Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Azithromycin Medication PDF
Azithromycin Medication PDF
Uploaded by
mp17570 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageAzithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria and is effective against certain gram-positive bacteria. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. It can also cause dizziness, seizures or prolong the QT interval. The medication should be taken as prescribed for the full treatment duration to ensure the infection is fully resolved and prevent complications or resistance. Patients should monitor for signs of infection progression or new symptoms and see their doctor if issues arise during treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
Azithromycin medication.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAzithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria and is effective against certain gram-positive bacteria. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. It can also cause dizziness, seizures or prolong the QT interval. The medication should be taken as prescribed for the full treatment duration to ensure the infection is fully resolved and prevent complications or resistance. Patients should monitor for signs of infection progression or new symptoms and see their doctor if issues arise during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageAzithromycin Medication PDF
Azithromycin Medication PDF
Uploaded by
mp1757Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria and is effective against certain gram-positive bacteria. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. It can also cause dizziness, seizures or prolong the QT interval. The medication should be taken as prescribed for the full treatment duration to ensure the infection is fully resolved and prevent complications or resistance. Patients should monitor for signs of infection progression or new symptoms and see their doctor if issues arise during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
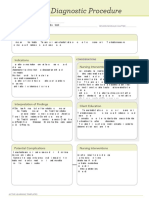
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication
Tommie Waiters
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
Azithromycin
MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________
CATEGORY CLASS__Macrolides
_____________________________________________________________________
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
It is a macrolide-type antibiotic. It works by stopping - Bacteriostatic action against susceptible
bacteria.
the growth of bacteria. This medication will not work - Active against the following gram
for viral infections (such as common cold, flu) positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus
aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, S.
pyogenes (group A strep)
Complications Medication Administration
- CNS: Vertigo, dizziness, mild to severe seizures, sleepiness, always tired, PO (Adults): 500 mg on 1st day,
migraine.
- CV: chest pain, hypotension and palpitations, QT interval prolongation. then 250 mg/day for 3-4 days
- GI: HEPATOTOXICITY, PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS, (total dose of 1.5 g); Acute
Stomach associated with severe diarrhea, stomach
nausea, cholestatic jaundice of the skin bacterial sinusitis—500 mg once
daily for 2-3 days or single 2-g
dose of extended-release
suspension (Zmax).
Contraindications/Precautions
Hypersensitivity to azithromycin seen in the patient, erythromycin, or other
macrolide anti-infectives; History of cholestatic jaundice or
hepatic dysfunction with prior use of azithromycin. QT Nursing Interventions
interval prolongation, hypokalemia, hypomagnese- mia, or
bradycardia; Concurrent use of quinidine, procainamide Check the patient for infection
ASAP (check vital signs,look for the
appearance of wounds, sores,
sputum,urine,or stool, have labs
checked with the WBC) at the start
Interactions of and the end of the therapy.
Drug-Drug: Quinidine, procainamide, dofetilide, sotalol, Follow-up with medical professional
and amiodar one may risk of QT interval prolongation; for further specimen collections
concurrent use should be avoided. Alumi-num- and
magnesium-containing antacids peak levels.
Nelfinavirq levels (monitor carefully); azithromycin
also pnelfinavir levels
Client Education
Inform the patient that they need to
report any symptoms related to chest
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness pains, chest palpitations, any yellowing
of their skin or eyes, and/or signs of the
Resolution of the signs and symptoms of infection. There person having
is a certain length of time for complete resolution will a super infection. have the patient
depends on the type of germ and location of infection. to contact their health care professional
if they develop a fever or diarrhea.
