Professional Documents
Culture Documents
72 - Skin Cancer
72 - Skin Cancer
Uploaded by
Rica Alyssa PepitoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Breast CA Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast CA Concept MapDianne Kate CadioganNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Vitreoretinal DegenerationsDocument11 pagesHereditary Vitreoretinal DegenerationsImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hull M. Medical English Clear and Simple WordDocument459 pagesHull M. Medical English Clear and Simple WordSaira88% (17)
- Oral Pathology Dent1411Document7 pagesOral Pathology Dent1411api-663458841No ratings yet
- Sarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasDocument3 pagesSarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasCharlie65129No ratings yet
- OB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFDocument1 pageOB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFrpascua123No ratings yet
- Jam Mikka G. Rodriguez (Cancer of The Male Reproductive 1)Document12 pagesJam Mikka G. Rodriguez (Cancer of The Male Reproductive 1)Dinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Surgery Subspecialty - Skin CancerDocument2 pagesSurgery Subspecialty - Skin CancerJonathan AiresNo ratings yet
- " Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyDocument10 pages" Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- URO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractDocument8 pagesURO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractHa Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Female NeoplasiaDocument4 pagesFemale NeoplasiaLily AmbroseNo ratings yet
- C13. Vaginal, Vulvar & CervicalDocument4 pagesC13. Vaginal, Vulvar & Cervicalhari dharshanNo ratings yet
- Etiopathogenesis: Investigation inDocument1 pageEtiopathogenesis: Investigation insnehasishk51No ratings yet
- ActaDV 100 11 5753Document9 pagesActaDV 100 11 5753NandaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalDocument4 pagesNeoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalDocument4 pagesNeoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- belindabombei,+MayJune20 NonmelanomaDocument5 pagesbelindabombei,+MayJune20 Nonmelanoma23712047No ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma PDFDocument3 pagesOsteosarcoma PDFkc andrea torresNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumorsDocument16 pagesSalivary Gland Tumorsmaria del mar RoblesNo ratings yet
- Applying Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in The Clinical Management of SCLCDocument67 pagesApplying Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in The Clinical Management of SCLCYasar HammorNo ratings yet
- Lung Ca Small Bx2 PDFDocument4 pagesLung Ca Small Bx2 PDFJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer: No Conflicts of Interest To DiscloseDocument44 pagesSkin Cancer: No Conflicts of Interest To DiscloseKristopher OwensNo ratings yet
- Tumors Algorithm MassoudDocument3 pagesTumors Algorithm MassoudKaramanyNo ratings yet
- Tumors Algorithm MassoudDocument3 pagesTumors Algorithm MassoudKaramanyNo ratings yet
- Notes DermaDocument17 pagesNotes DermaCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Didactics - ManzanoDocument49 pagesBreast Cancer Didactics - ManzanoJoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Onco ImDocument2 pagesOnco ImAlexandra BascoNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Cutaneous Melanoma: Atypical Variants and PresentationsDocument6 pagesCutaneous Melanoma: Atypical Variants and PresentationsMoet Moet KhineNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer: Dedicated To: Carlos Garcia MD Dermatology at OuhscDocument44 pagesSkin Cancer: Dedicated To: Carlos Garcia MD Dermatology at OuhscabrarashrafNo ratings yet
- Group 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaDocument5 pagesGroup 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaZazaNo ratings yet
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- Malignant Skin TumorsDocument18 pagesMalignant Skin TumorsGhaiidaa khhNo ratings yet
- Lungs Benign and MalignantDocument7 pagesLungs Benign and MalignantNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Radiotherapy in Cancer Management Adji 25 Juni 2023 HIMPONIDocument28 pagesRadiotherapy in Cancer Management Adji 25 Juni 2023 HIMPONInurul andriasariNo ratings yet
- Recent Modalities in The Management of Malignant Melanoma: Mohamed Mohamed AlhefnyDocument36 pagesRecent Modalities in The Management of Malignant Melanoma: Mohamed Mohamed AlhefnyHana SaadNo ratings yet
- Basic Plastic + Skin CancerDocument29 pagesBasic Plastic + Skin CancermitaNo ratings yet
