Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 ECBC Implementation-Hyd - Model
2 ECBC Implementation-Hyd - Model
Uploaded by
SharanyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 ECBC Implementation-Hyd - Model
2 ECBC Implementation-Hyd - Model
Uploaded by
SharanyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Conservation Building Code Implementation in the States of
Telangana and Andhra Pradesh: Hyderabad Model
Rajkiran V Bilolikar, Associate Professor, Administrative Staff College of India
Chinta Shree Sowmya, Consultant, Administrative Staff College of India
Sameer Kwatra, Natural Resources Defense Council, USA
Introduction
By constructing energy-efficient buildings, cities and states in India have an opportunity to
lock in energy savings for years to come and reduce climate warming carbon emissions,
while saving money and retaining occupant comfort. The Energy Conservation Building Code
(ECBC) is the model energy code that sets standards for making buildings more energy-
efficient. With a combined population of 85 million 1, the Telangana and Andhra Pradesh
region represent one of the fastest-growing regions in the country. Hyderabad, the capital
of Telangana State, has taken the lead in ECBC implementation by developing a model
framework for code compliance, which can be scaled to many other cities in the state and
across the country.
Taking the lead on energy efficiency, the Government of united Andhra Pradesh (AP),
supported by Administrative Staff College of India (ASCI), Hyderabad and Natural Resources
Defense Council (NRDC), USA adapted ECBC in the state and appointed a Technical
Committee which can look after the integration of ECBC into Andhra Pradesh Building Rules
(G.O.168) with a few modifications. On January 28, 2014, based on the Technical Committee
recommendations, the state announced mandatory ECBC compliance for all commercial
buildings by issuing Government Order MS NO. 30, (by Amendment of G.O.168) from
Municipal Administration and Urban Development Department and became the first state
in doing so. After bifurcation, both the states adapted the same GO (Government Order)
and continued the implementation of ECBC compliance for all commercial buildings.
Key Features of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh States ECBC (TSECBC/APECBC)
For effective implementation of the ECBC code, few revisions have been done by the
technical committee in the code before notifying it in the state of Telangana. They are as
follows:
• The applicability of ECBC compliance has been changed to ‘The code is
applicable to commercial buildings or building complexes with a plot area of
1,000 m2 or more or 2000 m2 built up area whichever is higher’ in
TSECBC/APECBC.
• Certain categories of buildings such as Multiplexes, Hospitals, Hotels, and
Convention Centers have been made TSECBC/APECBC mandatory irrespective of
their built up area.
1
Census India 2011. Accessed January 27, 2017. Available from
‘http://censusindia.gov.in/2011census/censusinfodashboard/stock/profiles/en/IND028_Andhra%20Pradesh.p
df’
Administrative Staff College of India 1|Page
• Star rating system has been incorporated in the code with AP*/TS*. The
maximum star rating allotted to the buildings is AP*****/TS***** stars (5 Stars)
with exemplary performance and minimum star rating is AP*/TS* (1 star) which
is mandatory for all commercial buildings. For buildings with AP**/TS** and
above, the buildings will be given an expedited process for building construction
approval and occupancy certificate with highest priority.
• The code compliance will be checked through third party agency at two stages:
first is at Building design approval stage and second is at Building occupancy
stage.
Third party Assessor Mode implementation
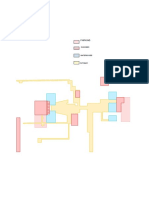
Figure 1: Schematic representation of building approval system showing the role of TPA.
Government of Telangana has adopted a two-tier code compliance approach. Third party
assessors, trained and empanelled by the government, inspect the building in two stages to
ensure effective compliance: one at Building design approval stage and second at Building
occupancy stage. This can be clearly understood in the picture.
In the First Stage (Building construction Stage), the Owner with the consultation of
Architects and MEP consultants designs his building. Once the drawings are finalized, the
building owner has to submit them to the TPA. The TPA checks the documents and drawings
and gives an ECBC compliance certificate to the owner. Thereafter, the owner has to submit
the documents/drawings to the building Committee of respective Urban local body (ULB) of
the State for approval. ULB/Development Authority is responsible for approval of the
documents in both the states.