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Therapeutic Procedure A7
You might also like
- Waiters Teaching New Parents PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Teaching New Parents PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Cefazolin Ancef Drug CardDocument1 pageCefazolin Ancef Drug CardSheri490100% (2)
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamoldamtere71% (7)
- DRUG STUDY DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY DoxycyclineAMIN BARINo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument1 pageVancomycinE100% (2)
- New Singulair MontelukastDocument1 pageNew Singulair MontelukastCassie100% (2)
- Anti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIIFrom EverandAnti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIINo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Waiters Nonstress Test PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Nonstress Test PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFmp1757100% (1)
- Waiters Postpartal Hemorrhage PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Postpartal Hemorrhage PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- 326 Mental - Status - Examination Directions and RubricDocument4 pages326 Mental - Status - Examination Directions and Rubricmp1757No ratings yet
- Cefuroxime ZoltaxDocument2 pagesCefuroxime ZoltaxMJformorejokes minecraftNo ratings yet
- Augmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Document2 pagesAugmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batch 2Document17 pagesDrug Study Batch 2John Philip M. Lacas RNNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin (Zithromycin)Document2 pagesAzithromycin (Zithromycin)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- DS Clarithromycin GI ARLEDDocument5 pagesDS Clarithromycin GI ARLEDvivi's eyebrowsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug Studyapi-3757116100% (4)
- Client Profile Log Antenatal - CompleteDocument5 pagesClient Profile Log Antenatal - CompleteLinea GreeneNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Zinacef: Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesZinacef: Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyDocument8 pagesPedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Continuation of PneumoniaDocument6 pagesContinuation of PneumoniagorresNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Classification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseDocument3 pagesClassification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormJessa Mae PagoboNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in Adults 2017Document11 pagesDiagnosis Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in Adults 2017Khayla Ray RondobioNo ratings yet
- Babon - MS Ward ReqtsDocument13 pagesBabon - MS Ward Reqtschristelleannebabon196No ratings yet
- Azithromycin (Zithromycin) IVPBDocument2 pagesAzithromycin (Zithromycin) IVPBAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Anti - Infectives AgentsDocument83 pagesAnti - Infectives AgentsRhien Yrah P. CabalongaNo ratings yet
- Invanz (Ertapenem)Document2 pagesInvanz (Ertapenem)E100% (1)
- 1 Omeprazole - EDHDocument2 pages1 Omeprazole - EDH1adie1907No ratings yet
- Linezolid (Zyvox)Document1 pageLinezolid (Zyvox)ENo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument9 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyericcrizzawalingNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseCameron JanzenNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument1 pagePrednisoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument3 pagesDrug Study ICURolina ParagasNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDocument1 pageTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Predacot PrednisoneDocument1 pagePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Predacot PrednisoneDocument1 pagePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- H. Influenza: 75-100 Mg/kg/day PO Divided q8hr For 10 Days Not To Exceed 4,000 Mg/dayDocument4 pagesH. Influenza: 75-100 Mg/kg/day PO Divided q8hr For 10 Days Not To Exceed 4,000 Mg/dayAlcala, Mariaden A.No ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- Bladder Cancer: By: Estigoy, Harriet and Galang, Cuttie AnneDocument18 pagesBladder Cancer: By: Estigoy, Harriet and Galang, Cuttie AnneCuttie Anne Galang100% (1)
- Cleocin Clindamycin Hydrochloride: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCleocin Clindamycin Hydrochloride: Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Drug Study With NCPDocument22 pagesGroup 8 - Drug Study With NCPHyun Jae WonNo ratings yet
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin)Document1 pageClarithromycin (Biaxin)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- DiflucanDocument1 pageDiflucanSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument17 pagesDrug Study OrthoMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesOmeprazole1adie1907No ratings yet
- Case Scenario Drug Study - VicenteDocument4 pagesCase Scenario Drug Study - VicenteLouraine VicenteNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument2 pagesNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheetsm_r0se_k0hNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Inquiry Into the Nature and Treatment of EpilepsyFrom EverandA Statistical Inquiry Into the Nature and Treatment of EpilepsyNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Waiters Pulmonary Function Test PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Pulmonary Function Test PDFmp17570% (1)
- Waiters Osteoarthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Osteoarthritis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Pulmonary Embolism Form PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Pulmonary Embolism Form PDFmp17570% (1)
- Waiters Morphine PDFDocument2 pagesWaiters Morphine PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Tommie Alajandro 1757 1068397665 Awp PDFDocument771 pagesWaiters Tommie Alajandro 1757 1068397665 Awp PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters-PneumoniaSystem Disorder Form PDFDocument1 pageWaiters-PneumoniaSystem Disorder Form PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Hope College of Arts & Sciences: Program of Study PlanDocument2 pagesHope College of Arts & Sciences: Program of Study Planmp1757No ratings yet