- General Stages and TX of Malignant Cells? Naming TumorsDocument11 pagesGeneral Stages and TX of Malignant Cells? Naming TumorsRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Tumor MarkerDocument4 pagesTumor Markerkimmynemil80No ratings yet
- Hybrid Genetic Algorithm - Artificial Neural Network Classifier For Skin Cancer DetectionDocument6 pagesHybrid Genetic Algorithm - Artificial Neural Network Classifier For Skin Cancer DetectionMd. Sazzad Mia 191-15-2503No ratings yet
- Djohan2010bening&malignan TumorDocument13 pagesDjohan2010bening&malignan Tumorkiki0% (1)
- Veterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookDocument6 pagesVeterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookMacarena Beatriz Piña ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Skin LesionsDocument26 pagesMalignant Skin LesionsdinahzrNo ratings yet
- Curr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal CarcinomasDocument14 pagesCurr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal Carcinomasdarmayanti ibnuNo ratings yet
- Kegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksDocument57 pagesKegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksChristian HarnatNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument83 pagesCellular AberrationA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet
- Skin Case 1 Kunwor, BishalDocument12 pagesSkin Case 1 Kunwor, BishalBishal JB KunworNo ratings yet
- 23 SkinDocument11 pages23 SkinBalaji DNo ratings yet
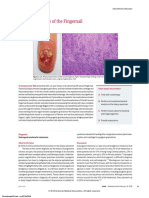
- Ulcerated Nodule of The FingernailDocument2 pagesUlcerated Nodule of The FingernailMr. LNo ratings yet
- Schwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EditionDocument13 pagesSchwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EditionKobe Brian Franco PeterosNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Malignant Melanoma: A Case StudyDocument3 pagesMetastatic Malignant Melanoma: A Case StudyDyerik LilingNo ratings yet
- Pedersen Babu LymphaticsDocument10 pagesPedersen Babu Lymphaticsrandy22002No ratings yet
- Nevo Congenito ArtigoDocument6 pagesNevo Congenito ArtigomarinaNo ratings yet
- Melanoma Belay Z July, 6 2005Document20 pagesMelanoma Belay Z July, 6 2005Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Skin and Endo 2022Document10 pagesSkin and Endo 2022Sure NavyasriNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalMelaniMomonNo ratings yet
- An Overview of MelanomaDocument22 pagesAn Overview of MelanomaSilviuNo ratings yet
- Managing Malignant Melanoma: Learning Objectives: After Reading This Article, The Participant Should Be AbleDocument15 pagesManaging Malignant Melanoma: Learning Objectives: After Reading This Article, The Participant Should Be AbleDian Ariska SNo ratings yet
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- 409 FullDocument11 pages409 FullMario QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Adult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDDocument11 pagesAdult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDJuan Diego Martinez LemusNo ratings yet
- 69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentDocument1 page69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 70 - Infections in Patients With CancerDocument1 page70 - Infections in Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersDocument1 page66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- (Concept Map) Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument1 page(Concept Map) Urinary Tract InfectionsRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 65 - Approach To Patients With CancerDocument1 page65 - Approach To Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Urodynamics For Urogynecologists Vignoli2018Document249 pagesUrodynamics For Urogynecologists Vignoli2018Griselda Pérez Alcántara100% (1)
- Antimanic DrugsDocument30 pagesAntimanic DrugsTJ Ng100% (4)
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - HendriawanDocument46 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - HendriawanRisky SidinNo ratings yet
- 12 2017 Vitamin D in European Children-Statement From The EuropeaDocument3 pages12 2017 Vitamin D in European Children-Statement From The Europeasheyla alegreNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingElliot TecamachaltziNo ratings yet
- Letter Head School Memo Brigada EskwelaDocument13 pagesLetter Head School Memo Brigada EskwelaJENEFER REYESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Workbook AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 21 Workbook Answersguido pirelaNo ratings yet