Administrative Staff College of India 2|Page
This can also be done by online approval system of ULBs and Greater Hyderabad Municipal
Corporation (GHMC) for the first time in India, incorporated ECBC compliance through its
online building construction approval system.
In the second stage of the process i.e., during the building occupancy stage, the owner
submits the data to TPA in order to undergo a physical inspection of building. TPA after
verification finally issues a compliance certificate mentioning that the building construction
is as per the code compliance.
Hyderabad Model
The city of Hyderabad is a leading destination of Indian and multinational hi-tech companies
including IT and IT-enabled services, software consulting firms and business process
outsourcing. Being the capital of Telangana State, Hyderabad is also a home to numerous
government office buildings to cater the administrative needs of the city and the state. This
rapid growth will exponentially increase the energy use. Thus, it is the right time to
intervene in building construction to create energy efficient built environment in future.
The Telangana State Government, supported by the Administrative Staff College of India
(ASCI) with the support of UNDP-BEE-GEF and in partnership with IIIT-Hyd and NRDC, has
focused on three key elements to develop the Hyderabad Model for effective, simple and
robust ECBC compliance as follows:
1. Training and Awareness
2. Resources and Tools
3. Simple and Effective Online Process
Figure 2: Schematic representation of Hyderabad model for ECBC Implementation
Training and Awareness
ASCI and NRDC, along with experts from Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) and International
Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Hyderabad, funded by UNDP, have trained more
Administrative Staff College of India 3|Page
than three hundred officials and real estate developers since the energy code became
mandatory in the State of Telangana under the UNDP-GEF-BEE project named “Energy
Efficiency Improvements in Commercial Buildings”. Training the stakeholders has been
transformative step towards the development of in depth understanding of the code along
with appreciation of complying the ECBC code. Leading developers in Hyderabad have
emerged as strong proponents of energy-efficiency.
As per the compliance process, Third Party Assessors (TPAs) who have been empaneled by
the government, are given an authority to review the building in design and post
construction phases. The state has published a database of all empanelled TPAs so that
project developers can contact them for compliance certification process. In anticipation of
increased volume of ECBC applications via the online approval system, the GHMC is now
conducting technical training workshops to expand the pool of third party assessors,
architects, engineers, and real estate developers with expertise in ECBC. Currently,
Telangana state comprises 38 empaneled Third Party Assessors with GHMC.
Simple and Effective Online Process
Figure 3: Screenshot of Online Application form in the GHMC website highlighting the clause of ECBC
mandatory compliance
The heart of the Hyderabad Model is its online compliance system. The Government of
Telangana is the first in the country to incorporate ECBC provisions in its online web portal
known as ‘development permission management system’. All new construction projects in
Administrative Staff College of India 4|Page
the city has to be submit an online application for getting permission of building
construction. Switching to the online system has helped to reduce the time required for
building approvals and also make the process transparent and accountable.
The online system, which is currently live, checks all new applications for ECBC eligibility and
prompts the applicants to enter the details of the Third Party Assessors in the web form.
Users can upload the supporting technical documents, which are then reviewed by the Chief
City Planner office in Hyderabad. NRDC, ASCI and other partners have worked with the
government and the software developers in establishing the online setup.
Technical Resources and FAQS in GHMC Website
Figure 4: Screenshot highlighting the FAQS section in the GHMC website
The Success in Implementation of the code largely depends on a strong technical support
structure. The Government of Telangana has established an ECBC Technical Cell, comprising
experts from ASCI, IIIT-H, and NRDC. The aim of establishing a technical cell is to quickly
Administrative Staff College of India 5|Page
address queries, especially in the initial stages as more projects start going through the code
compliance process and to provide a support in assessing the first 25 eligible commercial
buildings for ECBC compliance.
