Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evolution of Traditional To New Media
Evolution of Traditional To New Media
Uploaded by
Asterio Ornopia AsaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evolution of Traditional To New Media
Evolution of Traditional To New Media
Uploaded by
Asterio Ornopia AsaCopyright:
Available Formats
Media
Information Name ________________ ________ Grade 12 Score:
Literacy 12
MODULE
Evolution of Traditional to New Media
2
A. THE HISTORY OF MEDIA AND INFORMATION
Pre-Industrial Age (Before 1700s)- People discovered fire, developed paper from plants, and forged weapons and tools with
stone, bronze, copper, and iron.
Examples:
o Cave paintings (35, 00 BC) o Dibao in China (2nd Century)
o Clay tablets in Mesopotamia (2400 BC) o Printing press using wood blocks (220 AD)
o Papyrus in Egypt (2500 BC) o Codex in the Mayan region (5th Century)
o Acta Diurna in Rome (130 BC)
INDUSTRIAL AGE (1700S-1930S) - People used the power of steam, developed machine tools, established iron production, and
the manufacturing of various products (including books through the printing press). Examples:
Printing press for mass production (19th century)
Examples:
o Newspaper- The London Gazette (1640) o Commercial motion pictures (1913) •
o Typewriter (1800) o Motion picture with sound (1926)
o Telephone (1876) o Telegraph
o Motion picture photography/projection o Punch cards
(1890)
ELECTRONIC AGE (1930S-1980S) - The invention of the transistor ushered in the electronic age. People harnessed the power
of transistors that led to the transistor radio, electronic circuits, and the early computers. In this age, long distance communication
became more efficient. Examples:
Examples:
o Transistor Radio o Mainframe computers - i.e. IBM 704 (1960)
o Television (1941) o Personal computers - i.e. Hewlett Packard
o Large electronic computers- i.e. EDSAC 9100A (1968), Apple 1 (1976)
(1949) and UNIVAC 1 (1951)
INFORMATION AGE (1900S-2000S) - The Internet paved the way for faster communication and the creation of the social
network. People advanced the use of microelectronics with the invention of personal computers, mobile devices, and wearable
technology. Moreover, voice, image, sound and data are digitalized. We are now living in the information age.
Examples:
o Web browsers: Mosaic (1993), Internet o Video chat: Skype (2003), Google Hangouts
Explorer (1995) (2013)
o Blogs: Blogspot (1999), LiveJournal (1999), o Search Engines: Google (1996), Yahoo
WordPress (2003) (1995)
o Social networks: Friendster (2002), Multiply o Portable computers- laptops (1980), netbooks
(2003), Facebook (2004) (2008), tablets (1993)
o Microblogs: Twitter (2006), Tumblr (2007) o Smart phones
o Video: YouTube (2005) o Wearable technology
o Augmented Reality / Virtual Reality o Cloud and Big Data
Roles and functions of media in a democratic society:
Channel - provides opportunities for people to communicate, share ideas, speculate, tell stories and give information
Watchdog - exposes corrupt practices of the government and the private sector. Creating a space wherein governance
is challenged or scrutinized by the governed. It also guarantees free and fair elections
Resource center - acts as a gateway of information for the society’s consumption. Also, it becomes a keeper of
memories of the community, preserver of heritage and source of academic knowledge.
Advocate - through its diverse sources or formats, it bridges the gap of digital divide.
B. ETHICAL USE OF INFORMATION
Plagiarism: Using other people’s words and ideas without clearly acknowledging the source of the information
Common Knowledge: Facts that can be found in numerous places and are likely to be widely known
Example: John F. Kennedy was elected President of the United States in 1960. This is generally known information. You
do not need to document this fact
Interpretation: You must document facts that are not generally known, or ideas that interpret facts.
Example: Michael Jordan is the greatest basketball player ever to have played the game. This idea is not a fact but an
interpretation or an opinion. You need to cite the source.
MIL page 2 First Quarter
Quotation: Using someone’s words directly. When you use a direct quote, place the passage between quotation marks, and
document the source according to a standard documenting style.
Example: According to John Smith in The New York Times, “37% of all children under the age of 10 live below the
poverty line”. You need to cite the source.
