Professional Documents
Culture Documents
It App Notes
It App Notes
Uploaded by
FoshAtokCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Security Guard Business PlanDocument34 pagesSecurity Guard Business PlanJoseph100% (2)
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- A Project Report On "Smart Dustbin" Submitted To V.P.M.P. Polytechnic, Gandhinagar Department of Computer EngineeringDocument21 pagesA Project Report On "Smart Dustbin" Submitted To V.P.M.P. Polytechnic, Gandhinagar Department of Computer EngineeringAryan Banawadi100% (1)
- IT - Chapter 1Document5 pagesIT - Chapter 1mobylayNo ratings yet
- 8652 Articlekritikram2019Document9 pages8652 Articlekritikram2019lovelethrNo ratings yet
- Objectives Role and Scope of Management AccountingDocument9 pagesObjectives Role and Scope of Management AccountingEarl EzekielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Kathlene JaoNo ratings yet
- Is An Integrated Set of Components For Collecting, Storing, and Processing Data and For Providing Information, Knowledge, and Digital ProductsDocument3 pagesIs An Integrated Set of Components For Collecting, Storing, and Processing Data and For Providing Information, Knowledge, and Digital Productssachin pareekNo ratings yet
- BMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020Document8 pagesBMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020sicelo ncubeNo ratings yet
- C.A-I Chapter-1Document6 pagesC.A-I Chapter-1Tariku KolchaNo ratings yet
- Management Reporting NotesDocument12 pagesManagement Reporting NotesDustin PerezNo ratings yet
- HorizonalDocument72 pagesHorizonalg.canoneo.59990.dcNo ratings yet
- Clanak 5Document10 pagesClanak 5Linh KhánhNo ratings yet
- Management HierarchyDocument8 pagesManagement Hierarchysneha kotawadekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument10 pagesChapter 1: The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveAstxilNo ratings yet
- Fma - 1Document60 pagesFma - 1Hammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Module 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsDocument9 pagesModule 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsClaire BarbaNo ratings yet
- The Role of OrganisationDocument9 pagesThe Role of OrganisationMadhury MosharrofNo ratings yet
- Baccinsx CM Week1andweek2 Ais101 RrdeveraDocument13 pagesBaccinsx CM Week1andweek2 Ais101 RrdeveraMitchie FaustinoNo ratings yet
- It PrelimDocument16 pagesIt Prelimg.canoneo.59990.dcNo ratings yet
- AIS ReviewerDocument22 pagesAIS Reviewersky.dumpacc00No ratings yet
- Cost Chapter 1-5Document302 pagesCost Chapter 1-5chingNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Business Processes and Decision-Making SystemsDocument20 pagesWeek 3: Business Processes and Decision-Making SystemsỐc Sên NhỏNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems An OverviewDocument36 pagesAccounting Information Systems An OverviewJonathan Dave PagariganNo ratings yet
- Information System and MIS: Gagan Deep Rozy Computech Services 3 Gate, K.U., Kurukshetra-136119Document15 pagesInformation System and MIS: Gagan Deep Rozy Computech Services 3 Gate, K.U., Kurukshetra-136119Neel KamalNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Financial MGMT Gov UsDocument4 pagesDatasheet Financial MGMT Gov UsabsNo ratings yet
- AIS - Chapter 1Document51 pagesAIS - Chapter 1Hasan AbirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1NaveenNo ratings yet
- Mis VVFGCDocument114 pagesMis VVFGCArthiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Management Accounting and Business EnvironmentDocument7 pagesTopic 1 Management Accounting and Business EnvironmentdigididoghakdogNo ratings yet
- Impact of Top Management Support On Accounting Information System: A Case of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) SystemDocument8 pagesImpact of Top Management Support On Accounting Information System: A Case of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systemzelalem shiferawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial AccountingDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Managerial AccountingSahra PajarillaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's Perspective: CMEA2216 Accounting Information SystemsDocument25 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's Perspective: CMEA2216 Accounting Information SystemsMohd Nasrul AsrafNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of An Accounting Information System Inside A Financial Corporation A Case Study On Multi-Method Information at Haines Watts CorporationDocument7 pagesQualitative Characteristics of An Accounting Information System Inside A Financial Corporation A Case Study On Multi-Method Information at Haines Watts CorporationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument40 pagesChapter 1 The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveFarah Byun100% (1)
- Chapter 02 Overview of Accounting Information SystemDocument42 pagesChapter 02 Overview of Accounting Information Systemfennie lohNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Report BA701 Managerial Accounting & ControlDocument77 pagesGroup 1 Report BA701 Managerial Accounting & Controlrichard dehn medinaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant'S PerspectiveDocument5 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant'S PerspectivexxpinkywitchxxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Anika Gaudan PonoNo ratings yet
- 13 - Logistics Information Systems - All PartsDocument110 pages13 - Logistics Information Systems - All PartsMohamed NabalawyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledCyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 - AIS IntroductionDocument54 pages1 - AIS Introductionryuu35692No ratings yet
- Journal To CritiqueDocument5 pagesJournal To CritiqueEmieNo ratings yet
- MAS.2901 - Overview of MASDocument6 pagesMAS.2901 - Overview of MASdaemonspadechocoyNo ratings yet
- F5-18 Performance Management Information SystemsDocument26 pagesF5-18 Performance Management Information SystemsMohamed ElbariNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Chapter 1Document12 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 122100629No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Management AccountingDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Management AccountingOvi AndrestiNo ratings yet
- C19 - Group 1 - History and Trends in Management-ReportingDocument12 pagesC19 - Group 1 - History and Trends in Management-Reportingsharlyn graceNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 & 12 Types of Decision and Information SystemDocument29 pagesChap 2 & 12 Types of Decision and Information SystemJayesh GarachhNo ratings yet
- A Project Management Information System Serves Five Principal PurposesDocument9 pagesA Project Management Information System Serves Five Principal PurposesSumme Ma TigeNo ratings yet
- Management Science: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Document3 pagesManagement Science: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)KA TENo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - ITAPP Introduction To Accounting Information SystemDocument17 pagesMODULE 1 - ITAPP Introduction To Accounting Information SystemALYSSA LEIGH VILLAREALNo ratings yet
- Comercio Electronico 2018Document21 pagesComercio Electronico 2018maritzaNo ratings yet
- Stratcost LecturesDocument2 pagesStratcost LecturesAlyzza AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Chapter 1Document30 pagesManagement Accounting Chapter 1dawsonNo ratings yet
- C39IA Accounting Information, Communication & Technology: Not Just A Load of Old Numbers .Document34 pagesC39IA Accounting Information, Communication & Technology: Not Just A Load of Old Numbers .Sunil BawaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting and Cost ConceptsDocument11 pages1 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting and Cost ConceptsMARK KENNETH RULLEPANo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting-Notes For PrelimDocument18 pagesCost Accounting-Notes For PrelimAngelie BancaleNo ratings yet
- F2 - Section 1 - Accounting For ManagementDocument18 pagesF2 - Section 1 - Accounting For ManagementDiệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 MISDocument25 pagesChapter-9 MISRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Flows of Information Used Primarily at The Operations Level To Capture Transaction andDocument7 pagesHorizontal Flows of Information Used Primarily at The Operations Level To Capture Transaction andcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- MS ReviewerDocument4 pagesMS Reviewerangelinavalencia0307No ratings yet
- Ca 51012 Fin Man Quiz 1 - Example of Application Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesCa 51012 Fin Man Quiz 1 - Example of Application Type QuestionsFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Module 1Document16 pagesOblicon Module 1FoshAtokNo ratings yet
