Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comprehension
Comprehension
Uploaded by
javacodemikelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comprehension
Comprehension
Uploaded by
javacodemikelCopyright:
Available Formats
comprehension
(k m pr -h n sh n)
NOUN:
1.
a. The act or fact of grasping the meaning, nature, or importance of; understanding.
b. The knowledge that is acquired in this way.
c.
2. Capacity to include.
3.
4. Logic The sum of meanings and corresponding implications inherent in a term.
ETYMOLOGY:
Middle English comprehensioun, from Latin compreh nsi , compreh nsi n-, from
compreh nsus, past participle of comprehendere, to comprehend
What is comprehension?
Reading comprehension is understanding a text that is read, or
the process of "constructing meaning" from a text.
Comprehension is a "construction process" because it involves all
of the elements of the reading process working together as a
text is read to create a representation of the text in the
reader's mind.
What are comprehension strategies?
Comprehension strategies are conscious plans or sets of steps
that good readers use to make sense of text.
Commonly taught strategies include making
inferences/predictions, summarizing, self-monitoring and
clarification, visualization, schema connections, and question
generation.
Why is comprehension strategies instruction important?
Comprehension strategy instruction helps students become
purposeful, active readers who are in control of their own
reading comprehension.
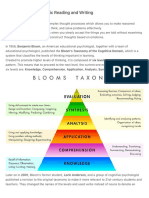
What are the different levels of
comprehension?
Literal level: the question and the answer are on the text you have read..
Interpretive level: you are attempting to understand what the author meant in the story..
Applied level: this is more harder than the other because you are attempting to elevate or
raise your thinking ideas because the answer and the question is not in the text..
Analysis level: you are making conclusions..
"There are four levels of comprehension. These include literal, inferential, evaluative, and
appreciative. Teachers evaluate student responses to reading questions based on these four levels
of comprehension.
The first, Literal comprehension - is the simplest and consists of facts that were clearly stated in
the reading.
Inferential comprehension - builds on stated facts and reveals whether or not the student is able to
interpret the facts, in other words, whether or not they can read between the lines.
Evaluative comprehension - shows an understanding of facts and opinions including bias and
assumptions which can be used to make comparison of works and conclusion as well as to relate
what they have learned to real-life experiences.
Appreciative comprehension - more abstract and is based on a deeper understanding and even
emotional reactions to the authors language, ideas, imagery, and values
You might also like
- Developmental Reading LET ReviewerDocument10 pagesDevelopmental Reading LET ReviewerRichmond Charles Viray100% (3)
- Theories of Reading ComprehensionDocument19 pagesTheories of Reading ComprehensionMetchell ManlimosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1. Learning TheoriesDocument5 pagesAssignment 1. Learning Theoriesmpumientombela2305No ratings yet
- Teach The Seven Strategies of Highly Effective Readers HTTPDocument4 pagesTeach The Seven Strategies of Highly Effective Readers HTTPlara bella mertoNo ratings yet
- Reading As A SkillDocument46 pagesReading As A SkillVelasquez Val85% (20)
- Receptive Skills: Reading Task 1Document6 pagesReceptive Skills: Reading Task 1Máté NémethNo ratings yet
- BTEC Command WordsDocument1 pageBTEC Command WordsJoshKellySwagMaster2100% (2)
- A Theory of Vocational DevelopmentDocument6 pagesA Theory of Vocational DevelopmentAntonio GomezNo ratings yet
- DLL Reading & Writing Week 1 Nov 5-9, 2018Document3 pagesDLL Reading & Writing Week 1 Nov 5-9, 2018marzi89% (54)
- Rand Presentation1Document9 pagesRand Presentation1Rand KamalNo ratings yet
- Reading For Comprehension IIDocument4 pagesReading For Comprehension IIDebbieNo ratings yet
- Bella Septian Almunda Pratama - CHAPTER IIDocument22 pagesBella Septian Almunda Pratama - CHAPTER IIFeya NuevoNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension SkillsDocument13 pagesReading Comprehension SkillsAmin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Course VI Practicum - EPC 1Document9 pagesCourse VI Practicum - EPC 1Adrija SinhaNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges Senior High School DepartmentDocument8 pagesPines City Colleges Senior High School DepartmentHannah DaddNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER II AYU AZ RevDocument10 pagesCHAPTER II AYU AZ RevLisa RLNo ratings yet
