Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)
Nitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)
Uploaded by
the lilly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesNitric acid (HNO3), also known as aqua fortis (Latin for "strong water") and spirit of niter, is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The pure compound is colorless, but older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen and water.
CHEMISTRY SUMMARY
Original Title
Nitric Acid [SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNitric acid (HNO3), also known as aqua fortis (Latin for "strong water") and spirit of niter, is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The pure compound is colorless, but older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen and water.
CHEMISTRY SUMMARY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesNitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)
Nitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)
Uploaded by
the lillyNitric acid (HNO3), also known as aqua fortis (Latin for "strong water") and spirit of niter, is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The pure compound is colorless, but older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen and water.
CHEMISTRY SUMMARY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Study of Compounds – Nitric Acid
Nitric Acid
Molecular formula: HNO3
Relative molecular mass: 63
Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid
Reactions:
KNO3 + H2SO4 KHSO4 + HNO3
NaNO3 + H2SO4 NaHSO4 + HNO3
Properties of Nitric Acid
(A) Physical Properties
Pure acid (98% conc.) is colourless, suffocating and sour to taste.
It is heavier than water, with a specific gravity of 1.54.
Boiling point is 86°C, and freezing point is −42°C
(B) Chemical Properties
Pure nitric acid is colourless, unstable and decomposes slightly even at room temperature and in the
presence of sunlight.
4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
Nitric acid is a very strong monobasic acid and ionises almost completely in aqueous solution.
HNO3 H+ + NO3−
Nitric acid neutralises alkalis to form salt and water.
CaO + 2HNO3 Ca (NO3)2 + H2O
CuO + 2HNO3
Cu (NO3)2 + H2O
NaOH + HNO3
NaNO3 + H2O
Nitric acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce salt, water and carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HNO3 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HNO3 NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
Nitric acid oxidises carbon, sulphur and phosphorus to their highest oxides or oxy-acids such as
carbon dioxide, sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid.
C + 4HNO3 2H2O + 4NO2 + CO2
S + 6HNO3
H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
P4 + 20HNO3
4H3PO4 + 4H2O + 20NO2
Cold and dilute nitric acid oxidises metals to their nitrates and liberates nitric oxide.
3Cu + 8HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
3Zn + 8HNO3
3Zn (NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO2
Concentrated nitric acid liberates nitrogen dioxide.
Cu + 4HNO3
Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
Zn + 4HNO3 Zn (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
Nitric acid (1 part by volume) mixed with conc. hydrochloric acid (3 parts by volume) produces a
mixture called aqua regia.
HNO3 + 3HCl NOCl + 2H2O + 2[Cl]
Aqua regia contains nascent chlorine and reacts with noble metals such as gold and platinum to
produce chlorides.
Pt + 4[Cl] PtCl4
Au +3[Cl] AuCl3
Uses of Nitric Acid
To etch designs on copper and brassware because it acts as a solvent for several metals except the
noble metals.
To purify gold with impurities of Cu, Ag and Zn which dissolve in nitric acid.
It acts as a rocket fuel oxidant.
In preparation of fertilisers such as Ca(NO3)2 and NH4NO3.
In the preparation of aqua regia, which dissolves noble metals.
You might also like
- Carbon and Its Compounds Shobhit NirwanDocument9 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Shobhit NirwanRishabh Joshi78% (9)
- 10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Document5 pages10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Ashraf Husain100% (4)
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 10 - Nitric Acid Revision NotesDocument2 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 10 - Nitric Acid Revision NotesShaunak OrigamiNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument9 pagesNitric Acidaditya varteNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument3 pagesNitric AciduniquestarNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument18 pagesAcid BasechaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases SummaryDocument8 pagesAcid Bases Summaryibraheemgamer786No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- All Chemical ReactionsDocument29 pagesAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chemistry - Study of Compounds Nitric Acid SolutionsDocument26 pagesClass 10 - Chemistry - Study of Compounds Nitric Acid Solutionsavadhut.malji19No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-4NotesDocument6 pages12th Chemistry CH-4NotesMajid HafeezNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document3 pagesSulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Study of Components Nitric AcidDocument3 pagesStudy of Components Nitric AcidKavya YadavNo ratings yet
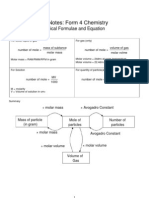