- StratCostMgmt 4 - Mock Test For Quiz 1 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesStratCostMgmt 4 - Mock Test For Quiz 1 Answer KeyFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Formative AssessmentDocument5 pagesFormative AssessmentFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory Services Antonio Jaramillo Dayag Management Accounting ConceptsDocument13 pagesManagement Advisory Services Antonio Jaramillo Dayag Management Accounting ConceptsFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- LogDocument23 pagesLogJeannel Joy GervacioNo ratings yet
- USER GuidelinesDocument15 pagesUSER GuidelinesdrfgdzfgNo ratings yet
- Standard Tool Bar Remains The Same Regardless The TransactionDocument17 pagesStandard Tool Bar Remains The Same Regardless The TransactionAnggun PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Diamond Select Ingenuity 128Document2 pagesDiamond Select Ingenuity 128Sepak OdokNo ratings yet
- Riss JS2 Second TermDocument15 pagesRiss JS2 Second TermkaylaNo ratings yet
- Frendx - 1985-05Document56 pagesFrendx - 1985-05Kasi XswlNo ratings yet
- AFNOR IPTDS BrochureDocument1 pageAFNOR IPTDS Brochurebdiaconu20048672No ratings yet
- Journal PakuDocument10 pagesJournal PakuPaku IslamiatiNo ratings yet
- Resume WordDocument2 pagesResume Wordapi-242422274No ratings yet
- DS-7204HI-VS Net DVR - V2.0 (080909)Document88 pagesDS-7204HI-VS Net DVR - V2.0 (080909)ANTONIO PEREZNo ratings yet
- DBMS Stored Function, Cursor & TriggerDocument10 pagesDBMS Stored Function, Cursor & TriggerAustinNo ratings yet
- Viva Android SettingDocument6 pagesViva Android SettingFawaz AlsaifNo ratings yet
- Measurement Procedure - Molspin Magnetometer: North Component Name/No of The SpecimenDocument10 pagesMeasurement Procedure - Molspin Magnetometer: North Component Name/No of The SpecimenShiva PatilNo ratings yet
- General Software Development Standards and GuidelinesDocument17 pagesGeneral Software Development Standards and GuidelinesSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument42 pagesPPTAbdul RifasNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Binary B-TreesDocument17 pagesSymmetric Binary B-TreesMEGUELLATI Fahd MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Introduction To Transaction ProcessingDocument69 pagesChapter 2: Introduction To Transaction ProcessingJanna Louisse Z. CervoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document8 pagesLecture 05Nebiye SolomonNo ratings yet
- Pyro Sim ManualDocument170 pagesPyro Sim ManualSerbian4096No ratings yet
- 2019 Hach BookletDocument16 pages2019 Hach Bookletwaikokpoh007No ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityOcubillo Froilan D.No ratings yet
- Finisher Q1 Q3 R1-Saddle Finisher Q2 Q4 R2 - PCDocument114 pagesFinisher Q1 Q3 R1-Saddle Finisher Q2 Q4 R2 - PCluis1984bolNo ratings yet
- Independent Government Cost Estimate (IGCE ... - (OUSD (AT&L) )Document2 pagesIndependent Government Cost Estimate (IGCE ... - (OUSD (AT&L) )joniNo ratings yet
- HD-R712 Specification V1.0Document5 pagesHD-R712 Specification V1.0quang nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Project Charter: Project Name: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Authorization Date: 25/09/2020Document8 pagesProject Charter: Project Name: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Authorization Date: 25/09/2020Leo DoeNo ratings yet
- M59209FP 1Document1 pageM59209FP 1irvan hardiansyahNo ratings yet
- BMGT 340 Syllabus Fall 2014Document10 pagesBMGT 340 Syllabus Fall 2014moshe feldmanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 01 - Objective Mapping - Safety and Professionalism - A+ Chapter 1 PDFDocument2 pages1.1 01 - Objective Mapping - Safety and Professionalism - A+ Chapter 1 PDFFlippencioNo ratings yet
It App Notes
It App Notes
Uploaded by
FoshAtokOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
It App Notes
It App Notes
Uploaded by
FoshAtokCopyright:
Available Formats
Information Technology Application Tools in
Business Introduction to Information System: Accountant’s
Perspective
● The biggest impact that IT has made on
accounting is the ability of companies to ● The rule of accounting system is of great
develop and use computerized system to track importance for business decision, making
and record financial transactions process, and management.
● IT network and computer systems have ● Accounting actually is an information system
shortened the time needed by accountants to and to be more precise, it is the practice of
prepare and present financial information to general theories of information in the field of
management effective economic activities and consists of
major part of the information which is
Course Objectives presented in the quantitative form.
● Prepare: ● An accounting information system is a part of
○ Accounting and audit related the overall information system whose main goal
documents using the functionalities of is to generate information for business
word processors decisions.
○ Structured accounting and audit related ● The way of gathering, analyzing, processing,
presentation using appropriate distribution and archiving of accounting
presentation tools and effectively information has been changed during the years.
deliver the presentation However, accounting information has always
○ Basic project management reports and been an important part of the business
documents using project management operations.
tools ● The most significant influence belongs to
○ A complete set of financial statements information technology.
with the corresponding package with
the use of word processing, Course Objectives:
spreadsheets, and database programs. ● Illustrate the primary information flows within
● Evaluate the impact of key trends in accounting the business environment and identify the
information systems and information functional areas of a business.
technology to the work of a financial ● Differentiate accounting information systems
statements auditor, an information systems and management information systems and
auditor and a management accountant. financial transactions and non-financial
transactions.
Flow of Discussion ● Describe the stages in the evolution of
1. Introduction to Accounting Information Systems information systems and the general model for
2. Basic Spreadsheet for Accountants information systems
3. Intermediate Spreadsheet for Accountants ● Explain the relationship between the three roles
4. Advanced Spreadsheet for Accountants of accountants in an information system
5. Introduction to Database System ● Distinguish between external auditing, internal
6. Basic Data Analysis auditing, and advisory services as they relate to
7. Selected Word Processing Topic for Accountants accounting information systems.
8. PowerPoint and Introduction to Project
Management Discussion Agenda:
9. Capstone Project ● Information Environment
● Organizational Structure
● Role of accountants to AIS
● Technology for Success
Information Environment
What is Information?
● Information is a business resource that:
○ Needs to be appropriately managed
○ Vital to the survival of contemporary
businesses
Fundamental objectives of information common to all
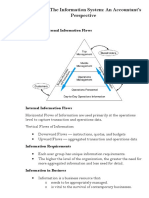
● Horizontal flows of information are used
organizations
primarily at the operations level to capture
● Support the firm’s day-to-day operations
transactions and operations data.
● Support management decision making
● As for vertical flows of information, downward
○ The accounting information is very
flows contain instructions, quotas and budgets.
important for the management or the
While upward flows are aggregated
decision making body of the
transactions and data.
organization. The management cannot
Each user group has unique information requirements. The
decide without reasonable information
higher the level of the organization, the greater the need for
for backing it up. To make a decision, it more aggregated information and less need for details.
has to be based on genuine facts and
figures. For deciding every level of What is an Information System?
management, information is crucial. For ● A system is a group of interrelated multiple
making the right decision, management components or subsystems that serve a
depends on statistical data and common purpose. Thus, an information system
information that accounting provides. is a set of formal procedures by which data are
● Support the stewardship function of collected, processed into information and
management distributed to users.
○ The role of the management is very ● Information system has two subsystems:
important in the overall development of ○ Management Information System (MIS)
a business organization. The functions ■ It is a system that processes
of management are planning, non-financial transactions, not
organizing, collecting business normally processed by
elements, motivating, coordinating, traditional accounting
controlling and budgeting, etc. information systems.
