Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871
4 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871
Uploaded by
fhtgerthrgergOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871
4 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871
Uploaded by
fhtgerthrgergCopyright:
Available Formats
Int. J. Mol. Sci.
2015, 16 12874
considered as functional food and used as an important part of a healthy diet. Their FAs compositions
are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Fatty acids composition of vegetable oils 1.
FAs [%] SAF GRP SIL HMP SFL WHG PMS SES RB ALM RPS PNT OL COC
C6:0 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 0.52
C8:0 nd 0.01 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 7.6
C10:0 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 0.01 nd nd 5.5
C12:0 nd 0.01 0.01 nd 0.02 0.07 nd nd nd 0.09 nd nd nd 47.7
C14:0 0.10 0.05 0.09 0.07 0.09 nd 0.17 nd 0.39 0.07 nd 0.04 nd 19.9
C15:0 nd 0.01 0.02 nd nd 0.04 nd nd nd nd 0.02 nd nd nd
C16:0 6.7 6.6 7.9 6.4 6.2 17.4 13.1 9.7 20.0 6.8 4.6 7.5 16.5 nd
C17:0 0.04 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.02 0.03 0.13 nd nd 0.05 0.04 0.07 nd nd
C18:0 2.4 3.5 4.5 2.6 2.8 0.7 5.7 6.5 2.1 2.3 1.7 2.1 2.3 2.7
C20:0 nd 0.16 2.6 nd 0.21 nd 0.47 0.63 nd 0.09 nd 1.01 0.43 nd
C22:0 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 0.14 nd nd nd nd 0.15 nd
C16:1 (n-7) 0.08 0.08 0.05 0.11 0.12 0.21 0.12 0.11 0.19 0.53 0.21 0.07 1.8 nd
C17:1 (n-7) nd nd 0.03 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd
C18:1cis (n-9) 11.5 14.3 20.4 11.5 28.0 12.7 24.9 41.5 42.7 67.2 63.3 71.1 66.4 6.2
C18:1trans (n-9) nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 0.14 nd nd nd
C20:1(n-9) nd 0.40 0.15 16.5 0.18 7.91 1.08 0.32 1.11 0.16 9.1 nd 0.30 nd
C18:2cis (n-6) 79.0 74.7 63.3 59.4 62.2 59.7 54.2 40.9 33.1 22.8 19.6 18.2 16.4 1.6
C18:3 (n-3) 0.15 0.15 0.88 0.36 0.16 1.2 0.12 0.21 0.45 nd 1.2 nd 1.6 nd
C18:3 (n-6) nd nd nd 3.0 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd
SFAs 9.3 10.4 15.1 9.2 9.4 18.2 19.6 16.9 22.5 9.3 6.3 10.7 19.4 92.1
MUFAs 11.6 14.8 20.7 28.1 28.3 20.9 26.1 42.0 44.0 67.9 72.8 71.1 68.2 6.2
PUFAs 79.1 74.9 64.2 62.8 62.4 61.0 54.3 41.2 33.6 22.8 20.9 18.2 18.0 1.6
n-3 PUFAs 0.2 0.2 0.9 0.4 0.2 1.2 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.0 1.2 0.0 1.6 0.0
n-6 PUFAs 79.0 74.7 63.3 62.4 62.2 59.7 54.2 40.9 33.1 22.8 19.6 18.2 16.4 1.6
1
Data are expressed as percentages of total fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs); nd means that FAs was not
determined. Abbreviations of the samples mean: SAF—safflower, GRP—grape, SIL—silybum marianum,
HMP—hemp, SFL—sunflower, WHG—wheat germ, PMS—pumpkin seed, SES—sesame, RB—rice bran,
ALM—almond, RPS—rapeseed, PNT—peanut, OL—olive, and COC—coconut oils.
Fatty acids composition of vegetable oils is formed by a mixture of saturated (SFAs) and unsaturated
(UNFAs) fatty acids classified according to the number of unsaturated bonds as monounsaturated
(MUFAs) or polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Nevertheless, each of analyzed vegetable oils has
specific fatty acid distribution depending on their plant sources. So, their impact on human health
could be assessed according to individual fatty acids because of their different influences on human
health and risks of serious diseases.
