Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop
Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop
Uploaded by
Andrea AcuñaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop
Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop
Uploaded by
Andrea AcuñaCopyright:
Available Formats
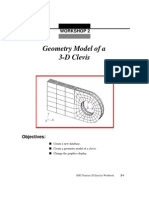
WORKSHOP 1
Geometry Model of a
3-D Clevis
Objectives:
■ Create a new database for the model.
■ Create the geometry of the clevis.
■ Alter the graphics display of the model.
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-1
1-2 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
Model Description:
In this exercise you will create an analytic solid model of a clevis by
defining MSC⁄PATRAN points, curves, surfaces, solids, and a user
defined coordinate system. Throughout this exercise you will become
more familiar with the use of the MSC⁄PATRAN select menu. You will
also be introduced to another viewing method and shown how to
change your model’s render style. Shown below is a drawing of the
model you will build and suggested steps for its construction.
8
1/4
3/4
4 Suggested surface boundaries
x
2 Dia 2 Radius
Exercise Procedure:
1. Open up a new database named clevis.db.
Type p3 in your xterm. The Main Window and Command Window will
appear.
File/New ...
New Database Name: clevis.db
OK
The viewport (PATRAN’s graphics window) will appear along with a
New Model Preference form. The New Model Preference sets all
the code specific forms and options inside MSC/PATRAN.
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-3
In the New Model Preference form set the Analysis Code to
MSC/ADVANCED_FEA.
Tolerance: ◆ Default
Analysis Code: MSC/ADVANCED_FEA
Analysis Type: Structural
OK
2. Change the geometric preference to PATRAN 2
convention.
The PATRAN 2 Convention convention represents a special class of
parameterized geometry known as parametric cubic. This option
allows the user to create geometry that can be exported and imported
into PATRAN 3 through the PATRAN 2 neutral files and IGES files.
Preferences/Geometry...
Geometry Representation: ■ PATRAN 2 Convention
Apply
Cancel
3. Create a point on the inner radius of the hole in the clevis.
First, make the geometry labels visible by using the following toolbar
icon:
Show Labels
◆ Geometry
Action: Create
Object: Point
Method: XYZ
Point Coordinates List: [ 1, 0, 0 ]
Apply
4. Use the point you just created to sweep 4 curves that will
define the upper half of the radius of the hole in the clevis.
Action: Create
1-4 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
Object: Curve
Method: Revolve
Total Angle: 180
Curves per Point: 4
Point List: select the point on the screen
The function autoexecutes, and four curves can now be seen in the
viewport.
5. Use Curvilinear Transformation to create the outer radius
of the lug by radially translating the curves that define a
quarter of the hole.
To accomplish this you will first need to create a cylindrical
coordinate frame located at the center of the hole.
Action: Create
Object: Coord
Method: 3 Point
Type: Cylindrical
Apply
Next, radially translate the curves.
Action: Transform
Object: Curve
Method: Translate
Type of Transformation: ◆ Curvilinear in Refer. CF
Refer. Coordinate Frame: select newly created
coord frame
Translation Vector: < 1, 0, 0 >
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-5
Figure 1.1 - Curves to Radially Translate
Curves to select
3
3 2
4 2
4 1
5 1
Z X
Curve List: select the two curves on
the right
Two new curves appear in the viewport.
6. Begin creating surfaces for the geometry model.
You have now created all the curves that you will need to complete
your clevis model. Next, you will create the necessary surfaces for the
model. You will start by creating a 4x2 surface that defines part of the
upper half of the clevis body.
Action: Create
Object: Surface
Method: XYZ
Vector Coordinates List: < -4, 2, 0>
Origin Coordinates List: [ -2, 0, 0 ]
Apply
7. Finish creating the surfaces surrounding the hole of the
model.
1-6 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
The next series of surfaces will be created using the Curve method.
First, create a surface by connecting two curves.