Successful completion of these ■ This supports the four
functions of management depends on functional areas of business
an efficient accounting system. accounting and finance, sales
and marketing, manufacturing
and distribution and human
resources.
■ Purely information, they
translate the financial
information into a narrative.
○ Accounting Information System (AIS)
■ Accounting is an information ■ Cost Accounting System
system. ■ Production and Planning
■ It identifies, collects, processes, Control System
and communicates economic ○ Revenue Cycle
information about a firm using ■ Sales Processing System
a wide variety of technologies. ■ Cash Receipts System
■ It captures and records the
financial effects of the firm’s Difference of MIS and MRS
transactions. Both support the four functional areas of business.
■ It distributes transaction MIS
information to operations - focus on non-financial transactions
personnel to coordinate many - purely information kasi yung financial information
key tasks. ginagawa nyang narrative
■ Process financial transactions - processed by traditional accounting information
(e.g. sale of goods) and system
non-financial transactions that
directly affect the processing of MRS
financial transactions (e.g. - discretionary that’s why they can choose what
addition of newly approved information to present and how they will present it
vendors) - financial transactions
Framework/ Subsystems of Accounting Information -for the use of management in their decision making
System
● General Ledger/ Financial Reporting System Accounting Information System are specialized subset
(GL/FRS) of information system that processes:
○ Non-discretionary reporting is a type of ● Financial transactions; e.g. sale of goods
reporting in which the organization has ● Non Financial transactions that directly affect
few or no choices in the information it the processing of financial transactions; e.g.
provides. Much of this information addition of newly approved vendor
consists of traditional financial
statements, tax returns and other legal
documents.
○ Summarized reports
● Management Reporting System (MRS)
○ Discretionary reporting is a type of
reporting in which the organization can An information system processes transactions to provide
choose what information to report and information that could assist in decision making.
how to present it. ● Transactions are events that affect the areas of
○ Purposely for the use of management interest to the organization and are processed
for their decision making by its information system as a unit of work. It
○ Under AIS, which is financial in nature can be categorized into two types:
● Transaction Processing System (TPS) ○ Financial Transactions: economic event
○ Expenditure Cycle that affects the assets and equities of
■ Purchase System the organization. It is measured in
■ Cash Disbursement System financial terms and is reflected in the
■ Payroll Processing System accounts of the firm
■ Fixed Asset System
○ Conversion Cycle
○ Non-financial Transactions: events that i. Capturing transaction data
do not hit the narrow definition of ii. Recording data on to forms
financial transactions. iii. Editing and validating data
3. Data Processing
○ Data processing is a group that
manages the computer resources used
to perform the day-to-day processing of
transactions.
○ It involves classifying, transcribing,
sorting, batching, merging, calculating,
summarizing, and comparing collected
data.
4. Database Management
○ Once processed, data is stored in a
repository or database.
AIS is a model that describes all of the information systems i. The organization’s database is
regardless of their technological architecture. its physical repository for
financial and non financial data.
1. Transactions or Data Sources It could be a filing cabinet or a
○ Data Sources are financial transactions computer disk.
that enter the information system from ○ Database Management includes storing,
internal and external sources. retrieving or deleting processed data.
i. External Source of Data: i. It can also refer to a special
External financial transactions software system that is
are the most common source of programmed to know which
data for most organizations. data elements each user is
Examples include sale of goods authorized to access.
or services, purchase of 5. Information Generation
inventory, receive of cash, and ○ The last step of transforming data into
disbursement of cash including information is information generation.
payroll. i. It is the process of compiling,
ii. Internal Sources of Data: arranging and preparing data
Internal financial transactions for presentation to the
involve the exchange or end-user.
movement of resources within ○ One must ensure that the information
the organization. Examples shared to the end-users are “useful
include the movement of raw information”. CARTS
materials to work in process i. Completeness: All essential
(WIP), application of labor and information to complete a
overhead to WIP, transfer of decision or task is present
WIP to finished goods ● All information
inventory, and depreciation of essential to a decision
equipment. or task is present
2. Transforming the Data into Information ii. Accuracy: Information is free
○ Data collection is the first operational from material errors
stage in the information system.
○ It involves:
iii. Relevance: Information must ○ In a form you may refer to them as a
serve the purpose of its data field.
generation ■ Example: Customer Account
● Serves a purpose Number, Customer Name,
iv. Timeliness: The timeline of the Customer Address, Customer
information is aligned with its Balance of Account, Customer
objectives. Credit Limit
● No longer than time ○ The collection of data attributes is
period of the action it known as the record.
supports 2. Record
v. Summarization: Information is ○ A record is a complete set of attributes
aggregated in accordance with for a single occurrence within an entity
the end-user’s needs class or collection of related fields.
6. Information is presented to the end-users ■ Example: Account Receivable
○ End users are users for whom the Records that includes the
system is built. Customer Account Number,
i. External End Users: creditors, Customer Name, Customer
stockholders, potential Address, Customer Balance of
investors, regulatory agencies, Account, Customer Credit Limit
tax authorities, suppliers, and 3. File: A complete set of records of an identical
customers class
ii. Internal End Users: ■ Example: multiple Account
management at all levels of the Receivable Records
organization as well as
operations personnel
7. Feedback Organizational Structure
○ Feedback is a form of output that is - is a system that outlines how certain activities
sent back to the system as a source of are directed in order to achieve the goals of an
data. organization. These activities can include rules,
○ It is usually used as a basis for roles and responsibilities.
improvement of the accounting The structure of an organization helps to allocate:
information system. ● responsibility
○ Data coming from external end users ● authority
● accountability
Data Hierarchy
Data hierarchy refers to the systematic organization of Physical AIS is composed of technologies of various
data. It is a basic concept in data and database theory types and configurations as well as people and tasks
that helps to show the relationship between smaller from across the organization because there is a need for
and larger components in a database or data file. It is segmentation.
used to give a better sense of understanding about the ● Segmentation
components of data and how they are related. ○ means to divide the organization into
parts or segments which are defined all
1. Data Attribute accessible actionable and profitable
○ The most elemental piece of potentially ○ segmenting by five business functions is
useful data in the database. a very common method of organizing.
○ It holds a single fact or attribute of an ○ Example: sales processing system is a
entity. subsystem of the revenue cycle,
including the following organizational the finished products meet the
functions: sales, credit, inventory firm’s quality standards
control, warehousing, shipping, billing, ■ Maintenance which keeps the
accounts receivable, general ledger and firm’s machinery and other
data processing. manufacturing facilities in
running order
How does an organization carry out the segmentation? ○ Marketing
- Business organizations consider the resources ■ Generates revenue
that they need to manage within a business. ■ Main tasks: to thoroughly
understand their potential
There are four resources that a business must manage customers and to determine
these resources are: how they will reach them
● materials ■ Major function: sales
● labor ○ Distribution
● financial capital ■ Main functions: warehousing
● information and shipping
From these resources the firm assigns a department for ■ Ensures that a product or
a group of people whose functions are focused on each service is available for the
aspect of the motion of resources. consumers or business users
who needs it
2. Labor
○ Managed by the personnel group
○ Supplies the organization with
personnel and takes care of their
well-being
○ Ensures that each one is fit for the role
they are chosen for
3. Financial Capital
○ Concentrates on forecasting and
budgeting of business revenues
○ Most business plans concentrate on this
area because they need loans for
1. Materials investments
○ Materials Management ○ One of its notable functions is credit
■ Incharge of purchasing and which ensures the credit worthiness of
receiving materials as well as the clients
managing the stores 4. Information
○ Production ○ Managed by the accounting and
■ Production planning which technology department
involves scheduling the flow of ○ Accounting functions:
materials, labor and machinery ■ Control of Inventory to
to efficiently meet production safeguard the assets
needs ■ Recording of the accounts
■ Quality control which monitors receivable and preparation of
the manufacturing process at billing, all of which are recorded
various points to ensure that in the general ledger
○ Accounting manages the financial ■ There are two methods of
resources of the firm: processing data that most
■ capturing and recording companies employs:
transactions as well Organizations employ a combination of both
■ distributing transaction types.
information to operations 1. Distributed Data Processing:
personnel Reorganizing the computer services
○ The value of the distributed information function into small information
is determined by its reliability. processing units that are distributed to
■ information should be end users and placed under their
complete, accurate, relevant, control
timely and summarized to the
needs of the user.
