Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enggzc112 May05 An PDF
Enggzc112 May05 An PDF
Uploaded by
dharmendra_kanthariaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enggzc112 May05 An PDF
Enggzc112 May05 An PDF
Uploaded by
dharmendra_kanthariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani
Work-Integrated Learning Programmes Division
Second Semester 2018-2019
Comprehensive Examination
(EC-3 Regular)
Course No. : ENGG ZC112
Course Title : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
Nature of Exam : Open Book
Weightage : 40% No. of Pages =3
Duration : 3 Hours No. of Questions = 8
Date of Exam : 05/05/2019 (AN)
Note:
1. Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book.
2. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page.
3. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer.
Q.1. Consider the circuit shown in Fig Q1. The resistance of 15 Ω in the circuit is the load
resistor.
(a) Determine Thevenin’s equivalent circuit as seen from the load terminals. [2]
(b) Using part (a) above, determine Norton’s equivalent circuit. [1]
(c) Determine the power drawn by the load resistor. [1]
(d) Determine the maximum power that can be delivered by this circuit. [1]
Fig. Q1
Q.2. Consider the circuit shown in Fig. Q2.
(a) Determine the current through 20 Ω resistor using superposition theorem. [2]
(b) Determine the voltage across 10 Ω resistor using nodal analysis. [2]
(c) Using the results obtained in part (b) above, determine the current through 15 Ω
resistor. [1]
Fig. Q2
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Regular) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 3
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Regular) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 2
Q.3. Consider the circuit shown in Fig. Q3. The supply frequency is 50 Hz.
(a) Determine the total impedance of the circuit. [1]
(b) Determine the current through the capacitor and the current through 15 Ω resistor. [2]
(c) Determine the total current drawn from the supply of 100 V and the power factor. [1]
(d) Draw a neat sketch of the phasor diagram showing the supply voltage, total current,
the current through the capacitor and the voltage across the capacitor. [1]
Fig. Q3
Q.4. A 2650 kVA, 6.6 kV, three-phase, star-connected synchronous generator has a per phase
synchronous impedance of (0.65 + j 7.5)Ω. Assume the speed and the exciting current
remain unaltered. A rated load at 0.85 lagging power factor is connected to its terminals at
the rated voltage.
(a) Calculate the emf generated in the armature. [2]
(b) Draw a neat sketch of the phasor diagram showing the terminal voltage, the load current,
and the generated emf. [2]
(c) Calculate the voltage regulation of the generator at this load. [1]
Q.5. A 415 V, 50 Hz, four pole, 1440 rpm, three phase induction motor is energized with a 415 V,
50 Hz three phase AC supply.
(a) Calculate the synchronous speed of the motor. [1]
(b) Calculate the percentage slip at the rated load. [1]
(c) If the slip is 0.035 at a certain load, then calculate the rotor speed (in rpm) at that load. [1]
(d) Suppose that the supply frequency is changed to 55 Hz. If the motor runs at 1440 rpm at a
certain load, then calculate the slip. [2]
Q.6. A four-pole, lap wound, 220 V DC shunt motor has 400 armature conductors. The useful flux
per pole is 0.025 Wb. The resistance of the armature circuit is 0.8 Ω and that of the field
winding is 250 Ω. The armature current is 15 A.
(a) Calculate the speed (in rpm) [2]
(b) Calculate the power developed in the machine. [1]
(c) Calculate the torque in N m. [1]
(d) Calculate the current drawn from the supply. [1]
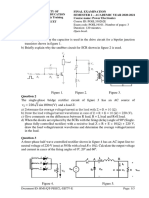
Q.7. In the circuit shown in Fig. Q7, Vm = 230 V, R = 100 Ω and VB = 115 V. The supply
frequency is 50 Hz.
(a) Find the peak current assuming that the diode is ideal. [1]
(b) Sketch vs(t), i(t) and the voltage across the resistor. [2]
(c) Determine the average value of the load voltage and the load current, assuming VB to be
zero. [2]
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Regular) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 2 of 3
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Regular) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 3
Fig. Q7
Q.8. A logical function is described as
F = NOT (F1 OR F2)
where
F1= A AND B, and F2 = B OR C.
Here, A, B and C are the inputs, and F is the output. Further, NOT, OR and AND denote the
logical operations (functions).