In addition to the above, ASCI-NRDC has conducted a number of round table discussions
with Architects and Engineers and, based on their feedback, it has developed a list of
“Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)” which are available on the GHMC website as shown in
the screenshot above. The technical cell will further work on providing recommendations
for streamlining the provisions of the Telangana State ECBC to be even more practical and
simpler while still saving time and energy.
Replicating Hyderabad Model in Other Cities
Clean energy development is a priority for the Indian government. Over a dozen states in
India are at an advanced stage of incorporating the ECBC into the state and local bylaws.
The Hyderabad model is exemplary in actual implementation. The online process provides a
simple, effective and scalable approach to building modern India. With growing focus on
smart cities in India, Hyderabad’s implementation of the code will generate significant
energy savings and lays a strong foundation for the city to set example as the leading energy
efficient city, and inspire other cities in India to follow suit.
Administrative Staff College of India 6|Page
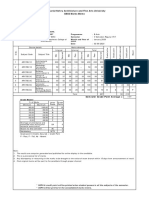
TSECBC Compliance Certificate at Design Stage
Administrative Staff College of India 7|Page
TSECBC Compliance Certificate at Occupancy Stage
Administrative Staff College of India 8|Page
You might also like
- Selling CFLs at Wal-MartDocument16 pagesSelling CFLs at Wal-MartAnsh LakhmaniNo ratings yet
- rfpeGovConsultancy 3479341873Document38 pagesrfpeGovConsultancy 3479341873ennova20060% (1)
- Nottingham Contemporary InformationDocument39 pagesNottingham Contemporary InformationJNo ratings yet
- Estidama Sustainability Specification-Pearl 2Document14 pagesEstidama Sustainability Specification-Pearl 2Modular Design TeamNo ratings yet
- Online Recruitment SystemDocument42 pagesOnline Recruitment SystemTanmay Abhijeet74% (19)
- Project Report of Bharti Airtel Ltd.Document67 pagesProject Report of Bharti Airtel Ltd.SachidanandRaj100% (1)
- Architectural Acoustics Assignment - 3Document7 pagesArchitectural Acoustics Assignment - 3SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Gpg268 Energy Efficient Ventilation in DwellingsDocument20 pagesGpg268 Energy Efficient Ventilation in DwellingsZrceia AzrieNo ratings yet
- Better Future Energy Saving Building Code HyderabadDocument4 pagesBetter Future Energy Saving Building Code HyderabadVamsidhar KavikondalaNo ratings yet
- Krishna Institute OF Engineering &technology: GhaziabadDocument49 pagesKrishna Institute OF Engineering &technology: GhaziabadRahul Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- ECBC - Transformer PDFDocument24 pagesECBC - Transformer PDFSOYAL CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Existing Building Energy Performance: Challenges and Way ForwardDocument3 pagesExisting Building Energy Performance: Challenges and Way ForwardAkNo ratings yet
- Car Rental Project by AbhishekDocument35 pagesCar Rental Project by Abhishekall new moviesNo ratings yet
- National E - Gov PlanDocument17 pagesNational E - Gov PlanShivendu Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- 8 The+Use+of+Construction+Management++ (82-89)Document8 pages8 The+Use+of+Construction+Management++ (82-89)fadhilah santriNo ratings yet
- MeityDocument8 pagesMeitysumeet.parmarNo ratings yet
- Developing An Energy Conservation Building Code Implementation Strategy in IndiaDocument17 pagesDeveloping An Energy Conservation Building Code Implementation Strategy in IndiadenzNo ratings yet
- DPAR (E Gov) STRATEGY PDFDocument8 pagesDPAR (E Gov) STRATEGY PDFakkisantosh7444No ratings yet
- Goods Service Tax (GST) For Super Market Project DocumentationDocument55 pagesGoods Service Tax (GST) For Super Market Project DocumentationVijaya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Central Checkpost ComputerisationDocument84 pagesCentral Checkpost Computerisationadi_xlncNo ratings yet
