- AV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsDocument32 pagesAV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsCuthbert Marshall100% (1)
- Application of Passive Solar SystemDocument38 pagesApplication of Passive Solar SystemRam Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- III. Complete The Sentences With The Future Continuous Form of The Verbs in The BoxDocument2 pagesIII. Complete The Sentences With The Future Continuous Form of The Verbs in The BoxGuen KitoNo ratings yet
- Computational Analysis of Centrifugal Compressor Surge Control Using Air InjectionDocument24 pagesComputational Analysis of Centrifugal Compressor Surge Control Using Air InjectionrafieeNo ratings yet
- Fa 5541Document46 pagesFa 5541Ricardo Nicolau WerlangNo ratings yet
- SK CatalougeDocument16 pagesSK CatalougeDevvratNo ratings yet
- 1SNC160001C0205 Cha1Document144 pages1SNC160001C0205 Cha1Nelson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual: 7000 Series ACTB Automatic Closed-Transition Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesDocument12 pagesOperator's Manual: 7000 Series ACTB Automatic Closed-Transition Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesJose PirulliNo ratings yet
- 79-Article Text-140-3-10-20170810Document5 pages79-Article Text-140-3-10-20170810Raihanah Fadhillah YulianiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Chapter 5 The Summit WithinDocument6 pagesClass 8 Chapter 5 The Summit WithinPrathamesh . M LaddhadNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Instrumen Bi PTTS 2023Document9 pagesSkema Jawapan Instrumen Bi PTTS 2023Darina Chin AbdullahNo ratings yet
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
Uploaded by
Harish DOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
Uploaded by
Harish DCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2018
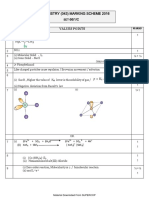
Marking Scheme – 2017-18
CHEMISTRY (043)/ CLASS XII
56/1
Q.No Value Points Marks
1 Shows metal deficiency defect / It is a mixture of Fe2+ and Fe3+/Some Fe2+ ions are 1
replaced by Fe3+ / Some of the ferrous ions get oxidised to ferric ions.
2 Selectivity of a catalyst 1
3 Coordination Number = 6 , Oxidation State = +2 ½, ½
4 Benzyl chloride ; ½
Due to resonance, stable benzyl carbocation is formed. ½
5 3,3 - Dimethylpentan-2-ol 1
6 ΔTf = Kf m
= Kf w2 x1000 ½
M2x w1
= 1.86 x 60 x 1000
180x250 ½
= 2.48 K ½
ΔTf = Tf o- Tf
2.48 = 273.15 - Tf
Tf = 270.67 K / 270.52 K / - 2.48 oC ½
7 𝟏 𝜟 𝑵𝑶𝟐 𝟏 𝜟 𝑵𝟐 𝑶𝟓 ½
𝑹𝒂𝒕𝒆 = =-
𝟒 𝜟 𝒕 𝟐 𝜟 𝒕
1 −3 1 𝛥 𝑁2 𝑂5
(2.8 × 10 )= - ½
4 2 𝛥 𝑡
𝜟 𝑵𝟐 𝑶𝟓 1
Rate of disappearance of N2O5 ( - ) = 1.4 × 10−3 M/s
𝜟 𝒕
(Deduct half mark
if unit is wrong or not written)
8 (a)PH3 ½
(b)NH3 ½
(c)NH3 ½
(d)BiH3 ½
9 (a)CH3CHO (i)CH3MgBr, Dry ether(ii)H2O/H+ CH3CH(OH)CH3 CrO3 CH3COCH3 1
(b)
(or any other correct method)
OR
9 (a) because the carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium 1
chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to the carboxyl group
(b) Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group (-I effect) so it stabilises the 1
carboxylate anion and strengthens the acid / Due to the presence of an
electron withdrawing Nitro group (-I effect).
(a)
10.
1
(b)
1
(Half mark to be deducted in each equation for not balancing)
11 (a) As compared to other colligative properties, its magnitude is large even for 1
very dilute solutions / macromolecules are generally not stable at higher
temperatures and polymers have poor solubility / pressure measurement is
around the room temperature and the molarity of the solution is used
instead of molality.
