Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enggzc112 May12 An
Enggzc112 May12 An
Uploaded by
dharmendra_kanthariaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Steel Works Inc - Case StudyDocument24 pagesSteel Works Inc - Case Studymwaqasiqbal100% (1)
- Analysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsJuan Carlos Álvarez SalazarNo ratings yet
- E3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFDocument12 pagesE3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFRobles Dresch71% (7)
- Microbiological Specifications Nestle PDFDocument24 pagesMicrobiological Specifications Nestle PDFmadiha altafNo ratings yet
- Index - Sybase 15.0 Replication Server AdministrationDocument29 pagesIndex - Sybase 15.0 Replication Server AdministrationAnonymous pJqNn8esMNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installations B (MBS4231) ExamDocument9 pagesElectrical Installations B (MBS4231) Examkryptos cNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Kung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- r059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesr059210302 Electrical Engineeringprakash.paruchuriNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- BEE Model Paper 1Document7 pagesBEE Model Paper 1Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Eoc Det20033 QuestionDocument3 pagesEoc Det20033 Questiondanialhaziq60No ratings yet
- R059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesR059210302 Electrical EngineeringJhonloyd Rosete LittauaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Kung ChinHan100% (1)
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BDocument8 pagesUniversity of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BVed PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 15ee53 PDFDocument2 pages15ee53 PDFManojNo ratings yet
- UEE001Document1 pageUEE001ishuNo ratings yet
- Edc 7Document8 pagesEdc 729viswa12100% (1)
- ChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Document4 pagesChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Rakibul RafiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1: CEO CBODocument9 pagesSet No. 1: CEO CBO29viswa12No ratings yet
- Week 1 Assignment 1 So LNDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Assignment 1 So LNLloyd Dackz ArenasNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QPDocument5 pages3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QP22u211No ratings yet
- ENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Document7 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Pe Question Paper PDFDocument2 pagesPe Question Paper PDFyr48No ratings yet
- EDSDocument8 pagesEDSSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Edc 3Document10 pagesEdc 329viswa12No ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Power Electronics: Sub code:-06EE45Document3 pagesModel Question Paper Power Electronics: Sub code:-06EE45GuruprasadNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Paper20222328129 - 1705355554570Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Paper20222328129 - 1705355554570family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Pe 2Document4 pagesPe 2Vaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 pagesRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- Leb30303-Electro Technique 2Document7 pagesLeb30303-Electro Technique 2Alif AkmalNo ratings yet
- 2022 - EE5102 - Distribution Systems-FinalDocument4 pages2022 - EE5102 - Distribution Systems-FinalChathura SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Eds PDFDocument4 pagesEds PDFvinayakshettypeNo ratings yet
- r05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsDocument7 pagesr05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- r05222104 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pagesr05222104 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Rr410207 Electrical Distribution SystemsDocument8 pagesRr410207 Electrical Distribution SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation and ControlDocument8 pagesPower System Operation and Controlrajaniram100% (2)
- Eet202 DC Machines and Transformers, July 2021Document3 pagesEet202 DC Machines and Transformers, July 2021Mohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- V1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Document8 pagesV1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Mohammed AlshatriNo ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Exp. - 4 Machine LabDocument7 pagesExp. - 4 Machine LabAbdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- Semester End Examinations - May 2023: USN 1 M SDocument2 pagesSemester End Examinations - May 2023: USN 1 M S25Mohit XI S3No ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - Namesheena mNo ratings yet
- EE402 Jan2006Document4 pagesEE402 Jan2006Amazing ElectricalNo ratings yet
- X10401 (Ee8552)Document3 pagesX10401 (Ee8552)Sujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- Section - A FOUR Questions in This Section. Answer Any THREEDocument8 pagesSection - A FOUR Questions in This Section. Answer Any THREEMir Noushad HussainNo ratings yet
- Rr211001electricaltechnologyDocument8 pagesRr211001electricaltechnologysridiviNo ratings yet
- KTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedDocument16 pagesKTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedsunNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems EC1021Document5 pagesElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- r05010203 Electrical CircuitsDocument14 pagesr05010203 Electrical CircuitsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisFrom EverandResistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Basic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class NotesDocument14 pagesBasic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class Notesdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Piping Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesPiping Interview Questiondharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document6 pagesQuiz 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document6 pagesQuiz 4dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MatlabDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 Matlabdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- TSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFDocument436 pagesTSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Drawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1Document118 pagesDrawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- SP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFDocument145 pagesSP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Print Able Version Noc 2011Document1,121 pagesPrint Able Version Noc 2011Anup Lal RajbahakNo ratings yet
- PDS Training Manual PDFDocument227 pagesPDS Training Manual PDFdharmendra_kantharia100% (1)
- Equity Portfolio SGDocument208 pagesEquity Portfolio SGdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- 1354 Nigeria Country SuDocument48 pages1354 Nigeria Country Sudharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- MF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0Document1,410 pagesMF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Weld SymbolsDocument150 pagesWeld Symbolsdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Rina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Document28 pagesRina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Osman ÖzenNo ratings yet
- 02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsDocument304 pages02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsJúlio Véras100% (2)
- Water Tank Design CalcDocument5 pagesWater Tank Design CalcUttam Kumar Ghosh100% (1)
- As 1767.2.3-1999 Insulating Liquids Test Methods - Method of Sampling Liquid DielectricsDocument8 pagesAs 1767.2.3-1999 Insulating Liquids Test Methods - Method of Sampling Liquid DielectricsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Internship PosterDocument1 pageInternship PosterJanice YizingNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathDocument88 pagesMobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathKhyati ZalawadiaNo ratings yet
- Michael Porter's: Five Forces ModelDocument17 pagesMichael Porter's: Five Forces ModelBindu MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Riksbanken Nat UpplagaDocument528 pagesRiksbanken Nat UpplagaOscar Ubeda SegmarNo ratings yet
- Nature Is The World Around UsDocument3 pagesNature Is The World Around UsKarthikgeyan Munesveran100% (1)
- Pressure Safety Valve-Preliminary Sizing: Input DataDocument6 pagesPressure Safety Valve-Preliminary Sizing: Input DataPIDNo ratings yet
- Power Calculation Drum MotorsDocument2 pagesPower Calculation Drum MotorsFitra VertikalNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu - CE Review: Geotechnical Eng'G Phases of Soil and ClassificationDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cebu - CE Review: Geotechnical Eng'G Phases of Soil and Classificationjovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- @must Read Before InstallDocument3 pages@must Read Before InstallClip ClapsNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing of Materials 155Document1 pageUltrasonic Testing of Materials 155joNo ratings yet
- Business Card Dungeon DelveDocument2 pagesBusiness Card Dungeon DelveTomás Heurtley0% (1)
- Grundfosliterature 146014Document12 pagesGrundfosliterature 146014Mario Daniel MoreiraNo ratings yet
- ICD-11 An International Classification of DiseasesDocument10 pagesICD-11 An International Classification of DiseasesMuhammad Farel Ikram MaulanaNo ratings yet
- PDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhDocument7 pagesPDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhvrsNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolDocument4 pagesThird Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Carta GafiDocument18 pagesCarta Gafiavsec5No ratings yet
- Case Analysis JollibeeDocument5 pagesCase Analysis JollibeeMicah Charish DomingoNo ratings yet
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- Training Staff IDDocument14 pagesTraining Staff IDRS DulayNo ratings yet
- Report - SharifDocument58 pagesReport - SharifNabilNo ratings yet
- T14 CalculatorDocument5 pagesT14 CalculatorUsamaNo ratings yet
- DDocument17 pagesDAlaa ElghazalyNo ratings yet
Enggzc112 May12 An
Enggzc112 May12 An
Uploaded by
dharmendra_kanthariaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enggzc112 May12 An
Enggzc112 May12 An
Uploaded by
dharmendra_kanthariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani
Work-Integrated Learning Programmes Division
Second Semester 2018-2019
Comprehensive Examination (EC-3 Make-up)
Course No. : ENGG ZC112
Course Title : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
Nature of Exam : Open Book
Weightage : 40% No. of Pages =3
Duration : 3 Hours No. of Questions = 8
Date of Exam : 12/05/2019 (AN)
Note:
1. Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book.
2. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page.
3. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer.
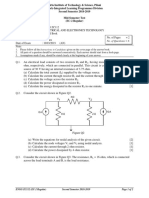
Q.1. Consider the circuit shown in Fig Q1. The resistance of 40 Ω in the circuit is the load
resistor.
(a) Determine Norton’s equivalent circuit. [2]
(b) Using part (a) above, determine Thevinin’s equivalent circuit. [1]
(c) Determine the power drawn by the load resistor. [1]
(d) If an additional load of 40 Ω resistance is connected across the load terminals, then
determine the load current drawn by the combined (parallel combination) load. [1]
Fig. Q1
Q.2. Consider the circuit shown in Fig. Q2.
(a) Determine the current through 20 Ω resistor using nodal analysis. [2]
(b) Determine the voltage across 6 Ω resistor using mesh analysis. [2]
(c) Calculate the total current supplied by the 20 V supply. [1]
Fig. Q2
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 3
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 2
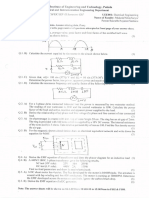
Q.3. Consider the circuit shown in Fig. Q3. The supply frequency is 50 Hz.
(a) Determine the total load impedance. [1]
(b) Determine the currents through the capacitor and the current through the inductor. [2]
(c) Draw a neat sketch of the phasor diagram showing the supply voltage, total current, the
current through the capacitor and the voltage across the capacitor. [1]
(d) Calculate the total active power supplied by the AC supply. [1]
Fig. Q3
Q.4. A 2.2 MVA, 6.6 kV, three-phase, star-connected synchronous generator has armature
resistance of 0.6 Ω per phase and a synchronous reactance of 6 Ω per phase. Assume that
the speed and the exciting current remain unaltered.
(a) Calculate the emf generated in the armature, if half the rated load is connected to its
terminals at the rated voltage and at 0.8 power factor leading. [2]
(b) Draw a neat sketch of the phasor diagram showing the terminal voltage, the load current,
and the generated emf. [2]
(c) Calculate the percentage voltage regulation at unity power factor. [1]
Q.5. A 440 V, 60 Hz, two pole, three phase induction motor is connected to its rated supply. The
frequency of the rotor currents at the rated load is 2.4 Hz.
(a) Calculate the rotor speed (in rpm) at the rated load. [2]
(b) If the frequency of the rotor currents at some other load is 3 Hz, then calculate the rotor
speed (in rpm). [1]
(c) If the same motor is connected to a supply at 50 Hz and is running at 2940 rpm, then
calculate the percentage slip. [2]
Q.6. A four pole, 1500 rpm, lap wound, 240 V DC shunt generator has 48 armature slots with 8
conductors per slot. It delivers a load current of 14.04 A at the rated terminal voltage. The
armature resistance and the field resistance are 0.5 Ω and 250 Ω, respectively. Neglect the
rotational losses.
(a) Calculate the emf generated in the armature and the power developed in the armature.
[2]
(b) Calculate the efficiency of the generator. [2]
(c) Calculate the useful flux per pole. [1]
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 2 of 3
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 3
Q.7. A full wave rectifier with a center-tapped transformer and two diodes is fed from a single
phase, 50 Hz, 240 V supply (vs (t)). A resistive load of 100 Ω is connected across the output
of the rectifier.
(a) Calculate the average voltage across the load and the average current through the load.
[2]
(b) Sketch the following waveforms on the same plot: supply voltage vs(t), the voltage across
the load, current through the load, voltage across one of the diodes and the current
through the same diode. [3]
Q.8. Consider a three-input logical function with inputs A, B and C, and the output F. The output
(F) is 1, when more than half of the inputs are 1.