○ Unreliable information has no value.
○ Information reliability requires
accounting independence:
■ Accounting activities must be
separate and independent of
the functional areas
maintaining resources
■ Accounting supports these
functions with information but
does not actively participate In this model, users process transactions locally with
■ Decisions makers in these each user segment, an IT needs to report their
functions require that such vital operations. The user functions independently, intends
information be supplied by an not to share data and information.
independent source to ensure Possible Disadvantages:
it’s integrity. ● Loss of control
○ Technology advancement has ● Mismanagement of company resources
enhanced the accountants ability to ● Hardware and software incompatibility
interpret data officially and effectively ● Redundant tasks and data problems
because of the readily ability of data ○ Data Storage- excessive storage costs of
and information needed. paper documents or magnetic form
■ Accountants now have the ○ Data Updating: changes or additions
ability to interpret the language must be performed multiple times
of business with such ease that ○ Currency of Information: potential
the accountant has become a problem of being failing to update
corporation‘s most trusted affected files
business advisor. ○ Task-Data Dependency;: user’s inability
■ Main role of technology and to obtain additional information
business: drive growth and ○ Data integration: separate files are
improve operations difficult to integrate across multiple
■ Most final task: data processing users
for its internal and external ● Consolidating test are usually segregated
users 2. Centralized Data Processing: All data
processing is performed by one or more
i. Data Processing
large computers housed at a central site Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a system
that serves users throughout the assembled of prefabricated software
organization. components.
2. Commercial software
○ pre-coded software that a user
purchases from a software vendor. It is
available for general accounting and
industry specific application.
○ Sometimes called turnkey systems
because they often can be
implemented by the user with little or
no modification
iii. Database and Network Administration
● Database Administration: Centrally organized
All data processing performed by a large computer or
companies with shared data use database
computers in a common data center that serves users
administration to ensure security and integrity.
throughout the organization, it lends itself to
● Network Administration: responsible for
intra-organization communication and data sharing.
effective functioning of hardware and software.
○ Network: collection of computers and
By applying both methods, the organization could
communication devices that allow users
address most of the disadvantages of the distributed
to communicate, access data and
data processing model while enjoying its advantages.
applications, and share information and
resources.
ii. System Development and Maintenance
● Due to the highly technical, and dynamically
● System Development: is the process
changing expenses of IT, many executives look
organization used to acquire information
towards IT outsourcing, where the organization
systems
IT resources and leases back IT services.
● System Maintenance: may be trivial or
● Cloud computing data centers deliver hosted IT
significant.
services over the Internet:
- Between 80% to 90% of the system’s total costs
○ Software as a service (SaaS)
is incurred because of maintenance activities
○ Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
○ Platform as a service (PaaS)
Two kinds of software that may be used by the
organization:
——————
1. Custom software
What is the role of an accountant in an Accounting
○ Built to individual specification
Information System?
○ Systems development life cycle is the
The role of an accountant has expanded due to the
software development process
development of accounting information of various
○ Requires in-house team of qualified
sectors. With the increase of the volume, and the
individuals
complexity of the information, an accountant will play
○ Custom systems are more expensive
an active and effective role in the process of designing
than commercial package
the systems in order to achieve an effective internal
system as well as the needs of the accounting
information users.
Roles: organization. The audit is often
● As a system information system user performed as part of a broader financial
○ Accountants eventually access the data audit.
in the company's AIS in order to ○ Fraud Audit: detailed examination of
perform their job functions. the financial records of the business
○ This includes preparing and analyzing with the intent of finding instances of
budgets and financial statements, fraud. It had increased in popularity as a
preparing tax returns and examining corporate tool
records for accuracy. ■ May be initiated by managers
○ (Because of their other roles towards to investigate employees
the AIS) Accountants are considered as ○ External Audit: an independent
SUPREME USERS attestation and opinion (audit report)
● As a system information system designer regarding financial statement
○ accountants play a prominent role on presentation
systems development as the main Attest Function: an independent auditor’s
experts responsibility to opine as to the fair
○ The accounting function is responsible presentation of a client firm’s financial
for the Conceptual System. statement.
■ Conceptual System determine ■ Requires auditors (independent
the nature of the information CPAs) to test internal controls
required, its sources, its and perform substantive tests
destination and the accounting of data.
rules that must be applied. Test of Controls: tests that establish whether
○ The computer function is responsible internal controls are functioning properly.
for the Physical System. Substantive Tests: tests that determine whether
■ Physical System is the medium database contents fairly reflect the
and method for capturing and organization’s transactions.
presenting the information. ■ Critical element is auditor
● As a system auditor independence, which means
○ An auditor is an expert who expresses the auditor is free from factors
opinion about the fairness of the that might influence the audit
company’s financial statements report.
○ Accountants perform audits which
typically involve the AIS. Prior to Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002, accounting
○ Internal Auditing: an independent, firms were npermitted to provide audit services to
objective assurance and consulting clients. SOX legislation restricts non-audit services that
activity designed to add value and auditors may provide and prohibits them from
improve an organization’s operations. providing:
■ Helps accomplish objectives by ● Other accounting services including
bringing a systematic, bookkeeping, financial information systems
disciplined approach to design and implementation, appraisal or
evaluate and improve the valuation, actuarial, and internal audit
effectiveness of risk outsourcing
management, control and ● Management or human resources, broker or
governance processes. dealer, investment advisee, or investment
○ IT Auditing: review of the banking services
computer-based components of an ● Legal and expert services unrelated to the audit
● Any other services that the Board determines, vacuum tubes which were used for
by regulation, is impermissible. processing.
Second Generation Computer
Introduction to Technology ● Computers of this generation used transistors
instead of vacuum tubes which were more
Technology reliable.
● The term came from the Greek word “techne” ● During this generation of computers, over 100
which means art and craft. It was first used to computer programming languages were
describe applied arts but now it is used to developed, computers had memory and
describe advancement and changes around us. operating systems.
● It starts with the beginning of life on earth, and ● Events:
goes until the founding of early modern a. 1951 - the first computer for
technologies, such as computer commercial use was introduced to the
public; the Universal Automatic
Computer (UNIVAC 1).
b. 1953 - the International Business
Machine (IBM) 650 and 700 series
computers made their mark in the
computer world.
