Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Life Cycle Management
Product Life Cycle Management
Uploaded by
Владислава Пономарева0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the product life cycle of Apple. It describes the stages Apple went through: introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and death or rebirth. During the introduction stage, Apple was small and relied on Jobs' leadership. In the growth stage, the successful Apple I and II expanded the company. In maturity, the Apple II became its main product. After Jobs left, Apple declined but was revived when Jobs returned as CEO and refocused the company.
Original Description:
Original Title
Product Life Cycle Management.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the product life cycle of Apple. It describes the stages Apple went through: introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and death or rebirth. During the introduction stage, Apple was small and relied on Jobs' leadership. In the growth stage, the successful Apple I and II expanded the company. In maturity, the Apple II became its main product. After Jobs left, Apple declined but was revived when Jobs returned as CEO and refocused the company.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views4 pagesProduct Life Cycle Management
Product Life Cycle Management
Uploaded by
Владислава ПономареваThe document summarizes the product life cycle of Apple. It describes the stages Apple went through: introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and death or rebirth. During the introduction stage, Apple was small and relied on Jobs' leadership. In the growth stage, the successful Apple I and II expanded the company. In maturity, the Apple II became its main product. After Jobs left, Apple declined but was revived when Jobs returned as CEO and refocused the company.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Product Life Cycle Management: Apple
introduction stage
The first stage is called birth. There is a lot of work
at this stage, the future of the company is
uncertain, and business processes can change
almost every day.
During this period, management is based on the
leader's charisma and persuasion. This is enough
when the organization is small and everyone
knows each other personally. Like at the dawn of
Apple, where Jobs' friends and acquaintances
became the first workers.
If a company overcomes the difficulties of the first
phase, certainty and stable processes appear in it,
it begins to grow.
Growth
The task of this stage is to actively conquer the
chosen niche. The time has come to change: new
employees and working methods are needed. The
time comes when you need to hire managers and
delegate authority to them.
How did this happen at Apple? After the success of
the Apple I, Jobs and Wozniak refined the
computer and created the Apple II, which was a
huge hit. The company received its first serious
contracts. With them came investments, began to
expand production, build offices and
representative offices. The number of employees
has grown, including the invitation of professional
managers to the company.
As a company grows, its structure becomes more
complex. It is very important at this stage to
describe business processes - to establish who
performs each action for whom and in what time
frame. This is the only way to maintain quality
when production grows and many new customers
appear.
Maturity A company in its maturity is one of the key players
in the chosen niche. Sales are growing, although
not as dynamically as during the growth period.
The market share either continues to grow slightly
or fluctuates within established limits. The
company invests most of its money in the products
that sell the best.
For Apple at maturity, the Apple II became the
main product. It became the first personal
computer to be produced by the millions. Since
then, it has sold about 5 million Apple IIs. The
company spent about 70% of the funds on it.
Decline The company is losing market share. The mistakes
made at the previous stage begin to take their toll.
Sales fall, customers leave. The company, trying to
cope with problems, pours budgets into failed
projects. Successful products are siphoned off the
last juices while competitors come up with better
solutions.
This is what started to happen to Apple after Jobs
left. This is not to say that his dismissal was the
only reason, after all, it is a systemic problem,
which led to many mistakes.
Death or rebirth
Apple gradually moved to a tipping point. It took
over the company NeXT in time, which Jobs
created after being fired. So he went back and
quickly became CEO. At that time, the company
had nothing left until its death.
Jobs first discontinued most of the products and
focused on core products. He also replaced a
significant part of the management, removing
those who opposed the change. The search and
development of new products began. Not without
luck. Microsoft got into trouble with antitrust laws
and gave Apple $ 200 million to keep it from
shutting down.
As a result, the company managed to avoid
collapse. First, it released several successful iMac
series, and then revolutionized again, first with the
iPod - "1000 songs in your pocket", and then with
the release of the iPhone and iPad. And in 2018 it
became worth $ 1 trillion.
Product Life Cycle Management: General Motors
introduction stage Formation of "GM" begins in 1897, when the
entrepreneur R. Olds built his first car, which he
named "Oldsmobile". Selling several of these cars,
Olds built in Detroit - the future automobile capital
of the United States - the first plant in America,
whose specialization was exclusively cars. In
Detroit, one after another automobile factories
open - first David Buick, and then Henry Leyland,
the founder of Cadillac. And in 1907 the Pontiac
Motor Division company was created. All these
companies merged in 1909 and formed "GM" In
1919, another well-known Detroit automobile
company, Chevrolet Motor, joined GM.