(a) Prepare the truth table of the function showing the inputs (A, B, and C), and the output
(F). [2]
(b) Prepare the truth table of a logical function F1 = AB + AC + BC showing the inputs (A,
B, and C), and the output (F1). Compare the truth table in part (a) with that of in part (b).
[2]
(c) Implement the function F1 using two-input AND gates and two-input OR gates. [1]
***********
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Steel Works Inc - Case StudyDocument24 pagesSteel Works Inc - Case Studymwaqasiqbal100% (1)
- Analysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsJuan Carlos Álvarez SalazarNo ratings yet
- E3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFDocument12 pagesE3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFRobles Dresch71% (7)
- Microbiological Specifications Nestle PDFDocument24 pagesMicrobiological Specifications Nestle PDFmadiha altafNo ratings yet
- Index - Sybase 15.0 Replication Server AdministrationDocument29 pagesIndex - Sybase 15.0 Replication Server AdministrationAnonymous pJqNn8esMNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installations B (MBS4231) ExamDocument9 pagesElectrical Installations B (MBS4231) Examkryptos cNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Kung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- r059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesr059210302 Electrical Engineeringprakash.paruchuriNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- BEE Model Paper 1Document7 pagesBEE Model Paper 1Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Eoc Det20033 QuestionDocument3 pagesEoc Det20033 Questiondanialhaziq60No ratings yet
- R059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesR059210302 Electrical EngineeringJhonloyd Rosete LittauaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Kung ChinHan100% (1)
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BDocument8 pagesUniversity of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BVed PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 15ee53 PDFDocument2 pages15ee53 PDFManojNo ratings yet
- UEE001Document1 pageUEE001ishuNo ratings yet
- Edc 7Document8 pagesEdc 729viswa12100% (1)
- ChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Document4 pagesChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Rakibul RafiNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1: CEO CBODocument9 pagesSet No. 1: CEO CBO29viswa12No ratings yet
- Week 1 Assignment 1 So LNDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Assignment 1 So LNLloyd Dackz ArenasNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QPDocument5 pages3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QP22u211No ratings yet
- ENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Document7 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Pe Question Paper PDFDocument2 pagesPe Question Paper PDFyr48No ratings yet
- EDSDocument8 pagesEDSSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Edc 3Document10 pagesEdc 329viswa12No ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Power Electronics: Sub code:-06EE45Document3 pagesModel Question Paper Power Electronics: Sub code:-06EE45GuruprasadNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Paper20222328129 - 1705355554570Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Paper20222328129 - 1705355554570family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Pe 2Document4 pagesPe 2Vaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 pagesRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- Leb30303-Electro Technique 2Document7 pagesLeb30303-Electro Technique 2Alif AkmalNo ratings yet
- 2022 - EE5102 - Distribution Systems-FinalDocument4 pages2022 - EE5102 - Distribution Systems-FinalChathura SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Eds PDFDocument4 pagesEds PDFvinayakshettypeNo ratings yet
- r05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsDocument7 pagesr05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- r05222104 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pagesr05222104 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Rr410207 Electrical Distribution SystemsDocument8 pagesRr410207 Electrical Distribution SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation and ControlDocument8 pagesPower System Operation and Controlrajaniram100% (2)
- Eet202 DC Machines and Transformers, July 2021Document3 pagesEet202 DC Machines and Transformers, July 2021Mohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- V1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Document8 pagesV1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Mohammed AlshatriNo ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Exp. - 4 Machine LabDocument7 pagesExp. - 4 Machine LabAbdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- Semester End Examinations - May 2023: USN 1 M SDocument2 pagesSemester End Examinations - May 2023: USN 1 M S25Mohit XI S3No ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - Namesheena mNo ratings yet
- EE402 Jan2006Document4 pagesEE402 Jan2006Amazing ElectricalNo ratings yet
- X10401 (Ee8552)Document3 pagesX10401 (Ee8552)Sujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- Section - A FOUR Questions in This Section. Answer Any THREEDocument8 pagesSection - A FOUR Questions in This Section. Answer Any THREEMir Noushad HussainNo ratings yet