Third Generation Computer
Computer
● Integrated circuits were invented, thus
● Generally speaking, computers can be classified
computers became smaller; more reliable and
into three generations. Each generation lasted
they are able to run many different programs at
for a certain period of time, and gave us, either
the same time
a new and improved computer, or an
● Events:
improvement to the existing computer.
a. 1980 - Microsoft Disk Operating System
(MS-Dos) was born
b. 1981 - IBM introduced the personal
First Generation Computer
computer (PC) for home and office
● Computers of this generation could only
c. 1984 - Apple gave us the M
acintosh
perform a single task, had no operating system,
computer with its icon driven interface
and mainly used vacuum tubes.
d. 1990s - Windows Operating System
● Events:
a. 1937 - the first electronic digital
As a result of the various improvements to the development
computer was built by Dr. John V. of the computer, we have seen the computer being used in all
Atanasoff and Clifford Berry. It was areas of life. It is a very useful tool that will continue to
called the Atanasoff-Berry Computer experience new development as time passes. In the 21st
(ABC). century, nothing has made more of an impact on our daily
b. 1943 - an electronic computer name the lives than technology. New technologies have spurred what
Colossus was built for the military now is called the f ourth industrial revolution.
c. 1946 - the first general purpose digital
computer; the Electronic Numerical Internet of Things (IoT)
Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) was ● The ability of devices to communicate with each
built. It is said that this computer other without human interference.
weighed 30 tons, and had 18000
● Such functionality makes it possible to Impact of Technology
continuously monitor, and measure various
elements through a data network connected to Whether we like it or not, technology is becoming a part of
the internet. our everyday lives. It impacts almost everything around us.
● How does IoT work?
○ Sensors and microchips (Embedded Personal use of technology
Computers) are installed in specific Today, most people simply can’t imagine life without
devices and from there, the collected smartphones. They have evolved to such an extent that
data are transmitted to an application, they’ve moved way beyond mere communication to
usually via the Internet, that will store, being a constant companion that’s geared to learn your
process, analyze and share this data in a unique needs and make your life easier to navigate.
cloud.
■ Embedded Computers are The technology behind it is Artificial Intelligence.
compact, have limited ● It affects us through the games and
hardware, and usually have a applications that we use on our smartphones.
single purpose of enhancing the ○ All applications use artificial intelligence
capabilities of everyday devices. to process specific data on behalf of the
○ The Internet of Things is also made user.
possible by artificial intelligence. ○ Games incorporate virtual reality to
■ It is the technological use of stimulate a different environment for
logic and prior experience to the user to enjoy.
stimulate human intelligence. ● It also affects us through digital assistance
■ Capabilities: which uses natural language processing that
● Speech Recognition interpret and digitize spoken words and
● Local Reasoning commands.
● Creative Responses ● One of the most beneficial effects is
● Immersive Technology accessibility options. This is particularly useful
■ Examples: Siri, Google Assistant, for person’s with sensory disabilities. It uses
and Alexa “AI”, such as screen readers, captioning and
■ Artificial Intelligence also gave speech recognition to assist the user despite
way to Immersive Technology their disability. Smartphones even allow special
input devices to be connected for such users.
Immersive Technology attempts to emulate a physical
world through the means of a digital or stimulated Workplace
world, by creating a surrounding sensory feeling, ● Intelligent Workplace offers integrated
thereby creating a sense of immersion. cognitive solutions that help companies
● Examples: collaborate across borders.
○ Virtual Reality (VR) - the use of ● Specifically, it offers:
computers to stimulate a real or ○ Online collaborative productivity
imagined environment that appears as software: allows employees to easily
a three-dimensional (3D) space. share information with stakeholders
■ Ex. Learning simulators without consuming much of the
○ Augmented Reality (AR) - a type of company’s resources such as paper
Virtual Reality (VR) that uses an image ○ Working Remotely/ Telecommuting:
of an actual place or things, then adds allows employees to carry out their task
digital information to it even if they are away from the
workplace
● This benefits the company, especially in patient’s vital signs and research
situations like the one we are experiencing right symptoms and diagnosis
now with the Covid-19 pandemic ○ mHealth: use of mobile and wireless
technologies to support the
Education achievement of health objectives
● Intelligent classroom is the inevitable outcome
of the available advanced computing network Manufacturing
and data communication technology. ● Robotics is the main influencer for this
● It mainly uses the Learning Management ○ It is useful in situations where it is
System (LMS) which is a web-based training impractical, dangerous, or inconvenient
that allows students to: to use a human
○ Check progress on a course ● Machine to machine communication introduced
○ Take practice tests Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) which
○ Exchange messages with involved streamlines production and allows for shipping
parties products more quickly
○ Take classes and earn degrees online
● It also uses E-books which allows students to Commerce
read and access content, such as videos, from ● The use of technology gave way to E-Commerce
devices ○ It is the buying and selling of goods and
● Social networking is also incorporated with the services, or the transmitting of funds or
intelligent classroom as it allows exchange of data, over an electronic network,
information and stories between individuals primarily the internet
● These business transactions occur either as:
Transportation ○ Business-to-Business (B2B)
● Global Positioning System (GPS) is a ■ Consists of business providing
radio-navigation system that allows land, sea, goods and services to other
and air-borne users to determine their exact businesses like the ones offered
location, velocity and time, 24 hours a day, in all by the business process
weather conditions, anywhere in the world outsourcing or BPO industry
● GPS technology is primarily being used to: ○ Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
○ Navigate routes and estimate ETAs ■ Involves the sale of goods and
○ Avoid unfavourable traffic conditions services to the general public or
○ Tracking parcels for delivery consumers such as what's
● Technology also affects the manner we travel happening with online shops
with the automations that technology brings to ○ Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
our modes of transportation. ■ Occurs when one consumer
sells directly to another like
Healthcare what occurs on a facebook
● We are all aware that our healthcare system marketplace
nowadays is using state of the art medical
equipment to treat or diagnose patients. Environment
● Examples: ● One may say that technology has a negative
○ 3D printers: used to replicate body effect on our environment but little do we know
parts used for medical studies or as a that it is also technology that gave way to green
substitute for the real stuff computing
○ Medical monitoring devices: provides
accurate and timely results to monitor
○ This is the environmentally responsible
and eco-friendly use of computers and 2. Storage Device is used for data and
their resources. information retention.
○ In broader terms, it is also defined as ● Computer Memory
the study of designing, manufacturing/
○ Responsible for holding data and
engineering, using and disposing of
programs as they are being
computing devices in a way that
reduces their environmental impact processed by the CPU
such as the reduction of the use of ○ Two basic types of memory used in a
papers in a paperless environment computer
● It also gave birth to the Energy Star Program ■ Random Access Memory
which reduces electricity consumption in (RAM)
environmental ways generated by modern - Main memory of a
appliances and machines computing device
- Stores data for a short period
of time or until the
Computer Hardware
computing device is kept
Refers to the physical, tangible computer
done
equipment and devices, which provide support for
- This type of memory is
major functions such as input, processing (internal
volatile
storage, computation and control), output,
■ Read Only Memory (ROM)
secondary storage (for data and programs), and
- Storage medium that
communication.
permanently stores data on a
computing device
Categories:
● Technology now offers a wide rate of
1. Processing Devices: process raw data
storage solutions
instructions into information
○ Internal Drives such as Hard Disk
● Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Drive (HDD), Solid State Drive (SDD)
○ A complex integrated circuit
○ External Drives such as External
consisting of millions of electronics
HDD, Flash Drive, Optical Drive
parts and is primarily responsible for
○ Cloud Storage: storing electronic
converting input (data) into
files on the Internet instead of a
meaningful output (information)
local computer
○ Data travels in and out of the CPU
■ Examples: Google Drive, MS
through a bus
OneDrive, Dropbox
■ A computer bus is a
communication system that
3. Input Device: input transactions or
transfers data between
commands to a computer
components inside a
Example: Joystick, Mouse, Keyboard, Light Pen,
computer or between
Touch Pad, Microphone, Scanner, Track Ball, Digital
computers
Camera
■ Covers all related
components such as wire or
optical fibers
4. Output Device: disseminate data and programs or provide a platform for other
information to the user software.
