Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Todua Fridon
Todua Fridon
Uploaded by
Tengiz VerulavaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Todua Fridon
Todua Fridon
Uploaded by
Tengiz VerulavaCopyright:
Available Formats
saqarT velos mecn ierebaTa erovnu li ak ad em iis moam be, t.
9, #1, 20 15
BULL ET IN OF THE GEORGIAN NATIONAL ACADEM Y OF SCIENCE S, vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
Medical Sciences
Cancer Incidence and Mortality - Major Patterns in
GLOBOCAN 2012, Worldwide and Georgia
Fridon Todua*, Rezo Gagua**, Marina Maglakelidze§,
David Maglakelidze§§
* Academy Member, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Tbilisi
**Department of Thoral Surgery, Universal Medical Centre, Tbilsi
§
Department of Oncology, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Tbilisi
§§
Faculty of Medicine, David Tvildiani Medical University, Tbilisi
ABSTRACT. Estimates of the worldwide incidence and mortality from 27 major cancers and for all
cancers combined for 2012 are now available in the GLOBOCAN series of the WHO International
Agency for Research on Cancer. We review the sources and methods used in compiling the national
cancer incidence and mortality estimates, and briefly describe the key results by cancer site worldwide
and in Georgia. Overall, there were 14.1 million new cases and 8.2 million deaths in 2012. More than
12000 new cancer cases and more than 7000 deaths were estimated in 2012 in Georgia. © 2015 Bull.
Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci.
Key words: cancer, incidence, mortality, prevalence.
Cancer Worldwide deaths occur in countries at a low or medium level of
Incidence. Cancer is a leading cause of disease world- the Human Development Index (HDI).
wide. The estimated 14.1 million new cancer cases Prevalence. 32.5 million people diagnosed with can-
occurred in 2012. Lung, female breast, colorectal and cer within the five years previously were alive at the
stomach cancers accounted for more than 40% of all end of 2012. Most were women after their breast can-
cases diagnosed worldwide. In men, lung cancer was cer diagnosis (6.3 million), men after their prostate
the most common cancer (16.7% of all new cases in cancer diagnosis (3.9 million), and men and women
men). Breast cancer was by far the most common after their colorectal cancer diagnosis (3.5 million).
cancer diagnosed in women (25.2% of all new cases Healthy Years of Life Lost (or Disability Adjusted
in women) [1,2,3]. Life Years, DALYs) - are the sum of life years lost to
Mortality. Cancer is a leading cause of death world- premature mortality (deaths before the age of 80 years
wide, with 8.2 million deaths in 2012. More than half for males and 82.5 for females) and the years lived
of all cancer deaths each year are due to lung, stom- with disability, given as a number or as a standard-
ach, liver, colorectal and female breast cancers. Ap- ised rate per 100,000).
proximately 44% of cancer cases and 53% of cancer The estimated 169.3 million years of healthy life
© 2015 Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci.
Cancer Incidence and Mortality - Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012 ... 169
Table 1. Estimated incidence, mortality and 5-year prevalence: Georgia, both sexes
Incidence Mortality 5-year prevalence
Cancer Number (%) ASR (W) Number (%) ASR (W) Number (%) Prop.