1
(b) Because oxygen is more soluble in cold water or at low temperature.
1
(c) Due to dissociation of KCl / KCl (aq) K+ + Cl- , i is nearly equal to 2
12
½
= 4 x 40
½
(4x10-8)3x6.022x1023
½
= 4.15 g/cm3
½
No of unit cells = total no of atoms /4
4 ½
=[ x 6.022x1023] / 4
40 ½
=1.5 x1022
(Or any other correct method)
13
k2 = 0.693 / 20, ½
k1 = 0.693/40 ½
𝑘2 𝐸𝑎 1 1
log = [ − ]
𝑘1 2.303𝑅 𝑇1 𝑇2 ½
k2/k1 = 2
𝐸𝑎 320 − 300 ½
log 2 = [ ]
2.303 × 8.314 320 × 300
Ea = 27663.8 J/mol or 27.66 kJ/ mol 1
14 (a)Peptisation occurs / Colloidal solution of Fe(OH)3 is formed 1
(b)Coagulation occurs 1
(c)Demulsification or breaks into constituent liquids 1
15 1
1
(No marks will be deducted for not balancing)
NaCN leaches gold/NaCN acts as a leacing agent / complexing agent ½
Zn acts as reducing agent / Zn displaces gold. ½
16 (a) The comparatively high value for Mn shows that Mn2+(d5) is particularly 1
stable / Much larger third ionisation energy of Mn (where the required change is from
d5 to d4)
(b)Due to higher number of unpaired electrons. 1
(c)Absence of unpaired d- electron in Sc3+ whereas in Ti3+ there is one unpaired 1
electron or Ti3+shows d-d transition.
17 1
(a) (i) /
(b) 1
(c) 1
or
18 (a)
A= CH3CH2CH2CHO ½
B = CH3COCH2CH3 ½
C= (CH3)2CHCHO ½
D= CH3CH2CH2CH3
½
(b) B
1
19.
(i)
1
1
(ii) C6H5CH(OH)CH3
1
(iii) C2H5I + C6H5OH (No splitting of marks)
20. a) To impart antiseptic properties 1
b) 2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol – water mixture / iodine dissolved in ½,½
alcohol , used as an antiseptic/ applied on wounds. 1
c) Sodium benzoate / Aspartame
21 (a)Carbohydrates that give large number of monosaccharide units on hydrolysis / ½
large number of monosaccharides units joined together by glycosidic linkage
Starch/ glycogen/ cellulose (or any other) ½
(b)Proteins that lose their biological activity / proteins in which secondary and ½
tertiary structures are destroyed
½
Curdling of milk (or any other)
( c)Amino acids which cannot be synthesised in the body. ½
Valine / Leucine (or any other) ½
OR
21 (a)Saccharic acid / COOH-(CHOH)4-COOH 1
(b)Due to the presence of carboxyl and amino group in the same molecule / due to 1
formation of zwitter ion or dipolar ion.
( c)α- helix has intramolecular hydrogen bonding while β pleated has intermolecular 1
hydrogen bonding / α- helix results due to regular coiling of polypeptide chains
while in β pleated all polypeptide chains are stretched and arranged side by side.
22 (a) Fe4[Fe (CN)6]3 1
(b) Ionisation isomerism 1
(c) sp3d2, 4 ½, ½
23 (a) Concerned about environment, caring, socially alert, law abiding citizen ( or any
other 2 values) ½,½
(b) Low density polythene is highly branched while high density polythene is linear. 1
(c) As it is non-biodegradable . 1
(d) Which can be degraded by microorganisms, eg PHBV(or any other correct ½,½
example)
24 a) (i) In +3 oxidation state of phosphorus tends to disproportionate to higher and 1
lower oxidation states / Oxidation state of P in H3PO3 is +3 so it undergoes
disproportionation but in H3PO4 it is +5 which is the highest oxidation state, so it
cannot. 1
(ii) F cannot show positive oxidation state as it has highest electronegativity/
Because Fluorine cannot expand its covalency / As Fluorine is a small sized 1
atom, it cannot pack three large sized Cl atoms around it.
