Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Uploaded by
Dzois DzoisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Do Schools Kill CreativityDocument13 pagesDo Schools Kill CreativityIrfanul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning: SPARK Your InterestDocument49 pagesAssessment of Learning: SPARK Your InterestMaria Angelica Martinez79% (19)
- Personalized Learning Plan (PLP) For Gifted & Talented Learner)Document6 pagesPersonalized Learning Plan (PLP) For Gifted & Talented Learner)Square JjNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Action VerbsDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonomy Action VerbsMR SIVAKUMAR TNo ratings yet
- The Blue-Print of ASSURE Instructional ModelsDocument3 pagesThe Blue-Print of ASSURE Instructional ModelsFery AshantiNo ratings yet
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumFrom EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumNo ratings yet
- Curriculum InnovationsDocument7 pagesCurriculum InnovationsAngelo LabadorNo ratings yet
- DALIG PPAs Accomplishment Report LONGDocument5 pagesDALIG PPAs Accomplishment Report LONGAiza Sillano100% (2)
- Performance Improvement Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesPerformance Improvement Plan TemplateSimao AndreNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy VerbsDocument2 pagesBlooms Taxonomy VerbsrevarzuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Learning in Affective and Psychomotor DomainDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Learning in Affective and Psychomotor DomainRodrick Sonajo RamosNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers: Gina O. Gonong Director, Research Center For Teacher QualityDocument52 pagesThe Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers: Gina O. Gonong Director, Research Center For Teacher QualityRush JaimeerNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDocument28 pagesLearning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDr. Azadeh AsgariNo ratings yet
- Core Principles of Effective AssessmentDocument6 pagesCore Principles of Effective AssessmentIrene Futalan LastimosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4Jack FrostNo ratings yet
- Properties of Assessment Method: ValidityDocument30 pagesProperties of Assessment Method: ValidityDANIEL LANCE RESPONTE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning: Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentDocument12 pagesFacilitating Learning: Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentRachelle YuNo ratings yet
- Handout Module6Document69 pagesHandout Module6Oana MirceaNo ratings yet
- EMA 511 Syllabus - Fall 2020Document27 pagesEMA 511 Syllabus - Fall 2020Sharney WilksNo ratings yet
- The Learner Centered ClassroomDocument16 pagesThe Learner Centered ClassroomJanine CanlasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategy Definition Teaching MethodDocument5 pagesTeaching Strategy Definition Teaching Methodmitchbitch69No ratings yet
- Development and Assessment: CurriculumDocument102 pagesDevelopment and Assessment: CurriculumNanatsu SensieNo ratings yet
- Tsl3109 PPG Module Managing The Primary Esl ClassroomDocument154 pagesTsl3109 PPG Module Managing The Primary Esl ClassroomARINI100% (1)
- Nick VujicicDocument4 pagesNick VujicicJosephine ReyNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument15 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of TeachingMark Pasang Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in ADM Content Evaluation RegionDocument7 pagesGuidelines in ADM Content Evaluation RegionCARMEL GRACE SIMAFRANCA100% (2)
- The Competent TeacherDocument9 pagesThe Competent TeacherjessaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Chapter 4F StudentsDocument34 pagesLesson 4 Chapter 4F StudentsShamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Document21 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Jamena abbasNo ratings yet
- Using Biggs' Model of Constructive Alignment in Curriculum Design:Continued - UCD - CTAGDocument3 pagesUsing Biggs' Model of Constructive Alignment in Curriculum Design:Continued - UCD - CTAG8lu3dz100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument6 pagesConcept Mapapi-3725139No ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 4Document3 pagesModule 5 Lesson 4Vincent Jay BalocaNo ratings yet
- AFFECTIVE TARGETS: AttitudeDocument19 pagesAFFECTIVE TARGETS: AttitudeJaika SedoroNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Describe WDocument3 pagesAnswer:: Describe WAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- The Different Purposes of AssessmentDocument16 pagesThe Different Purposes of AssessmentAlter joy MoralNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Studies Short NotesDocument7 pagesCurriculum Studies Short NotesPraveenNaiduNo ratings yet