- Bab IiDocument6 pagesBab Iiralf casagdaNo ratings yet
- Dev ReadingDocument2 pagesDev ReadingRhonalyn CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Let Review Guide Developmental ReadingDocument2 pagesLet Review Guide Developmental ReadinggeorgedelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ResearchDocument36 pagesChapter 2 ResearchRenge TañaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1vicentepadds7913No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Reading Comprehension and Levels of ComprehensionDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Reading Comprehension and Levels of ComprehensionjohnaprilestrellaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Reading ComprehensionDocument25 pagesLevels of Reading ComprehensionWinterMae BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension: Disusun OlehDocument9 pagesReading Comprehension: Disusun OlehDina LestariNo ratings yet
- Introduction: A Practical Guide For ReadingDocument31 pagesIntroduction: A Practical Guide For ReadingMarbie Joyce Aspe100% (1)
- Reading SkillsDocument3 pagesReading Skillsawoyemioyindamola9No ratings yet
- Grades 6 8Document103 pagesGrades 6 8riddle_oneNo ratings yet
- National Seminar Proceeding - 576Document9 pagesNational Seminar Proceeding - 576Chika Rizky AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Reading Concept Components and FactorsDocument5 pagesReflective Reading Concept Components and FactorsVeena Rani100% (1)
- Extensive Reading DoneDocument7 pagesExtensive Reading Donesuci apriliana pertiwiNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument20 pagesChapter IIwoiosajahNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Nonsense Strategy To Improve Reading ComprehensionDocument35 pagesMaking Sense of Nonsense Strategy To Improve Reading Comprehensionrebat100% (1)
- Chapter II SSRDocument13 pagesChapter II SSRLaila iqlimatuz Z I NNo ratings yet
- READINGDocument10 pagesREADINGmiliNo ratings yet
- Levels of ComprehensionDocument3 pagesLevels of ComprehensionMikaela Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument79 pagesChapter IIRobi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Teaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsDocument7 pagesTeaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsKrystel Mary SungaNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 PDFDocument25 pagesBab 2 PDFSutrisno TrisnoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER II (English)Document14 pagesCHAPTER II (English)Andi AldiNo ratings yet
- 5 Chapter IiDocument24 pages5 Chapter IiAzianti Bako As-singkiliNo ratings yet
- MacroSkills ListeningSkillsDocument25 pagesMacroSkills ListeningSkillsCastro, Princess Joy S.No ratings yet
- Document PentingDocument10 pagesDocument PentingYeci GuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Reading Comprehension and Levels of ComprehensionDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Reading Comprehension and Levels of ComprehensionjohnaprilestrellaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Related Liteature 2.1 The Nature of ReadingDocument6 pagesReview of The Related Liteature 2.1 The Nature of ReadingNinik HardiantiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Pre-Questioning in Reading ComprehensionDocument5 pagesThe Use of Pre-Questioning in Reading ComprehensionAnnisa LatifaNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading and Writing NotesDocument60 pagesAcademic Reading and Writing NotesEljhon Steve SatsatNo ratings yet
- Reading Remediation ProcessDocument54 pagesReading Remediation ProcessNancy R. SudarioNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Literacy Strategies WGUDocument3 pagesWhy Do We Need Literacy Strategies WGUCOCNo ratings yet
- Materials Development For ReadingskillsDocument22 pagesMaterials Development For ReadingskillszahraaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading Review Class For Teachers' Licensure Exam Metro Manila CollegeDocument97 pagesDevelopmental Reading Review Class For Teachers' Licensure Exam Metro Manila CollegeRuelyn RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Action Research AselaDocument18 pagesAction Research AselaASELA PE?FIELNo ratings yet
- 2310 5137 1 PBDocument8 pages2310 5137 1 PBNada NadiaNo ratings yet
- Konsep ReadingDocument9 pagesKonsep ReadingArinaMaftuhahNo ratings yet