- 07092015maud RT579Document3 pages07092015maud RT579Raghu RamNo ratings yet
- Krishna Institute of Engineering &technology: GhaziabadDocument45 pagesKrishna Institute of Engineering &technology: GhaziabadalsahariNo ratings yet
- Minor Work April - Jan2012Document18 pagesMinor Work April - Jan2012prateeksri10No ratings yet
- Implementation of ECBCDocument20 pagesImplementation of ECBCSankar SudhakarNo ratings yet
- GST Calculator For Supermarket: A Project Report OnDocument62 pagesGST Calculator For Supermarket: A Project Report OnVijaya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- PR No.14of2023 PDFDocument8 pagesPR No.14of2023 PDFVi BaNo ratings yet
- E-Governance Initiatives in Maharashtra (India) : Problems and ChallengesDocument9 pagesE-Governance Initiatives in Maharashtra (India) : Problems and Challengesnkr2294100% (1)
- Utomo 2019Document12 pagesUtomo 2019Annisa CarinaNo ratings yet
- Punjab State E-Governance Reform Society Directorate of Governance Reforms D241, Sector 74, Phase 8B Industrial Area, Mohali (Punjab)Document10 pagesPunjab State E-Governance Reform Society Directorate of Governance Reforms D241, Sector 74, Phase 8B Industrial Area, Mohali (Punjab)RajniNo ratings yet
- MIS EOI HimachalDocument26 pagesMIS EOI HimachalSatyajit RanaNo ratings yet
- Erection Testing and Commissioning of Transmission Lines & Sub-StationDocument19 pagesErection Testing and Commissioning of Transmission Lines & Sub-Stationarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Odisha PWD CDMS - CSF.User - GuideDocument8 pagesOdisha PWD CDMS - CSF.User - GuideSabyasachi Naik (Zico)No ratings yet
- Project Management Report On Delhi Metro Airport ExpressDocument17 pagesProject Management Report On Delhi Metro Airport ExpressPriyanka Khandelwal100% (1)
- Project Management MiniDocument14 pagesProject Management MiniI section MBA100% (1)
- Indian Institute of Management RanchiDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Management RanchiSrinivas NandikantiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Hi-Tech Park Authority WWW - Bhtpa.gov - BD Annual Report 2019-2020Document26 pagesBangladesh Hi-Tech Park Authority WWW - Bhtpa.gov - BD Annual Report 2019-2020Time to ShareNo ratings yet
- Minor Project 2 Shubham Bahri Bca MDocument78 pagesMinor Project 2 Shubham Bahri Bca MRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3824642Document13 pagesSSRN Id3824642Linh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Heavy InduDocument6 pagesHeavy Indumvnreddy.111No ratings yet
- Vechile Management SystemDocument110 pagesVechile Management SystemVivek Varma0% (1)
- SohamDocument25 pagesSohampatiladityaa09No ratings yet
- Final Project - MergedDocument17 pagesFinal Project - MergedPrince AtulNo ratings yet
- Op - Amp Design Using Pyxis: Bachelor of TechnologyDocument21 pagesOp - Amp Design Using Pyxis: Bachelor of TechnologyRaghav PuriNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice - 1 - 2022-02-15T150726.723Document23 pagesTendernotice - 1 - 2022-02-15T150726.723Monish MNo ratings yet
- Author Final VersionDocument48 pagesAuthor Final VersionGeorge MhinaNo ratings yet
- On "Mont Blanc Writing Instrument"Document19 pagesOn "Mont Blanc Writing Instrument"Bobby SodhiNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Nepal National Building Code Through Automated Building Permit SystemDocument8 pagesImplementation of Nepal National Building Code Through Automated Building Permit SystemMishal LimbuNo ratings yet
- E-Government Maturity ModelDocument10 pagesE-Government Maturity ModelMuhammad NawazNo ratings yet
- PWD Buildings CitizenDocument21 pagesPWD Buildings CitizenpgdyaneshNo ratings yet
- AjeethV EuroPass ResumeDocument4 pagesAjeethV EuroPass ResumeRagyaddy TeslaNo ratings yet
