Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tunnel Diode Definition
Tunnel Diode Definition
Uploaded by
shwet_v0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views12 pagesThis document discusses tunnel diodes. Key points include:
- A tunnel diode is a heavily doped p-n junction diode that exhibits negative resistance, where current decreases as voltage increases, due to the quantum tunneling effect.
- Tunnel diodes have a very narrow (~10nm) doped p-n junction and are used in high-frequency applications like oscillators and amplifiers that require negative resistance.
- The current-voltage characteristic curve of a tunnel diode shows a negative slope region, indicating negative resistance, when a small forward bias is applied due to tunneling current.
Original Description:
tunnel diode
Original Title
tunnel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses tunnel diodes. Key points include:
- A tunnel diode is a heavily doped p-n junction diode that exhibits negative resistance, where current decreases as voltage increases, due to the quantum tunneling effect.
- Tunnel diodes have a very narrow (~10nm) doped p-n junction and are used in high-frequency applications like oscillators and amplifiers that require negative resistance.
- The current-voltage characteristic curve of a tunnel diode shows a negative slope region, indicating negative resistance, when a small forward bias is applied due to tunneling current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views12 pagesTunnel Diode Definition
Tunnel Diode Definition
Uploaded by
shwet_vThis document discusses tunnel diodes. Key points include:
- A tunnel diode is a heavily doped p-n junction diode that exhibits negative resistance, where current decreases as voltage increases, due to the quantum tunneling effect.
- Tunnel diodes have a very narrow (~10nm) doped p-n junction and are used in high-frequency applications like oscillators and amplifiers that require negative resistance.
- The current-voltage characteristic curve of a tunnel diode shows a negative slope region, indicating negative resistance, when a small forward bias is applied due to tunneling current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
1 TUNNEL DIODE
2 DEFINITIONN
3 WHAT IS TUNNEL DIODE
4 WORKING
5 VI CHARACT
6 APPLICATIONS
7 ASSIGNMENT
Tunnel diode definition
A Tunnel diode is a heavily
doped p-n junction diode in which
the electric current decreases as
the voltage increases.
In tunnel diode, electric current is
caused by “Tunneling”. The tunnel
diode is used as a very fast
switching device in computers. It is
also used in high-frequency
oscillators and amplifiers.
Tunnel Diode Symbol
The symbol for a tunnel diode is
shown below.
What is a Tunnel Diode?
A tunnel diode (also known as a
Esaki diode) is a type of
semiconductor diode that has
effectively “negative resistance”
due to the quantum mechanical
effect called tunneling.
Tunnel diodes have a heavily
doped pn junction that is about 10
nm wide.
Many devices use the negative
conductance property of
semiconductors for these high
frequency applications. A tunnel
diode is one of the most commonly
used negative conductance
devices. It is also known as Esaki
diode after Leo Esaki for his work
on this effect. The concentration of
dopants in both p and n region is
very high.The pn junction is also
abrupt. For this reasons, the
depletion layer width is very
small. In the current voltage
characteristics of tunnel diode, we
can find a negative slope region
when a forward bias is applied.
working of Tunnel Diode
Unbiased Tunnel Diode
In an unbiased tunnel diode, no
voltage will be applied to the tunnel
diode. Here, due to heavy doping
conduction band of n – type
semiconductor overlaps with
valence band of p – type material.
Electrons from n side and holes
from p side overlap with each other
and they will be at same energy
level.
Some electrons tunnel from the
conduction band of n-region to the
valence band of p-region when
temperature increases. Similarly,
holes will move from valence band
of p-region to the conduction band
of n-region. Finally, the net current
will be zero since equal numbers of
electrons are holes flow in opposite
direction.
Small Voltage Applied to the
Tunnel Diode
When a small voltage, that has
lesser value than the built-in
voltage of the depletion layer, is
applied to the tunnel diode, there is
no flow of forward current through
the junction. Nevertheless, a
minimal number of electrons from
the conduction band of n region will
start tunneling to valence band in p
region.
Therefore, this movement creates
a small forward biased tunnel
current. When a small voltage is
applied, tunnel current starts to
flow.
Increased Voltage Applied to the
Tunnel Diode
When the amount of voltage
applied is increased, the number of
free electrons generated at n side
and holes at p side is also
increased. Due to voltage
increase, overlapping between the
bands are also increased.
Maximum tunnel current flows
when the energy level of n-side
conduction band and the energy
level of a p-side valence band
becomes equal.
Further Increased Voltage Applied
to the Tunnel Diode
A further increase in the applied
voltage will cause a slight
misalignment of the conduction
band and valence band. Still there
will be an overlap between
conduction band and valence
band. The electrons move from
conduction band to valence band
of p region. Therefore, this causes
small current to flow. Hence, tunnel
current starts decreasing.