- Kovachev 2014Document7 pagesKovachev 2014habibNo ratings yet
- 8ac - Balanced Diet 2Document17 pages8ac - Balanced Diet 2trisNo ratings yet
- JHP 9 112Document9 pagesJHP 9 112drugdrugNo ratings yet
- Cardiotonic Medications: Drugs Used To For Patients Experiencing Heart FailureDocument28 pagesCardiotonic Medications: Drugs Used To For Patients Experiencing Heart FailureMoxie MacadoNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-509669503No ratings yet
- FINAL Snake Bite Case PresDocument48 pagesFINAL Snake Bite Case PresMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument43 pagesExamFoxtrot NursingNo ratings yet
- CHN Lec - Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeDocument6 pagesCHN Lec - Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeArevalo, Denisse S.No ratings yet
- LungtengB3L1Reading and Voc (The Day I Broke the Rules) 1120816單字及課本句型答案Document88 pagesLungtengB3L1Reading and Voc (The Day I Broke the Rules) 1120816單字及課本句型答案雷佳惠No ratings yet
- 3 - Epidemiology: J 1 6 0 D Gih WitnDocument1 page3 - Epidemiology: J 1 6 0 D Gih WitnIkaKusumaWardhaniNo ratings yet
- MLC Management in Emergency DepartmentDocument23 pagesMLC Management in Emergency Departmentsandeep cNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentDocument2 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Stages of PregnancyDocument14 pagesStages of PregnancyRovilyn DizonNo ratings yet
- BEHA001: Behavioral and Social Sciences Joshua BenzonDocument44 pagesBEHA001: Behavioral and Social Sciences Joshua BenzonPeter Jay CorrosNo ratings yet
- 02 - Colilert-Procedure-EsDocument7 pages02 - Colilert-Procedure-EsRoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: Done By-Fatema Burhan Ravat Dtmu 4Th Year January 2020Document27 pagesNeurologic Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: Done By-Fatema Burhan Ravat Dtmu 4Th Year January 2020Fatema RavatNo ratings yet
- From A Tick Bite To Chronic Lyme DiseaseDocument50 pagesFrom A Tick Bite To Chronic Lyme DiseaseMatt MackeyNo ratings yet
- Health Management Information SystemDocument6 pagesHealth Management Information SystemNimco gureeyNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefDocument50 pagesPractical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefMateo LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Angiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DDocument9 pagesAngiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DAkazukin AineNo ratings yet
- Eyecheck Announces FDA IND Clearance of STRI Formula, The First-Ever Food-Based, Combination Product in The STRI Phase 2 Clinical Trial For COVID-19 SymptomsDocument3 pagesEyecheck Announces FDA IND Clearance of STRI Formula, The First-Ever Food-Based, Combination Product in The STRI Phase 2 Clinical Trial For COVID-19 SymptomsPR.comNo ratings yet
72 - Skin Cancer
72 - Skin Cancer
Uploaded by
Rica Alyssa PepitoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
72 - Skin Cancer
72 - Skin Cancer
Uploaded by
Rica Alyssa PepitoCopyright:
Available Formats
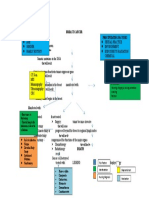
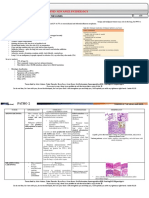
PEPITO, RICA ALYSSA M.
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Source: Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 20 th Edition
Cancer of the Skin (Ch. 72)
Nonmelanoma Skin
Melanoma
Cancer (NMSC)
Prevention and Clinical Prognostic Basal cell Squamous cell
Risk Factors Diagnostics SLNB Treatment
early detection classifications factors carcinoma carcinoma
Sunscreen
neural crest Best predictor of
Presence of Nevi (atleast SPF 30), Excisional biopsy Superficial
derived, usually For tumors >1 metastatic risk = Premalignant
(>40 melanocytic protective with 1- to 3-mm spreading M, Stage 1/2: Wide Subtypes Treatment Prevention Treatment Prevention
affects white- mm thick or Breslow Significant cause p53 and N-RAS forms
nevi; congenital clothing, tanning margins Lentigo maligna local excision,
skinned, M>F, thickness is UV radiation, electrodesiccatio active commonly
melanocytic nevi cessation (below) M, Acral SLNB
late 50s Monitoring of Incisional biopsy hedgehog n and curettage surveillance, affected; dotted
- small (≤1.5 cm)/ for large lesions lentiginous M: pathway, PTCH1 Superficial BCC - (ED&C) - most Synthetic Keratoacanthom
suspicious Anatomic site of or coiled vessels
medium (1.5–20 or lesions on the radial growth mutation, slowly erythematous common for retinoid, topical a - low grade,
lesions (ABCDE): Melanomas primary lesion are a hallmark of
cm)/giant (>20 face, hands, and enlarging, locally scaling plaques superficial, 5-FU, imiquimod, fast active
