Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 viewsStairwell Pressurization
Stairwell Pressurization
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Abd El-KaderCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ascs To The Acr Standard Manual 1Document142 pagesAscs To The Acr Standard Manual 1Luu DangNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Shell N TubeDocument21 pagesLab Report Shell N Tuberidzuwan rahimi100% (6)
- Stair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDocument2 pagesStair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDesigner Forever100% (1)
- Smoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerDocument4 pagesSmoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerMaaz Junaidi86% (7)
- Design Calculation Sheet: Date: Sheet No.: Project No.: 1203 Computed By: Alaa Ramadan Approved By: Checked byDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet: Date: Sheet No.: Project No.: 1203 Computed By: Alaa Ramadan Approved By: Checked byalialavi2No ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Document36 pagesStaircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Anish KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 FireSmoke Control Stair Pressurization.95110230Document7 pages4 FireSmoke Control Stair Pressurization.95110230adcaNo ratings yet
- Pressurization CalculationDocument6 pagesPressurization CalculationAbdul HakkimNo ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurization Calculations PDFDocument2 pagesStaircase Pressurization Calculations PDFSudhir Kulkarni100% (25)
- Stair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ADocument8 pagesStair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ALarry Bea100% (4)
- Chapter 2 AssignmentDocument1 pageChapter 2 Assignmentteguh100% (1)
- StairCase Press-Eclipse - (Printed 29.01.2020) PDFDocument3 pagesStairCase Press-Eclipse - (Printed 29.01.2020) PDFmhmdjdgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument2 pagesStair Pressurization Calculationnaruto256100% (1)
- Stair Pressurization - Allied ConsultantDocument4 pagesStair Pressurization - Allied ConsultantTiefSeeNo ratings yet
- Stairwell CalculationDocument8 pagesStairwell Calculationfarzinshahab100% (1)
- Design Calculation Sheet For Fire Lift Well Pressurisation S.NO. DescriptionDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet For Fire Lift Well Pressurisation S.NO. DescriptionpsjjoshiNo ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurization Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesStaircase Pressurization Calculation SheetTariq AsgharNo ratings yet
- Corridor Pressurization Calculation 20170310Document1 pageCorridor Pressurization Calculation 20170310wow proNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: System Class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Class FDocument3 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: System Class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Class FMohd Najeeb Ali FathaanNo ratings yet
- Staircase & Lift Pressurization-Hvac Ventilation System-DesignDocument8 pagesStaircase & Lift Pressurization-Hvac Ventilation System-DesignSHIBIN TNo ratings yet
- Elevator Lobby Pressurization 1Document2 pagesElevator Lobby Pressurization 1Mohamed MonamNo ratings yet
- @S V All FansDocument19 pages@S V All Fanshasanadel88No ratings yet
- Smoke Cal AtriumDocument3 pagesSmoke Cal AtriumBilal Hussein SousNo ratings yet
- CAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationDocument4 pagesCAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationAbdul Sami100% (1)
- Ashrae Design Manual For Smoke ControlDocument6 pagesAshrae Design Manual For Smoke Controlist93993100% (3)
- Smoke Management Calc For Car ParkDocument1 pageSmoke Management Calc For Car ParkSudhir KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationDocument33 pages3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationAshiq NishmaNo ratings yet
