Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Why Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1
Why Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1
Uploaded by
api-521773978Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Why Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1
Why Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1
Uploaded by
api-521773978Copyright:
Available Formats
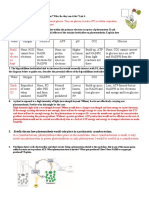
Why are cells so small?
Goal: Explain why cells are microscopically small using the surface area to volume ratio.
Background: Each lab table has a tray with 3 different size agar cubes that will represent cells of different
sizes. Agar is simply a Jell-O like substance that dissolves in water when heated up and solidifies when it cools
back down (we will use a nutrient agar to culture bacteria in lab 6).
These particular agar cubes also had some phenolphthalein mixed in while they still liquid. Phenolphthalein is
an indicator chemical that detects the presence of acids and bases (chemical is a clear color in acidic / neutral
pH and pink in basic pH).
The different agar cubes have already been pre-soaked in a dilute base solution (0.1 M sodium hydroxide or
NaOH). Thus, the cubes should be fully pink inside (the base has already diffused into all parts of the cube).
Your group will eventually place these pink cubes into an acidic solution (0.1 M hydrochloric acid or HCl). As
the acid diffuses in, it will neutralize the base and turn that part of the cube clear again.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=163&v=7zds4RfBx9M&feature=emb_title
Look at the video and answer the question:
Discussion:
1) Which of the cubes showed the most diffusion throughout its “cell”? Explain your results.
The smallest cube showed the most diffusion throughout its cell because it turned clear the fastest. The
indicators are already pink since they indicate a basic solution, and they should turn clear in the acidic solution.
Diffusion occurs that allows the acidic solution to turn clear, and the cube that turned clear faster would have
the faster diffusion.
2) What cell structure does the surface area of the agar cube represent in this modeling activity (hint: it is letting
the HCl “nutrients” in, every cell has this structure)? What does the volume inside the cube broadly represent?
Explain two advantages to having membrane bound organelle structure.
The surface area represents the cellular membrane, and the volume represents the things inside the cell. Having
membrane bound organelle structures would increase the surface area of the cell and increase diffusion rates
because the membranes of the organelle increase surface area and surface area increases diffusion rates.
Membrane bound organelle structures also regulate what comes in and out of the organelle and cell because the
membranes are selective and can control what enters and leaves.
3) Explain why cells are microscopically small in general.
In general, cells are microscopically small to maintain the surface area to volume ratio. Increasing the size of
cells would increase the volume while the surface area does not increase much, causing the cell to be inefficient
and slow in diffusion. In order to maintain metabolism, cells are small in size to match the volume to the surface
area so the cells are effective.
4) There are two ways to maximize the SA / V ratio – either ___increase___ surface area, and / or
____decrease____ volume. What would be the ideal shape for a large cell and as efficient as possible?
The large cell would need to be thin to be as efficient as possible.
You might also like
- Do Grasshoppers Sweat Note SheetDocument3 pagesDo Grasshoppers Sweat Note Sheetapi-521773978100% (4)
- POGIL Cell Size-KEYDocument5 pagesPOGIL Cell Size-KEYKali Warnke100% (1)
- Investigating The Need For Chlorophyll Igcse BiologyDocument13 pagesInvestigating The Need For Chlorophyll Igcse BiologyAminah ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Protein Folding Virtual Activity 1Document5 pagesProtein Folding Virtual Activity 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Study Guide Questions StudentDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Questions Studentapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Science Fair Research Report TEMPLATEDocument9 pagesScience Fair Research Report TEMPLATEAli BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Population DynamicsDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Science: Population DynamicsJohn-Paul Mollineaux100% (1)
- Cellgrow 10 AnsDocument6 pagesCellgrow 10 Ansprofesor_science100% (3)
- Bio 20 - Unit C - Unit PlanDocument21 pagesBio 20 - Unit C - Unit Planapi-199149636No ratings yet
- Biology 20 Unit A TableDocument4 pagesBiology 20 Unit A Tableapi-236289588No ratings yet
- Albino Seed ExperimentDocument9 pagesAlbino Seed ExperimentoriginalclutchNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan Using SIOP ModelDocument4 pagesSample Lesson Plan Using SIOP ModelTess EnglisNo ratings yet
- Why Are Cells So Small MyDocument2 pagesWhy Are Cells So Small Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Updated Chapter 5 Macromlecules HW 1Document4 pagesUpdated Chapter 5 Macromlecules HW 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Nutrition Label Ap ProjectDocument5 pagesNutrition Label Ap Projectapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Toward A Theory of DeceptionDocument37 pagesToward A Theory of DeceptionThe Angry ManNo ratings yet