Largely Increased Voltage Applied
to the Tunnel Diode
The tunneling current will be zero
when applied voltage is increased
more to the maximum. At this
voltage levels, the valence band
and the conduction band does not
overlap. This makes tunnel diode
to operate same as a PN junction
diode.
When applied voltage is more than
the built-in potential of the
depletion layer the forward current
starts flowing through the tunnel
diode. In this condition, current
portion in the curve decreases
when the voltage increases and
this is the negative resistance of
tunnel diode. Such diodes
operating in negative resistance
region is used as amplifier or
oscillator.
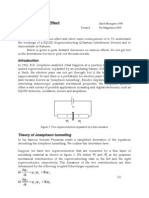
V-I Characteristics & of Tunnel
Diode
Due to forward biasing, because of
heavy doping conduction happens
in the diode. The maximum current
that a diode reaches is Ip and
voltage applied is Vp. The current
value decreases, when more
amount of voltage is applied.
Current keeps decreasing until it
reaches a minimal value.
The small minimal value of current
is Iv. From the above graph, it is
seen that from point A to B current
reduces when voltage increases.
That is the negative resistance
region of diode. In this region,
tunnel diode produces power
instead of absorbing it.
Tunnel Diode Applications
1 Tunnel diode is a type of sc
diode which is capable of very fast
and in microwave frequency
range.
2 Tunnel diodes can be used as
high frequency oscillators as the
transition between the high
electrical conductivity is very
rapid.
3 For microwave generators and
amplifiers tunnel diode are used.
4 Tunnel diodes are resistant to the
effects of magnetic fields, high
temperature and radioactivity.
That’s why these can be used in
modern military equipment.
5 These are used in nuclear
magnetic resource machine also.
But the most important field of its
use satellite communication
equipments.
You might also like
- Pioneer DDJ sx3 rrv4685Document56 pagesPioneer DDJ sx3 rrv4685Alex100% (3)
- Diamond Integrators Guide RevAADocument56 pagesDiamond Integrators Guide RevAAZeljko KrivokucaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Energy Generator (QEG) Manual - 3rd EditionDocument86 pagesQuantum Energy Generator (QEG) Manual - 3rd EditionFreeEnergyWorld100% (13)
- Scientech 2266Document33 pagesScientech 2266sarikapravinNo ratings yet
- Philips BV-29 - Service ManualDocument5 pagesPhilips BV-29 - Service ManualYoussef0% (1)
- Tunnel Diode PDFDocument9 pagesTunnel Diode PDFSONIKA R R 18BEC152No ratings yet
- CHAP 1 Part 2Document36 pagesCHAP 1 Part 2ksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Overview of Waveguides: Asmita Singhal Su/PdicDocument28 pagesOverview of Waveguides: Asmita Singhal Su/PdicAsmitaSinghalBairathiNo ratings yet
- (#3) Direct, Indirect, Ek Diagram, Effective Mass-1Document6 pages(#3) Direct, Indirect, Ek Diagram, Effective Mass-1zubairNo ratings yet
- Helium Neon LaserDocument10 pagesHelium Neon LaserSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument28 pagesExtrinsic SemiconductorsSahil AhujaNo ratings yet
- Step and Graded IndexDocument24 pagesStep and Graded IndexJustin LivingstonNo ratings yet
- Band To Band Radiative RecombinationDocument19 pagesBand To Band Radiative RecombinationnikithaNo ratings yet
- 5.fermi Level in Itrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorDocument10 pages5.fermi Level in Itrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Faraday EffectDocument5 pagesFaraday EffectSarveenaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory (EMT)Document7 pagesElectromagnetic Theory (EMT)Sudalai MadanNo ratings yet
- 7 Extrinsic Semiconductor-1Document11 pages7 Extrinsic Semiconductor-1api-462620165No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Semiconductor Physics-Edited PDFDocument57 pagesUnit 4 Semiconductor Physics-Edited PDFMUSICAL MASTI RINGTONENo ratings yet
- Polytechnic Physics TRB Reference BooksDocument3 pagesPolytechnic Physics TRB Reference BooksJagan EashwarNo ratings yet
- Vector Model For Orbital Angular MomentumDocument6 pagesVector Model For Orbital Angular MomentumAgrupación Astronomica de Alicante100% (2)
- Transition and Diffusion CapacitanceDocument15 pagesTransition and Diffusion CapacitanceRishi JhaNo ratings yet