- Abirami R - Internship - ReportDocument26 pagesAbirami R - Internship - Report003Abirami RCSENo ratings yet
- Simple Client Server Inventory Control SystemDocument66 pagesSimple Client Server Inventory Control SystemsomaacyNo ratings yet
- Procurement ManualDocument49 pagesProcurement ManualEmil LeauNo ratings yet
- Harisetiabudi PDFDocument4 pagesHarisetiabudi PDFSyaqila AnyeroNo ratings yet
- FINAL. REPORT CCDocument21 pagesFINAL. REPORT CCvenu pkNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Eis ProjectDocument16 pagesAbhishek Eis ProjectAbhishek TrivediNo ratings yet
- Framework4eGov SolutionsDocument17 pagesFramework4eGov SolutionsPrince BalaNo ratings yet
- Synopsy BCADocument12 pagesSynopsy BCASantosh KandariNo ratings yet
- Egovernance Lessons From Experiences PDFDocument9 pagesEgovernance Lessons From Experiences PDFannaicsdepartmentNo ratings yet
- Citizen CharterDocument48 pagesCitizen Chartersayeed6650% (2)
- NCRTC DGMITDocument4 pagesNCRTC DGMITno solutionsNo ratings yet
- Finance Dep Project IniciativeDocument7 pagesFinance Dep Project IniciativewkNo ratings yet
- Internship With Mini ProjectDocument38 pagesInternship With Mini ProjectJNeer SinghNo ratings yet
- Innovative Infrastructure Financing through Value Capture in IndonesiaFrom EverandInnovative Infrastructure Financing through Value Capture in IndonesiaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidebook for Demand Aggregation: Way Forward for Rooftop Solar in IndiaFrom EverandGuidebook for Demand Aggregation: Way Forward for Rooftop Solar in IndiaNo ratings yet
- Melbourne IssueDocument232 pagesMelbourne IssueSharanyaNo ratings yet
- The 15-Minute City Case StudiesDocument14 pagesThe 15-Minute City Case StudiesSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument17 pagesScanned With CamscannerSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Melbourne IssueDocument10 pagesMelbourne IssueSharanyaNo ratings yet
- 4 15 Minute CitiesDocument36 pages4 15 Minute CitiesSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Literature Study: Cultural CentreDocument11 pagesLiterature Study: Cultural CentreSharanya100% (2)
- Lalala PDFDocument1 pageLalala PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- PDF Cultural ComplexesDocument38 pagesPDF Cultural ComplexesSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Slum DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSlum DevelopmentSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Campus Design Brief 18092020-1Document1 pageCampus Design Brief 18092020-1SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Photograph Y: Assignment-1Document10 pagesPhotograph Y: Assignment-1SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Design Concept of CSCDocument9 pagesDesign Concept of CSCSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Nid CampusDocument8 pagesNid CampusSharanya100% (2)
- Sound: Behavior in Closed SpacesDocument48 pagesSound: Behavior in Closed SpacesSharanya100% (1)
- Acoustics: D.Sharanya Rollno:27 Sec-A Sem-6Document5 pagesAcoustics: D.Sharanya Rollno:27 Sec-A Sem-6SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Plan Ca PDFDocument1 pagePlan Ca PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustics Assignment - 5Document5 pagesArchitectural Acoustics Assignment - 5SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustics Assignment - 6Document7 pagesArchitectural Acoustics Assignment - 6SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Plansssssss PDFDocument1 pagePlansssssss PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Architecture and Fine Arts University CBCS Marks MemoDocument1 pageJawaharlal Nehru Architecture and Fine Arts University CBCS Marks MemoSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings: S.No Sheet Number Title Name Sub-Title Name 3 BHK Villa ResidenceDocument23 pagesWorking Drawings: S.No Sheet Number Title Name Sub-Title Name 3 BHK Villa ResidenceSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Plansssssss PDFDocument1 pagePlansssssss PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageDescriptive StatisticsSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Plan Ca PDFDocument1 pagePlan Ca PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- 2bhk1 PDFDocument1 page2bhk1 PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics (2) 27 PDFDocument5 pagesAcoustics (2) 27 PDFSharanyaNo ratings yet