asymmetry, 0.76–1.0 mm (favorable: SCC when Surgery and/or
cm) feet invasive, higher on trunks and minimally ingenol surveillance,
border thick, with high- forearm and leg Stage 3: Surgery, viewed through a RT (LN
risk in the face, proximal Wide local
invasive mebutate dermatoscope metastasis), synthetic
irregularity, color risk features (excluding the Immunotherapy,
Fluorescence in Nodular M: ears, or scalp extremities excision - for Actinic retinoid, topical
variegation, (ulceration, high feet); BCG, RT, IFN-a2b, Cisplatin, 5-FU,
situ hybridization vertical growth; invasive, keratoses/cheiliti 5-FU, imiquimod,
Personal and diameter >6 mm, mitotic index, or unfavorable: Imiquimod, Cetuximab
(FISH) early metastasis aggressive s - premalignant (advanced ingenol
Family History evolving (any lymphovascular scalp, hands, Talimogene MMStumors
(best for
Nodular BCC - disease) mebutate
change in size, invasion); wide feet, and mucous tissue
shape, color, or Comparative excision alone is membranes) pearly nodule,
preservation), Bowen's disease -
elevation or new genome the usual rolled borders,
Vismodegib/Soni intraepithelial
Light skin symptoms such hybridization definitive Desmoplastic M: central crust
Stage 4: degib (metastatic form
as bleeding, (CGH) therapy fibrotic response,
Age Metastasectomy, or advanced BCC
itching, and Labs - CBC, neural invasion, that recurred)
clinically Ipilimumab,
crusting) Complete local recurrence
negative lymph Nivolumab, Pigmented BCC -
Sun exposure metabolic panel, Pembrolizumab,
nodes - SLNB presence of
LDH Vemurafenib, melanin
Dabrafenib,
Trametinib,
Imaging - CT, PET Cobitenib,
Older age Talimogene, Morpheaform
Chemotherapy (fibrosing),
infiltrative, and
micronodular
BCC: most
Genetic
invasive,
Susceptibility
potentially
(CDKN2A germ
aggressive
line or MC1R
gene mutations)
You might also like
- Breast CA Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast CA Concept MapDianne Kate CadioganNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Vitreoretinal DegenerationsDocument11 pagesHereditary Vitreoretinal DegenerationsImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hull M. Medical English Clear and Simple WordDocument459 pagesHull M. Medical English Clear and Simple WordSaira88% (17)
- Oral Pathology Dent1411Document7 pagesOral Pathology Dent1411api-663458841No ratings yet
- Sarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasDocument3 pagesSarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasCharlie65129No ratings yet
- OB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFDocument1 pageOB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFrpascua123No ratings yet
- Jam Mikka G. Rodriguez (Cancer of The Male Reproductive 1)Document12 pagesJam Mikka G. Rodriguez (Cancer of The Male Reproductive 1)Dinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Surgery Subspecialty - Skin CancerDocument2 pagesSurgery Subspecialty - Skin CancerJonathan AiresNo ratings yet
- " Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyDocument10 pages" Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- URO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractDocument8 pagesURO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractHa Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Female NeoplasiaDocument4 pagesFemale NeoplasiaLily AmbroseNo ratings yet
- C13. Vaginal, Vulvar & CervicalDocument4 pagesC13. Vaginal, Vulvar & Cervicalhari dharshanNo ratings yet
- Etiopathogenesis: Investigation inDocument1 pageEtiopathogenesis: Investigation insnehasishk51No ratings yet
- ActaDV 100 11 5753Document9 pagesActaDV 100 11 5753NandaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalDocument4 pagesNeoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalDocument4 pagesNeoplasms of Lung, Pleura, and Mediastinum Classification Disease Etiology Epidemiology Pathology ClinicalMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- belindabombei,+MayJune20 NonmelanomaDocument5 pagesbelindabombei,+MayJune20 Nonmelanoma23712047No ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma PDFDocument3 pagesOsteosarcoma PDFkc andrea torresNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumorsDocument16 pagesSalivary Gland Tumorsmaria del mar RoblesNo ratings yet
- Applying Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in The Clinical Management of SCLCDocument67 pagesApplying Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in The Clinical Management of SCLCYasar HammorNo ratings yet
- Lung Ca Small Bx2 PDFDocument4 pagesLung Ca Small Bx2 PDFJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer: No Conflicts of Interest To DiscloseDocument44 pagesSkin Cancer: No Conflicts of Interest To DiscloseKristopher OwensNo ratings yet