- Ee Electron Theory, Quantum Free Electron Theory & Band Width TheoryDocument4 pagesEe Electron Theory, Quantum Free Electron Theory & Band Width TheoryAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Laser PPT 3 & 4Document29 pagesLaser PPT 3 & 4Akhil Saini100% (1)
- Lattice VibrationsDocument10 pagesLattice VibrationsVarun GovindNo ratings yet
- Expt. 3 Planck's ConstantDocument10 pagesExpt. 3 Planck's ConstantSandeepNo ratings yet
- London EquationsDocument5 pagesLondon Equationsyehtt0212No ratings yet
- What Is Semiconductor? Classify The Semiconductor Material? AnswerDocument6 pagesWhat Is Semiconductor? Classify The Semiconductor Material? AnswerSaidur Rahman SidNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument114 pagesBasic Electronics NotessmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- Del OperatorDocument6 pagesDel OperatorSupriya Aggarwal100% (1)
- Avalanche Transit Time DevicesDocument13 pagesAvalanche Transit Time Devicesuma_maduraiNo ratings yet
- Unit III Arp FullDocument55 pagesUnit III Arp FullKATHIRAVAN .NNo ratings yet
- Effective ApertureDocument10 pagesEffective ApertureLeo HambirepiNo ratings yet
- 8.work Function of MetalDocument3 pages8.work Function of MetalRavi Kanth M NNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic and Intrinsic SemiconductorDocument10 pagesExtrinsic and Intrinsic Semiconductorryan ong0% (1)
- DiodesDocument91 pagesDiodesMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Diode EquationDocument7 pagesDerivation of Diode EquationSatyaNo ratings yet
- On PN Junction DiodeDocument12 pagesOn PN Junction DiodeSATHEESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lect-1 PDFDocument21 pagesUnit 1 Lect-1 PDFECE A SRM VDP100% (2)
- 3rd LectureDocument40 pages3rd LectureAnasNo ratings yet
- Fermi EnergyDocument7 pagesFermi EnergyBobNo ratings yet
- Iare - Ece - Edc Notes PDFDocument223 pagesIare - Ece - Edc Notes PDFVamshi Krishna0% (1)
- 8.1 Behavior of Electric DipolesDocument12 pages8.1 Behavior of Electric DipolesKamalKiran Tata100% (1)
- Van Hove SingularityDocument3 pagesVan Hove SingularityChang Jae LeeNo ratings yet
- EDC Lecture NotesDocument187 pagesEDC Lecture NotesKARTHIKAMANI RNo ratings yet
- IV (M) QM Gamma Ray MicroscopeDocument2 pagesIV (M) QM Gamma Ray MicroscopeAbhigyan HazarikaNo ratings yet
- 6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1Document12 pages6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1api-462620165No ratings yet
- ConductorsDocument62 pagesConductorsRamon Lopez Lapiña100% (1)
- EDC Unit-4Document23 pagesEDC Unit-4laxmanabcdNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument35 pagesOperational AmplifierskunwarNo ratings yet
- BH Curve PDFDocument7 pagesBH Curve PDFAviteshNo ratings yet
- Updated PPT of Types of Laser and HolographyDocument27 pagesUpdated PPT of Types of Laser and HolographyTejo KanthNo ratings yet
- PN Junction IsolationDocument8 pagesPN Junction Isolationrenjith r nairNo ratings yet
- FEE Lab Manual FinalDocument86 pagesFEE Lab Manual FinalbalasubadraNo ratings yet
- Hall Effect PDFDocument26 pagesHall Effect PDFmangsuresh100% (1)
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocument44 pagesTransistor CharacteristicsNidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument6 pagesOptical FiberSarveenaNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument5 pagesTunnel DiodeKhanpurKing1No ratings yet
- SQUIDlab Rev3Document12 pagesSQUIDlab Rev3sujit_sekhar100% (1)
- Unit-5 Fiber Optics & Laser 1537178489135Document15 pagesUnit-5 Fiber Optics & Laser 1537178489135Zahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Hemant PPT New DC Ac Model H Parameters of BJTDocument48 pagesHemant PPT New DC Ac Model H Parameters of BJTHemant SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode - Working, Characteristics, Applications What Is A Tunnel Diode?Document9 pagesTunnel Diode - Working, Characteristics, Applications What Is A Tunnel Diode?Abhirup BiswasNo ratings yet
- EW - L-3 - Some Active Components-DiodesDocument9 pagesEW - L-3 - Some Active Components-Diodeswebip33713No ratings yet
- MSC Phy 62Document6 pagesMSC Phy 62Krishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Definition: Waveguides Are A Special Category of Transmission Line That Is UsedDocument4 pagesDefinition: Waveguides Are A Special Category of Transmission Line That Is Usedshwet_vNo ratings yet