Paraphrase: Using someone’s ideas but rephrasing them in your own words. Although you will use your own words to
paraphrase, you must still acknowledge and cite the source of the information.
Plagiarism has legal implications. While ideas themselves are not copyrightable, the artistic expression of an idea automatically
falls under copyright when it is created. Under fair use, small parts may be copied without permission from the copyright holder.
However, even under fair use - in which you can use some parts of the material for academic or non-profit purposes - you must
attribute the original source. What is considered fair use is rather subjective and can vary from country to country.
Strategies in Avoiding Plagiarism
1. Submit your own work for publication. You need to cite even your own work.
2. Put quotation marks around everything that comes directly from the text and cite the source.
3. Paraphrase, but be sure that you are not simply rearranging or replacing a few words and cite the source.
4. Keep a source journal, a notepad, or note cards- annotated bibliographies can be especially beneficial
5. Use the style manual in properly citing sources
6. Get help from the writing center or library
Challenge Yourself
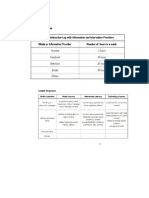
FT1 Fill the Table. Knowing the Media at Different Ages. Fill the table below.
What format/equipment did
What format/equipment did What format/equipment did
people use to store
Age people use to communicate with people use to share or
information?
each other? broadcast information?
Stone Tablet
Stone Tablet Cave paintings
Papyrus
Pre-industrial Age Papyrus Clay tablets in Mesopotamia
Printing press using wood
Sign and Symbols Acta Diurna in Rome
blocks
Telegraph Newspaper
Typewriter
Industrial Age Telephone Motion picture photography
Newspaper
Punch cards Commercial motion pictures
Large electronic computers Television
Transistor Radio
Electronic Age Mainframe computers Transistor Radio
Web browsers
Blogs Blogs
Social networks Social networks
Microblogs Microblogs
Video Video
Social networks
Search Engines Augmented Reality / Virtual
Video chat
Portable computers Reality
Information Age Microblogs
Smart phones Video chat
Smart phones
Wearable technology Search Engines
Portable computers
Cloud and Big Data Portable computers
Smart phones
Wearable technology
Cloud and Big Data
FT2 Express Your Thoughts. Discuss the following questions: (not more than 50 words)
1. Given the available media that we have now in the world, what are its roles and functions in a democratic society?
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________
MIL page 2 First Quarter
2. In what ways does media affect your life (personal, academic, social, others)?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________
FT3 Academic Field Trip. You will plan an academic trip. List pertinent information of two possible destinations
(somewhere in the country or abroad). To present valid and reliable information, consider the following:
Identify he information needed- what, where, who, when, why, how.
Determine all possible sources – the World Wide Web, travel guide, books, brochures, maps and atlases, tour
bureaus, family members, and friends.
Locate and find information within the sources – blogs, travel reviews, posts from social networking sites, travel
features, pictures, stories, and testimonials.
Extract the best relevant information and cite pertinent sources.
Fill this as your draft. Your finale output is to be sent in the Edmodo via Doc File.