- Tumors Algorithm MassoudDocument3 pagesTumors Algorithm MassoudKaramanyNo ratings yet
- Tumors Algorithm MassoudDocument3 pagesTumors Algorithm MassoudKaramanyNo ratings yet
- Notes DermaDocument17 pagesNotes DermaCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Didactics - ManzanoDocument49 pagesBreast Cancer Didactics - ManzanoJoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Onco ImDocument2 pagesOnco ImAlexandra BascoNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Cutaneous Melanoma: Atypical Variants and PresentationsDocument6 pagesCutaneous Melanoma: Atypical Variants and PresentationsMoet Moet KhineNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer: Dedicated To: Carlos Garcia MD Dermatology at OuhscDocument44 pagesSkin Cancer: Dedicated To: Carlos Garcia MD Dermatology at OuhscabrarashrafNo ratings yet
- Group 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaDocument5 pagesGroup 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaZazaNo ratings yet
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- Malignant Skin TumorsDocument18 pagesMalignant Skin TumorsGhaiidaa khhNo ratings yet
- Lungs Benign and MalignantDocument7 pagesLungs Benign and MalignantNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Radiotherapy in Cancer Management Adji 25 Juni 2023 HIMPONIDocument28 pagesRadiotherapy in Cancer Management Adji 25 Juni 2023 HIMPONInurul andriasariNo ratings yet
- Recent Modalities in The Management of Malignant Melanoma: Mohamed Mohamed AlhefnyDocument36 pagesRecent Modalities in The Management of Malignant Melanoma: Mohamed Mohamed AlhefnyHana SaadNo ratings yet
- Basic Plastic + Skin CancerDocument29 pagesBasic Plastic + Skin CancermitaNo ratings yet
- General Stages and TX of Malignant Cells? Naming TumorsDocument11 pagesGeneral Stages and TX of Malignant Cells? Naming TumorsRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Tumor MarkerDocument4 pagesTumor Markerkimmynemil80No ratings yet
- Hybrid Genetic Algorithm - Artificial Neural Network Classifier For Skin Cancer DetectionDocument6 pagesHybrid Genetic Algorithm - Artificial Neural Network Classifier For Skin Cancer DetectionMd. Sazzad Mia 191-15-2503No ratings yet
- Djohan2010bening&malignan TumorDocument13 pagesDjohan2010bening&malignan Tumorkiki0% (1)
- Veterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookDocument6 pagesVeterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookMacarena Beatriz Piña ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Skin LesionsDocument26 pagesMalignant Skin LesionsdinahzrNo ratings yet
- Curr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal CarcinomasDocument14 pagesCurr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal Carcinomasdarmayanti ibnuNo ratings yet
- Kegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksDocument57 pagesKegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksChristian HarnatNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument83 pagesCellular AberrationA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet
- Skin Case 1 Kunwor, BishalDocument12 pagesSkin Case 1 Kunwor, BishalBishal JB KunworNo ratings yet
- 23 SkinDocument11 pages23 SkinBalaji DNo ratings yet
- Ulcerated Nodule of The FingernailDocument2 pagesUlcerated Nodule of The FingernailMr. LNo ratings yet
- Schwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EditionDocument13 pagesSchwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EditionKobe Brian Franco PeterosNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Malignant Melanoma: A Case StudyDocument3 pagesMetastatic Malignant Melanoma: A Case StudyDyerik LilingNo ratings yet
- Pedersen Babu LymphaticsDocument10 pagesPedersen Babu Lymphaticsrandy22002No ratings yet
- Nevo Congenito ArtigoDocument6 pagesNevo Congenito ArtigomarinaNo ratings yet
- Melanoma Belay Z July, 6 2005Document20 pagesMelanoma Belay Z July, 6 2005Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Skin and Endo 2022Document10 pagesSkin and Endo 2022Sure NavyasriNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalMelaniMomonNo ratings yet
- An Overview of MelanomaDocument22 pagesAn Overview of MelanomaSilviuNo ratings yet
- Managing Malignant Melanoma: Learning Objectives: After Reading This Article, The Participant Should Be AbleDocument15 pagesManaging Malignant Melanoma: Learning Objectives: After Reading This Article, The Participant Should Be AbleDian Ariska SNo ratings yet