- What Is ReadingDocument12 pagesWhat Is ReadingRjay AgdonNo ratings yet
- Teaching Listening: There Are Two Cognitive Conversion Processes in CommunicationDocument12 pagesTeaching Listening: There Are Two Cognitive Conversion Processes in Communicationapple pieNo ratings yet
- Language Learning EvaluationDocument8 pagesLanguage Learning EvaluationcynthiaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Topic 1 ReadingDocument4 pagesPart 3 - Topic 1 ReadingApenton MimiNo ratings yet
- A. Background of The ResearchDocument26 pagesA. Background of The Researchhajrin hi abdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Reading: Mia Pearl R. RapatanDocument30 pagesReading: Mia Pearl R. RapatanJulie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Reading and Its LevelDocument8 pagesDefinition of Reading and Its LevelMuhammad Hidayatul Rifqi100% (1)
- TLS Comprehension 5.11.23Document24 pagesTLS Comprehension 5.11.23Hijab BatoolNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Reading Comprehension SkillsDocument8 pagesHow To Improve Reading Comprehension SkillsRsksamyNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan For Grade 8 Japanese Literature: The Tale of The Aged MotherDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan For Grade 8 Japanese Literature: The Tale of The Aged MotherJopao Pañgilinan100% (12)
- Here Are Six Types of ListeningDocument18 pagesHere Are Six Types of ListeningSamMitchRabaraVilogNo ratings yet
- Sdaie LessonDocument5 pagesSdaie Lessonapi-222178629No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Transfer of LearningDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Transfer of Learningapi-407073199No ratings yet
- RebeccaSinkerPhDTo Whay Extent Is The Internet Appropriate For Learning Throuogh and About Cont Visual ArtsDocument182 pagesRebeccaSinkerPhDTo Whay Extent Is The Internet Appropriate For Learning Throuogh and About Cont Visual ArtsDana ShuksterNo ratings yet
- Alcebiades I 2015Document17 pagesAlcebiades I 2015Carlos AugustoNo ratings yet
- CIDAM RESEARCH 1 2ND SEM-2nd QTRDocument2 pagesCIDAM RESEARCH 1 2ND SEM-2nd QTRCecille M. ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Fifth DisciplineDocument7 pagesFifth Disciplineokwute100% (1)
- Lesson Plan One: Variables and ExpressionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan One: Variables and ExpressionsHopeLauren02No ratings yet
- The Underground Man's Philosophy. An Analysis Based On Verbalisms From Dostoevsky's Notes From Underground Part I - Malte Joost - AcademiaDocument11 pagesThe Underground Man's Philosophy. An Analysis Based On Verbalisms From Dostoevsky's Notes From Underground Part I - Malte Joost - AcademiaRenan S. CarlettiNo ratings yet
- El 198912 Kagan PDFDocument6 pagesEl 198912 Kagan PDFLloyd GaleonNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument27 pagesLearning TheoriesJay-r Blanco67% (3)
- The Anti-Artist-statement Statement - Iris JaffeDocument3 pagesThe Anti-Artist-statement Statement - Iris JaffeKenneth CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Sobre Teoria Intuicionista de Conjuntos Difusos de Krassimir T. AtanassovDocument327 pagesSobre Teoria Intuicionista de Conjuntos Difusos de Krassimir T. AtanassovMaquiventa MelquisedekNo ratings yet
- Activity Completion ReportDocument5 pagesActivity Completion ReportDHARYL L. PIANDIONGNo ratings yet
- KikyDocument8 pagesKikysando fransukmaNo ratings yet
- 04 Chapter 4Document24 pages04 Chapter 4Gadies Machy100% (2)
- Empty Your Cup: An Old Buddhist TaleDocument99 pagesEmpty Your Cup: An Old Buddhist TaleJulz QuilarioNo ratings yet
- 5th Chapter. Data Collection and Processing - ppt.1Document32 pages5th Chapter. Data Collection and Processing - ppt.1Ravi HoneyNo ratings yet
- Effective Listening and Presenting 1227599875660377 8Document13 pagesEffective Listening and Presenting 1227599875660377 8c0080No ratings yet
- A Learning Process Model To Achieve Continuous Improvement and Innovation PDFDocument9 pagesA Learning Process Model To Achieve Continuous Improvement and Innovation PDFMust JokoNo ratings yet
- Motivation Emotions and LeadershipDocument224 pagesMotivation Emotions and Leadershipkanon4321100% (1)
- Critical Perspectives - Dissertation Proposal OGRDocument12 pagesCritical Perspectives - Dissertation Proposal OGRRachael HolyheadNo ratings yet
- Poster FinalDocument1 pagePoster Finalapi-295583127No ratings yet
- Sinergy Lds in QuantumDocument15 pagesSinergy Lds in QuantumadriantoNo ratings yet
- Neuroeducation: Learning, Arts and The BrainDocument120 pagesNeuroeducation: Learning, Arts and The BrainSusana Del Buono100% (3)