Lip, oral cavity 205 1.7 2.6 63 0.9 0.8 443 1.8 12.3
Nasopharynx 57 0.5 0.9 27 0.4 0.4 102 0.4 2.8
Other pharynx 103 0.8 1.4 70 1 0.9 209 0.8 5.8
Oesophagus 48 0.4 0.6 45 0.6 0.6 41 0.2 1.1
Stomach 711 5.8 9.6 597 8.2 7.6 864 3.5 24
Colorectum 605 4.9 8.5 350 4.8 4.6 1239 5 34.5
Liver 439 3.6 6 421 5.8 5.4 248 1 6.9
Gallbladder 35 0.3 0.5 33 0.5 0.4 45 0.2 1.3
Pancreas 182 1.5 2.3 177 2.4 2.2 121 0.5 3.4
Larynx 416 3.4 5.7 158 2.2 2.1 1059 4.3 29.5
Lung 1129 9.1 15.9 1011 14 13.9 934 3.8 26
Melanoma of skin 105 0.8 1.7 38 0.5 0.5 240 1 6.7
Breast 1541 13 44 530 7.2 13.2 5060 21 260
Cervix uteri 425 3.4 14.2 200 2.7 5.7 1122 4.5 57.7
Corpus uteri 432 3.5 14.2 147 2 3.9 1584 6.4 81.5
Ovary 128 1 3.7 82 1.1 2.1 304 1.2 15.6
Prostate 570 4.6 18.6 278 3.8 7.6 1407 5.7 85.3
Testis 82 0.7 3.3 28 0.4 1 278 1.1 16.9
Kidney 167 1.4 2.7 104 1.4 1.6 351 1.4 9.8
Bladder 331 2.7 4.1 133 1.8 1.5 813 3.3 22.6
Brain, nervous system 610 4.9 8.5 352 4.8 4.6 880 3.6 24.5
Thyroid 88 0.7 1.7 26 0.4 0.4 209 0.8 5.8
Hodgkin lymphoma 69 0.6 1.1 29 0.4 0.4 174 0.7 4.8
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma 148 1.2 2.6 91 1.2 1.4 239 1 6.7
Multiple myeloma 35 0.3 0.6 26 0.4 0.4 42 0.2 1.2
Leukaemia 214 1.7 3.3 161 2.2 2.3 194 0.8 5.4
All cancers excl. non-
12361 100 181 7319 100 97.9 24708 100 688
melanoma skin cancer
Incidence and mortality data for all ages. 5-year prevalence for adult population only.
ASR (W) and proportions per 100,000.
Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
170 Fridon Todua, Rezo Gagua, Marina Maglakelidze ...
Incidence Incidence
Lung Breast
Prostate Corpus uteri
Stomach Cervix uteri
Larynx Brain, CNS
Colo-rectal Stomach
Brain, CNS Colo-rectal
Bladder Lung
Liver Liver
Lip, oral cavity Ovary
Other and Other and
unspecified unspecified
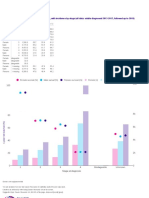
Fig. 1. Most frequent cancers (ranking defined by total number of cases) in men and women. Georgia, 2012.
were lost globally because of cancer in 2008. Colorectal, States of America, Ireland, Republic of Korea
lung, female breast and prostate cancers were the main and The Netherlands).
contributors in most regions of the world, explaining · The countries in the top ten come from
18%-50% of the total healthy years lost. Europe, Oceania, Northern America and Asia.
Men
World Cancer Trends
· The highest cancer rate was found in France
Approximately 44% of cancer cases and 53% of can- with 385 men per 100,000 being diagnosed in
cer deaths occur in countries at a low or medium level 2012.
of the HDI. · The age-standardised rate was at least 350
As low HDI countries become more developed per 100,000 in eight countries (France, Aus
through rapid societal and economic changes, they tralia, Norway, Belgium, Martinque, Slovenia,
are likely to become “westernised”. As such, the pat- Hungary and Denmark).
tern of cancer incidence is likely to follow that seen · The countries in the top ten come from
in high HDI settings, with likely declines in cervix Europe, Oceania and the Americas.
uteri and stomach cancer incidence rates, alongside Women
increasing incidence rates of female breast, prostate · The highest cancer rate was found in Den
and colorectal cancers. This “westernisation” effect mark with 329 women per 100,000 being diag
is a result of reductions in infection-related cancers, nosed in 2012.
outweighed by an increasing burden of cancers more · The age-standardised rate was at least 280
associated with reproductive, dietary and hormonal per 100,000 for Denmark, United States of
risk factors[1, 2, 3]. America, Republic of Korea, The Netherlands
Data for cancer frequency by country. Age-stand- and Belgium.
ardised rate for all cancers (excluding non-melanoma · The countries in the top ten come from
skin cancer) ordered by the countries with the 50 Europe, Oceania, Asia and Northern America.
highest rates. This factsheet would not have been possible with-
Both sexes out the data collected and available from population-
· The highest cancer rate for men and women based cancer registries. Knowledge about the can-
together was found in Denmark with 338 cer burden enables the development, implementation,
people per 100,000 being diagnosed in 2012. monitoring and evaluation of cancer strategies that
· The age-standardised rate was at least 300 prevent, cure and care. This knowledge lacks in many
per 100,000 for nine countries (Denmark, low- and middle income countries, making cancer
France, Australia, Belgium, Norway, United control efforts less effective [4, 5].
Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
Cancer Incidence and Mortality - Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012 ... 171
Mortality Mortality
Lung Breast
Prostate Corpus uteri
Stomach Cervix uteri
Larynx Brain, CNS
Colo-rectal Stomach
Brain, CNS Colo-rectal
Bladder Lung
Liver Liver
Lip, oral cavity Ovary
Other and Other and
unspecified unspecified
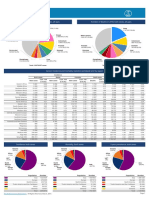
Fig. 2. Most frequent cancer death in men and women. Georgia, 2012
Projections to 2030 than 30 new cancer diagnoses each day.
If recent trends in major cancers are seen globally in Figure 1 indicates the most common cancers esti-
the future, the burden of cancer will increase to 23.6 mated to occur in men and women in 2012. Among
million new cases each year by 2030. This represents men, cancers of the lung and bronchus, prostate,
an increase of 68% compared with 2012 (66% in low stomach, larynx and colorectum account for about
and medium HDI countries and 56% in high and very 50% of all newly diagnosed cancers. Lung cancer
high HDI countries). In the European Union, there alone accounts for 15% (931) of incident cases in
are currently an estimated 2.66 million new cancer men. The 3 most commonly diagnosed types of can-
cases and 1.28 million cancer-related deaths per year. cer among women in 2012 were breast, corpus uteri
Moreover, due to the effects of population growth and cervix uteri, accounting for one-half of all cases
and ageing, the burden of cancer in Europe is projected in women. Breast cancer alone accounts more than
to increase in the coming years and decades [1]. 25% (1541) of all new cancers among women.
Figure 2 also shows the estimated numbers of
Cancer in Georgia deaths from cancer for 2012. It is estimated that about
The International Agency for Research on Cancer 7319 Georgians died from cancer per year, correspond-
(IARC), the specialized cancer agency of the World ing to about 20 deaths per day. Cancers of the lung
Health Organization (WHO) estimated the numbers and bronchus, prostate, and stomach in men and can-
of new cancer cases and deaths that occurred in the cers of the lung and bronchus, breast, and colorectum
World and published the most recent data on inci- in women continue to be the most common causes of
dence, mortality, and survival by populations and cancer death. These 4 cancers account for almost
cancers. This data can be used as a resource for can- half of the total cancer deaths among men and women,
cer control planning at the state level, as well as to with more than one-quarter of all cancer deaths due
address questions from the media or constituents. to lung cancer.
They are encouraged to use it with state and local Risk of getting cancer before age 75 (%)* in popu-
officials, reporters, and other public health and ad- lation of Georgia is 18.7% (22.0% among men and
vocacy groups in local communities. 16.2% among women).
According to the latest WHO/IARC data, pub- Risk of dying from cancer before age 75 (%)* in
lished in February 2014, there were more than 12.000 population of Georgia is 10.9% (14.2% among men
new cancer cases in Georgia in 2012 [1]. and 10.3% among women).
Table 1 presents the estimated numbers of new *The probability or risk of individuals dying from
cases of invasive cancer in Georgia in 2012. The overall cancer. It is expressed as the number of new born
estimate of 12361 new cases is the equivalent of more children (out of 100), who would be expected to de-
Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
172 Fridon Todua, Rezo Gagua, Marina Maglakelidze ...
velop/die from cancer before the age of 75, if they alongside the description of the varying distribution
had cancer rates (in the absence of other causes of of common cancers at both the regional and countries
death). level provide a basis for establishing priorities to can-
Conclusion. This estimation of cancer incidence would cer control actions. The important role of cancer regis-
not be possible without population-based cancer reg- tries in disease surveillance and in planning and evalu-
istries functioning in many European countries. ating national cancer plans is becoming increasingly
These up-to-date estimates of the cancer burden recognised and needs to be further advocated.
samedicino mecnierebani
kiboTi avadoba da sikvdiloba - GLOBOCAN
2012-is ZiriTadi maCveneblebi (msoflio da
saqarTvelo)
f. Todua*, r. gagua**, m. maRlakeliZe§, d. maRlakeliZe§§
* akademiis wevri, klinikuri medicinis samecniero-kvleviTi instituti, Tbilisi
**universaluri samedicino centri, Torakaluri qirurgiis ganyofileba, Tbilisi
§
klinikuri medicinis samecniero-kvleviTi instituti, onkologiis departamenti, Tbilisi
§§
daviT tvildianis saxelobis samedicino universiteti, medicinis fakulteti, Tbilisi
27 ZiriTadi lokalizaciis da yvela avTvisebiani simsivneebis avadobisa da sikvdilobis
gaangariSebuli maCveneblebi ukve xelmisawvdomia jandacvis msoflio organizaciis kibos
kvlevis saerTaSoriso saagentos GLOBOCAN-is gamocemebSi. Cven mier mimoxilul iqna
is uaxlesi wyaroebi da meTodebi, romlebic gamoiyeneba kibos avadobisa da sikvdilobis
regionuli maCveneblebis daTvlisas da mokled aRwerilia is ZiriTadi Sedegebi, rac
dafiqsirda mTlianad msofliosa da saqarTvelos masStabiT. globalurad, 14,1 mln
kibos axali SemTxveva da 8,2 mln sikvdili (letaloba) iyo dafiqsirebuli msoflioSi
2012 wels, xolo saqarTveloSi - 12000-ze meti axali da daaxloebiT 7300 letaluri
SemTxveva.
Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
Cancer Incidence and Mortality - Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012 ... 173
REFERENCES
1. Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Ervik M., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M., Parkin DM., Forman D.,
Bray F., GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon,
France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2014. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
2. World Health Report (2013) Research for universal health coverage
3. World Cancer Report (2014) Edited by Bernard W. Stewart and Christopher P. Wild. International Agency for
Research of Cancer/WHO.
4. http://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/data-cancer-frequency-country.
5. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Volume X, 2014.
Received November, 2014
Bull. Georg. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 9, no. 1, 2015
You might also like
- Truss Analysis and Shear Centre Lab ReportDocument33 pagesTruss Analysis and Shear Centre Lab ReportHamoodNo ratings yet
- ISA Brown Management GuideDocument18 pagesISA Brown Management Guidexman17us100% (3)
- Pearlin The Sociological Study of StressDocument17 pagesPearlin The Sociological Study of StressTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2007 National Cancer InstituteDocument41 pagesSEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2007 National Cancer Institutetoots2011No ratings yet
- 40 Austria Fact SheetsDocument3 pages40 Austria Fact Sheetsopiakelvin2017No ratings yet
- Reflection About Oral Health and Cancer AwarenessDocument2 pagesReflection About Oral Health and Cancer Awarenesscris addunNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer in India: D BeheraDocument7 pagesLung Cancer in India: D Beherajeevan georgeNo ratings yet
- CP On Breast CancerDocument100 pagesCP On Breast Cancerkathy50% (2)
- GastricDocument207 pagesGastricfavo riteNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Cancer RegistryDocument22 pagesMumbai Cancer RegistryKrishna Sireesha SNo ratings yet
- Public Health 150: Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument101 pagesPublic Health 150: Non-Communicable DiseasesCandra BumiNo ratings yet
- CINA Deluxe DQP SSFs For Prostate Cancer 2011 2015Document6 pagesCINA Deluxe DQP SSFs For Prostate Cancer 2011 2015MayNo ratings yet
- Case Ana Pancreatic CaDocument21 pagesCase Ana Pancreatic CakingpinNo ratings yet
- SLS TrendsDocument29 pagesSLS TrendsSohaib Mohammad KhanNo ratings yet
- CINA Deluxe DQP Unknown DxConf For Brain Tumor Years 2012 2016 Updated 2-24-2020Document10 pagesCINA Deluxe DQP Unknown DxConf For Brain Tumor Years 2012 2016 Updated 2-24-2020MayNo ratings yet
- Deteksi Dini Kanker PayudaraDocument43 pagesDeteksi Dini Kanker PayudaraLaeli Nur MaeniNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Cervical CancerDocument27 pagesNatural History of Cervical CancerAri AsriniNo ratings yet