Plan A Plan B
Sample Data
(make sure to put the sources) (make sure to put the sources)
Place / Location /
Destination
Activity / Schedule
Best time to visit / Length of
vacation
Transportation (Type,
budget, schedule, others)
Accommodation (type,
budget, schedule, others)
Food (type, budget,
schedule, others)
Things to bring / reminders
Other information you may
need
Total Budget
-end-
You might also like
- Reading 5 M2 Inferring Personality TraitsDocument2 pagesReading 5 M2 Inferring Personality TraitsAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Types of PhrasesDocument3 pagesModule 6 Types of PhrasesAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 African MythsDocument2 pagesModule 2 African MythsAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (2)
- Module 3 African FolktalesDocument2 pagesModule 3 African FolktalesAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (2)
- Module 3 African FolktalesDocument2 pagesModule 3 African FolktalesAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (2)
- Module 2 African MythsDocument2 pagesModule 2 African MythsAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (2)
- 01 The Evolution of TraditionalDocument18 pages01 The Evolution of Traditionaldiosyjeanne d. simyunnNo ratings yet
- Mil Q1Document14 pagesMil Q1STO. DOMINGO, Aneka MaghintayNo ratings yet
- SHS - MIL L02 - The Evolution of Traditional To New Media (Lec)Document55 pagesSHS - MIL L02 - The Evolution of Traditional To New Media (Lec)Ruel CarballoNo ratings yet
- L2 Media and Information LiteracyDocument3 pagesL2 Media and Information LiteracyRoveline GenonNo ratings yet
- 2 Evolution From Traditional To New MediaDocument13 pages2 Evolution From Traditional To New Mediapajaresmarineil12No ratings yet
- Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument48 pagesEvolution of Traditional To New MediaKayle CombisNo ratings yet
- Mil Q1Document7 pagesMil Q1STO. DOMINGO, Aneka MaghintayNo ratings yet
- The Evol. of Trad. To New Media - LecDocument2 pagesThe Evol. of Trad. To New Media - LecRicia GaelNo ratings yet
- Mil 2Document48 pagesMil 2Fernando PradoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Traditional To A New MediaDocument27 pagesEvolution of Traditional To A New MediaFe Lanny L. TejanoNo ratings yet
- DLP Mil 3Document3 pagesDLP Mil 3Richie Noy TenesoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MediaDocument7 pagesEvolution of MediaJules GajesNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesEvolution of Traditional Media To New Media: Learning ObjectivesJohn Brylle GuangcoNo ratings yet
- Mil 3Document24 pagesMil 3Catherine SalasNo ratings yet
- Mil Week 3Document23 pagesMil Week 3Ma Belle Jasmine DelfinNo ratings yet
- Evolution (Day 3-4)Document2 pagesEvolution (Day 3-4)Jim Carl MaasinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document16 pagesLesson 8Anrey David MacapasNo ratings yet
- Q1 - L2 The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument56 pagesQ1 - L2 The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaTrisha Anthony CortazNo ratings yet
- Media and Informaton Literacy PresentationDocument71 pagesMedia and Informaton Literacy PresentationBoyet TarucNo ratings yet
- 2 EvolutionDocument1 page2 EvolutionLavina TacobanzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument3 pagesLesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Module 2 2Document8 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Module 2 2Jacqueline ChanNo ratings yet
- Media & Information Literacy 4Document4 pagesMedia & Information Literacy 4Kristine Joy DefanteNo ratings yet
- MIL - Week 2Document10 pagesMIL - Week 2Aira Manuba MozoNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Traditional To New Media: Media and Information LiteracyDocument67 pagesThe Evolution of Traditional To New Media: Media and Information LiteracyBoyet TarucNo ratings yet
- Media HandoutDocument5 pagesMedia HandoutPomelo Tuquib LabasoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Media: Week 2-Media and Information Literacy Ms. ColaljoDocument31 pagesEvolution of Media: Week 2-Media and Information Literacy Ms. ColaljoIvilen Marie ColaljoNo ratings yet
- The Evolution From Traditional To New MediaDocument20 pagesThe Evolution From Traditional To New MediaKRISTINE MARIE SOMALONo ratings yet
- 4 Media EvolutionDocument24 pages4 Media EvolutionAPRIL ROSE VICENTENo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Q1 M1 LOLO 12 GATESDocument8 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Q1 M1 LOLO 12 GATESCriestefiel LoloNo ratings yet