2.1.1. Saturated Fatty Acids (SFAs)
Saturated fatty acids with fewer than 12 carbon atoms being called short and medium chain
saturated fatty acids (MCFAs) have been found only in coconut oil (COC) in the amount not exceeding
7.6% of total methylester of fatty acids (FAMEs) as can be seen in Table 1. Expectedly, SFAs were
You might also like
- J N H Tiratsoo - Pipeline Pigging and Integrity Technology PDFDocument519 pagesJ N H Tiratsoo - Pipeline Pigging and Integrity Technology PDFfhtgerthrgerg50% (2)
- Manage TEG Liquid and Corrosion in Sales Gas Pipelines PDFDocument7 pagesManage TEG Liquid and Corrosion in Sales Gas Pipelines PDFfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاDocument4 pagesTABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاIbrrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analisis Caracterización Suelos CacaoterosDocument40 pagesAnalisis Caracterización Suelos CacaoterosHENRRI SALOME ROJAS CARLOSNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاDocument4 pagesTABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاIbrrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاDocument4 pagesTABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاIbrrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاDocument4 pagesTABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاIbrrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Irc - SP 30-2019-72-305Document234 pagesIrc - SP 30-2019-72-305anand punuriNo ratings yet
- PJB42 (2) 1201Document12 pagesPJB42 (2) 1201Hussain RazaNo ratings yet
- Pult-total Ac b t TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاDocument1 pagePult-total Ac b t TABLE: Joint Reactions يضرلاا هدمعا لولاا هدمعا يناثلا هدمعا ثلاثلا هدمعاIbrrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AdejokeDocument6 pagesChapter 4 AdejokesdcrownjohnNo ratings yet
- Informe 5Document3 pagesInforme 5Abel Mauricio HuamánNo ratings yet
- Data FaoziahDocument1 pageData FaoziahElisa ErlaniNo ratings yet
- LMS1Document12 pagesLMS1THU TONG NGOC HONGNo ratings yet
- Análisis de La Consistencia de Un PVT - Black OilDocument23 pagesAnálisis de La Consistencia de Un PVT - Black OilDarwin MoroccoNo ratings yet
- Total 4.58 1525 2599Document76 pagesTotal 4.58 1525 2599Ahmad NaufalNo ratings yet
- SL - No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Oxides MPD-11 TPD-06 VPD-3 Chpd-01 NSKD - 06 VKPD - 03 CHPD - 03 NSKD - 07 Kopd - 10Document2 pagesSL - No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Oxides MPD-11 TPD-06 VPD-3 Chpd-01 NSKD - 06 VKPD - 03 CHPD - 03 NSKD - 07 Kopd - 10vanithaNo ratings yet
- Date: 7/7/2017 PIC: Des Saputro & Ijun Trial: Trial HSBO: ParameterDocument14 pagesDate: 7/7/2017 PIC: Des Saputro & Ijun Trial: Trial HSBO: ParameterMargareth RiriedNo ratings yet
- Results Lipidomics Claudia Grewe 12 - 2023Document3 pagesResults Lipidomics Claudia Grewe 12 - 2023Gonçalo BastosNo ratings yet
- Smith e IchigenDocument20 pagesSmith e IchigenBrianNo ratings yet
- Octane & RVP Calc SheetDocument8 pagesOctane & RVP Calc SheetAsifNo ratings yet
- Payment Systems EuropeDocument3 pagesPayment Systems EuropekNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Localizacion - Pmediana y CFLPDocument7 pagesEjemplo Localizacion - Pmediana y CFLPJp VidalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Mohammad Anas Ashraf GagaiNo ratings yet
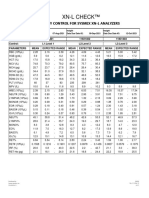
- XN L Check - 1183Document1 pageXN L Check - 1183brenda bivianoNo ratings yet
- VMA5Document1,146 pagesVMA5FranciusNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Reservoir ProblemsDocument1 pageOil and Gas Reservoir ProblemsJoseph YepezNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Reservoir ProblemsDocument1 pageOil and Gas Reservoir ProblemsJoseph YepezNo ratings yet
- T2 - Abastecimiento de Agua y AlcantarilladoDocument1 pageT2 - Abastecimiento de Agua y AlcantarilladoBrianNo ratings yet
- 0.1 N HCL, 2Ml Is Sample Volume: Titrant 1 (ML) TKN MG/L Titrant 2 (ML) TKN MG/L SD AvgDocument5 pages0.1 N HCL, 2Ml Is Sample Volume: Titrant 1 (ML) TKN MG/L Titrant 2 (ML) TKN MG/L SD AvgvasuNo ratings yet
- 12S (54X31) - MCDC - Foundation ReportDocument23 pages12S (54X31) - MCDC - Foundation ReportAung ThantNo ratings yet
- Orden de Merito CGR 372Document3 pagesOrden de Merito CGR 372Robert Diaz RNo ratings yet
- Analisis Gas NaturalDocument7 pagesAnalisis Gas NaturalMiguel OrtizNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios en Clase Gráficos de ControlDocument5 pagesEjercicios en Clase Gráficos de ControlDiego TavizónNo ratings yet
- OT 15 MarzoDocument163 pagesOT 15 Marzod1lf1x6hy9No ratings yet
- Laporan trb3Document21 pagesLaporan trb3Ariecandra MahesaNo ratings yet
- TableDocument1 pageTables3m3staNo ratings yet
- Metal Solid CopperDocument34 pagesMetal Solid CopperAnubhav LakhmaniNo ratings yet
- ASSAYDocument68 pagesASSAYDwi Dandy HNo ratings yet
- Planilha de Dimension Amen To Inst. Hidraulica Predial 2Document2 pagesPlanilha de Dimension Amen To Inst. Hidraulica Predial 2Marcony VerlyNo ratings yet
- Jo0c02423 - Si Year 2021Document34 pagesJo0c02423 - Si Year 2021pabitrapanigrahi02No ratings yet
- Estudio Ryr PromediosDocument20 pagesEstudio Ryr Promediosmartin gomezNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Ms. Excel TRB 3 - Kelompok 1Document160 pagesPerhitungan Ms. Excel TRB 3 - Kelompok 1Ariecandra MahesaNo ratings yet
- Jabeur Et Al 2014 (JAFC)Document12 pagesJabeur Et Al 2014 (JAFC)wassimguidara44No ratings yet
- Signal Script Exchange Big - SL SL Open Low Dyn - Atp LTP HighDocument18 pagesSignal Script Exchange Big - SL SL Open Low Dyn - Atp LTP HighSriheri DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio SeminarioDocument4 pagesEjercicio SeminarioManuel LealNo ratings yet
- HFY-OGMs CapacityDocument47 pagesHFY-OGMs CapacityVignesh PanchabakesanNo ratings yet
- Dholi Measurement Sheet1Document1 pageDholi Measurement Sheet1Surendra ShardaNo ratings yet
- Sampel RHSBO Ex Mobil 12-07-17Document10 pagesSampel RHSBO Ex Mobil 12-07-17Margareth RiriedNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Costo - Agrofyt S.A.S.Document7 pagesAnalisis de Costo - Agrofyt S.A.S.Tato Morales MedinaNo ratings yet
- Kuwaiti Gas & Oil Company: Bakr North South Amer Al Hamed Flow Rate Temp PressureDocument2 pagesKuwaiti Gas & Oil Company: Bakr North South Amer Al Hamed Flow Rate Temp PressureOmar WardehNo ratings yet
- CM y CR - SismosDocument6 pagesCM y CR - SismosJulio EspirituNo ratings yet
- Sem AllDocument20 pagesSem AllDogol HarjonoNo ratings yet
- 180724-27 WsocDocument67 pages180724-27 WsocOsqi C. BlancoNo ratings yet
- Volume GutterDocument2 pagesVolume GutterAnnisaNo ratings yet
- Process and Equipment Experiment: Fluid CircuitDocument25 pagesProcess and Equipment Experiment: Fluid CircuitNguyễn ThuNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Assay Report: OriginalDocument14 pagesCrude Oil Assay Report: Originaldassi99No ratings yet
- VMA1Document2,573 pagesVMA1FranciusNo ratings yet
- Estimating A Demand Function - It's About TimeDocument13 pagesEstimating A Demand Function - It's About TimeSebastián RojasNo ratings yet
- Δαi α C α C ΔC C cosα: alpha designDocument8 pagesΔαi α C α C ΔC C cosα: alpha designzorenNo ratings yet