(a) Prepare the truth table of the function showing the inputs, F1, F2 and the output F. [3]
(b) Implement this function, F, using two-input AND gates, two-input OR gates and a NOT
gate. [2]
***********
ENGG ZC112 (EC-3 Regular) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Your Electricity BillDocument3 pagesYour Electricity BillDannyNo ratings yet
- E3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFDocument12 pagesE3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFRobles Dresch71% (7)
- Programmed Instruction Handbook - Eddy CurrentDocument376 pagesProgrammed Instruction Handbook - Eddy CurrentShane82% (11)
- Enggzc112 May12 AnDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May12 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Kung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- ENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 201011Kung ChinHan100% (1)
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1: CEO CBODocument9 pagesSet No. 1: CEO CBO29viswa12No ratings yet
- 01 Ee001 3 2 Ae Fe QPDocument5 pages01 Ee001 3 2 Ae Fe QPMohamed AltijaniNo ratings yet
- Edc 3Document10 pagesEdc 329viswa12No ratings yet
- r059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesr059210302 Electrical Engineeringprakash.paruchuriNo ratings yet
- Edc 7Document8 pagesEdc 729viswa12100% (1)
- rr12302 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument12 pagesrr12302 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BDocument8 pagesUniversity of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Note: All Questions Are Compulsory For Section A and BVed PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Pe Question Paper PDFDocument2 pagesPe Question Paper PDFyr48No ratings yet
- r05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsDocument7 pagesr05221401 Semi Conductor Devices and CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- UEE001Document1 pageUEE001ishuNo ratings yet
- 133 BK 112017Document3 pages133 BK 1120172BL20EC096spoorti NidoniNo ratings yet
- 15ee53 PDFDocument2 pages15ee53 PDFManojNo ratings yet
- R059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesR059210302 Electrical EngineeringJhonloyd Rosete LittauaNo ratings yet
- EELXE - 7 - Y1 Analogue Electronics 2Document4 pagesEELXE - 7 - Y1 Analogue Electronics 2Sylvester WasongaNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat No58 EX Ramawat PankajNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Assignment 1 So LNDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Assignment 1 So LNLloyd Dackz ArenasNo ratings yet
- BT I/d 20Document3 pagesBT I/d 20LeoNo ratings yet
- Q1371 Analog ElectronicsDocument1 pageQ1371 Analog ElectronicsDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QPDocument5 pages3rd Sem Analog and LA Sem QP22u211No ratings yet
- Electrical Installations B (MBS4231) ExamDocument9 pagesElectrical Installations B (MBS4231) Examkryptos cNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy Conversion: Semester 2, 2022/23: 29 April 2023 SX NiuDocument6 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversion: Semester 2, 2022/23: 29 April 2023 SX NiujefsharemusicNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems EC1021Document5 pagesElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- 2002UNIT2PAPER2Document16 pages2002UNIT2PAPER2petey78No ratings yet
- Advanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations CouncilDocument15 pagesAdvanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations Councilpetey78No ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Reg No.: - Namesheena mNo ratings yet
- Elec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFDocument7 pagesElec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFchetsNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Document4 pagesChE 21 EEE 267 2014-15Rakibul RafiNo ratings yet
- Ee Sample PaperDocument19 pagesEe Sample Paperjayapriyadarshni12No ratings yet
- MST 2 P1 (Ex-502)Document36 pagesMST 2 P1 (Ex-502)ASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- BEE Model Paper 1Document7 pagesBEE Model Paper 1Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Ee307 2016 06Document3 pagesEe307 2016 06Simbarashe UsaiNo ratings yet
- Exp. - 4 Machine LabDocument7 pagesExp. - 4 Machine LabAbdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- Pe 2Document4 pagesPe 2Vaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- Iv Extc CB Linear Intg CKTSDocument2 pagesIv Extc CB Linear Intg CKTSPratibha Gandhi DumaneNo ratings yet
- V Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesV Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsSumant ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital CircuitsDocument8 pagesPulse and Digital CircuitsLalith KumarNo ratings yet
- r5100207 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesr5100207 Electronic Devices and CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- EEE307 Mid 1 ModeratedDocument1 pageEEE307 Mid 1 ModeratedMasud SarkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 22 Even 1Document28 pages2021 22 Even 1sarojkuldeepkumar181No ratings yet
- GR17 DCMT - Set1 Nov 2018Document3 pagesGR17 DCMT - Set1 Nov 2018P Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayTấn Long Đoàn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Document7 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- 07-01-2022 - EEE3100S 2022 November EXAM - 2Document6 pages07-01-2022 - EEE3100S 2022 November EXAM - 2Stalin KosterNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Tutorial Sheet 2: Single Phase AC NetworksDocument4 pagesElectrical Technology Tutorial Sheet 2: Single Phase AC NetworksShroyonNo ratings yet