Growth The stage of development of the organization
begins in the 20s. It was then that GM overtook
Ford, the leader of the auto industry of that
period, in terms of production volume, and
became the leading American automobile
manufacturer. All five car brands of Buick,
Chevrolet, Pontiac, Oldsmobile and Cadillac are
firmly established in the American market.
It was during this period that GM developed the
characteristics of an organization at this stage of
its life cycle: medium size, numerous shareholders,
a more heterogeneous and competitive
environment.
Maturity The maturity stage of the company came in the
50s. In 1954, GM's share of the global automobile
market was 54%. About 3% of US GDP at the time
came from this company. Since that time, the
company's strategy was no longer aimed at
growth, but at maintaining leadership positions,
the emphasis was on adaptation, and the
contribution to society was assessed.
And although, since the mid-70s, American car
manufacturers, and primarily GM, began to lose
their leading positions, this was due to external
factors, and does not indicate a transition to the
aging phase of the organization.
Decline From 2005 to 2008, the company regularly
suffered losses. In the third quarter of 2007, a
record loss in the entire history of the company
was recorded, amounting to $ 38.6 billion. The
reason for the unprecedented loss was the one-
time write-off of intangible tax assets on
operations in the USA, Canada and Germany over
the past three years.
The amount of losses of this company in 2008
reached 88 billion dollars. The September 2008
financial crisis dealt the final blow to GM.
Death or rebirth Bankruptcy of the company found it at a stage of
maturity. Thus, as noted above, the empirical
sequence of stages changed, and instead of the
expected stage of old age, the stage of
disappearance / revival suddenly began, which
may not be the last stage in the life of the
organization.
It must be said that the phase - revival /
disappearance in the life cycle of the company has
a very important place. The emerging “fork” either
gives the firm the opportunity to develop in the
future, or leads to the dying of the economic
organization.
You might also like
- Method Statement FOR SIKATOP SEAL 107Document4 pagesMethod Statement FOR SIKATOP SEAL 107faizbukhariNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Tim Cook LeadershipDocument5 pagesCase Study On Tim Cook Leadershipavikpoddar100% (1)
- Stress Management by AppleDocument12 pagesStress Management by AppleSaba Jamal100% (1)
- Behind The Cloud PDFDocument9 pagesBehind The Cloud PDFmfdemiNo ratings yet
- SuperCorp by Rosabeth Moss Kanter - ExcerptDocument38 pagesSuperCorp by Rosabeth Moss Kanter - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group67% (3)
- Business Strategy and Management PrinciplesDocument6 pagesBusiness Strategy and Management PrinciplesJohn Grant OkelloNo ratings yet
- STM A-3 Anoba ZaheerDocument7 pagesSTM A-3 Anoba ZaheerAnoba ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Change Management Full SheetDocument204 pagesChange Management Full Sheetatahar IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- True Lean LeadershipDocument5 pagesTrue Lean LeadershipshponNo ratings yet
- Abm 1 ArticlesDocument28 pagesAbm 1 ArticlesDeniece Raiza Angela Tipay100% (1)
- Transformationa L Leaders: Jeffrey Perez Dba StudentDocument29 pagesTransformationa L Leaders: Jeffrey Perez Dba StudentFlorante De LeonNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Apple CompanyDocument69 pagesMarketing Strategies of Apple CompanyMunir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- John Mathew ProjectDocument70 pagesJohn Mathew ProjectAsha MathewNo ratings yet
- ICONIC: How Organizations and Leaders Attain, Sustain, and Regain the Highest Level of DistinctionFrom EverandICONIC: How Organizations and Leaders Attain, Sustain, and Regain the Highest Level of DistinctionNo ratings yet
- 5 Case StudiesDocument6 pages5 Case StudiesRiangelli ExcondeNo ratings yet
- Dale PM203Document5 pagesDale PM203Dale DoctoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Foundations of BusinessDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Foundations of Businessms.grace4allNo ratings yet