- Q1 Mil Lesson2Document1 pageQ1 Mil Lesson2Dan Lloyd GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Week 3 MilDocument30 pagesWeek 3 MilBenilda Pensica SevillaNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication?Document3 pagesWhat Is Communication?Rhona Lyn Peñaflorida VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module in STSDocument5 pagesModule in STSAbriann Vince ImpenioNo ratings yet
- MIL-Lesson-4-SY-22-23 2Document8 pagesMIL-Lesson-4-SY-22-23 2Bellyx IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument4 pagesMil ReviewerKylen FajardoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MediaDocument2 pagesEvolution of MediaJasmine PagkaliwanganNo ratings yet
- Media Evolution DftaDocument39 pagesMedia Evolution DftaDANNAH FAYE ARDIENTENo ratings yet
- Mil Lesson 2Document4 pagesMil Lesson 2Mariel ObnascaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information ReviewerDocument3 pagesMedia and Information RevieweraisleNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Mil) : The Evolution of Traditional To New Media (Part 1)Document27 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Mil) : The Evolution of Traditional To New Media (Part 1)Neil John De VeraNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy 2Document46 pagesMedia and Information Literacy 2Valdez, Francine A.No ratings yet
- 6 The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument20 pages6 The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaGle SelNo ratings yet
- Media Information... Module1 BezosDocument5 pagesMedia Information... Module1 Bezosadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Intro ND EvoDocument3 pagesIntro ND EvoLeonie LanzadoNo ratings yet
- Diplahan National High School Activity Sheet 4 Objectives: at The End of The Discussion, The Learners Are Expected ToDocument2 pagesDiplahan National High School Activity Sheet 4 Objectives: at The End of The Discussion, The Learners Are Expected ToRica GraceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Definition of Terms: Handout # 1 Media and Information LiteracyDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Definition of Terms: Handout # 1 Media and Information LiteracyAngela Garcia100% (1)
- The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument6 pagesThe Evolution of Traditional To New MediaRamos, Casandra Jhane R.No ratings yet
- MIL HandoutDocument6 pagesMIL Handoutmosrifa mahdiNo ratings yet
- Media Information LiteracyDocument13 pagesMedia Information LiteracyChristianlloyd RagelNo ratings yet
- Titanic (April 14, 1912)Document36 pagesTitanic (April 14, 1912)Crystal Jaye R. BoadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Week 2Document16 pagesLesson 2 Week 2Gem CamachoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information LiteracyJEFFREY PALADONo ratings yet
- Mil Module 2Document8 pagesMil Module 2Joel Cabusao LacayNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology.Document3 pagesScience and Technology.memeslolol1311 reeNo ratings yet
- Mil4 1Document43 pagesMil4 1Karen RoyoNo ratings yet
- MIL Q1 T2 Evolution-of-Media 014055Document47 pagesMIL Q1 T2 Evolution-of-Media 014055Johnpaul OrozcoNo ratings yet
- MIL Q1 WK 3Document58 pagesMIL Q1 WK 3Carhl LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument16 pagesEvolution of Traditional To New MediaZhiel Nangit Abordo100% (1)
- Priming the Pump: How TRS-80 Enthusiasts Helped Spark the PC RevolutionFrom EverandPriming the Pump: How TRS-80 Enthusiasts Helped Spark the PC RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Reading 5 M5 Compound WordsDocument2 pagesReading 5 M5 Compound WordsAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Reading 6 M3 Noting DetailsDocument2 pagesReading 6 M3 Noting DetailsAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (2)
- Reading 5 M6 Using IdiomsDocument3 pagesReading 5 M6 Using IdiomsAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Reading 6 M4 Sequencing EventsDocument2 pagesReading 6 M4 Sequencing EventsAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Introduction To SyntaxDocument2 pagesModule 7 Introduction To SyntaxAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (1)
- Reading 6 M2 Types of Context CluesDocument2 pagesReading 6 M2 Types of Context CluesAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Context CluesDocument2 pagesModule 8 Context CluesAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 African EpicDocument2 pagesModule 4 African EpicAsterio Ornopia Asa0% (2)
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument4 pages21st Century LiteratureAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Characteristic, Subject Matter and Style in Contemporary ArtDocument37 pagesModule 1: Characteristic, Subject Matter and Style in Contemporary ArtAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 African EpicDocument2 pagesModule 4 African EpicAsterio Ornopia Asa0% (2)