Example: Printers and Copiers, Monitors, Three types of system software:
Projectors, Speakers, Headphones ● Operating system: a software that
communicates with the hardware and
Micro-Computer allows other programs to run.
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive ○ Examples: Windows OS series, Mac
computer with a microprocessor as its central OS series, Android and IOS series,
processing unit (CPU). In common usage, ● Language Processor: a computer program
“microcomputer” has been largely supplanted by that is designated or used to perform tasks,
the term “personal computer“ or “PC”, which such as processing program code to
specifies a computer that has been designed to be machine code.
used by one individual at a time. ○ It accesses the interpreter of your
● Desktop Computer computing device that interprets all
○ Consist of a system unit, monitor, the computer language and relays
keyboard and mouse them to your machine
○ More powerful and has more storage ● Utility Software: A software designed to
capability
help you analyze. configure, optimize or
○ Hardware components can be easily
maintain a computer or support its
upgraded
● All-in-One Computer infrastructure
○ Monitor and system unit are housed ○ Examples: Disk defragmenters,
together, thus take up less space System Profilers, Network
○ Difficult to service or upgrade Managers, Application Launchers,
○ More expensive than desktops Antivirus software, Backup software,
● Portable/ Mobile Device Disk repair, Disk Cleaners, Registry
○ Highly portable, but usually less Cleaners, Disk Space analyzer, file
powerful in specifications manager, File Compression, and
○ Difficult to service or upgrade
Hardware Drivers
Computer Software 2. Application Software
A program that enables a computer to perform a An app, application program or application
specific task, as opposed to the physical software is a computer program designed to help
components of the system or hardware. It has to people perform an activity. Depending on the
be “loaded” into the computer’s storage before it activity for which it is designed, an application can
can be executed. manipulate text, numbers, audio, graphics and a
- hardware cannot work by themselves, it combination of these elements.
needs instructions: commanding officer Four key types:
● Device Management Apps: provide tools for
Classifications: maintaining a computer or device
1. System Software is a type of computer ● Productivity Apps: allows creation of
program that is designed to run the documents, graphics and to interact with
computer's hardware and application digital media
● Communication Apps: allows the user to ■ Tools to analyze data
share or receive communications or
information ● Database Software
● Personal Interest Apps: provide users with ○ The phrase used to describe any
tools to pursue their personal interests software that is designed for
creating databases and managing
Software types can also be classified by their tasks. the information stored in them.
○ Sometimes referred to as database
management systems (DBMS),
database software tools are
primarily used for storing,
modifying, extracting and searching
for information within a database
○ Each piece of data is entered and
stored in a field
○ Tables are a collection of records for
● Spreadsheet Software a single subject
○ Let you interact with numbers, chart ○ A query extracts data based on
graphics text and data you can specified criteria, or conditions, for
perform calculations and data one or more fields
stored in a grid of cells and ○ A report is a user-designed layout of
recalculate values automatically database content
when the data changes ○ A form screen used to enter data
○ Worksheets are laid out in grid of into a database
rows and columns; they use letters ○ Key Features:
to identify each column and ■ Ability to collect data, in a
consecutive numbers to identify manner that allows access
each row. retrieval, and reporting of
○ A cell is the location formed by the that data
intersection of a column in a row. ■ Represent a query in
○ Key Features: Structured Query Language
■ Formatting tools to change a (SQL)
worksheet’s appearance ■ Execute database
■ Ability to create a printed applications such as, track
output of the created inventory, maintain
spreadsheet. customer lists, or manage
■ Web capabilities to share employee records
workbooks online, add
hyperlinks, and save
worksheets and as web Basic Computer Navigation
pages Once you press the power button in your
■ Developer to add customized computer.
functions
1. The computer receives power from the ● Save the computer, flash drive or cloud. If
power supply or battery and sent it to the creating or editing a file, it should be saved
circuitry frequently. Files you work on using a web
2. The processor runs the bootstrap program app save changes as you make them.
3. The bootstrap program execute a series of ● Use the Save As or Save a copy dialog box to
tests to check the components save a file with a new name or in a new
4. The computer does the operating system location.
files into RAM, including the kernel
5. The computer loads to system configuration
information and loads startup program
Upon locking in you will see the desktop window
and its components:
To access or initiate a computer application, one
just needs to double click on the application’s icon
● Every file has properties, such as name,
from the desktop window. If the application is not
type, location, and size.
found on the initial desktop window, you may click
● Dates: when the file was created, modified,
on the windows icon (for Windows OS) or the dock
last accessed
(for MAC OS)
● The operating system assigns some
properties to files, such as type or format,
Saving a file using Microsoft applications:
and updates other properties such as data,
● Name the file, you must give it a name that
size, and location.
follows your operating system’s rules for
file-naming conventions.
Manage Folder Names and Folder Placement
○ Most file names contain an
● You can create a new folder in a file
extension that tells about its
manager such as File Explorer or Finder
contents, such as the type of
● Within file manager, you can move, copy,
platform or app on which the file
and delete folders the same as file
can be used.
○ File name extensions are added
automatically when you save a
dilem but you can change the
extension in some cases.
Follow ethical guidelines in accessing from online
sources:
● Copying photos might violate intellectual
property rights
● A copyright gives authors and artists right
to sell, publish or distribute an original work
of authorship
Functions of a File Name Manager:
● Some online resources are protected by
● View frequently or recently opened files
digital right management (DRM), which
and folders
limit access to proprietary rights
● View the main folders on your computer or
● Some material is in the public domain and
device
can be used without permission
● Search by file name, content, date, and
● The fair use doctrine allows one to use a
more
sentence or paragraph of text without
permission with citation to the original
Information Literacy
source
● Ability to find, evaluate, organize, use, and
● Creative Commons (CC): a non profit
communicate information in all its various
organization that helps content creators
formats, most notably in situations
keep copyright to their materials while
requiring decision making, problem-solving,
allowing others to use, copy, or distribute
or the acquisition of knowledge.
their work
● Allows one to:
○ Navigate many sources of
information, including the Internet,
Safety and Security
online libraries, and popular media
Using a computer may impose hazards or risks
sites.
○ Select the right tool for finding the
Risk
information you need
- The possibility something might occur that
○ Recognize that not all information is
results in an injury or loss
created equal
Three main types of hazards or risks
○ Evaluate whether information is
1. Risk for Information
misleading, biased, or out of date.
● Data and programs, comes from attackers
● In evaluating the information from online
wants to steal information
sources, use the CARS checklist:
● Usually present in Online Banking,
○ Credibility: identify the author and
E-Commerce, Social Media, Data Mining,
check credentials
Fake Websites
○ Accuracy: verify facts and claims,
● Protecting your information from
check for bias
exploitation:
○ Reasonableness: examine whether
○ Give only necessary information on
the claims are fair and sensible
completing an online form
○ Support: look for reputable sources
○ Review the information that online
and authorities
sites such as Google, Facebook,
Microsoft, and others have stored ○ A strong password is a
about you longer combination of
○ Request to be removed from mailing letters, numbers, and
lists symbols
○ Create another email account to use ○ A longer password is always
my when a merchant or website more secure than the shorter
requires an address password regardless of
○ Do not use your social media complexity
account information to log in to ■ Most accurate
another site experts recommend
○ Shred paperwork that contains that a secure
personal information before password should be a
discarding minimum of 15-20
○ Do not carry a Social Security characters in length
number on a wallet or write it on a ● Other general recommendations:
check ○ Do not use passwords that
○ Do not provide personal information consist of dictionary words
either over the phone or through an or phonetic words
email message ○ Do not repeat characters or
○ Keep personal information in a use sequences (abc, 123)
secure location in home or ○ Do not use birthdays, family
apartment member names, pet names,
○ Be cautious about what information addresses, or any personal
is posted online and who can view information
your information ● Use a password manager
○ Keep only the last three months of ● Other forms of Authentication:
financial statements and shred older ● Authenticating with
documents biometrics
○ For paper documents that must be ○ Uses the unique
retained, use. scanner to provide a characteristics of your
PDF of the document and add a face, hands, or eyes
strong password that must be to authenticate you.