- VaractorDocument8 pagesVaractorshwet_vNo ratings yet
- Directional CouplerDocument9 pagesDirectional Couplershwet_v100% (1)
- Microwave Components Waveguide Tee E Plane Tee H Plane Tee Magic Tee Hybrid Tee AssignmentDocument14 pagesMicrowave Components Waveguide Tee E Plane Tee H Plane Tee Magic Tee Hybrid Tee Assignmentshwet_vNo ratings yet
- MCQ Comm-2Document18 pagesMCQ Comm-2shwet_vNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Ahmedabad: Congratulation!! You Have Passed This ExamDocument1 pageGujarat Technological University Ahmedabad: Congratulation!! You Have Passed This Examshwet_vNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Ahmedabad: Congratulation!! You Have Passed This ExamDocument1 pageGujarat Technological University Ahmedabad: Congratulation!! You Have Passed This Examshwet_vNo ratings yet
- EC For MastersDocument3 pagesEC For Mastersshwet_vNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Most Important Question BankDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics Most Important Question Bankshwet_v0% (1)
- Bachelor of Engineering: "Silicon IC-Fabrication Technology (VLSI) "Document46 pagesBachelor of Engineering: "Silicon IC-Fabrication Technology (VLSI) "Pradeep NavhalNo ratings yet
- 23R1476 - 0 - M039-H - Info Only PDFDocument463 pages23R1476 - 0 - M039-H - Info Only PDFChristianChalcoGonzales100% (3)
- 1 Transponders 140401230719 Phpapp01Document56 pages1 Transponders 140401230719 Phpapp01GaboxNo ratings yet
- Design and Production of An Automatic Solid Waste Sorting Machine With Smart Digital CounterDocument5 pagesDesign and Production of An Automatic Solid Waste Sorting Machine With Smart Digital CounterREYES, PATRICK HENDRYNo ratings yet
- TCS Datasheet Moore IndustriesDocument8 pagesTCS Datasheet Moore Industriessswoo8245No ratings yet
- Installing LegacyXperia For Dummies LegacyXperia - Wiki Wiki GitHubDocument5 pagesInstalling LegacyXperia For Dummies LegacyXperia - Wiki Wiki GitHubdasNo ratings yet
- Installation ManualDocument23 pagesInstallation ManualMaxcine ShuNo ratings yet
- Smaung Odyssey G9 NEO User ManualDocument57 pagesSmaung Odyssey G9 NEO User ManualMarc AnthonyNo ratings yet
- JAMMERsDocument60 pagesJAMMERsrahul kumar100% (8)
- Iasimp qr009 en P PDFDocument10 pagesIasimp qr009 en P PDFToni PrattNo ratings yet
- IEEE Base PaperDocument6 pagesIEEE Base PaperDeepti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Series 2000: The All-Rounders in The High Payload RangeDocument4 pagesSeries 2000: The All-Rounders in The High Payload RangeNahuel Rm100% (1)
- Buck Converter Basics & Selection of ComponentsDocument22 pagesBuck Converter Basics & Selection of ComponentsSateesh TalisettyNo ratings yet
- Samsung Firmware Langpacks Descriptions 09 2010Document173 pagesSamsung Firmware Langpacks Descriptions 09 2010Konstantin Yotov67% (3)
- Pc400lcse 8R PDFDocument14 pagesPc400lcse 8R PDFRieef 10No ratings yet
- Growatt HPS 50 Manual 2017-04Document22 pagesGrowatt HPS 50 Manual 2017-04Robin GomezNo ratings yet
- JNTUK Computer Organization Nov 2015 Question PaperDocument4 pagesJNTUK Computer Organization Nov 2015 Question PaperTSRKNo ratings yet
- Star 2230 enDocument16 pagesStar 2230 entrully69No ratings yet
- Dyson N248F v11 User Manual 2022 ANZ V2Document13 pagesDyson N248F v11 User Manual 2022 ANZ V2nzjottNo ratings yet
- BAB 1 BANJIR PmbetulanDocument5 pagesBAB 1 BANJIR PmbetulanAnonymous 6FUcbaPNo ratings yet
- Lighting Lighting: Greenvision XceedDocument2 pagesLighting Lighting: Greenvision XceednovaaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Lecher AntennaDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Lecher AntennaPt AkaashNo ratings yet
- Quiz-II Control Systems Engineering ECE327 Set-A: Total Marks: 20 Time: 1hrDocument1 pageQuiz-II Control Systems Engineering ECE327 Set-A: Total Marks: 20 Time: 1hrrabbitwarfighterNo ratings yet
- Nias 3P User's Guide - V 1Document54 pagesNias 3P User's Guide - V 1RositaNo ratings yet
- Solapur University, SolapurDocument32 pagesSolapur University, SolapurvipulkondekarNo ratings yet
- LED and BJTDocument72 pagesLED and BJTpusaitim sapuitimNo ratings yet