- Rr211001electricaltechnologyDocument8 pagesRr211001electricaltechnologysridiviNo ratings yet
- KTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedDocument16 pagesKTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedsunNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems EC1021Document5 pagesElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- r05010203 Electrical CircuitsDocument14 pagesr05010203 Electrical CircuitsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisFrom EverandResistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Basic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class NotesDocument14 pagesBasic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class Notesdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Piping Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesPiping Interview Questiondharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document6 pagesQuiz 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document6 pagesQuiz 4dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MatlabDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 Matlabdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- TSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFDocument436 pagesTSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Drawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1Document118 pagesDrawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- SP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFDocument145 pagesSP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Print Able Version Noc 2011Document1,121 pagesPrint Able Version Noc 2011Anup Lal RajbahakNo ratings yet
- PDS Training Manual PDFDocument227 pagesPDS Training Manual PDFdharmendra_kantharia100% (1)
- Equity Portfolio SGDocument208 pagesEquity Portfolio SGdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- 1354 Nigeria Country SuDocument48 pages1354 Nigeria Country Sudharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- MF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0Document1,410 pagesMF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Weld SymbolsDocument150 pagesWeld Symbolsdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Rina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Document28 pagesRina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Osman ÖzenNo ratings yet
- 02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsDocument304 pages02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsJúlio Véras100% (2)
- Water Tank Design CalcDocument5 pagesWater Tank Design CalcUttam Kumar Ghosh100% (1)
- As 1767.2.3-1999 Insulating Liquids Test Methods - Method of Sampling Liquid DielectricsDocument8 pagesAs 1767.2.3-1999 Insulating Liquids Test Methods - Method of Sampling Liquid DielectricsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Internship PosterDocument1 pageInternship PosterJanice YizingNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathDocument88 pagesMobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathKhyati ZalawadiaNo ratings yet
- Michael Porter's: Five Forces ModelDocument17 pagesMichael Porter's: Five Forces ModelBindu MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Riksbanken Nat UpplagaDocument528 pagesRiksbanken Nat UpplagaOscar Ubeda SegmarNo ratings yet
- Nature Is The World Around UsDocument3 pagesNature Is The World Around UsKarthikgeyan Munesveran100% (1)
- Pressure Safety Valve-Preliminary Sizing: Input DataDocument6 pagesPressure Safety Valve-Preliminary Sizing: Input DataPIDNo ratings yet
- Power Calculation Drum MotorsDocument2 pagesPower Calculation Drum MotorsFitra VertikalNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu - CE Review: Geotechnical Eng'G Phases of Soil and ClassificationDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cebu - CE Review: Geotechnical Eng'G Phases of Soil and Classificationjovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- @must Read Before InstallDocument3 pages@must Read Before InstallClip ClapsNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing of Materials 155Document1 pageUltrasonic Testing of Materials 155joNo ratings yet
- Business Card Dungeon DelveDocument2 pagesBusiness Card Dungeon DelveTomás Heurtley0% (1)
- Grundfosliterature 146014Document12 pagesGrundfosliterature 146014Mario Daniel MoreiraNo ratings yet
- ICD-11 An International Classification of DiseasesDocument10 pagesICD-11 An International Classification of DiseasesMuhammad Farel Ikram MaulanaNo ratings yet
- PDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhDocument7 pagesPDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhvrsNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolDocument4 pagesThird Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Carta GafiDocument18 pagesCarta Gafiavsec5No ratings yet
- Case Analysis JollibeeDocument5 pagesCase Analysis JollibeeMicah Charish DomingoNo ratings yet
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- Training Staff IDDocument14 pagesTraining Staff IDRS DulayNo ratings yet
- Report - SharifDocument58 pagesReport - SharifNabilNo ratings yet
- T14 CalculatorDocument5 pagesT14 CalculatorUsamaNo ratings yet
- DDocument17 pagesDAlaa ElghazalyNo ratings yet