Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsCrack
Crack
Uploaded by
Piyush GuptaThe simulation models crack propagation in a rotating shaft using static analyses with cracks in different locations and orientations. It simulates a transverse straight crack with varying depth ratios and calculates the percentage of closed crack area from the applied rotational force and crack geometry. Crack closure behavior is analyzed by applying contact properties that prevent penetration or sliding between crack surfaces during fatigue loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Shear Strength of Soil Part 1 PDFDocument53 pagesShear Strength of Soil Part 1 PDFVal GallanoNo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument33 pagesSlopeMuhammadImranShahzad100% (1)
- ME 498 - 6 - Nanoindentation and NanoscratchDocument23 pagesME 498 - 6 - Nanoindentation and NanoscratchTt Ownsqq100% (1)
- Critical Resolved Shear StressDocument31 pagesCritical Resolved Shear StressLumamba ChiyabiNo ratings yet
- Presantation Picketplot PDFDocument15 pagesPresantation Picketplot PDFEbake ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Part 2 - Dewangan SirDocument87 pagesSlope Stability Part 2 - Dewangan SirAnshul yadavNo ratings yet
- Mae 493n 593t Lec4Document16 pagesMae 493n 593t Lec4kostas.sierros9374No ratings yet
- 04 Steel - MDocument32 pages04 Steel - M22ev06002No ratings yet
- Rotational ViscometerDocument17 pagesRotational ViscometerShivam PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument12 pagesClutchesAbebaw AyeleNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Shear Strength of SoilDocument7 pagesModule 3 Shear Strength of SoilJeth LawNo ratings yet
- Beng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 16-56Document43 pagesBeng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 16-56Tom WhanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Ii-Ecv 308: Bachelor of Science in Civil EngineeringDocument33 pagesSoil Mechanics Ii-Ecv 308: Bachelor of Science in Civil EngineeringGarol BaveriaNo ratings yet
- Transverse Shear - Part 1Document17 pagesTransverse Shear - Part 1Talat ÇelebiNo ratings yet
- PC-FT 403: Lecture (3) byDocument62 pagesPC-FT 403: Lecture (3) byFT 19 Suparno DasNo ratings yet
- Stability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurDocument89 pagesStability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurAastha SoniNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress AnisotrpyDocument53 pagesPlane Stress AnisotrpyInam UllahNo ratings yet
- X Ray ReflectivityDocument14 pagesX Ray Reflectivityjmdq2000No ratings yet
- Unit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityDocument78 pagesUnit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityNirav LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document47 pagesChap 2Amanu WorkuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document36 pagesChapter 9Vaibhav GhuleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Contacts 2ndDocument26 pagesAnalysis of The Contacts 2ndGurjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis: Presented By: Engr. Kyle Emmanuel R. Murillo, CE, RMPDocument41 pagesSlope Stability Analysis: Presented By: Engr. Kyle Emmanuel R. Murillo, CE, RMPRenee AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Beng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 57-88Document34 pagesBeng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 57-88Tom WhanNo ratings yet
- CCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 16-56Document43 pagesCCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 16-56MultimediaUniversityCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 06 Print CE311 SHEAR - STRENGTHDocument46 pages06 Print CE311 SHEAR - STRENGTHsahin.hazalNo ratings yet
- Reoort ch2Document22 pagesReoort ch2إحسان خالد جودة الشحات ٣٥٧٣No ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document73 pagesLecture 6yeshi janexoNo ratings yet
- Dry FrictionDocument18 pagesDry FrictionMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength TheoryDocument32 pagesShear Strength TheoryChikkanna TNo ratings yet
- CCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 57-88Document34 pagesCCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 57-88MultimediaUniversityCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Surfaces, Tribology, Dimensional Characteristics, Inspection and Product Quality AssuranceDocument43 pagesSurfaces, Tribology, Dimensional Characteristics, Inspection and Product Quality AssurancewatsopNo ratings yet
- Chapt 11a Rock MechanicsokDocument21 pagesChapt 11a Rock MechanicsokMarcelo Ayllón RiberaNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsDocument63 pagesUnit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsSwethaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprliDocument22 pagesAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprlialpegambarliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprliDocument22 pagesAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprlialpegambarliNo ratings yet
- Flow Over Immersed BodiesDocument63 pagesFlow Over Immersed Bodiesrana abdul waasayNo ratings yet
- Thin Sheets Story: Plastic Anisotropy, Formability and Strain LocalisationDocument9 pagesThin Sheets Story: Plastic Anisotropy, Formability and Strain LocalisationJavier Felipe AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure InteractionDocument10 pagesSoil Structure InteractionKRISHNANUNNI K TNo ratings yet
- MTM 5Document11 pagesMTM 5RajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Flat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustDocument17 pagesFlat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Idealización de Estructuras II (Sección Abierta)Document22 pagesIdealización de Estructuras II (Sección Abierta)David Felipe Vargas OrtizNo ratings yet
