Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An RLCPR
An RLCPR
Uploaded by
jose pepeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 2Document32 pagesLab 2AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Ece KCLDocument7 pagesEce KCLFunny Video Compilation NivNo ratings yet
- Comm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1Document17 pagesComm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1anthdbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document9 pagesLesson 11Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- KCL and KVLDocument113 pagesKCL and KVLmanjuvenammaNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitDocument21 pagesCommunication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitUsama AkramNo ratings yet
- LC Circuit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesLC Circuit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAdrian TanaseNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisProsenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- RLC Series and ParallelDocument8 pagesRLC Series and ParallelFaizanAshrafNo ratings yet
- An LC CircuitDocument11 pagesAn LC CircuitHRM, BAPEXNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab Report 12Document12 pagesLCA Lab Report 12ayleeNo ratings yet
- Parallel ResonanceDocument14 pagesParallel ResonanceSubhuNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis ANALYSISDocument43 pagesCircuit Analysis ANALYSISAJIN RIBIA PNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Aims of The Exercise: EquipmentDocument3 pagesAims of The Exercise: Equipmentwala alabedNo ratings yet
- The RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonanceDocument5 pagesThe RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonancePrince LawrenceNo ratings yet
- 7 - Parallel ResonanceDocument14 pages7 - Parallel ResonanceSenjuti De0% (1)
- KirchhoffDocument33 pagesKirchhoffRalph GeddesNo ratings yet
- Sem III Bee301circuit TheoryDocument70 pagesSem III Bee301circuit TheoryBishal BanikNo ratings yet
- Experiment #5Document9 pagesExperiment #5Imaizumi RieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document26 pagesLesson 12Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- Harmonics and PFDocument20 pagesHarmonics and PFchavdapgNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit Analysisengrsana ullahNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- Concept of RLRC and RLC Circuit 32Document9 pagesConcept of RLRC and RLC Circuit 32sayem12No ratings yet
- RC CircuitDocument36 pagesRC CircuitMaryam Adila Jusoh100% (2)
- Series and Parallel Circuits: TutorialDocument18 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits: TutorialBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 2n3055 NPN PNP Bipolar TransistorsDocument6 pages2n3055 NPN PNP Bipolar TransistorsdllabarreNo ratings yet
- Parallel TheoryDocument9 pagesParallel Theoryvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document12 pagesAnswer 1xto07No ratings yet
- RLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezDocument24 pagesRLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezSul SyaNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document6 pagesExp 10abdelmalekhadiakNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit Analysis and RLC Series CircuitsDocument6 pagesSeries RLC Circuit Analysis and RLC Series CircuitsProsenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Networksshort2011 12pdfDocument10 pagesNetworksshort2011 12pdfvenki249No ratings yet
- IV Characteristic TransistorDocument7 pagesIV Characteristic TransistorNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Unit - 3Document44 pagesBasic Electronics Unit - 3MohitNo ratings yet
- Exp 20Document5 pagesExp 20davyl91No ratings yet
- Theory 11625041162504Document6 pagesTheory 11625041162504Anonymous rD1KcPG98No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawDocument5 pagesKirchhoff's LawJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Gustav KirchhoffDocument25 pagesGustav KirchhoffSICEL GRACE AMODIANo ratings yet
- Antennas and Transmission Lines v1Document74 pagesAntennas and Transmission Lines v1Nishant SharanNo ratings yet
- Mesh Current MethodDocument18 pagesMesh Current MethodabhiknitNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current in RLC CircuitDocument5 pagesVoltage and Current in RLC Circuitاياد النعيميNo ratings yet
- 21 RccirDocument7 pages21 Rcciracademic19No ratings yet
- Short Circuit CurrentDocument6 pagesShort Circuit CurrentuplbselesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Transistor Switching With A Reactive Load: (Old ECE 311 Note Revisited)Document5 pagesTransistor Switching With A Reactive Load: (Old ECE 311 Note Revisited)Riyas V IsmailNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Do Not Behave The Same As ResistorsDocument14 pagesCapacitors Do Not Behave The Same As Resistorsmtheo20No ratings yet
- LC CircuitDocument15 pagesLC CircuitKing SharmaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Power FactorDocument6 pagesCalculating Power FactorFahrul MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Lessons in Electric Circuits - Volume I (DC) - Chapter 10Document62 pagesLessons in Electric Circuits - Volume I (DC) - Chapter 10chatuusumitavaNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesSeries RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisMartNo ratings yet
- Ecn RLCPDocument11 pagesEcn RLCPharshsuryawanshi2021No ratings yet
- Electronics Viva Based QuestionsDocument5 pagesElectronics Viva Based QuestionsArpitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology (p121-160)Document40 pagesElectrical Technology (p121-160)mugiwaraluffy10235No ratings yet
- RLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesRLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisShah Zeb Yousafzai100% (1)
- Parallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitDocument9 pagesParallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitRoboconDKNo ratings yet
- Postlab Report #3Document8 pagesPostlab Report #3Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit BoardsDocument61 pagesMod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit Boardsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- When Engineers Become Whistleblowers: They're Often The First To Notice Waste, Fraud and Safety IssuesDocument4 pagesWhen Engineers Become Whistleblowers: They're Often The First To Notice Waste, Fraud and Safety Issuesjose pepeNo ratings yet
- ClassNotesDigitales PDFDocument117 pagesClassNotesDigitales PDFjose pepeNo ratings yet
- An Trbi3Document1 pageAn Trbi3jose pepeNo ratings yet
- AC Power DistributionDocument2 pagesAC Power Distributionjose pepeNo ratings yet
- Continue: Grade AnswerDocument1 pageContinue: Grade Answerjose pepeNo ratings yet
An RLCPR
An RLCPR
Uploaded by
jose pepeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An RLCPR
An RLCPR
Uploaded by
jose pepeCopyright:
Available Formats
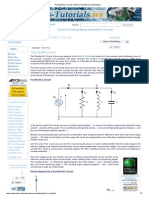
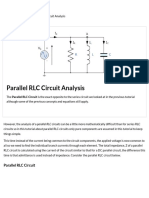
Parallel resonance is the special case where XL and XC are equal, or very near equal, in a
parallel RLC or LC circuit. The capacitor current, IC, and the inductor current, IL, are in
opposite directions in parallel RLC and LC circuits. The inductor current and capacitor current
cancel each other as viewed from the source. In reality the IC and IL currents circulate between
the capacitor and inductor. These circulating currents can be many times larger than the total
circuit current. A vector diagram of a parallel RLC circuit is shown in figure one. Notice that the
inductor current and capacitor current are in opposite directions. The source sees only the resistor
current as shown in figure two. A fully worked out parallel resonant RCL circuit analysis can be
seen by clicking on the example tab at the upper left of this page.
Click on the “Begin” button when you are ready to start the exercise. Each use of the activity
will have new component values and voltages assigned. The exercise has a help option that will
give formulas and procedures for analyzing the circuit. A small score penalty is applied for each
use of the help option. One should practice without concern for scores until the solution
procedure has been mastered. You should then attempt to get high scores in minimum time
without the using the help option. Keep in mind that there may be more than one approach to
analyzing the circuit.
You might also like
- Lab 2Document32 pagesLab 2AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Ece KCLDocument7 pagesEce KCLFunny Video Compilation NivNo ratings yet
- Comm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1Document17 pagesComm. Electronics (2011 s11) - l300ppt 1anthdbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document9 pagesLesson 11Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- KCL and KVLDocument113 pagesKCL and KVLmanjuvenammaNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitDocument21 pagesCommunication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitUsama AkramNo ratings yet
- LC Circuit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesLC Circuit - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAdrian TanaseNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisProsenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- RLC Series and ParallelDocument8 pagesRLC Series and ParallelFaizanAshrafNo ratings yet
- An LC CircuitDocument11 pagesAn LC CircuitHRM, BAPEXNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab Report 12Document12 pagesLCA Lab Report 12ayleeNo ratings yet
- Parallel ResonanceDocument14 pagesParallel ResonanceSubhuNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis ANALYSISDocument43 pagesCircuit Analysis ANALYSISAJIN RIBIA PNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Aims of The Exercise: EquipmentDocument3 pagesAims of The Exercise: Equipmentwala alabedNo ratings yet
- The RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonanceDocument5 pagesThe RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonancePrince LawrenceNo ratings yet