entered before it can be read Some of the different
○ Be cautious with a website or app types of biometrics
request to collect data that are used today
○ Websites that request more for authentication
information than would normally be include:
expected to be avoided ■ Retina/ Iris
● Exposure to risks can greatly be reduced by ■ Fingerprint
authentication measures such as: ■ Voice
● Use strong passwords ■ Face
● Two Factor Authentication
- Uses two levels of security: passwords and beryllium, barium, nickel, arsenic, lead and
codes mercury. When these chemicals are broken
● After correctly entering your password, a down in landfills, they tend to leak these
4-6 digit code is sent to your cell phone. The hazardous materials in both the air and soil
code must then be entered as a second creating extremely unhealthy environment
authentication method ● Tips to reduce e-waste
Encryption
● also a way to protect your information
● The process of “scrambling” information so
it cannot be read unless the user process is
the “key” to unlock it (decryption)
3. Risk in Health
○ Can apply to data-at-rest (harddrive)
● eye strain, poor posture when using
or data-in-transit (Internet)
devices, and muscle fatigue from keyboard
○ The encryption key must be kept
typing
secure
● Physical Health Issues:
● Digital certificate: a technology used to
○ Repetitive Strain Injuries
verify a user’s identity and key that has
been “signed” by a trusted third-party
All these precautions are used to prevent Identity
theft.
Identity Theft involves using someone’s personal
● Social Health Issues:
information to commit financial fraud
○ Cyberbullying: bullying that takes
- Attackers are called Script kitties, Hactivists,
place on technology devices using
Cyberterrorists, Nation state actors, Insiders
online social media platforms, public
online forums, gaming sites, text
Protect your Online Profile:
messaging, and email. Considered
● Be cautious about what information you
more harmful than general bullying
post
○ Cyberstalking: involves the use of
● Be cautious about who can view your
that knowledge to stalk another
information
person through email, text
● Pay close attention to information about
messages, phone calls, and other
new or updated security settings and
forms of communication
fine-tune profile options accordingly
Protect Computer Equipment from the risks and
2. Risk for Environment
hazards that may affect it.
● Toxic electronic components of computers
● A surge protector can defend computer
and other digital devices that are exposed
equipment from spikes, surges, and noise.
when devices are discarded
● An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can
● E-waste or electronic waste contains
be used to protect against blackouts and
harmful chemicals such as cathode rays,
brownouts
Protect Computers from theft:
● Use a cable lock
● Keep devices out of sight when in a
high-risk area
● Avoid being distracted by the device and
maintain awareness of surroundings
● Hold devices with both hands
● Do not use the device on escalators or near
train doors
● Do not use white or red headphone cords
● Do not give chase if a device is stolen
● Enable device security features
Connecting your devices on wireless connections
may also expose it to risks such as:
● Reading wireless transmission
● Viewing to stealing computer data
● Injecting malware
● Downloading harmful content
Precautions:
● Only connect to an approved wireless
network in public
● Limit the type of activity you do on public
networks to simple web surfing or watching
online videos
● Configure routers for a high level of security
Data Backup
- Creating a data backup means copying files
from a computer's hard drive that are
stored in a remote location
- Can protect against hardware malfunctions,
user error, software corruption, natural
disasters, and cyberattacks
- Options: online or to external hard drive
You might also like
- Security Guard Business PlanDocument34 pagesSecurity Guard Business PlanJoseph100% (2)
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- A Project Report On "Smart Dustbin" Submitted To V.P.M.P. Polytechnic, Gandhinagar Department of Computer EngineeringDocument21 pagesA Project Report On "Smart Dustbin" Submitted To V.P.M.P. Polytechnic, Gandhinagar Department of Computer EngineeringAryan Banawadi100% (1)
- IT - Chapter 1Document5 pagesIT - Chapter 1mobylayNo ratings yet
- 8652 Articlekritikram2019Document9 pages8652 Articlekritikram2019lovelethrNo ratings yet
- Objectives Role and Scope of Management AccountingDocument9 pagesObjectives Role and Scope of Management AccountingEarl EzekielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Kathlene JaoNo ratings yet
- Is An Integrated Set of Components For Collecting, Storing, and Processing Data and For Providing Information, Knowledge, and Digital ProductsDocument3 pagesIs An Integrated Set of Components For Collecting, Storing, and Processing Data and For Providing Information, Knowledge, and Digital Productssachin pareekNo ratings yet
- BMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020Document8 pagesBMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020sicelo ncubeNo ratings yet
- C.A-I Chapter-1Document6 pagesC.A-I Chapter-1Tariku KolchaNo ratings yet
- Management Reporting NotesDocument12 pagesManagement Reporting NotesDustin PerezNo ratings yet
- HorizonalDocument72 pagesHorizonalg.canoneo.59990.dcNo ratings yet
- Clanak 5Document10 pagesClanak 5Linh KhánhNo ratings yet
- Management HierarchyDocument8 pagesManagement Hierarchysneha kotawadekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument10 pagesChapter 1: The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveAstxilNo ratings yet
- Fma - 1Document60 pagesFma - 1Hammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Module 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsDocument9 pagesModule 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsClaire BarbaNo ratings yet
- The Role of OrganisationDocument9 pagesThe Role of OrganisationMadhury MosharrofNo ratings yet
- Baccinsx CM Week1andweek2 Ais101 RrdeveraDocument13 pagesBaccinsx CM Week1andweek2 Ais101 RrdeveraMitchie FaustinoNo ratings yet
- It PrelimDocument16 pagesIt Prelimg.canoneo.59990.dcNo ratings yet
- AIS ReviewerDocument22 pagesAIS Reviewersky.dumpacc00No ratings yet
- Cost Chapter 1-5Document302 pagesCost Chapter 1-5chingNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Business Processes and Decision-Making SystemsDocument20 pagesWeek 3: Business Processes and Decision-Making SystemsỐc Sên NhỏNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems An OverviewDocument36 pagesAccounting Information Systems An OverviewJonathan Dave PagariganNo ratings yet
- Information System and MIS: Gagan Deep Rozy Computech Services 3 Gate, K.U., Kurukshetra-136119Document15 pagesInformation System and MIS: Gagan Deep Rozy Computech Services 3 Gate, K.U., Kurukshetra-136119Neel KamalNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Financial MGMT Gov UsDocument4 pagesDatasheet Financial MGMT Gov UsabsNo ratings yet
- AIS - Chapter 1Document51 pagesAIS - Chapter 1Hasan AbirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1NaveenNo ratings yet
- Mis VVFGCDocument114 pagesMis VVFGCArthiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Management Accounting and Business EnvironmentDocument7 pagesTopic 1 Management Accounting and Business EnvironmentdigididoghakdogNo ratings yet
- Impact of Top Management Support On Accounting Information System: A Case of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) SystemDocument8 pagesImpact of Top Management Support On Accounting Information System: A Case of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systemzelalem shiferawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial AccountingDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Managerial AccountingSahra PajarillaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's Perspective: CMEA2216 Accounting Information SystemsDocument25 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's Perspective: CMEA2216 Accounting Information SystemsMohd Nasrul AsrafNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of An Accounting Information System Inside A Financial Corporation A Case Study On Multi-Method Information at Haines Watts CorporationDocument7 pagesQualitative Characteristics of An Accounting Information System Inside A Financial Corporation A Case Study On Multi-Method Information at Haines Watts CorporationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument40 pagesChapter 1 The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveFarah Byun100% (1)