- Canine and Feline Liver Cytology Carlo Masserdotti Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCanine and Feline Liver Cytology Carlo Masserdotti Full Chapterrosanne.hahn846100% (8)
- Kanker Payudara: Epidemiologi Penyebab Dan Faktor Resiko Gejala Dan Tanda Stadium Tindak LanjutDocument46 pagesKanker Payudara: Epidemiologi Penyebab Dan Faktor Resiko Gejala Dan Tanda Stadium Tindak LanjutAulia DYAH FEBRIANTINo ratings yet
- Liver Cancer (C22) : 2000-2007: Age-Standardised Five-Year Relative Survival, Adults (Aged 15+), European CountriesDocument8 pagesLiver Cancer (C22) : 2000-2007: Age-Standardised Five-Year Relative Survival, Adults (Aged 15+), European CountriesVelibor VasovicNo ratings yet
- Christy 3Document1 pageChristy 3api-300767876No ratings yet
- Knowledge Attitude About Breast Cancer and PracticDocument7 pagesKnowledge Attitude About Breast Cancer and PracticBùi Thảo LyNo ratings yet
- PN PDFDocument59 pagesPN PDFAmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa2007621 AppendixDocument11 pagesNejmoa2007621 AppendixhdjebarNo ratings yet
- Common Cancer in MenDocument6 pagesCommon Cancer in MenomeirNo ratings yet
- A Review of Ear, Nose and Throat Foreign Bodies in Sarawak General Hospital. A Five Year ExperienceDocument4 pagesA Review of Ear, Nose and Throat Foreign Bodies in Sarawak General Hospital. A Five Year ExperienceChlo14No ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Challenges and Opportunities in Pediatric Patients of Saiful Anwar General Hospital MalangDocument33 pagesThalassemia: Challenges and Opportunities in Pediatric Patients of Saiful Anwar General Hospital MalangdanyfaridaNo ratings yet
- M7. MIII. O6a. Screening de CADocument29 pagesM7. MIII. O6a. Screening de CARogerio FernandesNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Hematological Findings On "Degnala", A Disease of Buffalo in Eastern NepalDocument4 pagesClinical and Hematological Findings On "Degnala", A Disease of Buffalo in Eastern NepalRamesh JØshiNo ratings yet
- DR. PAUL REGANIT - Nutrition Lecture March 1Document49 pagesDR. PAUL REGANIT - Nutrition Lecture March 1Sophie RoseNo ratings yet
- NCR 2017 MoH Final Report Nov 2018 10.12.2018Document33 pagesNCR 2017 MoH Final Report Nov 2018 10.12.2018Veden SoobenNo ratings yet
- Safe Motherhood Project Updated PresentationDocument43 pagesSafe Motherhood Project Updated Presentationmohamedamiinhassan6No ratings yet
- CINA Deluxe DQP For Breast ER PR and Her2 Prognostic Factors Manxia 2 9 ..Document12 pagesCINA Deluxe DQP For Breast ER PR and Her2 Prognostic Factors Manxia 2 9 ..MayNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Cancer StatisticsDocument136 pagesMalaysia Cancer Statisticsdigital896100% (1)
- Articles of Thai AlcoholicDocument4 pagesArticles of Thai Alcoholicsatrio_utamaNo ratings yet
- Stomach One Year Survival NewDocument5 pagesStomach One Year Survival NewVelibor VasovicNo ratings yet
- 39 All Cancers Fact SheetDocument2 pages39 All Cancers Fact SheetRobertOktaChandraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ReadingDocument18 pagesJurnal ReadingYohanis Primus SongmenNo ratings yet
- Srep 40521Document10 pagesSrep 40521Luz María NBNo ratings yet
- Gait Speed and Survival JAMA 2011Document9 pagesGait Speed and Survival JAMA 2011Priscila DanieleNo ratings yet
- Cancer Statistics, 2014Document21 pagesCancer Statistics, 2014ikhyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To CancerDocument42 pagesAn Introduction To CancerAmjadRashidNo ratings yet
- Anemia en RNDocument21 pagesAnemia en RNDaniel Martinez DiazNo ratings yet
- Annie Anderson Obesity The Elephant in The RoomDocument18 pagesAnnie Anderson Obesity The Elephant in The RoomVignesh JayaNo ratings yet
- Inter HeartDocument40 pagesInter HeartEvangeline SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 69 Current Philippine Health SituationDocument51 pages69 Current Philippine Health SituationkatlisayNo ratings yet
- Ichthyptoxic ARF After Fish Gallbladder IngestionDocument5 pagesIchthyptoxic ARF After Fish Gallbladder IngestionLê Mỹ Khánh LyNo ratings yet
- Hiperbar O2Document22 pagesHiperbar O2Zekany AndreiNo ratings yet