- Kobaian - English DictionaryDocument3 pagesKobaian - English Dictionarysabbao100% (1)
- SM CH PDFDocument18 pagesSM CH PDFHector NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Why Are Cells So Small Virtual LabDocument1 pageWhy Are Cells So Small Virtual Labapi-522789883No ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis ExperimentDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis ExperimentstjustinsNo ratings yet
- Ib-Course-Planner - Yr 11 and 12Document12 pagesIb-Course-Planner - Yr 11 and 12abdullahiosman753No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusionDocument1 pageVenn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusioncolacastellNo ratings yet
- 1 Levels of Bio Organization, Cell Theory, Cell PartsDocument15 pages1 Levels of Bio Organization, Cell Theory, Cell PartsHunzala Rasheed AlamNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument21 pagesSCIENCEAbello BadayosNo ratings yet
- Biology 20 Long Range Plans Grid FormatDocument5 pagesBiology 20 Long Range Plans Grid Formatapi-427321002No ratings yet
- 5th Grade Lesson Plan: The Cell: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument13 pages5th Grade Lesson Plan: The Cell: The Building Blocks of LifeCherry Mae B. CorriaNo ratings yet
- Gummy Bear Lab 2Document4 pagesGummy Bear Lab 2api-233187566No ratings yet
- CellTransportMatchingWorksheetforRevieworAssessment 1Document12 pagesCellTransportMatchingWorksheetforRevieworAssessment 1Diana MoyNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- CloningDocument6 pagesCloningkikkabuttigieg1466No ratings yet
- Plant Science NotesDocument14 pagesPlant Science NotesMerve ÖzkayaNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Cell TransportDocument3 pages7.3 Cell TransportSafa-99No ratings yet
- 5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesDocument11 pages5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- 4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsDocument12 pages4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsNayani Snigdha0% (1)
- Scientific Method and Experimental DesignDocument40 pagesScientific Method and Experimental Designsheila may valiao-de asisNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Science Lesson Planapi-547284812No ratings yet
- Population Dynamics Research Project Introduction PlanDocument2 pagesPopulation Dynamics Research Project Introduction Planapi-346185380100% (1)
- Grade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesGrade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesCharlesNo ratings yet
- Unit Assessment Plan - Biology 20 Unit BDocument9 pagesUnit Assessment Plan - Biology 20 Unit Bapi-545998611No ratings yet
- Butterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesButterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanPeter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Genotype Phenotype WorksheetDocument3 pagesGenotype Phenotype WorksheetJohn G Villar100% (1)
- Sbi4u Population Dynamics - Part IVDocument4 pagesSbi4u Population Dynamics - Part IVmarNo ratings yet
- Cell DifferentiationDocument26 pagesCell DifferentiationQusai Haimone100% (1)
- 3 - IB Biology Required Practical 3 - Enzymes - IBDP - Complete Experiment GuideDocument13 pages3 - IB Biology Required Practical 3 - Enzymes - IBDP - Complete Experiment GuidemelindahofmannNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument94 pagesChapter 4: Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesDigital Unit Plan Templateapi-324405732No ratings yet
- Test 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisDocument3 pagesTest 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisYan MLNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Quiz + MarkschemeDocument3 pagesMeiosis Quiz + MarkschemeMarie CNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Week 6Document71 pagesSci 9 Week 6Yael Ellie SumandiNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Cells and Micro k5 CellDocument7 pagesUnit Plan Cells and Micro k5 Cellapi-371640211No ratings yet
- Pysiology of Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesPysiology of Digestive SystemSamreen SammarNo ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson Plan Grid: Name Grade (S) Subject Unit Week of To Anchorin G Activity For Lesson Element M T W R FDocument3 pagesWeekly Lesson Plan Grid: Name Grade (S) Subject Unit Week of To Anchorin G Activity For Lesson Element M T W R Fthong dinhNo ratings yet
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 pagesCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Formative Assessment Biology BookDocument1 page2.1 Formative Assessment Biology Bookabdullah adNo ratings yet
- Community Service ReflectionDocument1 pageCommunity Service Reflectionapi-479453127No ratings yet
- Egg Osmosis LabDocument4 pagesEgg Osmosis Labapi-371081506No ratings yet
- HAP 2 6 Unit Plan TissuesDocument12 pagesHAP 2 6 Unit Plan TissuesFranchesca BeningoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Tos Science 10Document2 pages2020 Tos Science 10Marvin ObraNo ratings yet