- 01-Pressurization Staircase Fan Calculation SheetDocument9 pages01-Pressurization Staircase Fan Calculation SheetHamdy AdelNo ratings yet
- DAR Stair Case PressurizationDocument10 pagesDAR Stair Case Pressurization123 123100% (1)
- Lift Well Pressurization Calculation TOWER C - (G+17)Document4 pagesLift Well Pressurization Calculation TOWER C - (G+17)KoushikNo ratings yet
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument7 pagesSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsAhmedNo ratings yet
- Smoke - Ventilation CalculationsDocument8 pagesSmoke - Ventilation CalculationsdasmechNo ratings yet
- Smoke Management Calc For Shopping Mall PDFDocument1 pageSmoke Management Calc For Shopping Mall PDFSudhir KulkarniNo ratings yet
- SPF Stair Case FanDocument2 pagesSPF Stair Case FanAla ShakerNo ratings yet
- Kazma SMOKE VENTILATION SYSTEMDocument2 pagesKazma SMOKE VENTILATION SYSTEMRoin BanerjiNo ratings yet
- 2 Smoke Calculation r4.Document11 pages2 Smoke Calculation r4.muhammed sabir v a100% (1)
- Smoke Spill 2Document2 pagesSmoke Spill 2Briana JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument9 pagesSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsMarcin NowelNo ratings yet
- Stairwel and Lobby Pressurization CalculationDocument4 pagesStairwel and Lobby Pressurization CalculationLarry Bea67% (3)
- Staircase Pressurization Fan, What Is The Equation To Calculate The Air Flow and Static Pressure For Fan - Bayt PDFDocument3 pagesStaircase Pressurization Fan, What Is The Equation To Calculate The Air Flow and Static Pressure For Fan - Bayt PDFDesigner ForeverNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Fans Calculations & Sand Trap LouversDocument1 pageExhaust Fans Calculations & Sand Trap LouversAhmed HashimNo ratings yet
- GDL Louvre CalculatorDocument1 pageGDL Louvre CalculatorAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Atrium Natural Smoke CalculationsDocument5 pagesAtrium Natural Smoke CalculationsRamiAl-fuqahaNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction - TECDocument1 pageSmoke Extraction - TECdasmechNo ratings yet
- OVERPRESSURE Neutre PDFDocument50 pagesOVERPRESSURE Neutre PDFIgor SpirovNo ratings yet
- Pressurization BSIDocument3 pagesPressurization BSIRaja Antony100% (4)
- PressurizationDocument1 pagePressurizationKarthy Ganesan100% (2)
- Zoned Smoke Control Applications: Using HVAC Systems To Limit SmokeDocument5 pagesZoned Smoke Control Applications: Using HVAC Systems To Limit SmokeNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Apd CalculationDocument4 pagesApd CalculationRashel Hasan100% (1)
- Presurization CalculationsDocument10 pagesPresurization CalculationsvinaygvmNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction - TECDocument1 pageSmoke Extraction - TECdasmechNo ratings yet
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument9 pagesStair Pressurization CalculationHaymanot BaynesagnNo ratings yet
- Cooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFDocument5 pagesCooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFSundar Ramasamy100% (1)
- Staircase Pressurization SPV BuildingDocument2 pagesStaircase Pressurization SPV BuildingNandan RajeNo ratings yet
- 03.pressurisation Calculation Semenyih Blok ADocument3 pages03.pressurisation Calculation Semenyih Blok ABriana JenkinsNo ratings yet
- DAR Stair Case PressurizationDocument10 pagesDAR Stair Case Pressurizationmansidev100% (3)
- Stair Case-01 Pressurisation Calculation: 3.3 7.255 2.56 64.78 2.2 1.1 - 6.6 Walls (Tight) Door Frame (Single Leaf)Document7 pagesStair Case-01 Pressurisation Calculation: 3.3 7.255 2.56 64.78 2.2 1.1 - 6.6 Walls (Tight) Door Frame (Single Leaf)Shabeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Fans All RevisedDocument6 pagesVentilation Fans All RevisedBilal Hussein SousNo ratings yet
- Aldesme - Flash25 Stair PressurisationDocument8 pagesAldesme - Flash25 Stair PressurisationjaicektmNo ratings yet
- Detail of Calculation Staircase 26 Sty Pressurisation SystemDocument3 pagesDetail of Calculation Staircase 26 Sty Pressurisation SystemMyoNo ratings yet