(iii) Oxygen has multiple bonding whereas sulphur shows catenation / Due to
pπ-pπ bonding in oxygen whereas sulphur does not / Oxygen is diatomic
therefore held by weak intermolecular force while sulphur is polyatomic held by
strong intermolecular forces.
b) (i) (ii)
1, 1
OR
24 a) (i) A = NO2 , B = N2O4 ½, ½
(ii)
½,½
,
(iii) Because NO2 dimerises to N2O4 / NO2 is an odd electron species. 1
b) HI > HBr > HCl > HF 1
c) XeF4 + SbF5 [XeF3]+ [SbF6]- 1
25 (a) Sn + 2 H+ Sn2+ + H2 (Equation must be balanced) 1
E = Eo - 0.059 log [Sn2+] ½
2 [H+]2
(0.004)
= [0 – (- 0.14) ] – 0.0295 log 2 ½
(0.02)
= 0.14 – 0.0295 log 10 = 0.11 V / 0.1105 V 1
(b) (i) Due to overpotential/ Overvoltage of O2 1
(ii) The number of ions per unit volume decreases. 1
OR
25 a) ΔGo = - nFEo ½
-43600 = - 2 × 96500 ×Eo
o
E = 0.226 V ½
E = Eo - 0.059/2 log ( [H+]2 [Cl-]2 / [H2] ) ½
= 0.226 – 0.059/2 log[ (0.1)2 ×(0.1)2 ] / 1
½
= 0.226 -0.059 /2 log 10-4
1
= 0.226 + 0.118 = 0.344 V (Deduct half mark if unit is wrong or not written)
1
b) Cells that convert the energy of combustion of fuels (like hydrogen, methane,
methanol, etc.) directly into electrical energy are called fuel cells. ½ ,½
Advantages : High efficiency, non polluting (or any other suitable advantage)
26 (a)(i) Ar/ R-CONH2 + Br2 + 4 NaOH Ar/ R-NH2 + 2NaBr + Na2CO3 + 2 H2O 1
(ii)
1
(or any other correct equation)
(iii)
(b)(i)Because of the combined factors of inductive effect and solvation or
hydration effect 1
(ii)Due to resonance stabilisation or structural representation / resonating
structures. 1
OR
26 (a) (i) C6H5NHCOCH3 1
(ii) C6H5SO2N(CH3)2 1
(iii) C6H6 1
(b) Add chloroform in the presence of KOH and heat , Aniline gives a offensive smell 1
while N,N dimethylaniline does not. (or any other correct test)
(c)C2H5NH2< C6H5NHCH3< C6H5NH2
1
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 29 - Test: (60 Minutes)Document3 pagesChapter 29 - Test: (60 Minutes)Minh ThanhNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2018 Chemistry Set 1Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2018 Chemistry Set 1Saran.kNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 1Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 1Jenish DadhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination 2018 Marking Scheme - ChemistryDocument6 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination 2018 Marking Scheme - ChemistryNipun JainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5NitilNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme N-Set-2 2016Document7 pagesMarking Scheme N-Set-2 2016Suraj TankNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry MS PDFMeeralekshmi RNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 3Document26 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2017 Chemistry Set 3Sucharita GraceNo ratings yet
- Scoring Key Sample Paper (Chemistry) Class Xii Q.No Answers MarksDocument8 pagesScoring Key Sample Paper (Chemistry) Class Xii Q.No Answers MarksShubhanshu RaiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2015 Chemistry Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2015 Chemistry Set 1SA EEDNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerDocument10 pages12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2016 Foreign Set 1 AnswerAlagu MurugesanNo ratings yet
- MS Chemistry Blind 2018Document5 pagesMS Chemistry Blind 2018AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry MS PDFArun PravinNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2014 Delhi Set 2 AnswerDocument8 pages12 Chemistry CBSE Exam Papers 2014 Delhi Set 2 AnswerKhushi JhaNo ratings yet
- Act Thrissur +1 Chem KeyDocument6 pagesAct Thrissur +1 Chem KeyYADUKRISHNAN K NAIRNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Marking Scheme Term 2 For 2021 22sydneymazuba2024No ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSPankaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chem Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesChem Marking SchemeForzen flamesNo ratings yet
- Set 2 MSDocument7 pagesSet 2 MSsanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSNafeesNo ratings yet
- Che Ans 1Document9 pagesChe Ans 1Aditi KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination 2017 Marking Scheme - ChemistryDocument15 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination 2017 Marking Scheme - ChemistryBinayak SahuNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Chemistry - 2014Document7 pagesMarking Scheme: Chemistry - 2014Nidhi PrasadNo ratings yet