- MDP Module 4Document65 pagesMDP Module 4ADITYA RAJ CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Rock MechDocument15 pagesPresentation1 Rock MechTemesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- Spring Design Ii: Prepared and Presented byDocument11 pagesSpring Design Ii: Prepared and Presented byDhiraj NayakNo ratings yet
- Stress-Intensity Factors For A Single-Edge-Notch Tension Specimen by Boundary Collocation of A Stress FunctionDocument16 pagesStress-Intensity Factors For A Single-Edge-Notch Tension Specimen by Boundary Collocation of A Stress FunctionJeremy TohNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument27 pagesClutchessamrawitzeleke634No ratings yet
- Clutch DesignDocument22 pagesClutch DesignLalitkumar JugulkarNo ratings yet
- Stress-Intensity Factors For A Wide Range of Semi-Elliptical Surface Cracks in Finite-Thickness PlatesDocument13 pagesStress-Intensity Factors For A Wide Range of Semi-Elliptical Surface Cracks in Finite-Thickness PlatesYASHANSHU DIXITNo ratings yet
- ES 102 ST1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesES 102 ST1 ReviewerClarenceMillaresNo ratings yet
- Nano IndentationDocument43 pagesNano Indentationportakal0660No ratings yet
- Week 4 With NoteDocument36 pagesWeek 4 With NoteAlton S H ChenNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of SoilsDocument14 pagesShear Strength of SoilsAnkit NagpalNo ratings yet
- Torsion - Part 1Document20 pagesTorsion - Part 1Talat ÇelebiNo ratings yet
- Notes/Lect 4 MMTDocument19 pagesNotes/Lect 4 MMTKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Critical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BDocument265 pagesCritical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BJishnu Ramabhadran100% (1)
- Bending of Beams SolleroDocument34 pagesBending of Beams SolleroPedroLemosNo ratings yet
- OedometerDocument34 pagesOedometerdildarali.ce98No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- φ x N φ x xi, i, , - . -, n NDocument2 pagesφ x N φ x xi, i, , - . -, n NPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Plate FEM AnalysisDocument2 pagesPlate FEM AnalysisPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- H, The Total Potential Energy May Be Written AsDocument2 pagesH, The Total Potential Energy May Be Written AsPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1 Weak Form: XeiweieixqwxxxxxxxDocument2 pages6.2.1 Weak Form: XeiweieixqwxxxxxxxPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- X and Q Is The Load Intensity (Load Per Unit Length)Document1 pageX and Q Is The Load Intensity (Load Per Unit Length)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- EntropyDocument2 pagesEntropyPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ij Are Assumed Known The Unknowns Are The ThreeDocument2 pagesIj Are Assumed Known The Unknowns Are The ThreePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- DX (2) at Position P Which Are Deformed Into Vectors DX (1) and DX (2)Document1 pageDX (2) at Position P Which Are Deformed Into Vectors DX (1) and DX (2)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- KinematiDocument3 pagesKinematiPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Of Time Steps and It: Plot (T, Transl (TS) ) Plot (T, Tr2rpy (TS) )Document2 pagesOf Time Steps and It: Plot (T, Transl (TS) ) Plot (T, Tr2rpy (TS) )Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Mechanical Properties:: Density Modulus of Elasticity Poisson's RatioDocument2 pages1.1 Mechanical Properties:: Density Modulus of Elasticity Poisson's RatioPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- V, Where R D/C.: F MaxDocument2 pagesV, Where R D/C.: F MaxPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocument2 pagesRigid Body DynamicsPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Multiscale MFGDocument2 pagesMultiscale MFGPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument2 pagesExamplePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Scaling in GeometryDocument2 pagesScaling in GeometryPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
Crack
Crack
Uploaded by
Piyush Gupta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThe simulation models crack propagation in a rotating shaft using static analyses with cracks in different locations and orientations. It simulates a transverse straight crack with varying depth ratios and calculates the percentage of closed crack area from the applied rotational force and crack geometry. Crack closure behavior is analyzed by applying contact properties that prevent penetration or sliding between crack surfaces during fatigue loading.
Original Description:
Original Title
crack
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe simulation models crack propagation in a rotating shaft using static analyses with cracks in different locations and orientations. It simulates a transverse straight crack with varying depth ratios and calculates the percentage of closed crack area from the applied rotational force and crack geometry. Crack closure behavior is analyzed by applying contact properties that prevent penetration or sliding between crack surfaces during fatigue loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageCrack
Crack
Uploaded by
Piyush GuptaThe simulation models crack propagation in a rotating shaft using static analyses with cracks in different locations and orientations. It simulates a transverse straight crack with varying depth ratios and calculates the percentage of closed crack area from the applied rotational force and crack geometry. Crack closure behavior is analyzed by applying contact properties that prevent penetration or sliding between crack surfaces during fatigue loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
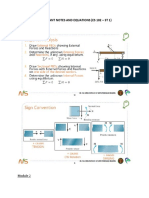
• The simulation is conducted as a series of static problems
with different crack locations along the shaft length in axial
and angular positions.