- Center - SPF Calculation DataDocument1 pageCenter - SPF Calculation DataPAul JoHn MeNdozaNo ratings yet
- Lift Well Pressurisation - Old - 20240317Document1 pageLift Well Pressurisation - Old - 20240317kundur088No ratings yet
- SipDocument16 pagesSipAlison LewisNo ratings yet
- Components of Sedimentation Tank PDFDocument19 pagesComponents of Sedimentation Tank PDFrupender100% (1)
- Engineering Evaluation Centrifugal Pumps For Fire Protection Nfpa 20Document5 pagesEngineering Evaluation Centrifugal Pumps For Fire Protection Nfpa 20Fernando VallesterosNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Calculation of Turbine For Tara Khola, BaglungDocument2 pagesPreliminary Design Calculation of Turbine For Tara Khola, BaglungkiranrauniyarNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump FundamentalsDocument62 pagesCentrifugal Pump FundamentalsRitesh Poojary100% (1)
- AJVG Aeronet 2011Document28 pagesAJVG Aeronet 2011Bheemesh GudelliNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 1Document78 pagesPricelist 1sandeepbhallaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications, Cengel, Mcgraw Hill, Chapter 10Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications, Cengel, Mcgraw Hill, Chapter 10jcaza20No ratings yet
- Saline WaterDocument20 pagesSaline WaterAdroNo ratings yet
- Re92735 - 2023 05 17Document46 pagesRe92735 - 2023 05 17jimmy norambuenaNo ratings yet
- Design Two-Phase Separators Within The Right LimitsDocument8 pagesDesign Two-Phase Separators Within The Right Limitschipiloo100% (1)
- Rupture Disk EquationsDocument13 pagesRupture Disk EquationsMehta MehulNo ratings yet
- Line Single PhaseDocument2 pagesLine Single PhasehussamNo ratings yet
- Plumbing FinalDocument30 pagesPlumbing Finalashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Control Structures HydaDocument8 pagesControl Structures Hydaprasadnn2001No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance InstructionsDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance Instructionsdreamboy87No ratings yet
- Jordan University of Science and Technology Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Lab (CE354)Document9 pagesJordan University of Science and Technology Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Lab (CE354)Abdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument57 pagesWaste Waterashe zinab100% (1)
- Hydrotest Pressure Procedure - 2023Document15 pagesHydrotest Pressure Procedure - 2023Amit HasanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Process Piping - ASME313Document110 pagesOverview of Process Piping - ASME313Ese Ichekor100% (4)
- C3 Method of SeparationDocument9 pagesC3 Method of SeparationHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Skid: Pre-Engineered Water Treatment SolutionsDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Pump Skid: Pre-Engineered Water Treatment SolutionsWai Ee YapNo ratings yet
- Basic Hyd PDFDocument89 pagesBasic Hyd PDFThang TongNo ratings yet
- Production Chemistry in Flow AssuranceDocument63 pagesProduction Chemistry in Flow AssuranceSyafiqah Rosmarina AhmadNo ratings yet
- Waterco FPI Valves: Engineered For Optimal PerformanceDocument2 pagesWaterco FPI Valves: Engineered For Optimal Performanceethan8888No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document27 pagesChapter 2ebrahim aliNo ratings yet
- CF PumpsDocument133 pagesCF PumpsNilesh GohelNo ratings yet
- OADDocument8 pagesOADMarcelo ArayaNo ratings yet
Stairwell Pressurization
Stairwell Pressurization
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Abd El-Kader0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesOriginal Title
stairwell pressurization.xlsx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesStairwell Pressurization
Stairwell Pressurization
Uploaded by
Mahmoud Abd El-KaderCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
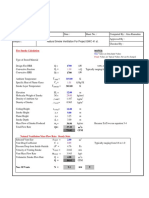
Project Name :- ….......................................
Stair Case Pressurization For Internal Stairs .
DATA INPUT
NO. OF FLOORS 30 NOS.