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument14 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationanisnazihahNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 Revision NotesMd TaaseenNo ratings yet
- Nitric oxide-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesNitric oxide-WPS Officemanas mallikNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument27 pagesNitric Acidaanika5411No ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument6 pagesAcid Base and SaltRajnish kumarNo ratings yet
- Acids - 2Document2 pagesAcids - 2Anushka ShendageNo ratings yet
- Industrial Inorganic ChemistryDocument17 pagesIndustrial Inorganic ChemistryMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Answer KeyDocument6 pagesNitric Acid Answer KeyGurjapsingh SandhuNo ratings yet
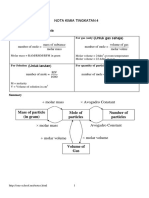
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationJasmeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Wan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffDocument33 pagesWan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffThilagavathyNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument48 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionDavid MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Practicle Org ChemistryDocument8 pagesPracticle Org ChemistryjjknarutotokyoNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document12 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4api-292313678No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis (XII)Document18 pagesSalt Analysis (XII)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument21 pagesNitric AcidLATHA JANARTHANANNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Document28 pagesChapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Aditya VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document14 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Heng HoweNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Acids, Bases and Salts: PropertiesDocument2 pagesChapter-2 Acids, Bases and Salts: PropertiesAkASHNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Semester 2Document11 pagesNitric Acid Semester 2Aditya M GuptaNo ratings yet
- P-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)Document42 pagesP-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)hsjbsjsNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Gas:: Other Endothermic ReactionsDocument7 pagesEvolution of Gas:: Other Endothermic Reactionssara parkNo ratings yet
- D BlockDocument20 pagesD BlockRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- General EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral EquationsPyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- Study of Components Sulphuric AcidDocument4 pagesStudy of Components Sulphuric AcidKavya YadavNo ratings yet
- Quiz ChemDocument4 pagesQuiz ChemCherryNo ratings yet
- 4 Acid, Base and SaltDocument8 pages4 Acid, Base and Saltjosephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- Chang Chap 4Document72 pagesChang Chap 4MR no oneNo ratings yet
- Word Equation PracticeDocument20 pagesWord Equation PracticePrimoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Chemical Word: EquationsDocument20 pagesChemistry: Chemical Word: EquationsPrimoNo ratings yet
- Acid, Bases and Salts - NotesDocument5 pagesAcid, Bases and Salts - NotespritiNo ratings yet
- Cations ReactionsDocument33 pagesCations ReactionsValentino AndreNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 Simplifed NotesDocument15 pagesChemistry 10 Simplifed NotesFaina VeraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Class XDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions Class Xaprajita royNo ratings yet
- s.4 Chem Self Study WorkDocument44 pagess.4 Chem Self Study Workmusisi ahmedNo ratings yet
- 100L Lecture 4 SaltsDocument6 pages100L Lecture 4 SaltsMichael EhondorNo ratings yet
- Csec Identification of Cations and AnionsDocument6 pagesCsec Identification of Cations and AnionsDarrion BruceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Name: Azad Abdullahi Class: Ss3S Teacher: Mr. AdekunleDocument14 pagesChemistry Project: Name: Azad Abdullahi Class: Ss3S Teacher: Mr. Adekunleapi-383198550% (2)
- IoneqwrkshtDocument2 pagesIoneqwrkshtpixniteplayzNo ratings yet
- Grade: 8 B & G Revison Work Sheet (Answers) ChemistryDocument5 pagesGrade: 8 B & G Revison Work Sheet (Answers) Chemistrysanaboumohamed24No ratings yet
- Sülfürik AsitDocument5 pagesSülfürik Asitsamet şenNo ratings yet
- P-Block Board Youtube Part-2Document53 pagesP-Block Board Youtube Part-2vaibhav sainiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument8 pagesCirculatory System Notesthe lillyNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry-1Document7 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry-1the lillyNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)Document22 pagesTranspiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- WS On Circulatory System PDFDocument5 pagesWS On Circulatory System PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument3 pagesAbsorption by Rootsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Diagram-Based QuestionsDocument9 pagesTranspiration Diagram-Based Questionsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocument9 pagesX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Photosynthesis - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-2020) - Unlocked PDFDocument22 pagesCh. 6 - Photosynthesis - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-2020) - Unlocked PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 - Absorption by Roots - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-20) - Unlocked PDFDocument11 pagesCh. 4 - Absorption by Roots - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-20) - Unlocked PDFthe lilly100% (1)