Action: Create
Object: Surface
Method: Curve
Option: 2 Curve
Figure 1.2 - Curves Selected to Create Lug Surface Geometry
<ctrl> click to
select outer
curves
11 10 8
6
1 3 3 2
4 T 2 5
4 1
12 9 5 1
Z R 1 6
Drag to select
inner curves
Y
Z X
Starting Curve List: drag to select the two
inner right curves
Ending Curve List: <ctrl> click to select the
two outer right curves
Next, create a surface using a curve and a surface edge.
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-7
Figure 1.3 - Curve and Edge for Next Surface
Edge to select
11 10 8
6
3 7
1 3 3 2
4 T 2 5
2
4 1
12 9 5 1
Z R 1 6
Curve to select
Y
Z X
Starting Curve List: select the lower left inner
curve (Curve 4)
Click in the Ending Curve List databox and select the following entity
select icon:
Edge
Ending Curve List: select the right edge of
the rectangular surface
Finally, create a surface using a curve and two defined points.
1-8 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
Figure 1.4 - Curve and Points for Final Surface
Points to select
11 10 8
6
3 7
1 3 3 2
4 4 T 2 5
2
4 1
12 9 5 1
Z R 1 6
Curve to select
Y
Z X
When you click in the Starting Curve databox, you will have to select
the following entity select icon:
Curve
Starting Curve List: select the remaining inner
curve (Curve 3)
Click in the Ending Curve List databox and select the following entity
select icon:
Two Points
Ending Curve List: select the two points where
the remaining curve should be
located (Pts 8 and 10)
8. Create the solids of the geometry model.
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-9
You will now use the Surfaces you have just created as patterns to
define solids (3-dimensional entities).
Action: Create
Object: Solid
Method: Normal
Thickness: 0.25
Surface List: select all surfaces
Five solids have now been created. In order to get a better view of the
model, use the following toolbar icon:
Iso 1 View
Figure 1.5 - Isometric View of Half-Lug Geometry
15
11
14
10
21
11 8
55 6
16
12
33 19
44 22 7
233 3
4 2
13 4 T 20
9 2
24 5
5 1 22
1
Z R 17
1
18
6
Z X
9. Create the lower half of the model by mirroring the solid.
Action: Transform
Object: Solid
Method: Mirror
1-10 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
Click in the Define Mirror Plane Normal databox and pick the
following entity select icon:
Frame Direction 2
Define Mirror Plane Normal: select second direction of
original coord frame
Solid List: select all solids
10. Create the remaining solids using the Translate method.
Action: Transform
Object: Solid
Method: Translate
Translation Vector: < 0, 0, -0.25 >
Repeat Count: 2
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-11
Figure 1.6 - Solids to Select for Lug Base
1115
14
10
21
11 8
55 6
16
12
33 19
44 3 22 7
3
4 23 2
4 T 20
13 2
9
5 24 1 22 5
6 1
Z R 1 17
9
27 3738 6 18
25
31 7
35 29
33
10
28 8
26
32
30
Y 36
34
Solids to select
Z X
Solid List: select only the two left
solids (Solids 1 and 6)
The left portion of the clevis should now appear.
The final geometry model construction step is to translate copies of the
solids which surround the hole.
Click in the Translation Vector databox and pick the following entity
select icon:
Tip and Base Points
1-12 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
To define the translation vector, pick Point 10 then Point 40 as
shown below. Use the View Corners toolbar icon to zoom in. After
selecting the points use Fit View toolbar icon to zoom out.
Figure 1.7 - Points to Select for Solid Translation Vector
Point 40
Point 10
Z X
4147
1115
46
40
14
10
13
11
48 11 21
42 8
16
12 55 6
44 22 33 19
23
3945 4 3 3 2 7
14 913 4 T
2
20
12 24
5
49 6
1 1 22 5
2743
25 9 R 1 17
38Z 18
37 6
35 29 31 7
Y 50 33
44 10
28
26 8
X 36 3032
Z 34
Fit View
View Corners
Repeat Count: 1
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-13
Figure 1.8 - Solids to Translate to Complete Lug Geometry
47
1541
11
Solids to select
46
1440
10
13 21
11
11 8
48 55 6
1642
12
33
44 3 3 22 7 19
4 23 2
45 T
1339 4 2
20
9
14 5 24 1 22 5
6 12 1
Z R 1 17
49 9
2743 3738 6 18
25
31 7
29
3335
50 10
2844 8
26
3032
Y 36
34
Z X
Solid List: select all solids which
surround the hole
11. Change the display to see the model without labels and
without the wireframe view.