- 1993 Free Response Answers: Return To Questions Return To Additional Materials MenuDocument10 pages1993 Free Response Answers: Return To Questions Return To Additional Materials MenuNightNo ratings yet
- Case Marking Scheme 2016Document8 pagesCase Marking Scheme 2016Aditi KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- ( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument67 pages( ) (1) ( ) Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6Document54 pagesChemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6reneeyeung001No ratings yet
- G12 Exam Sept 2022 P2 MEMODocument4 pagesG12 Exam Sept 2022 P2 MEMOmichaelNo ratings yet
- MARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ADocument5 pagesMARKING SCHEME (2021-22) Term - Ii Chemistry Theory (043) Set ASyed ShammazNo ratings yet
- 2018 Mark Scheme Final VersionDocument13 pages2018 Mark Scheme Final VersionJackieWilsonNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - 2017 Chemistry (043) / Class Xii Chemistry 56 (B)Document5 pagesMarking Scheme - 2017 Chemistry (043) / Class Xii Chemistry 56 (B)GreatNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Qualitative Chemistry ADocument67 pagesCHM1 Qualitative Chemistry AGM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- GgasfjofwojfosDocument68 pagesGgasfjofwojfosG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- A-Level Ap1 Paper 1 MsDocument9 pagesA-Level Ap1 Paper 1 MsumerNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Transition Metals General Properties MSDocument11 pages2.1 Transition Metals General Properties MSJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument67 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Chemistry-MS 22-23Document14 pagesCLASS XII Chemistry-MS 22-23Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument9 pagesChemistry MSSatyam YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MS Term2Document6 pagesChemistry MS Term2Divya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in BondDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in BondG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument7 pagesChemistry MSaneeshNo ratings yet
- N. B. An Energy Diagram Scores 0 MarksDocument65 pagesN. B. An Energy Diagram Scores 0 MarksG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 11-Chemistry UT-1 MS (2023-24)Document2 pages11-Chemistry UT-1 MS (2023-24)AnantNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Negative)Document66 pagesMathematical Negative)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- MS Chemistry Class XIDocument6 pagesMS Chemistry Class XIattitudes933No ratings yet
- UuydghdgdgtertstrwtDocument66 pagesUuydghdgdgtertstrwtG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Section A: 2018 Y6 H2 Chemistry Term 2 Common Test - Suggested SolutionsDocument18 pagesSection A: 2018 Y6 H2 Chemistry Term 2 Common Test - Suggested SolutionsImagreenbucklegirl SGNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JEE Solutions 2022Document17 pagesChemistry JEE Solutions 2022himesh himeshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2011: Expected Answers/Value PointsDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2011: Expected Answers/Value PointsYashika PuriNo ratings yet
- Correct Cycle in Any Possible Answers 0. 11, 0.110, 0.1111 (CL In) OCIDocument66 pagesCorrect Cycle in Any Possible Answers 0. 11, 0.110, 0.1111 (CL In) OCIG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of ADocument67 pagesEnthalpy/heat Change For Formation of 1 Mole of AG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (043) Marking Scheme 2016: Values PointsDocument8 pagesChemistry (043) Marking Scheme 2016: Values PointstarunNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Paper-1Document8 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Paper-1rahulNo ratings yet
- Error Is Mathematical Negative)Document65 pagesError Is Mathematical Negative)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Average Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentDocument68 pagesAverage Values From Many Compounds Used in Bond Actual Values For These Compounds Probably Slightly DifferentG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument47 pagesComputerHarish DNo ratings yet