- Hole - ID Hill Depth - Fr. Depth - To Interval Z - From Z - ToDocument4 pagesHole - ID Hill Depth - Fr. Depth - To Interval Z - From Z - ToLouis WirdunaNo ratings yet
- Field Installation ChallengesDocument1 pageField Installation ChallengesfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Thermal Movement Protective Tent: 3.2. RainforestDocument1 pageThermal Movement Protective Tent: 3.2. RainforestfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Wayne Hodgins and Robert Buchanan, Both of Canusa-CPS, CanadaDocument1 pageWayne Hodgins and Robert Buchanan, Both of Canusa-CPS, CanadafhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Vegetable Oils Fatty Acids Cardiovascular Diseases Coronary Heart DiseasesDocument1 pageKeywords: Vegetable Oils Fatty Acids Cardiovascular Diseases Coronary Heart DiseasesfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFsam PDFsam TP 01Document1 page3 PDFsam PDFsam TP 01fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Sandstorm On The Right-of-Way Partially Buried CutbackDocument1 pageSandstorm On The Right-of-Way Partially Buried CutbackfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- 20-PRCI MEAS-6-22 Turbine-USM Inert Gas 6 Feb 2019Document29 pages20-PRCI MEAS-6-22 Turbine-USM Inert Gas 6 Feb 2019fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871Document1 page1 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871Document1 page3 PDFsam PDFsam Ijms-16-12871fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Dissolution of Iron Oxides by Oxalic Acid: Sung Oh LeeDocument229 pagesDissolution of Iron Oxides by Oxalic Acid: Sung Oh LeefhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- KreeftG.J.2017 STOREGO EuropeanLegislativeandRegulatoryFrameworkonPower To GasDocument99 pagesKreeftG.J.2017 STOREGO EuropeanLegislativeandRegulatoryFrameworkonPower To GasfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Year in Review PIPELINE RESEARCH COUNCIL INTERNATIONAL. 2013 Year in ReviewDocument32 pagesYear in Review PIPELINE RESEARCH COUNCIL INTERNATIONAL. 2013 Year in ReviewfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Number 05 Lit Rev Geogenics ContainmentsDocument49 pagesTechnical Report Number 05 Lit Rev Geogenics ContainmentsfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Internal Corrosions in Oil and Gas Transport PipelinesDocument8 pagesInternal Corrosions in Oil and Gas Transport PipelinesfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Internal Coating-A Must in Gas Pipelines: March 2017Document28 pagesInternal Coating-A Must in Gas Pipelines: March 2017fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Water Scrubbing For Removal of CO2 Carbon DioxideDocument7 pagesWater Scrubbing For Removal of CO2 Carbon DioxidefhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Protecting Pipelines From Corrosion - GPT Industries PDFDocument3 pagesProtecting Pipelines From Corrosion - GPT Industries PDFfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Minerals 09 00044Document14 pagesMinerals 09 00044fhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Study of Corrosion Pattern in Gas Dehydration System Handling Sour Gas PDFDocument14 pagesStudy of Corrosion Pattern in Gas Dehydration System Handling Sour Gas PDFfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Detection and Monitoring of Deposits in Multiphase Ow Pipelines Using Pressure Pulse TechnologyDocument13 pagesDetection and Monitoring of Deposits in Multiphase Ow Pipelines Using Pressure Pulse TechnologyfhtgerthrgergNo ratings yet
- Take and Process OrdersDocument7 pagesTake and Process OrdersHelene ForteNo ratings yet
- Cut Diet Lean MassDocument62 pagesCut Diet Lean Masspakzeeshan167% (3)