First, turn off the entity labels using the following toolbar icon:
Hide Labels
Next, display the model in hidden line rendering style by selecting the
following toolbar icon:
Hidden Line
1-14 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
WORKSHOP 1 Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis
Figure 1.9 - Hidden Line view of Lug Geometry
1
Z R
Z X
When done viewing, change the rendering style back to wireframe.
Wireframe
Close the database.
File/Close
This concludes this exercise.
PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook 1-15
1-16 PATRAN 322 Exercise Workbook
You might also like
- SOLIDWORKS 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UserFrom EverandSOLIDWORKS 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UserNo ratings yet
- Rhino Ship Hull TutorialDocument32 pagesRhino Ship Hull TutorialMark Pavkov100% (27)
- Pit DesignDocument96 pagesPit DesignStajic Milan100% (2)
- Surpac Block ModellingDocument111 pagesSurpac Block ModellingPaul100% (1)
- Surpac Underground Ring DesignDocument50 pagesSurpac Underground Ring DesignP100% (1)
- Study of Laminar and Turbulent Flow On Flat Plate Using SOLIDWORKSDocument14 pagesStudy of Laminar and Turbulent Flow On Flat Plate Using SOLIDWORKSMohd Amman SadiqueNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-212-412Document201 pages1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-212-412Andrea AcuñaNo ratings yet
- 8P - Relative - Motion - WRT - Translating AxesDocument19 pages8P - Relative - Motion - WRT - Translating AxesIsaias ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: LessonDocument16 pagesGeometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: LessonAndrea AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2Document16 pagesGeometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2hfathollahiNo ratings yet
- Shape Optimization of A Fly Wheel: Workshop Problem 5Document20 pagesShape Optimization of A Fly Wheel: Workshop Problem 5276763420No ratings yet
- Topology Optimization of A Notch ProblemDocument20 pagesTopology Optimization of A Notch Problem276763420No ratings yet
- Creating Parts With SketchesDocument70 pagesCreating Parts With SketchesAmol ChakankarNo ratings yet
- Toc Nx8.5 EvalDocument11 pagesToc Nx8.5 Evaldharminderarora0% (1)
- Orthographic Views in Multiview Drawings: Autocad 2015 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals 5-1Document30 pagesOrthographic Views in Multiview Drawings: Autocad 2015 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals 5-1Uma MageshwariNo ratings yet
- Lesson08 3D FEM ClevisDocument10 pagesLesson08 3D FEM Clevisaiyubi2No ratings yet
- Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2Document16 pagesGeometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2Karla SaraNo ratings yet
- Block Modelling PDFDocument104 pagesBlock Modelling PDFKamara100% (1)
- Spring TutorialDocument20 pagesSpring TutorialSia Ping ChongNo ratings yet
- Meen2111011082 7Document11 pagesMeen2111011082 7candylandkefantyNo ratings yet
- 5 6087102766021345335 PDFDocument109 pages5 6087102766021345335 PDFKhaerul WahyuNo ratings yet
- Using Groups and Lists: Workshop 6Document24 pagesUsing Groups and Lists: Workshop 6hfathollahiNo ratings yet
- Patran Lesson16 Post Processing of Displacement ResultsDocument12 pagesPatran Lesson16 Post Processing of Displacement ResultsstaedtlerpNo ratings yet
- Name: Roll No: Sub:: AIM Geometric ModellingDocument9 pagesName: Roll No: Sub:: AIM Geometric ModellinghoneyfunnyNo ratings yet
- Bản finalllDocument9 pagesBản finalllBẢO ĐẶNG THÁINo ratings yet
- Lab: Computer Aided EngineeringDocument9 pagesLab: Computer Aided Engineeringdr_ar_marwatNo ratings yet
- Meshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3Document12 pagesMeshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3karthekeyanmenonNo ratings yet
- Meshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3Document12 pagesMeshing and Property Assignment: Workshop 3hfathollahiNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis Standard CAD Rev 2 - V28Document17 pages3 Axis Standard CAD Rev 2 - V28Fatima NayabNo ratings yet
- 01 First Modeling StepsDocument27 pages01 First Modeling StepsMoisés SolisNo ratings yet
- 2021R1 SpaceClaimDocument30 pages2021R1 SpaceClaimbraulisonNo ratings yet
- Guide For Finite Element ModelingDocument28 pagesGuide For Finite Element ModelingImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Ansys Airfoil 2DDocument11 pagesAnsys Airfoil 2Dmonidogar88No ratings yet
- Construct Hybrid Microcircuit Geometry: Exercise 1Document342 pagesConstruct Hybrid Microcircuit Geometry: Exercise 1AJones394No ratings yet
- Halcon 6.1 Shape Matching PDFDocument46 pagesHalcon 6.1 Shape Matching PDFJonathan PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Dedication Preface Chapter 1: Drawing Sketches in The Sketcher Workbench-IDocument8 pagesDedication Preface Chapter 1: Drawing Sketches in The Sketcher Workbench-ILiviu MihonNo ratings yet
- T3424-380-02 Overheads ENDocument98 pagesT3424-380-02 Overheads ENAnonymous KMWzXegkNo ratings yet
- Exercise 04 Multi-Step Cant BeamDocument18 pagesExercise 04 Multi-Step Cant BeamTrường ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Phase2 TutorialDocument22 pagesPhase2 Tutorialmed AmineNo ratings yet
- Road Eng CivilDocument198 pagesRoad Eng Civilcato1223No ratings yet
- CATIA Lab ManualDocument79 pagesCATIA Lab ManualPavaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision 8th Sem Lab ManualDocument29 pagesComputer Vision 8th Sem Lab ManualJaikishanNo ratings yet
- Gender & Emotion Classification PresentDocument31 pagesGender & Emotion Classification PresenttensuNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document39 pagesDay 4tonystark8052No ratings yet
- Unigraphics NX Sketching Fundamentals MT10028 (Workbook)Document32 pagesUnigraphics NX Sketching Fundamentals MT10028 (Workbook)cyclotolNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDocument43 pagesManual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- T8-Basic Event Handling, Mapping ModesDocument35 pagesT8-Basic Event Handling, Mapping Modesmichael.ferrarisNo ratings yet
- Frame Surface Model AnalysisDocument37 pagesFrame Surface Model AnalysisManasses juniorNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document14 pagesModule 3santosh gillNo ratings yet
- Catia Lab ManualDocument110 pagesCatia Lab ManualShiva Shankar100% (2)
- CATIA CAD NotesDocument161 pagesCATIA CAD Notesshubhamukey628No ratings yet
- AEDT Icepak Intro 2019R1 L5 Solving and PostProcessingDocument18 pagesAEDT Icepak Intro 2019R1 L5 Solving and PostProcessingAbhishek yadavNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Windtunnel2020-21Document9 pagesSimulation of A Windtunnel2020-21abdul5721No ratings yet
- Practifa Final PetrelDocument23 pagesPractifa Final PetrelJesusMamaniMamaniNo ratings yet
- MSC Patran-301 Introduction To PatranDocument24 pagesMSC Patran-301 Introduction To Patranmussie5No ratings yet
- Solid Edge 2023 for Designers, 20th EditionFrom EverandSolid Edge 2023 for Designers, 20th EditionNo ratings yet
- Advanced AutoCAD 2024: A Problem-Solving Approach, 3D and Advanced, 27th EditionFrom EverandAdvanced AutoCAD 2024: A Problem-Solving Approach, 3D and Advanced, 27th EditionNo ratings yet
- SOLIDWORKS 2023 for Designers, 21st EditionFrom EverandSOLIDWORKS 2023 for Designers, 21st EditionNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-1-211Document211 pages1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-1-211Andrea AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: LessonDocument16 pagesGeometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: LessonAndrea AcuñaNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-413-651Document239 pages1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-413-651Andrea Acuña100% (1)