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- 409 FullDocument11 pages409 FullMario QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Adult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDDocument11 pagesAdult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDJuan Diego Martinez LemusNo ratings yet
- 69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentDocument1 page69 - Principles of Cancer TreatmentRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 70 - Infections in Patients With CancerDocument1 page70 - Infections in Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersDocument1 page66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- (Concept Map) Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument1 page(Concept Map) Urinary Tract InfectionsRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- 65 - Approach To Patients With CancerDocument1 page65 - Approach To Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Urodynamics For Urogynecologists Vignoli2018Document249 pagesUrodynamics For Urogynecologists Vignoli2018Griselda Pérez Alcántara100% (1)
- Antimanic DrugsDocument30 pagesAntimanic DrugsTJ Ng100% (4)
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - HendriawanDocument46 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - HendriawanRisky SidinNo ratings yet
- 12 2017 Vitamin D in European Children-Statement From The EuropeaDocument3 pages12 2017 Vitamin D in European Children-Statement From The Europeasheyla alegreNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingElliot TecamachaltziNo ratings yet
- Letter Head School Memo Brigada EskwelaDocument13 pagesLetter Head School Memo Brigada EskwelaJENEFER REYESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Workbook AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 21 Workbook Answersguido pirelaNo ratings yet
- Kovachev 2014Document7 pagesKovachev 2014habibNo ratings yet
- 8ac - Balanced Diet 2Document17 pages8ac - Balanced Diet 2trisNo ratings yet
- JHP 9 112Document9 pagesJHP 9 112drugdrugNo ratings yet
- Cardiotonic Medications: Drugs Used To For Patients Experiencing Heart FailureDocument28 pagesCardiotonic Medications: Drugs Used To For Patients Experiencing Heart FailureMoxie MacadoNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-509669503No ratings yet
- FINAL Snake Bite Case PresDocument48 pagesFINAL Snake Bite Case PresMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument43 pagesExamFoxtrot NursingNo ratings yet
- CHN Lec - Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeDocument6 pagesCHN Lec - Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeArevalo, Denisse S.No ratings yet
- LungtengB3L1Reading and Voc (The Day I Broke the Rules) 1120816單字及課本句型答案Document88 pagesLungtengB3L1Reading and Voc (The Day I Broke the Rules) 1120816單字及課本句型答案雷佳惠No ratings yet
- 3 - Epidemiology: J 1 6 0 D Gih WitnDocument1 page3 - Epidemiology: J 1 6 0 D Gih WitnIkaKusumaWardhaniNo ratings yet
- MLC Management in Emergency DepartmentDocument23 pagesMLC Management in Emergency Departmentsandeep cNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentDocument2 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Stages of PregnancyDocument14 pagesStages of PregnancyRovilyn DizonNo ratings yet
- BEHA001: Behavioral and Social Sciences Joshua BenzonDocument44 pagesBEHA001: Behavioral and Social Sciences Joshua BenzonPeter Jay CorrosNo ratings yet
- 02 - Colilert-Procedure-EsDocument7 pages02 - Colilert-Procedure-EsRoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: Done By-Fatema Burhan Ravat Dtmu 4Th Year January 2020Document27 pagesNeurologic Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: Done By-Fatema Burhan Ravat Dtmu 4Th Year January 2020Fatema RavatNo ratings yet
- From A Tick Bite To Chronic Lyme DiseaseDocument50 pagesFrom A Tick Bite To Chronic Lyme DiseaseMatt MackeyNo ratings yet
- Health Management Information SystemDocument6 pagesHealth Management Information SystemNimco gureeyNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefDocument50 pagesPractical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefMateo LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Angiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DDocument9 pagesAngiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DAkazukin AineNo ratings yet
- Eyecheck Announces FDA IND Clearance of STRI Formula, The First-Ever Food-Based, Combination Product in The STRI Phase 2 Clinical Trial For COVID-19 SymptomsDocument3 pagesEyecheck Announces FDA IND Clearance of STRI Formula, The First-Ever Food-Based, Combination Product in The STRI Phase 2 Clinical Trial For COVID-19 SymptomsPR.comNo ratings yet