- 023 How Tim Cook Made Apple His Own - WSJDocument9 pages023 How Tim Cook Made Apple His Own - WSJRahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs LeadershipDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs LeadershipAbdul SaboorkhanNo ratings yet
- Secret Talk About AppleDocument9 pagesSecret Talk About ApplemallaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Apple Inc. 1Document12 pagesRunning Head: Apple Inc. 1Bruce OderaNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument5 pagesAppleSardor JuraevNo ratings yet
- 5 Case Studies About Successful Change ManagementDocument2 pages5 Case Studies About Successful Change ManagementSilvia BonacinaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Harvard Business Case Study: Apple Inc. 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: Harvard Business Case Study: Apple Inc. 1chandan singh0% (1)
- Steve Jobs and AppleDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs and AppleAxe Effect100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Business 2eDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Fundamentals of Business 2eJULIUS CAEZAR CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument11 pagesLeadershipHussain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Definition - Why - Case Studies - Business PlanDocument31 pagesIntroduction - Definition - Why - Case Studies - Business PlanchenboontaiNo ratings yet
- Scott Anthony An Excerpt From The SILVER LINING1Document4 pagesScott Anthony An Excerpt From The SILVER LINING1fischertNo ratings yet
- Date: August 9, 2020Document9 pagesDate: August 9, 2020angelNo ratings yet
- Presentation WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesPresentation WPS OfficejoviensuganoNo ratings yet
- The Effective Executive - What Needs To Be DoneDocument2 pagesThe Effective Executive - What Needs To Be DoneJorrian GelinkNo ratings yet
- The Halo Effect RevisedDocument9 pagesThe Halo Effect Revisedapi-500092727No ratings yet
- 5 Life Lessons From CEOsDocument5 pages5 Life Lessons From CEOsKarishma KoulNo ratings yet
- Successful IBs Ch1Document5 pagesSuccessful IBs Ch1Teesha AggrawalNo ratings yet
- SWOT and PEST Analysis of Apple Inc.Document5 pagesSWOT and PEST Analysis of Apple Inc.CheapestPapers100% (1)
- Apple AssignmentDocument8 pagesApple AssignmentAlisher ShuxratovichNo ratings yet
- U2. CompaniesDocument43 pagesU2. CompaniesPhạm Phương ThưNo ratings yet
- The Age of The Platform: SampleDocument13 pagesThe Age of The Platform: SamplePhil SimonNo ratings yet
- Apple 2 Weeks LaterDocument4 pagesApple 2 Weeks LaterFeargal Mac ConuladhNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Harvard Business Case Study: Apple Inc. 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: Harvard Business Case Study: Apple Inc. 1Shubhankar ShakhariNo ratings yet
- Business Awareness Reading MaterialDocument42 pagesBusiness Awareness Reading MaterialSubhash SinghNo ratings yet
- Marketing Myopia - LearningsDocument12 pagesMarketing Myopia - Learningsdeepak yadavNo ratings yet
- Marketing Myopia - Learnings From Kodak FailureDocument12 pagesMarketing Myopia - Learnings From Kodak Failuredeepak yadavNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs of Apple Inc: Successful Entrepreneur Case StudyDocument4 pagesSteve Jobs of Apple Inc: Successful Entrepreneur Case StudyLâm Lê VănNo ratings yet
- Business PolicyDocument21 pagesBusiness PolicyJohanna Grace BolanosNo ratings yet
- C13 AOL Final ReportDocument13 pagesC13 AOL Final ReportI knowNo ratings yet
- Manage Theory 2Document7 pagesManage Theory 2api-640981642No ratings yet
- in Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Document5 pagesin Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Priyanka MurthyNo ratings yet
- Dell CaseDocument3 pagesDell CasevincentNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Business Decisions of TimeDocument16 pagesThe Greatest Business Decisions of Timefetox36526No ratings yet
- U2 Homework WorksheetDocument7 pagesU2 Homework WorksheetAn Hạ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assignment 5Document23 pagesStrategic Management Assignment 5Jabri JuhininNo ratings yet
- Ceos Get Too Much Credit and Blame For Their Organization'S Outcomes - ForDocument17 pagesCeos Get Too Much Credit and Blame For Their Organization'S Outcomes - ForTapan JainNo ratings yet