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- B E Regular B E July 2013 Electrical S E Sem III 15512141836712810530111 11Document2 pagesB E Regular B E July 2013 Electrical S E Sem III 15512141836712810530111 11rajuchandanshive047No ratings yet
- Eel301 2022Document2 pagesEel301 2022rraj09102002No ratings yet
- Eoc Det20033 QuestionDocument3 pagesEoc Det20033 Questiondanialhaziq60No ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Basic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class NotesDocument14 pagesBasic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class Notesdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Piping Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesPiping Interview Questiondharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May12 AnDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May12 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document6 pagesQuiz 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document6 pagesQuiz 4dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MatlabDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 Matlabdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 Sun10 AnDocument2 pagesEnggzc112 Sun10 Andharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Engg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEngg Zc112 (Ec-2 Make-Up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- TSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFDocument436 pagesTSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Drawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1Document118 pagesDrawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- SP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFDocument145 pagesSP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Print Able Version Noc 2011Document1,121 pagesPrint Able Version Noc 2011Anup Lal RajbahakNo ratings yet
- PDS Training Manual PDFDocument227 pagesPDS Training Manual PDFdharmendra_kantharia100% (1)
- Equity Portfolio SGDocument208 pagesEquity Portfolio SGdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- 1354 Nigeria Country SuDocument48 pages1354 Nigeria Country Sudharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- MF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0Document1,410 pagesMF Portfolio Tracker - India v3.0dharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Weld SymbolsDocument150 pagesWeld Symbolsdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- World Plug Input Voltage GuideDocument4 pagesWorld Plug Input Voltage GuideRiski DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Unbalance and It's Impact On The Performance of Three Phase Induction Motor: A ReviewDocument6 pagesVoltage Unbalance and It's Impact On The Performance of Three Phase Induction Motor: A ReviewSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- DLL September 4 7Document3 pagesDLL September 4 7DENVER MOSCOSONo ratings yet
- POLIM-S To 245kV - 2GNM110077 - 7-11 PDFDocument14 pagesPOLIM-S To 245kV - 2GNM110077 - 7-11 PDFByron David MoralesNo ratings yet
- Bohn Bel SsDocument60 pagesBohn Bel SsErixon RamírezNo ratings yet
- DS ANT TNA352A33rDocument3 pagesDS ANT TNA352A33rEdelNo ratings yet
- Octal Transparent Latch With 3-State Outputs Octal D-Type Flip-Flop With 3-State Output SN54/74LS373 SN54/74LS374Document2 pagesOctal Transparent Latch With 3-State Outputs Octal D-Type Flip-Flop With 3-State Output SN54/74LS373 SN54/74LS374Miyuki_22No ratings yet
- Clarke 100E ManualDocument35 pagesClarke 100E ManualdjDangerBurgersNo ratings yet
- Brochure-QES-LCR - GeneratorsDocument16 pagesBrochure-QES-LCR - GeneratorsDaniel IdubeNo ratings yet
- Triac PDFDocument3 pagesTriac PDFyuj oNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument20 pagesStatic Electricityc jNo ratings yet
- Stability Performance of New Static Excitation System With Boost-Buck ConverterDocument8 pagesStability Performance of New Static Excitation System With Boost-Buck ConverterMartua MarioNo ratings yet
- MC225 OwnDocument12 pagesMC225 OwnmozNo ratings yet
- Inverter 3,6Document56 pagesInverter 3,6igor.keareNo ratings yet
- No. 5, Jalan 22/6, Seksyen 22, 40300 Shah Alam, Selangor, MalaysiaDocument2 pagesNo. 5, Jalan 22/6, Seksyen 22, 40300 Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysiavajiravel407No ratings yet
- 2301A Electronic Load Sharing and Speed Controls: 9907 Series UL Listed E97763Document60 pages2301A Electronic Load Sharing and Speed Controls: 9907 Series UL Listed E97763Erick FalconiNo ratings yet
- NEC Table 310.77 (Detail 1 - One Circuit, 3-1/c in Single Duct)Document3 pagesNEC Table 310.77 (Detail 1 - One Circuit, 3-1/c in Single Duct)gyanendra_vatsa4380No ratings yet
- WM-FX651 y 653Document26 pagesWM-FX651 y 653london335No ratings yet
- Haltech Dual Channel Wideband Instructions1Document2 pagesHaltech Dual Channel Wideband Instructions1Glenn-anthony Sending-State HortonNo ratings yet
- Specification For Fittings For Rigid Non-Metallic F Second Revision) ConduitsDocument16 pagesSpecification For Fittings For Rigid Non-Metallic F Second Revision) ConduitsAvinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Service BulletinDocument4 pagesService BulletinMohammad yasinNo ratings yet
- PV Testing White Paper Harnessing The PotentialDocument20 pagesPV Testing White Paper Harnessing The PotentialphilipnartNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 1Document2 pagesProblem Set No. 1russelpagaoNo ratings yet
- Gabs SSR - Maxis - Imsi - Revb PDFDocument62 pagesGabs SSR - Maxis - Imsi - Revb PDFAnildip SinghNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla - The Wireless Transmission of PowerDocument13 pagesNikola Tesla - The Wireless Transmission of PowerMitch100% (11)
- KF5N60D IDocument7 pagesKF5N60D IAlceu DluzniewskiNo ratings yet
- Fco560 Id 3090Document2 pagesFco560 Id 3090viniciustasilNo ratings yet