- Staa 04 EpidemiologyofchildhoodfracturesinbritiainDocument6 pagesStaa 04 Epidemiologyofchildhoodfracturesinbritiainanon_634779017No ratings yet
- Kanker Growtf Factor Dan Tirosin KinaseDocument142 pagesKanker Growtf Factor Dan Tirosin KinaseNovi KhamiliaNo ratings yet
- Oijesity: W I SP Ec e - ExDocument5 pagesOijesity: W I SP Ec e - ExtangledprincessNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit of ChickensDocument5 pagesHematocrit of ChickensRowzFerlTanutanNo ratings yet
- NE Cancer03Document7 pagesNE Cancer03jamesyu100% (1)
- 15 Lung Fact Sheet PDFDocument2 pages15 Lung Fact Sheet PDFFrancess LeveauNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Malariae: Parasite and Disease: William E. Collins and Geoffrey M. JefferyDocument14 pagesPlasmodium Malariae: Parasite and Disease: William E. Collins and Geoffrey M. JefferyReynaldi FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- 13 Uterine Cervix - Libre PathologyDocument21 pages13 Uterine Cervix - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- Pathology for Toxicologists: Principles and Practices of Laboratory Animal Pathology for Study PersonnelFrom EverandPathology for Toxicologists: Principles and Practices of Laboratory Animal Pathology for Study PersonnelElizabeth McInnesNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer Therapy - What You Must KnowFrom EverandProstate Cancer Therapy - What You Must KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Body Fluids in Small Animal CytologyFrom EverandDifferential Diagnosis of Body Fluids in Small Animal CytologyNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance in GermanyDocument4 pagesHealth Insurance in GermanyTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Ejm 47374 Original - Article PurutDocument7 pagesEjm 47374 Original - Article PurutTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Does Insurance Market Activity Promote Economic GrowthDocument27 pagesDoes Insurance Market Activity Promote Economic GrowthTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- ვაქცინაცია სტუდებტებშDocument6 pagesვაქცინაცია სტუდებტებშTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Important During Acute HospitalisationDocument13 pagesImportant During Acute HospitalisationTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- ReviuDocument8 pagesReviuTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- IDU062 B 1Document62 pagesIDU062 B 1Tengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- მშობლების უარი ბავშვების ვაქცინაციაზეDocument7 pagesმშობლების უარი ბავშვების ვაქცინაციაზეTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy Among Primary Healthcare Workers in SingaporeDocument9 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy Among Primary Healthcare Workers in SingaporeTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- სტუდენტების ცოდნა კოვიდ 19Document13 pagesსტუდენტების ცოდნა კოვიდ 19Tengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of Affective DisordersDocument20 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of Affective DisordersTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Employment As Experienced by Disabled People: A Qualitative Analysis in Calgary and Regina, CanadaDocument15 pagesBarriers To Employment As Experienced by Disabled People: A Qualitative Analysis in Calgary and Regina, CanadaTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- FMPCR Art 42280-10Document6 pagesFMPCR Art 42280-10Tengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- 4 McDonald Hernandez McDonald Et Al ERRJ 2008Document8 pages4 McDonald Hernandez McDonald Et Al ERRJ 2008Tengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Mood Disorders in Patients Undergoing Cardiac SurgeryDocument6 pagesPreoperative Mood Disorders in Patients Undergoing Cardiac SurgeryTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Health Care Market Deviations From The Ideal MarkeDocument11 pagesHealth Care Market Deviations From The Ideal MarkeTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Access To Employment in Kenya: The Voices of Persons With