- Silabo ML214 20201Document3 pagesSilabo ML214 20201Andrea AcuñaNo ratings yet
- BMATS201Document5 pagesBMATS201Nithin GowdruNo ratings yet
- Vector LessonsDocument36 pagesVector LessonsMarc RiveraNo ratings yet
- M21C GridGeneratorDocument80 pagesM21C GridGeneratorFrenki Tres WidyantoroNo ratings yet
- Basics of MechanicsDocument132 pagesBasics of MechanicsSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2008 Bookmatter FluidMechanics PDFDocument60 pages2008 Bookmatter FluidMechanics PDFDaniela Forero RamírezNo ratings yet
- Calculus Iii: CHAPTER 5: Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument24 pagesCalculus Iii: CHAPTER 5: Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Mathematical Physics - 1 - Web CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: Mathematical Physics - 1 - Web CourseRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Applied Mathematics For Engineers and ScientistsDocument897 pagesMethods of Applied Mathematics For Engineers and ScientistsSandeep Sai100% (5)
- Fluid Dynamics CreteDocument204 pagesFluid Dynamics CreteDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Vectors Tensors CompleteDocument206 pagesVectors Tensors CompleteSukrit GhoraiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Tensor in Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Field Tensor in Curvilinear CoordinatesAscanio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- 3 Curvilinear MotionDocument50 pages3 Curvilinear Motiongarhgelh100% (1)
- Ch.1 Vector AnalysisDocument27 pagesCh.1 Vector AnalysisFilip NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Research Article / Research Project / Literature Review: Faculty of Engineering - Shoubra Benha UniversityDocument3 pagesResearch Article / Research Project / Literature Review: Faculty of Engineering - Shoubra Benha UniversitySayed RedaNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Fundamentals of Computational Fluid Dynamics The Finite Volume Method 1St Edition Clovis R Maliska Online PDF All ChapterDocument52 pagesFull Ebook of Fundamentals of Computational Fluid Dynamics The Finite Volume Method 1St Edition Clovis R Maliska Online PDF All Chapterleahsailor875607100% (7)
- PART4 Tensor CalculusDocument43 pagesPART4 Tensor CalculusAjoy SharmaNo ratings yet
- 272829291919Document36 pages272829291919SOHON SINHA MAHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Chapter - 2 - Kinematics - of - Particles Rectilinear Motion To Normal Tangential Coordinates PDFDocument56 pagesDynamics - Chapter - 2 - Kinematics - of - Particles Rectilinear Motion To Normal Tangential Coordinates PDFJP NielesNo ratings yet
- Plane Curvilinear Motion:: DisplacementDocument18 pagesPlane Curvilinear Motion:: Displacementyalexca100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0263823121006352 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0263823121006352 MainkoulliredouaneNo ratings yet
- Journal of Computational Physics: L. Chacón, G. ChenDocument10 pagesJournal of Computational Physics: L. Chacón, G. ChenSanghita BiswasNo ratings yet
- Snider Robert F. Irreducible Cartesian TensorsDocument269 pagesSnider Robert F. Irreducible Cartesian TensorsDaniela Saboya BenavidezNo ratings yet
- A S Mishchenko, Yu.P.Solovyev, A T Fomenko-Problems in Differential Geometry and Topology-Mir Publishers (1985) PDFDocument209 pagesA S Mishchenko, Yu.P.Solovyev, A T Fomenko-Problems in Differential Geometry and Topology-Mir Publishers (1985) PDFPrashant Pandey100% (1)
- RGFGRID User ManualDocument140 pagesRGFGRID User ManualcocoNo ratings yet
- Mathmatical PhysicsDocument7 pagesMathmatical PhysicsMr. DILLUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 ENGR 243 DynamicsDocument45 pagesLecture 4 ENGR 243 DynamicsRobby RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus SummaryDocument8 pagesVector Calculus SummaryPedro Galvani100% (1)