• A transverse straight crack with non-dimensional crack
depth ratio, 𝜇 = ℎ⁄𝑅, has been simulated and the
unbalance force has been taken as a rotational force and its
angular position 𝛽 with respect to the crack direction on the
shaft cross-section plane is shown in Fig.
• The crack breathing behavior is analyzed by the calculated
percentage of the closed area of a crack, Ʌ
Ʌ (in %) = X 100
Acrack = R2cos-1(1-µ) – R2(1-µ) √
• Crack closure is a phenomenon in fatigue loading where
the opposing face of a crack remain in contact even with an
external load acting on the material.
• To prevent the penetration between the crack surfaces when
the crack closes, the normal property ‘hard contact’ is
selected.
• To avoid the sliding between the crack surfaces the
tangential property ‘rough friction’ is applied to generate an
infinite friction coefficient.
You might also like
- Shear Strength of Soil Part 1 PDFDocument53 pagesShear Strength of Soil Part 1 PDFVal GallanoNo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument33 pagesSlopeMuhammadImranShahzad100% (1)
- ME 498 - 6 - Nanoindentation and NanoscratchDocument23 pagesME 498 - 6 - Nanoindentation and NanoscratchTt Ownsqq100% (1)
- Critical Resolved Shear StressDocument31 pagesCritical Resolved Shear StressLumamba ChiyabiNo ratings yet
- Presantation Picketplot PDFDocument15 pagesPresantation Picketplot PDFEbake ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Part 2 - Dewangan SirDocument87 pagesSlope Stability Part 2 - Dewangan SirAnshul yadavNo ratings yet
- Mae 493n 593t Lec4Document16 pagesMae 493n 593t Lec4kostas.sierros9374No ratings yet
- 04 Steel - MDocument32 pages04 Steel - M22ev06002No ratings yet
- Rotational ViscometerDocument17 pagesRotational ViscometerShivam PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument12 pagesClutchesAbebaw AyeleNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Shear Strength of SoilDocument7 pagesModule 3 Shear Strength of SoilJeth LawNo ratings yet
- Beng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 16-56Document43 pagesBeng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 16-56Tom WhanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Ii-Ecv 308: Bachelor of Science in Civil EngineeringDocument33 pagesSoil Mechanics Ii-Ecv 308: Bachelor of Science in Civil EngineeringGarol BaveriaNo ratings yet
- Transverse Shear - Part 1Document17 pagesTransverse Shear - Part 1Talat ÇelebiNo ratings yet
- PC-FT 403: Lecture (3) byDocument62 pagesPC-FT 403: Lecture (3) byFT 19 Suparno DasNo ratings yet
- Stability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurDocument89 pagesStability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurAastha SoniNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress AnisotrpyDocument53 pagesPlane Stress AnisotrpyInam UllahNo ratings yet
- X Ray ReflectivityDocument14 pagesX Ray Reflectivityjmdq2000No ratings yet
- Unit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityDocument78 pagesUnit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityNirav LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document47 pagesChap 2Amanu WorkuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document36 pagesChapter 9Vaibhav GhuleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Contacts 2ndDocument26 pagesAnalysis of The Contacts 2ndGurjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis: Presented By: Engr. Kyle Emmanuel R. Murillo, CE, RMPDocument41 pagesSlope Stability Analysis: Presented By: Engr. Kyle Emmanuel R. Murillo, CE, RMPRenee AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Beng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 57-88Document34 pagesBeng-Soil Mechanics IB-Slides 57-88Tom WhanNo ratings yet
- CCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 16-56Document43 pagesCCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 16-56MultimediaUniversityCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 06 Print CE311 SHEAR - STRENGTHDocument46 pages06 Print CE311 SHEAR - STRENGTHsahin.hazalNo ratings yet
- Reoort ch2Document22 pagesReoort ch2إحسان خالد جودة الشحات ٣٥٧٣No ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document73 pagesLecture 6yeshi janexoNo ratings yet
- Dry FrictionDocument18 pagesDry FrictionMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength TheoryDocument32 pagesShear Strength TheoryChikkanna TNo ratings yet
- CCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 57-88Document34 pagesCCE 2312-Soil Mechanics II-slides 57-88MultimediaUniversityCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Surfaces, Tribology, Dimensional Characteristics, Inspection and Product Quality AssuranceDocument43 pagesSurfaces, Tribology, Dimensional Characteristics, Inspection and Product Quality AssurancewatsopNo ratings yet
- Chapt 11a Rock MechanicsokDocument21 pagesChapt 11a Rock MechanicsokMarcelo Ayllón RiberaNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsDocument63 pagesUnit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsSwethaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprliDocument22 pagesAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprlialpegambarliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprliDocument22 pagesAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures 2: Dr. Hasan AlbegmprlialpegambarliNo ratings yet