- Educ 8 Lesson 2Document5 pagesEduc 8 Lesson 2Jamira Inoc SoboNo ratings yet
- Who Should Be Involved in Curriculum EvaluationDocument5 pagesWho Should Be Involved in Curriculum EvaluationRuth MatrianoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design Instructional Analysis: Needs Analysis WorksheetDocument1 pageInstructional Design Instructional Analysis: Needs Analysis WorksheetSheen AponNo ratings yet
- The Classroom Climate: Reporters: Perandos, Vince Robert L. Laurora, TrishaDocument10 pagesThe Classroom Climate: Reporters: Perandos, Vince Robert L. Laurora, TrishartrengyggNo ratings yet
- Basog, Jemay Module 1and 2 Educ 129 MaamcurdevDocument59 pagesBasog, Jemay Module 1and 2 Educ 129 MaamcurdevJemay BasogNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Learning Outcomes ApproachDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Learning Outcomes ApproachVanessa L. VinluanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Original & Revised Taxonomy PyramidsDocument4 pagesBloom's Original & Revised Taxonomy Pyramidsapi-3836734100% (8)
- Implementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomDocument34 pagesImplementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomHazel LavapizNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1Document27 pagesAssessment in Learning 1Jonalyn RogandoNo ratings yet
- View Your Speaker Notes Privately, While Delivering A Presentation On Multiple Monitors - PowerPointDocument4 pagesView Your Speaker Notes Privately, While Delivering A Presentation On Multiple Monitors - PowerPointKKKNo ratings yet
- InstructionalDesignandTechnologyMicromasters DesignDocument April22022Document14 pagesInstructionalDesignandTechnologyMicromasters DesignDocument April22022Patricia PricopNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 201/1/2020: The Educator As Learning Programme DeveloperDocument11 pagesTutorial Letter 201/1/2020: The Educator As Learning Programme DeveloperRochelle Govender100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Ed123Document3 pagesLesson 2 Ed123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING New MODULESDocument26 pagesASSESSMENT OF LEARNING New MODULESPrincess Sharief100% (2)
- Data Collection and AnalysisDocument4 pagesData Collection and AnalysisEmmanuella MonicaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of Educational ObjectivesDocument7 pagesTaxonomies of Educational ObjectivesrajNo ratings yet
- Misamis Oriental Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument6 pagesMisamis Oriental Institute of Science and TechnologyChristy EXAMINADANo ratings yet
- Top 5 Types of Supervision Available in EducationDocument9 pagesTop 5 Types of Supervision Available in EducationJEVELYN LIBRESNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyDocument1 pageChanges in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Learned BehaviorDocument80 pagesLearned BehaviorAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- San Pablo Colleges Master of Arts in NursingDocument35 pagesSan Pablo Colleges Master of Arts in NursingMike Ong100% (1)
- Project Based ApproachDocument7 pagesProject Based ApproachMarie Belle SembranoNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Training and Adult Education: Data TechnologyDocument37 pagesSkills Framework For Training and Adult Education: Data TechnologyokelloNo ratings yet
- 7 Mindful Assessment ToolsDocument4 pages7 Mindful Assessment ToolsLex HenonNo ratings yet
- Slow LearnersDocument4 pagesSlow LearnersSadiq Merchant100% (7)
- Implementing The CurriculumDocument17 pagesImplementing The CurriculumRosejen Mangubat100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentma_tabora6283No ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument3 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingErwin Labayog MedinaNo ratings yet
- Domains Adjectives For LPDocument4 pagesDomains Adjectives For LPnove quimpoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument4 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingYoleen SirkNo ratings yet
- ID Analisis Kualitas Pengelolaan Kelas PembDocument19 pagesID Analisis Kualitas Pengelolaan Kelas PembMumutTeaNo ratings yet
- 4DX of Execution - SummaryDocument10 pages4DX of Execution - SummaryARLY MAY S. ESPAÑOLNo ratings yet
- Sean Freeman ResumeDocument2 pagesSean Freeman Resumeapi-405746943No ratings yet
- Meet A Senior Reflection EssayDocument2 pagesMeet A Senior Reflection Essayapi-439389090No ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLL ENGLISH 6 Q4 Week 7Document4 pagesGrade 6 DLL ENGLISH 6 Q4 Week 7MA. ASTERIA AGUSTINA CENALNo ratings yet
- An Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Integrated Basic Education Department St. Anne College Lucena, Inc. Lucena CityDocument25 pagesAn Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Integrated Basic Education Department St. Anne College Lucena, Inc. Lucena Cityapril anthonette aguirreNo ratings yet
- The Role of Education in Maintaining Social OrderDocument9 pagesThe Role of Education in Maintaining Social OrderMaria MohammedNo ratings yet
- SeeingStars Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSeeingStars Lesson PlanMaria Maqsoudi-KarimiNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching 1 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMicro Teaching 1 Lesson Planbobbymaf750% (2)
- A Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Physics Students in Laboratory ClassesDocument9 pagesA Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Physics Students in Laboratory ClassesCara Luz BuarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math DLL Week 2 Day 1Document1 pageGrade 10 Math DLL Week 2 Day 1Janrie NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Olive International School, Qatar: SESSION 2020 - 21Document3 pagesOlive International School, Qatar: SESSION 2020 - 21Boban ThomasNo ratings yet
- Action Plan On Learning Continuity in Remote AreasDocument3 pagesAction Plan On Learning Continuity in Remote AreasJulius CudiamatNo ratings yet
- Test ErrorsDocument6 pagesTest ErrorsDasha HalkaNo ratings yet
- IFFA6312 - Activity 3 Touch PointDocument12 pagesIFFA6312 - Activity 3 Touch Pointzmagadla0808No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - PED 104Document8 pagesTopic 3 - PED 104KAETH LAURENCE ORILLA NOTARIONo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 12 Quarter 1Document5 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 12 Quarter 1Precious Gregorio100% (1)
- Philosophy and Professionalism: ©2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Edition Kauchak and EggenDocument4 pagesPhilosophy and Professionalism: ©2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Edition Kauchak and EggenMhae NaragNo ratings yet
- English Home Language ATPDocument8 pagesEnglish Home Language ATPkanimoletsane3No ratings yet
- Bukidnon National High School: Classroom ProgramDocument15 pagesBukidnon National High School: Classroom ProgramMarnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- Study Path ECOFDocument1 pageStudy Path ECOFabcNo ratings yet
- Describing Teachers and Roles of TeachersDocument15 pagesDescribing Teachers and Roles of TeachersBernardus DanibaoNo ratings yet
- (The Correlation of Organizational Role Stressors With Stress Level of ICU NursesDocument18 pages(The Correlation of Organizational Role Stressors With Stress Level of ICU NursesAnggriani Puspita AyuNo ratings yet
- POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES BACHELOR IN BUSINESS TEACHER EDUCATION MAJOR IN BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL YEAR 2012-2013 STUDENT TEACHERS’ THINKING PROCESSES ON ICT INTEGRATION: PREDICTORS OF PROSPECTIVE TEACHING BEHAVIOR WITH EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGYDocument23 pagesPOLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES BACHELOR IN BUSINESS TEACHER EDUCATION MAJOR IN BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL YEAR 2012-2013 STUDENT TEACHERS’ THINKING PROCESSES ON ICT INTEGRATION: PREDICTORS OF PROSPECTIVE TEACHING BEHAVIOR WITH EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGYJhojoy VersozaNo ratings yet
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Uploaded by
Dzois DzoisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 Domains
Uploaded by
Dzois DzoisCopyright:
Available Formats
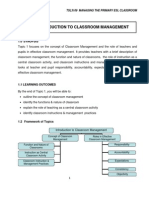
Verbs Reflecting Learning in the Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains
Cognitive Domain
According to various researchers there are six levels of cognitive complexity: knowledge, comprehension,
application, analysis, synthesis, evaluation. In the chart below, note the hierarchical arrangement, which
means that higher levels subsume ability in lower levels. The higher the level, the presumably more
complex mental operation is required. Higher levels are not necessarily more desirable than lower levels,
because one cannot achieve the higher levels without an ability to use the lower levels. As one moves up
into higher levels, however, the more applicable the skills are to those needed in daily life.
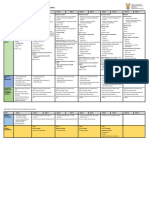
Action Verbs Describing
Level Description Learning Outcomes
Evaluation Requires the formation of judgments and decisions Appraise Judge
about the value of methods, ideas, people, Compare Justify
products. Must be able to state the bases for Contrast Support
judgments (e.g., external criteria or principles used Criticize Validate
to reach conclusions.) Defend
Sample question: Evaluate the quality or worth of
a value as applied to pharmacy.
Synthesis Requires production of something unique or Categorize Devise
original. At this level, one is expected to solve Compile Formulate
unfamiliar problems in unique way, or combine Compose Predict
parts to form a unique or novel solution. Create Produce
Design
Sample question: Integrate data from several
sources (e.g., various readings and observations at
the service site).
Analysis Identification of logical errors (e.g., point out Break down Infer
contradictions, erroneous inference) or differentiate Deduce Outline
among facts, opinions, assumptions, hypotheses, Diagram Point out
conclusions. One is expected to draw relations Differentiate Relate
among ideas and to compare and contrast. Distinguish Separate
out
Sample question: Deduce a client’s beliefs Illustrate Subdivide
regarding preventive health actions.
Application Use previously acquired information in a setting Change Organize
other than the one in which it was learned. Compute Prepare
Because problems at this level are presented in a Demonstrate Relate
different and applied way, one cannot rely on Develop Solve
content or context to solve the problem. Modify Transfer
Operate Use
Sample question: Organize your observations at a
site to demonstrate a particular value.
Comprehension Some degree of understanding is required in order Convert Extend
to change the form of communication, translate, Defend
restate what has been read or heard, see Generalize
connections or relationships among parts of a Discriminate Infer
communication (interpretation), draw conclusions, Distinguish
see consequences from information (inference). Paraphrase
Estimate Predict
Sample Question: Explain pharmaceutical care. Explain
Summarize
Knowledge Remember or recall information such as facts, Define Name
terminology, problem-solving strategies, rules DescribeOutline
[Borich, G.D. (1996). Identify Recall
Effective teaching methods Sample question: Define pharmaceutical care. Label Recite
(3rd Ed.). Englewood cliffs, List Select
NJ: Merrill.] Match State
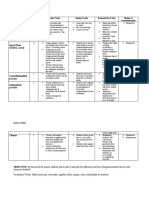
Affective Domain
Like the cognitive domain, the affective domain is hierarchical with higher levels being more complex and
depending upon mastery of the lower levels. With movement to more complexity, one becomes more
involved, committed, and self-reliant. Note the parallel between external and internal motivation. As one
moves from being externally to internally motivated, one moves to higher levels.
Action Verbs Describing
Level Description Learning Outcomes
Characteri- All behavior displayed is consistent with one’s Avoid
zation value system. Values are integrated into a Display
pervasive philosophy that never allows Exhibit
expressions that are out of character with Internalize
those values. Evaluation at this level involves Manage
the extent to which one has developed a Require
consistent philosophy of life (e.g., exhibits Resist
respect for the worth and dignity of human Resolve
beings in all situations). Revise
Organization Commitment to a set of values. This level Abstract Formulate
involves 1) forming a reason why one values Balance Select
certain things and not others, and 2) making Compare Systemize
appropriate choices between things that are Decide Theorize
and are not valued. One is expected to Define
organize likes and preferences into a value
system and then to decide which ones will be
dominant.
Valuing Display behavior consistent with a single Act Express
belief or attitude in situations where one is Argue Help
neither forced or asked to comply. One is Convince Organize
expected to demonstrate a preference or Debate Prefer
display a high degree of certainty and Display
conviction.
Responding One is required to comply with given Applaud Participate
expectations by attending or reacting to certain Comply Play
stimuli. One is expected to obey, participate, Discuss Practice
or respond willingly when asked or directed to Follow Volunteer
do something. Obey
Receiving One is expect to be aware of or to passively Attend Listen
attend to certain stimuli or phenomena. Be aware Look
Simply listening and being attentive are the Control Notice
expectations. Discern Share
Hear
Psychomotor Domain
This domain is given primarily for information. Other courses within the curriculum stress this various
levels of psychomotor performance (e.g., Clinical Skills Laboratory, Pharmacy Practice I).
Psychomotor behaviors are performed actions that are neuromuscular in nature and demand certain levels
of physical dexterity.