- Contemporary Arts: Grade 12Document17 pagesContemporary Arts: Grade 12Asterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Literature During The Spanish PeriodDocument2 pagesModule 2 Literature During The Spanish PeriodAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- 2 Skills, Technique, Production and Appreciating Contemporary ArtDocument2 pages2 Skills, Technique, Production and Appreciating Contemporary ArtAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Media and Information and Evaluating Information: Medlit 12 - Page 2-First QuarterDocument2 pagesIndigenous Media and Information and Evaluating Information: Medlit 12 - Page 2-First QuarterAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- The More Common Literary Approaches Being Used IncludeDocument2 pagesThe More Common Literary Approaches Being Used IncludeAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Types of Media: Print, Broadcast and New MediaDocument2 pagesTypes of Media: Print, Broadcast and New MediaAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Tle 8Document2 pagesTle 8Asterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Niel Francis JDocument1 pageNiel Francis JAsterio Ornopia AsaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase Studyaachabaniya382No ratings yet
- Ndalianis, Angela - Neo-Baroque Aesthetics and Contemporary Entertainment (Media in Transition)Document341 pagesNdalianis, Angela - Neo-Baroque Aesthetics and Contemporary Entertainment (Media in Transition)mehtapserimNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Building Your Personal BrandDocument12 pagesA New Approach To Building Your Personal Brandmailmehere05No ratings yet
- Media in Gujarati LanguageDocument11 pagesMedia in Gujarati LanguagemarshmelloNo ratings yet
- Sukamto, M., Hamidah, & FajrianthiDocument14 pagesSukamto, M., Hamidah, & FajrianthiAndi Putri MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Bands ADocument2 pagesBands Arockerangi3707No ratings yet
- Analysis On Exercise 6Document1 pageAnalysis On Exercise 6Sharmz SalazarNo ratings yet
- A Dissertation Report: BY Lucky Dewangan 20201011Document32 pagesA Dissertation Report: BY Lucky Dewangan 20201011SHIVAM SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- Getting Hooked On Electricity andDocument4 pagesGetting Hooked On Electricity andChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Media PlanDocument8 pagesMedia PlanketanshekharNo ratings yet
- Chordu Guitar Chords Lelaki Cadangan t2 Cover by Regita Chordsheet Id - AowCWswtSzY PDFDocument3 pagesChordu Guitar Chords Lelaki Cadangan t2 Cover by Regita Chordsheet Id - AowCWswtSzY PDFMuhammad FathurNo ratings yet
- Left Margins Top, Bottom Right Margins Not-Indented ParagraphDocument1 pageLeft Margins Top, Bottom Right Margins Not-Indented ParagraphPinky NE OrtegaNo ratings yet
- What Is Multimedia?Document8 pagesWhat Is Multimedia?jishamanojNo ratings yet
- Micro - A Resort HotelDocument1 pageMicro - A Resort Hotelrovic beltranNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project ReportDocument31 pagesSummer Training Project ReportbheemNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Preparing Files For PrintDocument12 pagesA Guide To Preparing Files For PrintMiriam Campillo BayonaNo ratings yet
- Indian Weekender 8 June 2017Document72 pagesIndian Weekender 8 June 2017Indian WeekenderNo ratings yet
- MEDIA LAW ProjectDocument4 pagesMEDIA LAW ProjectAASTHA ASMITANo ratings yet
- Interactive MultimediaDocument34 pagesInteractive MultimediaPrechi E. DecipoloNo ratings yet
- Advertising and Imc Principles and Practice 10th Edition Moriarty Test BankDocument41 pagesAdvertising and Imc Principles and Practice 10th Edition Moriarty Test Bankquyenthamrww6100% (32)
- Q2 MIL Week 3 LessonDocument24 pagesQ2 MIL Week 3 LessonHasañon Judy AnnNo ratings yet
- The Operations StrategyDocument5 pagesThe Operations StrategyDr. Syed Masrur100% (1)
- Natasha Jha-CvDocument2 pagesNatasha Jha-Cvapi-349002748No ratings yet
- Visual ArtsDocument47 pagesVisual ArtsJoaquinGabrielLugay100% (1)
- Custom UrlDocument5 pagesCustom UrlSyrif 11No ratings yet
- نماذج امتحانات التوفل عين شمس pdf 1Document3 pagesنماذج امتحانات التوفل عين شمس pdf 1Ahmed HashimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Development CommunicationDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Development Communicationnt201No ratings yet
- FM RadioDocument7 pagesFM RadioAswiniSamantrayNo ratings yet
- Adriana Diaz Communications ResumeDocument1 pageAdriana Diaz Communications ResumeAdriana DiazNo ratings yet
- Chris Arthur) Religion and The Media An IntroducDocument317 pagesChris Arthur) Religion and The Media An IntroducMichael AdedejiNo ratings yet