- Absorption by RootsDocument12 pagesAbsorption by Rootsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- (Absorption by Roots - Notes) PDFDocument6 pages(Absorption by Roots - Notes) PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document5 pagesMole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- 05 - BIO IX ICSE Seeds - Structure and Germination PDFDocument6 pages05 - BIO IX ICSE Seeds - Structure and Germination PDFthe lilly0% (1)
- The Flower - BIOLOGY IX ICSEDocument8 pagesThe Flower - BIOLOGY IX ICSEthe lillyNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFDocument5 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Square Root TableDocument4 pagesSquare Root Tablethe lillyNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument6 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document3 pagesSulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Water Resources of India - ICSEDocument11 pagesWater Resources of India - ICSEthe lilly100% (1)
- Injection Moulding Processing Guide To Nylon - Moulding OverviewDocument60 pagesInjection Moulding Processing Guide To Nylon - Moulding OverviewStarchyLittleOleMeNo ratings yet
- Baking Powder Dan VinegarDocument2 pagesBaking Powder Dan VinegarSyakur Hakim PauziNo ratings yet
- Silicon Containing Hybrid Copolymers Synthesis Properties and Applications Zibiao Li All ChapterDocument67 pagesSilicon Containing Hybrid Copolymers Synthesis Properties and Applications Zibiao Li All Chaptercandice.levay987100% (6)
- Advanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFDocument144 pagesAdvanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFdustinthewindNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons. Section 21.1 Introduction To HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesHydrocarbons. Section 21.1 Introduction To HydrocarbonsAhmad asaNo ratings yet
- Block 2 SpectrosDocument27 pagesBlock 2 SpectrosCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: TopicDocument22 pagesAgriculture: TopicRajendra WakchaureNo ratings yet
- Fire RetardantDocument26 pagesFire Retardantrahul raj100% (1)
- Ondina 15Document2 pagesOndina 15Milos Stojanovic100% (1)
- Novel Formulation and Evaluation Herbal Based Lotion For The Antimicrobial and Antifungal PropertiesDocument9 pagesNovel Formulation and Evaluation Herbal Based Lotion For The Antimicrobial and Antifungal PropertiesMr.S. p.royNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nanotechnology in Edible Oils and FatDocument35 pagesApplications of Nanotechnology in Edible Oils and FatmmkharatNo ratings yet
- Functionality of Barley Proteins Extracted and Fractionated by Alkaline and Alcohol MethodsDocument10 pagesFunctionality of Barley Proteins Extracted and Fractionated by Alkaline and Alcohol MethodsMarcela Jarpa ParraNo ratings yet
- Plastics in Dentistry and EstrogenicityDocument144 pagesPlastics in Dentistry and EstrogenicitySurya TejaNo ratings yet
- PRODUCT: Mediplex-L Syrup: Manufacturing FormulaDocument7 pagesPRODUCT: Mediplex-L Syrup: Manufacturing FormulaMohammed Zubair100% (1)
- Final Research PaperDocument22 pagesFinal Research PaperSirjules Acoba TelanNo ratings yet
- 2 Vol. 6 Issue 1 RE 1410 IJPSR 2015 Paper 2Document18 pages2 Vol. 6 Issue 1 RE 1410 IJPSR 2015 Paper 2Pedro AugustoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Polarity and Itermolecular ForcesDocument28 pagesModule 5 Polarity and Itermolecular ForcesJhon AlbadosNo ratings yet
- Density of Organic CompoundDocument10 pagesDensity of Organic Compoundcap n3moNo ratings yet
- Liquichek Immunology Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: MétodoDocument2 pagesLiquichek Immunology Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: MétodoJose Adán Abdala PalmaNo ratings yet
- Essay ExplosivesDocument43 pagesEssay ExplosivesOscar PamosNo ratings yet
- Question 16 - Carbocations Can Be Stabilized (Lowe... - CheggDocument3 pagesQuestion 16 - Carbocations Can Be Stabilized (Lowe... - CheggAD DNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes - Class 7 - Science - Nutrition in PlantsDocument7 pagesAdditional Notes - Class 7 - Science - Nutrition in PlantsTestEmailForScribd TestEmailForScribdNo ratings yet
- Thesis-Huda SalamDocument142 pagesThesis-Huda SalamA1234 AJEFNo ratings yet
- Ketjenlube 16 PDSDocument1 pageKetjenlube 16 PDSDarius IraniNo ratings yet
- Production of Bioethanol From Guinea Cornhusk and Millet HuskDocument7 pagesProduction of Bioethanol From Guinea Cornhusk and Millet HuskaoiNo ratings yet
- Biosafety CabinetsDocument8 pagesBiosafety CabinetsTheeya Gallar OlbinarNo ratings yet
- Nima Mohammadi Chem Homework Chapter 14Document5 pagesNima Mohammadi Chem Homework Chapter 14Nima MohammadiNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionGedamu KurabachewNo ratings yet
- Chap03 CarbonylsDocument10 pagesChap03 CarbonylsAPLCTNNo ratings yet