Action Verbs Describing
Level Description Learning Outcomes
Naturali- High level of proficiency is necessary. The Automatically Spontaneously
zation behavior is performed with the least Effortlessly With ease
expenditure of energy, becomes routine, Naturally With
automatic, and spontaneous. perfection
Professionally With poise
Routinely
Articulation Requires the display of coordination of a series Confidence Smoothness
of related acts by establishing the appropriate Coordination Speed
sequence and performing the acts accurately, Harmony Stability
with control as well as with speed and timing. Integration Timing
Proportion
Precision Requires performance of some action Accurately Proficiently
independent of either written instructions or a Errorlessly With balance
visual model. One is expected to reproduce an Independently With control
action with control and to reduce errors to a
minimum.
Manipulation Performance of an action with written or Align Place
verbal directions but without a visual model or Balance Repeat
direct observation. The action may be Follow Rest (on)
performed crudely or without neuromuscular Grasp Step (here)
coordination at this stage. Notice that the Hold
action verbs are the same as those for the
imitation stage. The difference is that these
actions are performed with the aid of written
and verbal instruction, not visual
demonstration.
Imitation The learner observes and then imitates an Align Place
action. These behaviors may be crude and Balance Repeat
imperfect. The expectation that the individual Follow Rest (on)
is able to watch and then repeat an action. Grasp Step (here)
Hold
You might also like
- Do Schools Kill CreativityDocument13 pagesDo Schools Kill CreativityIrfanul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning: SPARK Your InterestDocument49 pagesAssessment of Learning: SPARK Your InterestMaria Angelica Martinez79% (19)
- Personalized Learning Plan (PLP) For Gifted & Talented Learner)Document6 pagesPersonalized Learning Plan (PLP) For Gifted & Talented Learner)Square JjNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Action VerbsDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonomy Action VerbsMR SIVAKUMAR TNo ratings yet
- The Blue-Print of ASSURE Instructional ModelsDocument3 pagesThe Blue-Print of ASSURE Instructional ModelsFery AshantiNo ratings yet
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumFrom EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumNo ratings yet
- Curriculum InnovationsDocument7 pagesCurriculum InnovationsAngelo LabadorNo ratings yet
- DALIG PPAs Accomplishment Report LONGDocument5 pagesDALIG PPAs Accomplishment Report LONGAiza Sillano100% (2)
- Performance Improvement Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesPerformance Improvement Plan TemplateSimao AndreNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy VerbsDocument2 pagesBlooms Taxonomy VerbsrevarzuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Learning in Affective and Psychomotor DomainDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Learning in Affective and Psychomotor DomainRodrick Sonajo RamosNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers: Gina O. Gonong Director, Research Center For Teacher QualityDocument52 pagesThe Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers: Gina O. Gonong Director, Research Center For Teacher QualityRush JaimeerNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDocument28 pagesLearning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDr. Azadeh AsgariNo ratings yet
- Core Principles of Effective AssessmentDocument6 pagesCore Principles of Effective AssessmentIrene Futalan LastimosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4Jack FrostNo ratings yet
- Properties of Assessment Method: ValidityDocument30 pagesProperties of Assessment Method: ValidityDANIEL LANCE RESPONTE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning: Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentDocument12 pagesFacilitating Learning: Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentRachelle YuNo ratings yet
- Handout Module6Document69 pagesHandout Module6Oana MirceaNo ratings yet
- EMA 511 Syllabus - Fall 2020Document27 pagesEMA 511 Syllabus - Fall 2020Sharney WilksNo ratings yet
- The Learner Centered ClassroomDocument16 pagesThe Learner Centered ClassroomJanine CanlasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategy Definition Teaching MethodDocument5 pagesTeaching Strategy Definition Teaching Methodmitchbitch69No ratings yet
- Development and Assessment: CurriculumDocument102 pagesDevelopment and Assessment: CurriculumNanatsu SensieNo ratings yet
- Tsl3109 PPG Module Managing The Primary Esl ClassroomDocument154 pagesTsl3109 PPG Module Managing The Primary Esl ClassroomARINI100% (1)