FLOOR HEIGHT 4 M
DOOR DIMENSIONS WIDTH 1 M
HEIGHT 2.2 M
STAIRWELL DIMENSIONS LENGTH 5 M
WIDTH 4 M
HEIGHT 100 M
STAIRWELL PRESSURIZATION IN THE CASE OF CLOSED DOORS
Sr. Stairwell Reference Units ST1 & ST2
A Design Criteria tight construction
1 Butcher Parenell Equation.
2 NFPA 92A-Recommended practice for smoke control system
3 NFPA 92B - Guide for Smoke Management Systems.
4 BSEN 121016 - Part 5 "Code of Practice for Fire Fighting Stair
5 Design Pressure Differential - 50 Pa across stair/accomodation Pa 50
6 d of Doors Open for-doors Exiting / Evacuation. No. No.s 0
B Airflow from closed doors & walls due to pressurization leakage
1 area
Doorofdimensions.
closed doors Width Height Crack
Width
a Door size m 1 2.2 0.01
b sq.m 2.2
c No. of Doors No. 30
d Total crack area of closed doors sq.m 0.66
2 Leakage area of walls. Internal wall size Length Width Height
a Leakage area factor (Stair well - tight for stair-1 & stair-2 ) m 5 4 100
b Total wall area 1.4E-05
c Total leakage area for internal walls sq.m 2000
d sq.m 0.028
3 Total leakage area of closed doors & tight const. Walls Area
sq.m 0.688
4 Airflow through leakage areas of closed doors & walls Q=0.839 M3/Sec. 4.08164661517873
X Total lkge area X 1000 X sqrt of press. Diff. cfm 8652
C Airflow through open doors for pressurization.
1 Door dimensions. Width Height Area
a Door size m 1 2.2 2.2
b Velocity (0.75 m/s open door as per BSEN 121016 - Part 5) m/s 0.75
c No. of open doors No. 0
2 Total Airflow through open doors l/s 0
cfm 0
D Total airflow required for closed doors, walls & open doors M3/Sec. 4.08164661517873
cfm 8652
E Safety factor % 10%
F Total airflow required for closed doors, walls & open doors cf M3/Sec. 4.48981127669661
cfm 9518
G Airflow each floor l/s 139
cfm 295
H FAN CAPACITY IN THE CASE OF CLOSED DOORS cfm 9518
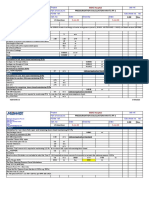
STAIRWELL PRESSURIZATION IN THE CASE OF OPEN DOORS
Sr. Stairwell Reference Units ST1 & ST2
A Design Criteria tight construction
1 Butcher Parenell Equation.
2 NFPA 92A-Recommended practice for smoke control system
3 NFPA 92B - Guide for Smoke Management Systems.
4 BSEN 121016 - Part 5 "Code of Practice for Fire Fighting Stair
5 Design Pressure Differential - 10 Pa across stair/accomodation Pa 10
6 No.of Doors Open for-doors Exiting / Evacuation. No.s 2
B Airflow from closed doors & walls due to pressurization leakage
1 area
Doorof closed doors
dimensions. Width Height Crack
Width
a Door size m 1 2.2 0.01
b Crack area of one door sq.m 2.2
c No. of Doors No. 30
d Total crack area of closed doors sq.m 0.66
2 Leakage area of walls. Internal wall size Length Width Height
a Leakage area factor (Stair well - tight for stair-1 & stair-2 ) m 5 4 100
b Total wall area 1.4E-05
c Total leakage area for internal walls sq.m 2000
d sq.m 0.028
3 Total leakage area of closed doors & tight const. Walls Area
sq.m
0.688
4 Airflow through leakage areas of closed doors & walls Q=0.839 M3/Sec. 1.82536785833431
X Total lkge area X 1000 X sqrt of press. Diff. cfm 3869
C Airflow through open doors for pressurization.