- 2020 Solution PDFDocument9 pages2020 Solution PDFHarish DNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2019Document6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2019Harish DNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument47 pagesComputer NotesHarish DNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Vector Algebra - QuestionsDocument7 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Chapter Wise Question Bank: Vector Algebra - QuestionsHarish DNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Koordinasi Relay Ocr PDFDocument2 pagesContoh Soal Koordinasi Relay Ocr PDFEdi CarnediNo ratings yet
- WorkShop Supervisor Management NotesDocument10 pagesWorkShop Supervisor Management NotesWeyih ReganNo ratings yet
- What Causes HallucinationsDocument2 pagesWhat Causes Hallucinationslook at meNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Document26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Bank 1690183665Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Released FOR Manufacturing: 2509 ANTAMINA PERU SMC 100/14400 Truck Bridge Assembly Truck Bridge Steel Structure - RightDocument1 pageReleased FOR Manufacturing: 2509 ANTAMINA PERU SMC 100/14400 Truck Bridge Assembly Truck Bridge Steel Structure - RightCarlos ParedesNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems DE-40 EE - Semester 4 Spring 2020: Lab Report # 06Document21 pagesSignals and Systems DE-40 EE - Semester 4 Spring 2020: Lab Report # 06Muhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- 50 Milisimal PotencyDocument8 pages50 Milisimal PotencyDr. Surendra Singh100% (3)
- Offset Flail Mowers: OFM3678, OFM3690 & OFM3698Document38 pagesOffset Flail Mowers: OFM3678, OFM3690 & OFM3698gomezcabellojosemanuelNo ratings yet
- Lipke-Perry, Tracy D. Integrating Piano Technique, Physiology, and Motor Learning - Strategies For Performing The Chopin EtudesDocument206 pagesLipke-Perry, Tracy D. Integrating Piano Technique, Physiology, and Motor Learning - Strategies For Performing The Chopin EtudesNoMoPoMo576No ratings yet
- DimpuDocument27 pagesDimpuDippu SihombingNo ratings yet
- Formulation - of - Corrosion - Inhibitors-Yun Chen and Wenzhong Yang 23 PAGESDocument23 pagesFormulation - of - Corrosion - Inhibitors-Yun Chen and Wenzhong Yang 23 PAGESChoice Organo100% (4)
- Gregory, D. Imagery and Possibility 2020Document19 pagesGregory, D. Imagery and Possibility 2020IdrilNo ratings yet
- BEVAE-181 Sample PPR 2Document4 pagesBEVAE-181 Sample PPR 2saketsharmaytNo ratings yet
- Cloze Passage For SMP Kls 3Document7 pagesCloze Passage For SMP Kls 3DibaPertiwiNo ratings yet
- Dell Service ManualDocument220 pagesDell Service ManualYeik ThaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Fundamentals - Rían DorisDocument7 pagesSleep Fundamentals - Rían Dorisseristudies007No ratings yet
- ProposalDocument1 pageProposalrahim bakhshNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument32 pagesProjectFavour NwachukwuNo ratings yet
- AV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsDocument32 pagesAV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsCuthbert Marshall100% (1)
- Application of Passive Solar SystemDocument38 pagesApplication of Passive Solar SystemRam Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- III. Complete The Sentences With The Future Continuous Form of The Verbs in The BoxDocument2 pagesIII. Complete The Sentences With The Future Continuous Form of The Verbs in The BoxGuen KitoNo ratings yet
- Computational Analysis of Centrifugal Compressor Surge Control Using Air InjectionDocument24 pagesComputational Analysis of Centrifugal Compressor Surge Control Using Air InjectionrafieeNo ratings yet
- Fa 5541Document46 pagesFa 5541Ricardo Nicolau WerlangNo ratings yet
- SK CatalougeDocument16 pagesSK CatalougeDevvratNo ratings yet
- 1SNC160001C0205 Cha1Document144 pages1SNC160001C0205 Cha1Nelson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual: 7000 Series ACTB Automatic Closed-Transition Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesDocument12 pagesOperator's Manual: 7000 Series ACTB Automatic Closed-Transition Transfer & Bypass-Isolation SwitchesJose PirulliNo ratings yet
- 79-Article Text-140-3-10-20170810Document5 pages79-Article Text-140-3-10-20170810Raihanah Fadhillah YulianiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Chapter 5 The Summit WithinDocument6 pagesClass 8 Chapter 5 The Summit WithinPrathamesh . M LaddhadNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Instrumen Bi PTTS 2023Document9 pagesSkema Jawapan Instrumen Bi PTTS 2023Darina Chin AbdullahNo ratings yet