- Acceptance LetterDocument2 pagesAcceptance Lettermp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Uterine Curette PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Uterine Curette PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters. Eng 101Document3 pagesWaiters. Eng 101mp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Salmeterol PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Salmeterol PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHDocument3 pagesWaiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Proning PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Proning PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Remdesivir - Drug - CardDocument6 pagesWaiters Remdesivir - Drug - Cardmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters, Tommie POS Spring 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesWaiters, Tommie POS Spring 2019 PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Short Term: Short Term: After 3-4Document2 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Short Term: Short Term: After 3-4esteffie21No ratings yet
- Waiters Newborn Care PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Newborn Care PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- The Nursing Process in Psychiatric/Mental Health NursingDocument30 pagesThe Nursing Process in Psychiatric/Mental Health Nursingmp17570% (1)
- 20 List Office SuppliesDocument2 pages20 List Office Suppliesmp1757No ratings yet
- Mapeh ReviewerDocument4 pagesMapeh ReviewerArianne Macy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDateDocument32 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pathology, and Etiology in Adults - UpToDatecuentaparatrabajosdelau10No ratings yet
- Asthma Vs BronchitisDocument4 pagesAsthma Vs BronchitisEmma CebanNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesDocument3 pagesAsia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- Kel. 6 Analisis Faktor Kebiasaan Merokok Terhadap Kejadian Ispa Di Kelurahan Kandai Kecamatan Kendari Kota KendariDocument15 pagesKel. 6 Analisis Faktor Kebiasaan Merokok Terhadap Kejadian Ispa Di Kelurahan Kandai Kecamatan Kendari Kota KendariNafa TryantiNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Medicine Studi KasusDocument27 pagesEvidence-Based Medicine Studi KasusIntan Dewi SaputriNo ratings yet
- Tumor Payudara: I Made Andre PradnyanaDocument38 pagesTumor Payudara: I Made Andre PradnyanaAndre PradnyanaNo ratings yet
- Articel About Corona VirusDocument7 pagesArticel About Corona VirusChristy MilityaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of First Line Antiretroviral Therapy Treatment Failure Among Adult Patients On ART at Central Ethiopia: Un-Matched Case Control StudyDocument13 pagesDeterminants of First Line Antiretroviral Therapy Treatment Failure Among Adult Patients On ART at Central Ethiopia: Un-Matched Case Control Studyn.m.l.h.189No ratings yet
- Do Brazil's Covid-19 Government Response Measures Meet The WHO'sDocument95 pagesDo Brazil's Covid-19 Government Response Measures Meet The WHO'sAdolfo Oroso Oubiña NetoNo ratings yet
- AIIMS New Pattern 2019 Model Questions: AnnexuresDocument4 pagesAIIMS New Pattern 2019 Model Questions: AnnexuresSauharda DhakalNo ratings yet
- DMAC 34 Rev. 1 - Dec 2021 - Guidance For Medical Examiners of Divers Conducting Face-to-FaceDocument6 pagesDMAC 34 Rev. 1 - Dec 2021 - Guidance For Medical Examiners of Divers Conducting Face-to-FaceC. de JongNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Strong Choice Bring Up The Strong ConfidenceDocument12 pagesStrong Choice Bring Up The Strong ConfidenceB. M. Mekail Sarwar (192051056)No ratings yet
- The Bubonic Plague of 1896Document7 pagesThe Bubonic Plague of 1896Monidipa Bose DeyNo ratings yet
- Puerperal PyrexiaDocument20 pagesPuerperal Pyrexiaهلا اكرم عقل طميزهNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Qustion, Final Qualifying Exam, 240907Document3 pagesEpidemiology, Qustion, Final Qualifying Exam, 240907tesfaye gelan100% (1)
- Questions About Tuberculosis For ReferenceDocument24 pagesQuestions About Tuberculosis For ReferenceRoam SimenthyNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology Part 4Document108 pagesImmunology and Serology Part 4UnixoftNo ratings yet
- Non Communicable DiseasesDocument28 pagesNon Communicable DiseasesPositive Infinity TutorialsNo ratings yet
- STI - HerpesDocument1 pageSTI - HerpesDanii LuvNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine: INTERNAL MEDICINE - 3rd YEAR SCHEDULE (5-Years Dentistry Program) Schedule - Gr. CDocument2 pagesInternal Medicine: INTERNAL MEDICINE - 3rd YEAR SCHEDULE (5-Years Dentistry Program) Schedule - Gr. CAliceNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 5 Nutritional Status AssessmentNicole BeronioNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: About This BookletDocument2 pagesCervical Cancer: About This BookletFitri Wahyuni PutriNo ratings yet
- Cares Assistance in Developing Independent Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Mantuil Village, Banjarmasin Selatan DistrictDocument5 pagesCares Assistance in Developing Independent Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Mantuil Village, Banjarmasin Selatan DistrictCANDRA KUSUMANEGARANo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument9 pagesTUBERCULOSISRahma WatiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Ag Test Kit: (For Medical Professional Use Only)Document2 pagesCOVID-19 Ag Test Kit: (For Medical Professional Use Only)threwawayNo ratings yet
- Infection Prevention and You YmicDocument1 pageInfection Prevention and You YmicKhadiga AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gastritis: Dr. Indri Pratiwi Divisi Pelayanan Medik RS Hermina Grand WisataDocument27 pagesGastritis: Dr. Indri Pratiwi Divisi Pelayanan Medik RS Hermina Grand Wisataindri pratiwi tobingNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Volume-Deficit Sample NCPDocument1 pageFluid-Volume-Deficit Sample NCPDuane LilocNo ratings yet