1 Door dimensions. Width Height Area
a Door size m 1 2.2 2.2
b Velocity (0.75 m/s open door as per BSEN 121016 - Part 5) m/s 0.75
c No. of open doors No. 2
2 Total Airflow through open doors M3/Sec. 3.3000
cfm 6995
D Total airflow required for closed doors, walls & open doors M3/Sec. 5.1254
cfm 10865
E Safety factor % 10%
F Total airflow required for closed doors, walls & open doors cf M3/Sec. 5.63790464416775
cfm 11951
G Airflow each floor M3/Sec. 0.1879
cfm 398
I FAN CAPACITY IN THE CASE OF OPEN DOOR cfm 11951
TOTAL FAN CAPACITY IN THE CASE OF CLOSED AND OPEN DOORS cfm 21469
Notes:
The calculation if performed on the basis of 10Pa of differential pressure will be maintained with 2
doors open and 50pa of differential pressure will be maintained with all doors remains close.
The maximum flow from the above two scenarios is selected as required fan flow.
You might also like
- Ascs To The Acr Standard Manual 1Document142 pagesAscs To The Acr Standard Manual 1Luu DangNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Shell N TubeDocument21 pagesLab Report Shell N Tuberidzuwan rahimi100% (6)
- Stair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDocument2 pagesStair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDesigner Forever100% (1)
- Smoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerDocument4 pagesSmoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerMaaz Junaidi86% (7)
- Design Calculation Sheet: Date: Sheet No.: Project No.: 1203 Computed By: Alaa Ramadan Approved By: Checked byDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet: Date: Sheet No.: Project No.: 1203 Computed By: Alaa Ramadan Approved By: Checked byalialavi2No ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Document36 pagesStaircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Anish KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 FireSmoke Control Stair Pressurization.95110230Document7 pages4 FireSmoke Control Stair Pressurization.95110230adcaNo ratings yet
- Pressurization CalculationDocument6 pagesPressurization CalculationAbdul HakkimNo ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurization Calculations PDFDocument2 pagesStaircase Pressurization Calculations PDFSudhir Kulkarni100% (25)
- Stair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ADocument8 pagesStair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ALarry Bea100% (4)
- Chapter 2 AssignmentDocument1 pageChapter 2 Assignmentteguh100% (1)
- StairCase Press-Eclipse - (Printed 29.01.2020) PDFDocument3 pagesStairCase Press-Eclipse - (Printed 29.01.2020) PDFmhmdjdgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument2 pagesStair Pressurization Calculationnaruto256100% (1)
- Stair Pressurization - Allied ConsultantDocument4 pagesStair Pressurization - Allied ConsultantTiefSeeNo ratings yet
- Stairwell CalculationDocument8 pagesStairwell Calculationfarzinshahab100% (1)
- Design Calculation Sheet For Fire Lift Well Pressurisation S.NO. DescriptionDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet For Fire Lift Well Pressurisation S.NO. DescriptionpsjjoshiNo ratings yet
- Staircase Pressurization Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesStaircase Pressurization Calculation SheetTariq AsgharNo ratings yet
- Corridor Pressurization Calculation 20170310Document1 pageCorridor Pressurization Calculation 20170310wow proNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: System Class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Class FDocument3 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: System Class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Class FMohd Najeeb Ali FathaanNo ratings yet
- Staircase & Lift Pressurization-Hvac Ventilation System-DesignDocument8 pagesStaircase & Lift Pressurization-Hvac Ventilation System-DesignSHIBIN TNo ratings yet
- Elevator Lobby Pressurization 1Document2 pagesElevator Lobby Pressurization 1Mohamed MonamNo ratings yet
- @S V All FansDocument19 pages@S V All Fanshasanadel88No ratings yet
- Smoke Cal AtriumDocument3 pagesSmoke Cal AtriumBilal Hussein SousNo ratings yet
- CAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationDocument4 pagesCAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationAbdul Sami100% (1)
- Ashrae Design Manual For Smoke ControlDocument6 pagesAshrae Design Manual For Smoke Controlist93993100% (3)
- Smoke Management Calc For Car ParkDocument1 pageSmoke Management Calc For Car ParkSudhir KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationDocument33 pages3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationAshiq NishmaNo ratings yet
- 01-Pressurization Staircase Fan Calculation SheetDocument9 pages01-Pressurization Staircase Fan Calculation SheetHamdy AdelNo ratings yet
- DAR Stair Case PressurizationDocument10 pagesDAR Stair Case Pressurization123 123100% (1)
- Lift Well Pressurization Calculation TOWER C - (G+17)Document4 pagesLift Well Pressurization Calculation TOWER C - (G+17)KoushikNo ratings yet
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument7 pagesSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsAhmedNo ratings yet
- Smoke - Ventilation CalculationsDocument8 pagesSmoke - Ventilation CalculationsdasmechNo ratings yet
- Smoke Management Calc For Shopping Mall PDFDocument1 pageSmoke Management Calc For Shopping Mall PDFSudhir KulkarniNo ratings yet
- SPF Stair Case FanDocument2 pagesSPF Stair Case FanAla ShakerNo ratings yet
- Kazma SMOKE VENTILATION SYSTEMDocument2 pagesKazma SMOKE VENTILATION SYSTEMRoin BanerjiNo ratings yet
- 2 Smoke Calculation r4.Document11 pages2 Smoke Calculation r4.muhammed sabir v a100% (1)
- Smoke Spill 2Document2 pagesSmoke Spill 2Briana JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument9 pagesSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsMarcin NowelNo ratings yet
- Stairwel and Lobby Pressurization CalculationDocument4 pagesStairwel and Lobby Pressurization CalculationLarry Bea67% (3)
- Staircase Pressurization Fan, What Is The Equation To Calculate The Air Flow and Static Pressure For Fan - Bayt PDFDocument3 pagesStaircase Pressurization Fan, What Is The Equation To Calculate The Air Flow and Static Pressure For Fan - Bayt PDFDesigner ForeverNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Fans Calculations & Sand Trap LouversDocument1 pageExhaust Fans Calculations & Sand Trap LouversAhmed HashimNo ratings yet
- GDL Louvre CalculatorDocument1 pageGDL Louvre CalculatorAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Atrium Natural Smoke CalculationsDocument5 pagesAtrium Natural Smoke CalculationsRamiAl-fuqahaNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction - TECDocument1 pageSmoke Extraction - TECdasmechNo ratings yet
- OVERPRESSURE Neutre PDFDocument50 pagesOVERPRESSURE Neutre PDFIgor SpirovNo ratings yet
- Pressurization BSIDocument3 pagesPressurization BSIRaja Antony100% (4)
- PressurizationDocument1 pagePressurizationKarthy Ganesan100% (2)
- Zoned Smoke Control Applications: Using HVAC Systems To Limit SmokeDocument5 pagesZoned Smoke Control Applications: Using HVAC Systems To Limit SmokeNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Apd CalculationDocument4 pagesApd CalculationRashel Hasan100% (1)
- Presurization CalculationsDocument10 pagesPresurization CalculationsvinaygvmNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction - TECDocument1 pageSmoke Extraction - TECdasmechNo ratings yet
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument9 pagesStair Pressurization CalculationHaymanot BaynesagnNo ratings yet
- Cooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFDocument5 pagesCooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFSundar Ramasamy100% (1)
- Staircase Pressurization SPV BuildingDocument2 pagesStaircase Pressurization SPV BuildingNandan RajeNo ratings yet
- 03.pressurisation Calculation Semenyih Blok ADocument3 pages03.pressurisation Calculation Semenyih Blok ABriana JenkinsNo ratings yet
- DAR Stair Case PressurizationDocument10 pagesDAR Stair Case Pressurizationmansidev100% (3)