- Nick VujicicDocument4 pagesNick VujicicJosephine ReyNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument15 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of TeachingMark Pasang Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in ADM Content Evaluation RegionDocument7 pagesGuidelines in ADM Content Evaluation RegionCARMEL GRACE SIMAFRANCA100% (2)
- The Competent TeacherDocument9 pagesThe Competent TeacherjessaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Chapter 4F StudentsDocument34 pagesLesson 4 Chapter 4F StudentsShamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Document21 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Jamena abbasNo ratings yet
- Using Biggs' Model of Constructive Alignment in Curriculum Design:Continued - UCD - CTAGDocument3 pagesUsing Biggs' Model of Constructive Alignment in Curriculum Design:Continued - UCD - CTAG8lu3dz100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument6 pagesConcept Mapapi-3725139No ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 4Document3 pagesModule 5 Lesson 4Vincent Jay BalocaNo ratings yet
- AFFECTIVE TARGETS: AttitudeDocument19 pagesAFFECTIVE TARGETS: AttitudeJaika SedoroNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Describe WDocument3 pagesAnswer:: Describe WAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- The Different Purposes of AssessmentDocument16 pagesThe Different Purposes of AssessmentAlter joy MoralNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Studies Short NotesDocument7 pagesCurriculum Studies Short NotesPraveenNaiduNo ratings yet
- Educ 8 Lesson 2Document5 pagesEduc 8 Lesson 2Jamira Inoc SoboNo ratings yet
- Who Should Be Involved in Curriculum EvaluationDocument5 pagesWho Should Be Involved in Curriculum EvaluationRuth MatrianoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design Instructional Analysis: Needs Analysis WorksheetDocument1 pageInstructional Design Instructional Analysis: Needs Analysis WorksheetSheen AponNo ratings yet
- The Classroom Climate: Reporters: Perandos, Vince Robert L. Laurora, TrishaDocument10 pagesThe Classroom Climate: Reporters: Perandos, Vince Robert L. Laurora, TrishartrengyggNo ratings yet
- Basog, Jemay Module 1and 2 Educ 129 MaamcurdevDocument59 pagesBasog, Jemay Module 1and 2 Educ 129 MaamcurdevJemay BasogNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Learning Outcomes ApproachDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Learning Outcomes ApproachVanessa L. VinluanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Original & Revised Taxonomy PyramidsDocument4 pagesBloom's Original & Revised Taxonomy Pyramidsapi-3836734100% (8)
- Implementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomDocument34 pagesImplementing A Curriculum in A Daily ClassroomHazel LavapizNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1Document27 pagesAssessment in Learning 1Jonalyn RogandoNo ratings yet
- View Your Speaker Notes Privately, While Delivering A Presentation On Multiple Monitors - PowerPointDocument4 pagesView Your Speaker Notes Privately, While Delivering A Presentation On Multiple Monitors - PowerPointKKKNo ratings yet
- InstructionalDesignandTechnologyMicromasters DesignDocument April22022Document14 pagesInstructionalDesignandTechnologyMicromasters DesignDocument April22022Patricia PricopNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 201/1/2020: The Educator As Learning Programme DeveloperDocument11 pagesTutorial Letter 201/1/2020: The Educator As Learning Programme DeveloperRochelle Govender100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Ed123Document3 pagesLesson 2 Ed123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING New MODULESDocument26 pagesASSESSMENT OF LEARNING New MODULESPrincess Sharief100% (2)
- Data Collection and AnalysisDocument4 pagesData Collection and AnalysisEmmanuella MonicaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of Educational ObjectivesDocument7 pagesTaxonomies of Educational ObjectivesrajNo ratings yet
- Misamis Oriental Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument6 pagesMisamis Oriental Institute of Science and TechnologyChristy EXAMINADANo ratings yet
- Top 5 Types of Supervision Available in EducationDocument9 pagesTop 5 Types of Supervision Available in EducationJEVELYN LIBRESNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyDocument1 pageChanges in The Developing Level.: Role and Importance of Educational TechnologyNikki DavisNo ratings yet
- Learned BehaviorDocument80 pagesLearned BehaviorAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- San Pablo Colleges Master of Arts in NursingDocument35 pagesSan Pablo Colleges Master of Arts in NursingMike Ong100% (1)
- Project Based ApproachDocument7 pagesProject Based ApproachMarie Belle SembranoNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Training and Adult Education: Data TechnologyDocument37 pagesSkills Framework For Training and Adult Education: Data TechnologyokelloNo ratings yet