- Chapter 02 Overview of Accounting Information SystemDocument42 pagesChapter 02 Overview of Accounting Information Systemfennie lohNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Report BA701 Managerial Accounting & ControlDocument77 pagesGroup 1 Report BA701 Managerial Accounting & Controlrichard dehn medinaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant'S PerspectiveDocument5 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant'S PerspectivexxpinkywitchxxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Anika Gaudan PonoNo ratings yet
- 13 - Logistics Information Systems - All PartsDocument110 pages13 - Logistics Information Systems - All PartsMohamed NabalawyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledCyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 - AIS IntroductionDocument54 pages1 - AIS Introductionryuu35692No ratings yet
- Journal To CritiqueDocument5 pagesJournal To CritiqueEmieNo ratings yet
- MAS.2901 - Overview of MASDocument6 pagesMAS.2901 - Overview of MASdaemonspadechocoyNo ratings yet
- F5-18 Performance Management Information SystemsDocument26 pagesF5-18 Performance Management Information SystemsMohamed ElbariNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Chapter 1Document12 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 122100629No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Management AccountingDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Management AccountingOvi AndrestiNo ratings yet
- C19 - Group 1 - History and Trends in Management-ReportingDocument12 pagesC19 - Group 1 - History and Trends in Management-Reportingsharlyn graceNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 & 12 Types of Decision and Information SystemDocument29 pagesChap 2 & 12 Types of Decision and Information SystemJayesh GarachhNo ratings yet
- A Project Management Information System Serves Five Principal PurposesDocument9 pagesA Project Management Information System Serves Five Principal PurposesSumme Ma TigeNo ratings yet
- Management Science: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Document3 pagesManagement Science: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)KA TENo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - ITAPP Introduction To Accounting Information SystemDocument17 pagesMODULE 1 - ITAPP Introduction To Accounting Information SystemALYSSA LEIGH VILLAREALNo ratings yet
- Comercio Electronico 2018Document21 pagesComercio Electronico 2018maritzaNo ratings yet
- Stratcost LecturesDocument2 pagesStratcost LecturesAlyzza AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Chapter 1Document30 pagesManagement Accounting Chapter 1dawsonNo ratings yet
- C39IA Accounting Information, Communication & Technology: Not Just A Load of Old Numbers .Document34 pagesC39IA Accounting Information, Communication & Technology: Not Just A Load of Old Numbers .Sunil BawaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting and Cost ConceptsDocument11 pages1 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting and Cost ConceptsMARK KENNETH RULLEPANo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting-Notes For PrelimDocument18 pagesCost Accounting-Notes For PrelimAngelie BancaleNo ratings yet
- F2 - Section 1 - Accounting For ManagementDocument18 pagesF2 - Section 1 - Accounting For ManagementDiệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 MISDocument25 pagesChapter-9 MISRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Flows of Information Used Primarily at The Operations Level To Capture Transaction andDocument7 pagesHorizontal Flows of Information Used Primarily at The Operations Level To Capture Transaction andcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- MS ReviewerDocument4 pagesMS Reviewerangelinavalencia0307No ratings yet
- Ca 51012 Fin Man Quiz 1 - Example of Application Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesCa 51012 Fin Man Quiz 1 - Example of Application Type QuestionsFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Module 1Document16 pagesOblicon Module 1FoshAtokNo ratings yet
- StratCostMgmt 4 - Mock Test For Quiz 1 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesStratCostMgmt 4 - Mock Test For Quiz 1 Answer KeyFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Formative AssessmentDocument5 pagesFormative AssessmentFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory Services Antonio Jaramillo Dayag Management Accounting ConceptsDocument13 pagesManagement Advisory Services Antonio Jaramillo Dayag Management Accounting ConceptsFoshAtokNo ratings yet
- LogDocument23 pagesLogJeannel Joy GervacioNo ratings yet
- USER GuidelinesDocument15 pagesUSER GuidelinesdrfgdzfgNo ratings yet
- Standard Tool Bar Remains The Same Regardless The TransactionDocument17 pagesStandard Tool Bar Remains The Same Regardless The TransactionAnggun PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Diamond Select Ingenuity 128Document2 pagesDiamond Select Ingenuity 128Sepak OdokNo ratings yet
- Riss JS2 Second TermDocument15 pagesRiss JS2 Second TermkaylaNo ratings yet
- Frendx - 1985-05Document56 pagesFrendx - 1985-05Kasi XswlNo ratings yet
- AFNOR IPTDS BrochureDocument1 pageAFNOR IPTDS Brochurebdiaconu20048672No ratings yet
- Journal PakuDocument10 pagesJournal PakuPaku IslamiatiNo ratings yet
- Resume WordDocument2 pagesResume Wordapi-242422274No ratings yet
- DS-7204HI-VS Net DVR - V2.0 (080909)Document88 pagesDS-7204HI-VS Net DVR - V2.0 (080909)ANTONIO PEREZNo ratings yet
- DBMS Stored Function, Cursor & TriggerDocument10 pagesDBMS Stored Function, Cursor & TriggerAustinNo ratings yet
- Viva Android SettingDocument6 pagesViva Android SettingFawaz AlsaifNo ratings yet
- Measurement Procedure - Molspin Magnetometer: North Component Name/No of The SpecimenDocument10 pagesMeasurement Procedure - Molspin Magnetometer: North Component Name/No of The SpecimenShiva PatilNo ratings yet
- General Software Development Standards and GuidelinesDocument17 pagesGeneral Software Development Standards and GuidelinesSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument42 pagesPPTAbdul RifasNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Binary B-TreesDocument17 pagesSymmetric Binary B-TreesMEGUELLATI Fahd MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Introduction To Transaction ProcessingDocument69 pagesChapter 2: Introduction To Transaction ProcessingJanna Louisse Z. CervoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document8 pagesLecture 05Nebiye SolomonNo ratings yet
- Pyro Sim ManualDocument170 pagesPyro Sim ManualSerbian4096No ratings yet
- 2019 Hach BookletDocument16 pages2019 Hach Bookletwaikokpoh007No ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityOcubillo Froilan D.No ratings yet
- Finisher Q1 Q3 R1-Saddle Finisher Q2 Q4 R2 - PCDocument114 pagesFinisher Q1 Q3 R1-Saddle Finisher Q2 Q4 R2 - PCluis1984bolNo ratings yet
- Independent Government Cost Estimate (IGCE ... - (OUSD (AT&L) )Document2 pagesIndependent Government Cost Estimate (IGCE ... - (OUSD (AT&L) )joniNo ratings yet
- HD-R712 Specification V1.0Document5 pagesHD-R712 Specification V1.0quang nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Project Charter: Project Name: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Authorization Date: 25/09/2020Document8 pagesProject Charter: Project Name: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Authorization Date: 25/09/2020Leo DoeNo ratings yet
- M59209FP 1Document1 pageM59209FP 1irvan hardiansyahNo ratings yet
- BMGT 340 Syllabus Fall 2014Document10 pagesBMGT 340 Syllabus Fall 2014moshe feldmanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 01 - Objective Mapping - Safety and Professionalism - A+ Chapter 1 PDFDocument2 pages1.1 01 - Objective Mapping - Safety and Professionalism - A+ Chapter 1 PDFFlippencioNo ratings yet