- Stair Case-01 Pressurisation Calculation: 3.3 7.255 2.56 64.78 2.2 1.1 - 6.6 Walls (Tight) Door Frame (Single Leaf)Document7 pagesStair Case-01 Pressurisation Calculation: 3.3 7.255 2.56 64.78 2.2 1.1 - 6.6 Walls (Tight) Door Frame (Single Leaf)Shabeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Fans All RevisedDocument6 pagesVentilation Fans All RevisedBilal Hussein SousNo ratings yet
- Aldesme - Flash25 Stair PressurisationDocument8 pagesAldesme - Flash25 Stair PressurisationjaicektmNo ratings yet
- Detail of Calculation Staircase 26 Sty Pressurisation SystemDocument3 pagesDetail of Calculation Staircase 26 Sty Pressurisation SystemMyoNo ratings yet
- Center - SPF Calculation DataDocument1 pageCenter - SPF Calculation DataPAul JoHn MeNdozaNo ratings yet
- Lift Well Pressurisation - Old - 20240317Document1 pageLift Well Pressurisation - Old - 20240317kundur088No ratings yet
- SipDocument16 pagesSipAlison LewisNo ratings yet
- Components of Sedimentation Tank PDFDocument19 pagesComponents of Sedimentation Tank PDFrupender100% (1)
- Engineering Evaluation Centrifugal Pumps For Fire Protection Nfpa 20Document5 pagesEngineering Evaluation Centrifugal Pumps For Fire Protection Nfpa 20Fernando VallesterosNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Calculation of Turbine For Tara Khola, BaglungDocument2 pagesPreliminary Design Calculation of Turbine For Tara Khola, BaglungkiranrauniyarNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump FundamentalsDocument62 pagesCentrifugal Pump FundamentalsRitesh Poojary100% (1)
- AJVG Aeronet 2011Document28 pagesAJVG Aeronet 2011Bheemesh GudelliNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 1Document78 pagesPricelist 1sandeepbhallaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications, Cengel, Mcgraw Hill, Chapter 10Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications, Cengel, Mcgraw Hill, Chapter 10jcaza20No ratings yet
- Saline WaterDocument20 pagesSaline WaterAdroNo ratings yet
- Re92735 - 2023 05 17Document46 pagesRe92735 - 2023 05 17jimmy norambuenaNo ratings yet
- Design Two-Phase Separators Within The Right LimitsDocument8 pagesDesign Two-Phase Separators Within The Right Limitschipiloo100% (1)
- Rupture Disk EquationsDocument13 pagesRupture Disk EquationsMehta MehulNo ratings yet
- Line Single PhaseDocument2 pagesLine Single PhasehussamNo ratings yet
- Plumbing FinalDocument30 pagesPlumbing Finalashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Control Structures HydaDocument8 pagesControl Structures Hydaprasadnn2001No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance InstructionsDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance Instructionsdreamboy87No ratings yet
- Jordan University of Science and Technology Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Lab (CE354)Document9 pagesJordan University of Science and Technology Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Lab (CE354)Abdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument57 pagesWaste Waterashe zinab100% (1)
- Hydrotest Pressure Procedure - 2023Document15 pagesHydrotest Pressure Procedure - 2023Amit HasanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Process Piping - ASME313Document110 pagesOverview of Process Piping - ASME313Ese Ichekor100% (4)
- C3 Method of SeparationDocument9 pagesC3 Method of SeparationHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Skid: Pre-Engineered Water Treatment SolutionsDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Pump Skid: Pre-Engineered Water Treatment SolutionsWai Ee YapNo ratings yet
- Basic Hyd PDFDocument89 pagesBasic Hyd PDFThang TongNo ratings yet
- Production Chemistry in Flow AssuranceDocument63 pagesProduction Chemistry in Flow AssuranceSyafiqah Rosmarina AhmadNo ratings yet
- Waterco FPI Valves: Engineered For Optimal PerformanceDocument2 pagesWaterco FPI Valves: Engineered For Optimal Performanceethan8888No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document27 pagesChapter 2ebrahim aliNo ratings yet
- CF PumpsDocument133 pagesCF PumpsNilesh GohelNo ratings yet
- OADDocument8 pagesOADMarcelo ArayaNo ratings yet