- Case Study 1 Nut 116alDocument6 pagesCase Study 1 Nut 116alapi-249635202No ratings yet
- Amavata - Causes Pathology Treatment Panchakarma MedicinesDocument4 pagesAmavata - Causes Pathology Treatment Panchakarma MedicinesSN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- MENU KNOWLEDGE Notes SteveDocument4 pagesMENU KNOWLEDGE Notes SteveBilha WambuiNo ratings yet
- Preview Cure YourselfDocument111 pagesPreview Cure YourselfShareef Ghouse50% (2)
- Nutritional Awareness Among Lactating Indian WomenDocument7 pagesNutritional Awareness Among Lactating Indian WomenJuniper PublishersNo ratings yet
- Pires 2015Document14 pagesPires 2015hamzamursandi87No ratings yet
- Hubungan Status Gizi Ibu Saat Hamil Dengan Berat Lahir Bayi Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Pegantenan PamekasanDocument5 pagesHubungan Status Gizi Ibu Saat Hamil Dengan Berat Lahir Bayi Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Pegantenan PamekasanRinaERpienaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q1 W2Document25 pagesCookery 10 Q1 W2Gwyneth Joy CasiquinNo ratings yet
- 1200 Calorie Meal Plan BookDocument31 pages1200 Calorie Meal Plan Bookvaldric6653No ratings yet
- Nutrition ProgramDocument30 pagesNutrition Programmaria erika100% (2)
- Short Functional Text: Greeting Cards A. E. Example of Greeting CardsDocument13 pagesShort Functional Text: Greeting Cards A. E. Example of Greeting CardsMamik PrihatiNo ratings yet
- Soybean Meal An Excellent Protein Source For Poultry FeedsDocument16 pagesSoybean Meal An Excellent Protein Source For Poultry FeedsJohn HonestNo ratings yet
- SEO Strategy - ProtyzeDocument6 pagesSEO Strategy - Protyzebro digital marketingNo ratings yet
- Nuyritional Impact of Biodiversity According To World Health Organization (WHO) Biodiversity Is A Vital Element of A Human Being'sDocument1 pageNuyritional Impact of Biodiversity According To World Health Organization (WHO) Biodiversity Is A Vital Element of A Human Being'sSimang MamucudNo ratings yet
- SD ChallengeDocument13 pagesSD ChallengeGwen Lakeman-LeivaNo ratings yet
- The Food and Beverage DepartmentDocument40 pagesThe Food and Beverage DepartmentChristian CandareNo ratings yet
- OmegaEquis Fish Oil Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageOmegaEquis Fish Oil Technical Data SheetKatherine Leyla Anchayhua TorresNo ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education (TVE) : Quarter 2-Module 1Document39 pagesTechnical and Vocational Education (TVE) : Quarter 2-Module 1Gerry SegubienceNo ratings yet
- Soft Drinks and School-Age ChildrenDocument6 pagesSoft Drinks and School-Age ChildrenkalikNo ratings yet
- Affective DomainDocument5 pagesAffective Domainnhoj eca yabujNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Potato Chips, Extruded & Fried Snacks: Detail Project Report OnDocument98 pagesManufacturing of Potato Chips, Extruded & Fried Snacks: Detail Project Report OnNavneet RankNo ratings yet
- CB6 End of Level KeyDocument3 pagesCB6 End of Level KeyQuỳnh MaiNo ratings yet
- The 21-Day Intermittent Fasting Weight Loss PlanDocument271 pagesThe 21-Day Intermittent Fasting Weight Loss PlanAndrew Morton100% (11)
- Binggris Kelas 5Document2 pagesBinggris Kelas 5Fibie LionaNo ratings yet
- Vegan Certification: About VegecertDocument3 pagesVegan Certification: About VegecertHuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Isadiet DataDocument3 pagesIsadiet DataMarc CureNo ratings yet
- Olive OilDocument10 pagesOlive OilSiva Prasad KalariNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status Record: Department of EducationDocument1 pageNutritional Status Record: Department of EducationLea TanNo ratings yet