- Diffusion LabDocument8 pagesDiffusion LabGioVanna GVNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate Virtual LabDocument5 pagesReaction Rate Virtual LabRemi OkunlolaNo ratings yet
- Las Sci 10 Melc 3 Week-1-3-SummativeDocument5 pagesLas Sci 10 Melc 3 Week-1-3-SummativeSamad Recca T. NatividadNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Reading GuideDocument13 pagesCH 6 Reading GuideKapil NathanNo ratings yet
- Microscope Homework Assignment / Study GuideDocument6 pagesMicroscope Homework Assignment / Study GuideJavid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Student Guide To Vce Unit 1 BiologyDocument8 pagesStudent Guide To Vce Unit 1 Biologyapi-348068677No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AP BioDocument2 pagesChapter 7 AP Biomadeleine867% (3)
- Why Are Cells So Small Virtual LabDocument1 pageWhy Are Cells So Small Virtual Labapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Reviewing Mitosis Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesReviewing Mitosis Discussion Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Inihibitors ReviewDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Inihibitors Reviewapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument4 pagesFeedback Mechanismapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Model Two Show 1 Signaling PathwaysDocument1 pageModel Two Show 1 Signaling Pathwaysapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cell Transport HWDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Cell Transport HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Organism Energetics ReviewDocument2 pagesOrganism Energetics Reviewapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Ws 1Document3 pagesCell Organelle Ws 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-521773978No ratings yet
- HW Proteins Enzymes 1Document2 pagesHW Proteins Enzymes 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Propteries of Water HWDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Propteries of Water HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Embroidery Assistant: User Instruction GuideDocument92 pagesEmbroidery Assistant: User Instruction GuideAhlia Waqas AnjumNo ratings yet
- IT 16 - Neurogenic Bladder - SMDocument31 pagesIT 16 - Neurogenic Bladder - SMRurie Awalia SuhardiNo ratings yet
- Z-009-03-2015 - NCS Core Abilities Level 3Document53 pagesZ-009-03-2015 - NCS Core Abilities Level 3Aini KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Apply For Car Loan in Canada From Canadian Auto CenterDocument1 pageApply For Car Loan in Canada From Canadian Auto CenterCanadian Auto CenterNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Transformations PDFDocument16 pagesGrade 8 Transformations PDFFaizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Company Law - TUT 101Document17 pagesCompany Law - TUT 101Tia LakhrajNo ratings yet
- Lab Programs.Document21 pagesLab Programs.ramNo ratings yet
- Describe One Memory Model With Reference To Research!Document10 pagesDescribe One Memory Model With Reference To Research!Thuý ThanhNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument23 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesNanaNo ratings yet
- HR Governance As A Part of The Corporate Governance ConceptDocument24 pagesHR Governance As A Part of The Corporate Governance ConceptRudi HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Question CHP 5Document5 pagesQuestion CHP 5pearlynpuayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2suresh avaduthaNo ratings yet
- Simulink TutorialDocument15 pagesSimulink Tutorialsukhbir24No ratings yet
- Clear Choice: TurbomatrixDocument10 pagesClear Choice: TurbomatrixSaleh HamadanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HRMDocument77 pagesChapter 2 HRMStephanie AndalNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Two Marks HMTDocument5 pagesUNIT - I Two Marks HMTHARI B SNo ratings yet
- Total Marks: 25 Duration: One Hour: Xii-Msths Case Study Questions - Test Term-IDocument8 pagesTotal Marks: 25 Duration: One Hour: Xii-Msths Case Study Questions - Test Term-ISABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- How The Leopard Got His Spots by Rudyard KiplingDocument4 pagesHow The Leopard Got His Spots by Rudyard KiplingProxten DsilvaNo ratings yet
- Home - Link - 4.6 PerimeterDocument2 pagesHome - Link - 4.6 Perimetergiselle andalanNo ratings yet
- Research Process - StepsDocument31 pagesResearch Process - StepsPulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metodo Hach HierroDocument6 pagesMetodo Hach HierroJESSICA VANESSA ARISMENDI AVILEZNo ratings yet
- 1 Notes and HW On Even Odd and NeitherDocument3 pages1 Notes and HW On Even Odd and NeitherAlin LyndaNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsDocument76 pagesModule 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsHồngPhúc100% (1)
- Pioneer BDP 09fdDocument162 pagesPioneer BDP 09fdJirawan Sirin100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 9Document25 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 9Randy Edrada0% (1)
- Powerful Words To Use in PresentationsDocument9 pagesPowerful Words To Use in PresentationsGlobal CommNo ratings yet
- How Deep Is Your LoveDocument1 pageHow Deep Is Your LoveJanina JaworskiNo ratings yet