- Running Head: SWOT ANALYSIS 1Document8 pagesRunning Head: SWOT ANALYSIS 1Tim WriterNo ratings yet
- Global Final Paper - Apple Inc.Document69 pagesGlobal Final Paper - Apple Inc.badoadNo ratings yet
- Jones, 2012. Five Ways Branding Is ChangingDocument3 pagesJones, 2012. Five Ways Branding Is Changingc3memoNo ratings yet
- Built To Last: Successful Habits of Visionary CompaniesDocument28 pagesBuilt To Last: Successful Habits of Visionary CompaniesHarish KarthikNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Disruptive InnovationDocument5 pagesCase Analysis Disruptive InnovationmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Assignment - A Strategic Analysis of Apple CorporationDocument17 pagesAssignment - A Strategic Analysis of Apple CorporationsbhamidNo ratings yet
- Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Department of Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesBannari Amman Institute of Technology Department of Information Technologyinvincible_shalin6954No ratings yet
- 04 Prescription InterpretationDocument32 pages04 Prescription InterpretationBalsam Zahi Al-HasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheets On Maxima & Minima (22!09!15)Document1 pageWorksheets On Maxima & Minima (22!09!15)ib elite tutorNo ratings yet
- List of Units Competency: Daftar Unit KompetensiDocument1 pageList of Units Competency: Daftar Unit KompetensiBagus Fitri UtomoNo ratings yet
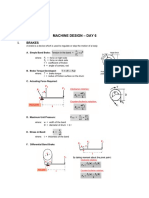
- Handouts MD Day 6Document8 pagesHandouts MD Day 6James Ivan AnoreNo ratings yet
- Putting Words TogetherDocument28 pagesPutting Words TogetherKatherinaNo ratings yet
- Timber Frame Solutions 03Document20 pagesTimber Frame Solutions 03sertackcdgNo ratings yet
- THE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDocument54 pagesTHE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDevilleres Eliza DenNo ratings yet
- PM265 ch2Document47 pagesPM265 ch2M. AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ourlog 9089Document4 pagesOurlog 9089Prin PinkyNo ratings yet
- Final Health EducDocument139 pagesFinal Health EducsprrwgoldenNo ratings yet
- Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C: To Cite This Article: John R. Martin, Julian F. Johnson & Anthony R. CooperDocument145 pagesJournal of Macromolecular Science, Part C: To Cite This Article: John R. Martin, Julian F. Johnson & Anthony R. CooperRicky Iqbal SNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Pesticidas Usandom FragmentacionDocument159 pagesAnalisis de Pesticidas Usandom FragmentacionroxanaNo ratings yet
- Final Fortran Questions 1Document5 pagesFinal Fortran Questions 1Serdar BilgeNo ratings yet
- KFC225 Operating HandbookDocument25 pagesKFC225 Operating HandbooksunaryaNo ratings yet
- Rs Means Data 2005Document42 pagesRs Means Data 2005Sujib Barman0% (3)
- MaldivesDocument15 pagesMaldivesRyhan AbuNo ratings yet
- Make Predictions Using TransitsDocument2 pagesMake Predictions Using Transitscnugoud2011100% (1)
- Paypal SecurityDocument5 pagesPaypal SecurityNazer Mo GNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument254 pagesPreviewIgor OkNo ratings yet
- Kerala University of Health Sciences Thrissur - 680 596: Application For Duplicate Mark Lists / CertificatesDocument2 pagesKerala University of Health Sciences Thrissur - 680 596: Application For Duplicate Mark Lists / CertificatesDevassy KVNo ratings yet
- Command Center Processing and Display System ReplacementDocument2 pagesCommand Center Processing and Display System ReplacementImranNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument9 pagesREVIEWERangel alabadoNo ratings yet
- CAR-T TherapyDocument14 pagesCAR-T TherapyrameshaachariarNo ratings yet
- BCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesAlvy SyukrieNo ratings yet
- Engine RT-flex Operation Practical AdvancedDocument3 pagesEngine RT-flex Operation Practical AdvancedPiotr StankiewiczNo ratings yet
- Status of Organic Farming and Research Experiences in RiceDocument14 pagesStatus of Organic Farming and Research Experiences in RiceAtinNo ratings yet
- Multithreaded Airport Simulation SystemsDocument6 pagesMultithreaded Airport Simulation Systemsphanikrishnajagadesh666No ratings yet
- GE-102 - Natural Sciences - OutlinesDocument3 pagesGE-102 - Natural Sciences - Outlinesm.zulaid.motivationNo ratings yet