- 7 Mindful Assessment ToolsDocument4 pages7 Mindful Assessment ToolsLex HenonNo ratings yet
- Slow LearnersDocument4 pagesSlow LearnersSadiq Merchant100% (7)
- Implementing The CurriculumDocument17 pagesImplementing The CurriculumRosejen Mangubat100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentma_tabora6283No ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument3 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingErwin Labayog MedinaNo ratings yet
- Domains Adjectives For LPDocument4 pagesDomains Adjectives For LPnove quimpoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument4 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingYoleen SirkNo ratings yet
- ID Analisis Kualitas Pengelolaan Kelas PembDocument19 pagesID Analisis Kualitas Pengelolaan Kelas PembMumutTeaNo ratings yet
- 4DX of Execution - SummaryDocument10 pages4DX of Execution - SummaryARLY MAY S. ESPAÑOLNo ratings yet
- Sean Freeman ResumeDocument2 pagesSean Freeman Resumeapi-405746943No ratings yet
- Meet A Senior Reflection EssayDocument2 pagesMeet A Senior Reflection Essayapi-439389090No ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLL ENGLISH 6 Q4 Week 7Document4 pagesGrade 6 DLL ENGLISH 6 Q4 Week 7MA. ASTERIA AGUSTINA CENALNo ratings yet
- An Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Integrated Basic Education Department St. Anne College Lucena, Inc. Lucena CityDocument25 pagesAn Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Integrated Basic Education Department St. Anne College Lucena, Inc. Lucena Cityapril anthonette aguirreNo ratings yet
- The Role of Education in Maintaining Social OrderDocument9 pagesThe Role of Education in Maintaining Social OrderMaria MohammedNo ratings yet
- SeeingStars Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSeeingStars Lesson PlanMaria Maqsoudi-KarimiNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching 1 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMicro Teaching 1 Lesson Planbobbymaf750% (2)
- A Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Physics Students in Laboratory ClassesDocument9 pagesA Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Physics Students in Laboratory ClassesCara Luz BuarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math DLL Week 2 Day 1Document1 pageGrade 10 Math DLL Week 2 Day 1Janrie NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Olive International School, Qatar: SESSION 2020 - 21Document3 pagesOlive International School, Qatar: SESSION 2020 - 21Boban ThomasNo ratings yet
- Action Plan On Learning Continuity in Remote AreasDocument3 pagesAction Plan On Learning Continuity in Remote AreasJulius CudiamatNo ratings yet
- Test ErrorsDocument6 pagesTest ErrorsDasha HalkaNo ratings yet
- IFFA6312 - Activity 3 Touch PointDocument12 pagesIFFA6312 - Activity 3 Touch Pointzmagadla0808No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - PED 104Document8 pagesTopic 3 - PED 104KAETH LAURENCE ORILLA NOTARIONo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 12 Quarter 1Document5 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 12 Quarter 1Precious Gregorio100% (1)
- Philosophy and Professionalism: ©2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Edition Kauchak and EggenDocument4 pagesPhilosophy and Professionalism: ©2005 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Edition Kauchak and EggenMhae NaragNo ratings yet
- English Home Language ATPDocument8 pagesEnglish Home Language ATPkanimoletsane3No ratings yet
- Bukidnon National High School: Classroom ProgramDocument15 pagesBukidnon National High School: Classroom ProgramMarnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- Study Path ECOFDocument1 pageStudy Path ECOFabcNo ratings yet
- Describing Teachers and Roles of TeachersDocument15 pagesDescribing Teachers and Roles of TeachersBernardus DanibaoNo ratings yet
- (The Correlation of Organizational Role Stressors With Stress Level of ICU NursesDocument18 pages(The Correlation of Organizational Role Stressors With Stress Level of ICU NursesAnggriani Puspita AyuNo ratings yet
- POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES BACHELOR IN BUSINESS TEACHER EDUCATION MAJOR IN BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL YEAR 2012-2013 STUDENT TEACHERS’ THINKING PROCESSES ON ICT INTEGRATION: PREDICTORS OF PROSPECTIVE TEACHING BEHAVIOR WITH EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGYDocument23 pagesPOLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES BACHELOR IN BUSINESS TEACHER EDUCATION MAJOR IN BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL YEAR 2012-2013 STUDENT TEACHERS’ THINKING PROCESSES ON ICT INTEGRATION: PREDICTORS OF PROSPECTIVE TEACHING BEHAVIOR WITH EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGYJhojoy VersozaNo ratings yet