- CORBUSIER (I)Document53 pagesCORBUSIER (I)SharanyaNo ratings yet
- Lit Two Stage Ts01enDocument12 pagesLit Two Stage Ts01ennino16041973No ratings yet
- IGV-Agile 2019 - ENGDocument6 pagesIGV-Agile 2019 - ENGTom MetNo ratings yet
- BLD Main Eric ChanDocument7 pagesBLD Main Eric Chansellitt ngNo ratings yet
- MyCrest Construction Stage CertificationDocument115 pagesMyCrest Construction Stage CertificationJoanne WongNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco-Oil-Injected Rotary Screw Compressors enDocument16 pagesAtlas Copco-Oil-Injected Rotary Screw Compressors enndakota1987No ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of LPG Plant From Flare Gas For Community Utilization in The Niger Delta, Nigeria.Document14 pagesModeling and Simulation of LPG Plant From Flare Gas For Community Utilization in The Niger Delta, Nigeria.ockiyacliffcNo ratings yet
- Repairs and Maintenance AppendixDocument27 pagesRepairs and Maintenance AppendixDhurai MuthuNo ratings yet
- Role of Education in Energy ConservationDocument4 pagesRole of Education in Energy ConservationrvnesariNo ratings yet
- 772 PUB Report Wp12Document64 pages772 PUB Report Wp12Bushra AsifNo ratings yet
- Flexible Future For Combined Cycle.Document6 pagesFlexible Future For Combined Cycle.Uhrin Imre100% (1)
- CNBC SE TheNewEnergyWorld FINALREPORTDocument28 pagesCNBC SE TheNewEnergyWorld FINALREPORTkriteriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Sustainable Construction Techniques: What Is Green Building?Document9 pagesChapter 7: Sustainable Construction Techniques: What Is Green Building?Yu HanaNo ratings yet
- DOE22Vol4 LibrariesDocument251 pagesDOE22Vol4 LibrariesMario MendozaNo ratings yet
- Jody Howard Director, Social Responsibility Caterpillar, IncDocument17 pagesJody Howard Director, Social Responsibility Caterpillar, IncJanak ValakiNo ratings yet
- Part C - GCED and Global WamingDocument4 pagesPart C - GCED and Global WamingIrisNo ratings yet
- Journal of Sustainable TourismDocument16 pagesJournal of Sustainable TourismJane DDNo ratings yet
- Iso Samrt CitiesDocument9 pagesIso Samrt CitiesAntónio Ferreira100% (1)
- Steel Asia - Company Case StudyDocument3 pagesSteel Asia - Company Case StudyRaymond VillegasNo ratings yet
- Speech For Energy ConservationDocument8 pagesSpeech For Energy Conservationchamp1792No ratings yet
- Green New Deal For Public Housing ActDocument61 pagesGreen New Deal For Public Housing ActNick PopeNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gas and Energy Efficiency Report - BrownDocument32 pagesGreenhouse Gas and Energy Efficiency Report - BrownAnyanwu EugeneNo ratings yet
- Vermont City Electric - IcDocument14 pagesVermont City Electric - Icashutosh bhaikNo ratings yet
- ST - Energy Efficiency Initiatives Overview by Energy CommissionDocument47 pagesST - Energy Efficiency Initiatives Overview by Energy CommissionFizz FirdausNo ratings yet
- LEED v4.1 Cities and Communities Plan and Design GuideDocument107 pagesLEED v4.1 Cities and Communities Plan and Design GuideAshutoshNo ratings yet
- 0354-98361800278F Dolomite Sintering in Shaft Kiln PDFDocument13 pages0354-98361800278F Dolomite Sintering in Shaft Kiln PDFtaghdirimNo ratings yet
- Ameresco - Final ReportDocument15 pagesAmeresco - Final ReportRobert FellingerNo ratings yet