DisabilitiesDocument11 pagesAccess To Employment in Kenya: The Voices of Persons With DisabilitiesTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction Among Public Sector PhyDocument94 pagesJob Satisfaction Among Public Sector PhyTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Change Management in An Environment of Ongoing Primary Health Care System Reform A Case Study in AustraliaDocument13 pagesChange Management in An Environment of Ongoing Primary Health Care System Reform A Case Study in AustraliaTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles of Military Hospital ManagersDocument7 pagesLeadership Styles of Military Hospital ManagersTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Telephone Consultation in Primary Health Care During COVID-19 PandemicDocument8 pagesThe Use of Telephone Consultation in Primary Health Care During COVID-19 PandemicTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss Within A Marriage Perceptions of The Spouse With Normal HearingDocument8 pagesHearing Loss Within A Marriage Perceptions of The Spouse With Normal HearingTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- School Management SystemDocument12 pagesSchool Management Systemxx9No ratings yet
- Step 7 Err Code125936644Document37 pagesStep 7 Err Code125936644mohammadNo ratings yet
- DUBAI International Business PPT-2Document30 pagesDUBAI International Business PPT-2vignesh vikeyNo ratings yet
- SNAKE PLANT (Sansevieria Trifasciata) FIBER AS A POTENTIAL SOURCE OF PAPERDocument38 pagesSNAKE PLANT (Sansevieria Trifasciata) FIBER AS A POTENTIAL SOURCE OF PAPERandrei100% (1)
- Order SchedulingDocument26 pagesOrder Schedulingabhishek_s_gupta4753100% (1)
- Drills MSDocument5 pagesDrills MSTomzki CornelioNo ratings yet
- Assignement 2Document3 pagesAssignement 2Ma Vanessa Rose TacuyanNo ratings yet
- LKPD IDocument5 pagesLKPD Isri rahayuppgNo ratings yet
- WLC UpgradeDocument13 pagesWLC Upgradeapi-3703368No ratings yet
- (Lesson2) Cultural, Social, and Political Institutions: Kinship, Marriage, and The HouseholdDocument5 pages(Lesson2) Cultural, Social, and Political Institutions: Kinship, Marriage, and The HouseholdPlat JusticeNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyNguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- L.chandra Vs Union of IndiaDocument15 pagesL.chandra Vs Union of IndiaKashish GaurNo ratings yet
- Sample Term PaperDocument15 pagesSample Term Paperalchwarizmi abubakarNo ratings yet
- R19M TECHThermalEnggISemDocument32 pagesR19M TECHThermalEnggISemSuchiNo ratings yet
- Tony Thrasher (Editor) - Emergency Psychiatry (PRIMER ON SERIES) - Oxford University Press (2023)Document537 pagesTony Thrasher (Editor) - Emergency Psychiatry (PRIMER ON SERIES) - Oxford University Press (2023)Stefan100% (1)
- Nishan SahibDocument2 pagesNishan SahibthelangarhallNo ratings yet
- Game Theory - Course Outline 2021Document4 pagesGame Theory - Course Outline 2021Mayank RanjanNo ratings yet
- Use of Realism in Mulk Raj Anand's Novels: Karan SharmaDocument2 pagesUse of Realism in Mulk Raj Anand's Novels: Karan SharmasirajahmedsNo ratings yet
- McDonald Family History v35Document45 pagesMcDonald Family History v35David McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Miss Gee by AudenDocument5 pagesMiss Gee by AudenVandana100% (1)
- Jadual Alimah 2021.V3Document6 pagesJadual Alimah 2021.V3maryam cookNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR Root Words ChartDocument1 pageGRAMMAR Root Words ChartbonruizNo ratings yet
- Hvpe Syl andDocument9 pagesHvpe Syl andosho_peaceNo ratings yet
- Stricklin I WOULD NOT...Document17 pagesStricklin I WOULD NOT...Karl LammNo ratings yet
- 21 Days Prayer Fasting RiversideDocument5 pages21 Days Prayer Fasting RiversideAnaPereiraNo ratings yet
- PD60009511 - 000 Quorum Class TrainingDocument2 pagesPD60009511 - 000 Quorum Class Trainingperaldo24No ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument9 pagesMarketing ManagementShashi mehtaNo ratings yet
- FIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyDocument2 pagesFIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyAlexMartinNo ratings yet