- 7 - Parallel ResonanceDocument14 pages7 - Parallel ResonanceSenjuti De0% (1)
- KirchhoffDocument33 pagesKirchhoffRalph GeddesNo ratings yet
- Sem III Bee301circuit TheoryDocument70 pagesSem III Bee301circuit TheoryBishal BanikNo ratings yet
- Experiment #5Document9 pagesExperiment #5Imaizumi RieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document26 pagesLesson 12Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- Harmonics and PFDocument20 pagesHarmonics and PFchavdapgNo ratings yet
- Parallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesParallel RLC Circuit and RLC Parallel Circuit Analysisengrsana ullahNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- Concept of RLRC and RLC Circuit 32Document9 pagesConcept of RLRC and RLC Circuit 32sayem12No ratings yet
- RC CircuitDocument36 pagesRC CircuitMaryam Adila Jusoh100% (2)
- Series and Parallel Circuits: TutorialDocument18 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits: TutorialBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 2n3055 NPN PNP Bipolar TransistorsDocument6 pages2n3055 NPN PNP Bipolar TransistorsdllabarreNo ratings yet
- Parallel TheoryDocument9 pagesParallel Theoryvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document12 pagesAnswer 1xto07No ratings yet
- RLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezDocument24 pagesRLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezSul SyaNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document6 pagesExp 10abdelmalekhadiakNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit Analysis and RLC Series CircuitsDocument6 pagesSeries RLC Circuit Analysis and RLC Series CircuitsProsenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Networksshort2011 12pdfDocument10 pagesNetworksshort2011 12pdfvenki249No ratings yet
- IV Characteristic TransistorDocument7 pagesIV Characteristic TransistorNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Unit - 3Document44 pagesBasic Electronics Unit - 3MohitNo ratings yet
- Exp 20Document5 pagesExp 20davyl91No ratings yet
- Theory 11625041162504Document6 pagesTheory 11625041162504Anonymous rD1KcPG98No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawDocument5 pagesKirchhoff's LawJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Gustav KirchhoffDocument25 pagesGustav KirchhoffSICEL GRACE AMODIANo ratings yet
- Antennas and Transmission Lines v1Document74 pagesAntennas and Transmission Lines v1Nishant SharanNo ratings yet
- Mesh Current MethodDocument18 pagesMesh Current MethodabhiknitNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current in RLC CircuitDocument5 pagesVoltage and Current in RLC Circuitاياد النعيميNo ratings yet
- 21 RccirDocument7 pages21 Rcciracademic19No ratings yet
- Short Circuit CurrentDocument6 pagesShort Circuit CurrentuplbselesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Transistor Switching With A Reactive Load: (Old ECE 311 Note Revisited)Document5 pagesTransistor Switching With A Reactive Load: (Old ECE 311 Note Revisited)Riyas V IsmailNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Do Not Behave The Same As ResistorsDocument14 pagesCapacitors Do Not Behave The Same As Resistorsmtheo20No ratings yet
- LC CircuitDocument15 pagesLC CircuitKing SharmaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Power FactorDocument6 pagesCalculating Power FactorFahrul MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Lessons in Electric Circuits - Volume I (DC) - Chapter 10Document62 pagesLessons in Electric Circuits - Volume I (DC) - Chapter 10chatuusumitavaNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesSeries RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisMartNo ratings yet
- Ecn RLCPDocument11 pagesEcn RLCPharshsuryawanshi2021No ratings yet
- Electronics Viva Based QuestionsDocument5 pagesElectronics Viva Based QuestionsArpitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology (p121-160)Document40 pagesElectrical Technology (p121-160)mugiwaraluffy10235No ratings yet
- RLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesRLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisShah Zeb Yousafzai100% (1)
- Parallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitDocument9 pagesParallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitRoboconDKNo ratings yet
- Postlab Report #3Document8 pagesPostlab Report #3Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit BoardsDocument61 pagesMod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit Boardsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- When Engineers Become Whistleblowers: They're Often The First To Notice Waste, Fraud and Safety IssuesDocument4 pagesWhen Engineers Become Whistleblowers: They're Often The First To Notice Waste, Fraud and Safety Issuesjose pepeNo ratings yet
- ClassNotesDigitales PDFDocument117 pagesClassNotesDigitales PDFjose pepeNo ratings yet
- An Trbi3Document1 pageAn Trbi3jose pepeNo ratings yet
- AC Power DistributionDocument2 pagesAC Power Distributionjose pepeNo ratings yet
- Continue: Grade AnswerDocument1 pageContinue: Grade Answerjose pepeNo ratings yet