- Flow Over Immersed BodiesDocument63 pagesFlow Over Immersed Bodiesrana abdul waasayNo ratings yet
- Thin Sheets Story: Plastic Anisotropy, Formability and Strain LocalisationDocument9 pagesThin Sheets Story: Plastic Anisotropy, Formability and Strain LocalisationJavier Felipe AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure InteractionDocument10 pagesSoil Structure InteractionKRISHNANUNNI K TNo ratings yet
- MTM 5Document11 pagesMTM 5RajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Flat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustDocument17 pagesFlat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Idealización de Estructuras II (Sección Abierta)Document22 pagesIdealización de Estructuras II (Sección Abierta)David Felipe Vargas OrtizNo ratings yet
- MDP Module 4Document65 pagesMDP Module 4ADITYA RAJ CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Rock MechDocument15 pagesPresentation1 Rock MechTemesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- Spring Design Ii: Prepared and Presented byDocument11 pagesSpring Design Ii: Prepared and Presented byDhiraj NayakNo ratings yet
- Stress-Intensity Factors For A Single-Edge-Notch Tension Specimen by Boundary Collocation of A Stress FunctionDocument16 pagesStress-Intensity Factors For A Single-Edge-Notch Tension Specimen by Boundary Collocation of A Stress FunctionJeremy TohNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument27 pagesClutchessamrawitzeleke634No ratings yet
- Clutch DesignDocument22 pagesClutch DesignLalitkumar JugulkarNo ratings yet
- Stress-Intensity Factors For A Wide Range of Semi-Elliptical Surface Cracks in Finite-Thickness PlatesDocument13 pagesStress-Intensity Factors For A Wide Range of Semi-Elliptical Surface Cracks in Finite-Thickness PlatesYASHANSHU DIXITNo ratings yet
- ES 102 ST1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesES 102 ST1 ReviewerClarenceMillaresNo ratings yet
- Nano IndentationDocument43 pagesNano Indentationportakal0660No ratings yet
- Week 4 With NoteDocument36 pagesWeek 4 With NoteAlton S H ChenNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of SoilsDocument14 pagesShear Strength of SoilsAnkit NagpalNo ratings yet
- Torsion - Part 1Document20 pagesTorsion - Part 1Talat ÇelebiNo ratings yet
- Notes/Lect 4 MMTDocument19 pagesNotes/Lect 4 MMTKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Critical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BDocument265 pagesCritical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BJishnu Ramabhadran100% (1)
- Bending of Beams SolleroDocument34 pagesBending of Beams SolleroPedroLemosNo ratings yet
- OedometerDocument34 pagesOedometerdildarali.ce98No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- φ x N φ x xi, i, , - . -, n NDocument2 pagesφ x N φ x xi, i, , - . -, n NPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Plate FEM AnalysisDocument2 pagesPlate FEM AnalysisPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- H, The Total Potential Energy May Be Written AsDocument2 pagesH, The Total Potential Energy May Be Written AsPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1 Weak Form: XeiweieixqwxxxxxxxDocument2 pages6.2.1 Weak Form: XeiweieixqwxxxxxxxPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- X and Q Is The Load Intensity (Load Per Unit Length)Document1 pageX and Q Is The Load Intensity (Load Per Unit Length)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- EntropyDocument2 pagesEntropyPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ij Are Assumed Known The Unknowns Are The ThreeDocument2 pagesIj Are Assumed Known The Unknowns Are The ThreePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- DX (2) at Position P Which Are Deformed Into Vectors DX (1) and DX (2)Document1 pageDX (2) at Position P Which Are Deformed Into Vectors DX (1) and DX (2)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- KinematiDocument3 pagesKinematiPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Of Time Steps and It: Plot (T, Transl (TS) ) Plot (T, Tr2rpy (TS) )Document2 pagesOf Time Steps and It: Plot (T, Transl (TS) ) Plot (T, Tr2rpy (TS) )Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Mechanical Properties:: Density Modulus of Elasticity Poisson's RatioDocument2 pages1.1 Mechanical Properties:: Density Modulus of Elasticity Poisson's RatioPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- V, Where R D/C.: F MaxDocument2 pagesV, Where R D/C.: F MaxPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocument2 pagesRigid Body DynamicsPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Multiscale MFGDocument2 pagesMultiscale MFGPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument2 pagesExamplePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Scaling in GeometryDocument2 pagesScaling in GeometryPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet