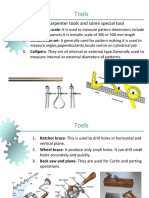
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Moulding Sand
Properties of Moulding Sand
Uploaded by
vijayanandan thekkethodikayilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Moulding Sand
Properties of Moulding Sand
Uploaded by
vijayanandan thekkethodikayilCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Moulding sand
The basic properties required in moulding sand and core
sand are adhesiveness, cohesiveness, collapsibility, flowability, dry strength, green
strength, permeability, refractoriness described as under.
1) Adhesiveness
Adhesiveness is a property of moulding sand to get the stick or adhere to
foreign material such sticking of moulding sand with the inner wall of moulding box.
2) Cohesiveness
Cohesiveness is property of moulding sand by virtue which the sand grain
particles interact and attract each other within the moulding sand. Thus, the
binding capability of the moulding sand gets enhanced to increase the green, dry
and hot strength property of moulding and core sand.
3) Collapsibility
After the molten metal in the mould gets solidified, the sand mould must be
collapsible so that free contraction of the metal occurs and this would naturally
avoid the tearing or cracking of the contracting metal. In absence of collapsibility
property the contraction of the metal is hindered by the mould and thus results in
tears and cracks in the casting. This property is highly required in cores.
4) Dry strength
As soon as the molten metal is poured into the mould, the moisture in the
sand layer adjacent to the hot metal gets evaporated and this dry sand layer must
have sufficient strength to its shape in order to avoid erosion of mould wall during
the flow of molten metal. The dry strength also prevents the enlargement of mould
cavity cause by the metallostatic pressure of the liquid metal.
5) Flowability or plasticity
Flowability or plasticity is the ability of the sand to get compacted and
behave like a fluid. It will flow uniformly to all portions of pattern when rammed
and distribute the ramming pressure evenly all around in all directions. Generally
sand particles resist moving around corners or projections. In general, flowability
increases with decrease in green strength and vice versa. Flowability increases with
decrease in grain size of sand. The flowability also varies with moisture and clay
content in sand.
6) Green strength
The green sand after water has been mixed into it, must have sufficient
strength and toughness to permit the making and handling of the mould. For this,
the sand grains must be adhesive, i.e. they must be capable of attaching
themselves to another body and. therefore, and sand grains having high
adhesiveness will cling to the sides of the moulding box. Also, the sand grains must
have the property known as cohesiveness i.e. ability of the sand grains to stick to
one another. By virtue of this property, the pattern can be taken out from the
mould without breaking the mould and also erosion of mould wall surfaces does not
occur during the flow of molten metal. The green strength also depends upon the
grain shape and size, amount and type of clay and the moisture content.
7) Permeability
Permeability is also termed as porosity of the moulding sand in order to allow
the escape of any air, gases or moisture present or generated in the mould when
the molten metal is poured into it. All these gaseous generated during pouring and
solidification process must escape otherwise the casting becomes defective.
Permeability is a function of grain size, grain shape, and moisture and clay contents
in the moulding sand. The extent of ramming of the sand directly affects the
permeability of the mould. Permeability of mould can be further increased by
venting using vent rods.
8) Refractoriness
Refractoriness is defined as the ability of moulding sand to withstand high
temperatures without breaking down or fusing thus facilitating to get sound casting.
It is a highly important characteristic of moulding sands. Refractoriness can only be
increased to a limited extent. Moulding sand with poor refractoriness may burn on
to the casting surface and no smooth casting surface can be obtained. The degree
of refractoriness depends on the SiO2 i.e. quartz content, and the shape and grain
size of the particle. The higher the SiO2 content and the rougher the grain
volumetric composition the higher is the refractoriness of the moulding sand and
core sand. Refractoriness is measured by the sinter point of the sand rather than its
melting point.
Miscellaneous properties of moulding sand
In addition to above requirements, the moulding sand should not stick to the
casting and should not chemically react with the metal. Moulding sand need be
economically cheap and easily available in nature. It need be reusable for economic
reasons. Its coefficients of thermal expansion need be sufficiently low.
You might also like
- Assignment-2 Problems On Electricity Markets, Transmission Operations PDFDocument5 pagesAssignment-2 Problems On Electricity Markets, Transmission Operations PDFAhmed Khairi0% (1)
- Properties of Moulding SandDocument16 pagesProperties of Moulding SandNilesh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Concrete TechnologyDocument36 pagesConcrete Technologyshalu R FNo ratings yet
- FLUIDSDocument55 pagesFLUIDSMonville RedNo ratings yet
- Publication 11 21839 1710Document4 pagesPublication 11 21839 1710Dimi BelNo ratings yet
- Course: Metal Casting: Lecture No-6 Sand Composition & Material PropertiesDocument4 pagesCourse: Metal Casting: Lecture No-6 Sand Composition & Material PropertieszombieNo ratings yet
- Casting Part2Document76 pagesCasting Part2mallyvohra2010No ratings yet
- Course: Metal Casting Module No.7: Testing of SandDocument4 pagesCourse: Metal Casting Module No.7: Testing of SandSriman GhoshNo ratings yet
- Casting & Forging Notes - 2022Document13 pagesCasting & Forging Notes - 2022MuktaNo ratings yet
- Prianka Binte Zaman Assistant Professor Dept. of IPE, BUETDocument17 pagesPrianka Binte Zaman Assistant Professor Dept. of IPE, BUETKibria Prangon100% (1)
- Casting and Casting Processes: Prof. (DR.) Dalgobind Mahto 3/10/2015Document28 pagesCasting and Casting Processes: Prof. (DR.) Dalgobind Mahto 3/10/2015keethanNo ratings yet
- Moulding & Moulding Materials: Casting ProcessesDocument97 pagesMoulding & Moulding Materials: Casting ProcessesTrung Quoc LeNo ratings yet
- Types of Pattern Allowances in CastingDocument7 pagesTypes of Pattern Allowances in CastingDr.S.Ravi CITNo ratings yet
- Sand MouldingDocument17 pagesSand MouldingbvbprasadNo ratings yet
- Foundry TechnologiesDocument144 pagesFoundry TechnologiesSujoy ShivdeNo ratings yet
- MPI Unit IDocument54 pagesMPI Unit IArun PatilNo ratings yet
- Properties of Moulding SandDocument2 pagesProperties of Moulding SandXid ChangNo ratings yet
- Lec 22Document20 pagesLec 22Simanchal KarNo ratings yet
- Molding Material: Refractory SandsDocument26 pagesMolding Material: Refractory SandsAbhay ThakurNo ratings yet
- MP 2Document8 pagesMP 2Empty DivineNo ratings yet
- Foundry Trade 27112020Document45 pagesFoundry Trade 27112020Jeevan MandalaNo ratings yet
- Moulding Sand PropertyDocument6 pagesMoulding Sand PropertyAppu MukundanNo ratings yet
- 05 Casting Part 5Document17 pages05 Casting Part 5Shweta raiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sand Grading On Characteristics of MortarDocument48 pagesEffect of Sand Grading On Characteristics of Mortarmaniram7100% (4)
- ME317 Manufacturing Technology Lab ManualDocument22 pagesME317 Manufacturing Technology Lab ManualLakshmi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2casting Process PPT BMP Unit 2Document61 pagesUnit 2casting Process PPT BMP Unit 2Bhaskar KandpalNo ratings yet
- Sand CastingDocument8 pagesSand CastingHaryad HewaNo ratings yet
- Molding SandDocument4 pagesMolding Sand2210169No ratings yet
- Green Sand For HPMLDocument2 pagesGreen Sand For HPMLvivek1312No ratings yet
- Sand Moulding Sand Types, Cores, Machines: Hareesha N G Lecturer, Dept. of Aeronautical Engg, DSCE, Bangalore-78Document50 pagesSand Moulding Sand Types, Cores, Machines: Hareesha N G Lecturer, Dept. of Aeronautical Engg, DSCE, Bangalore-78upender100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Casting Surface DefectsDocument72 pagesLecture 3 Casting Surface DefectsLuis Arturo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Vol-1 Issue-3Document5 pagesVol-1 Issue-3RakeshNo ratings yet
- Group 9 PPT REPORTDocument61 pagesGroup 9 PPT REPORTAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Constructoin 11Document39 pagesConstructoin 11ariganyira FrancisNo ratings yet
- LAB SESSION No 2 ManufacturingDocument4 pagesLAB SESSION No 2 Manufacturingm.sheraz malikNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Pavement MaterialsDocument167 pagesModule-1: Pavement Materialsmanjunatha100% (1)
- Chapter Three: Technology of Moulding and Core MakingDocument30 pagesChapter Three: Technology of Moulding and Core MakingSeare TekesteNo ratings yet
- Various Types of CastingDocument146 pagesVarious Types of CastingKaushik SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Concrete 5.1 OverviewDocument7 pagesConcrete 5.1 Overviewg7711637No ratings yet
- HC Module I AddnDocument49 pagesHC Module I Addndeekshith gowdaNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement LectureDocument38 pagesPortland Cement LectureAli BajwaNo ratings yet
- CH 3-Moulding and Core MakingDocument49 pagesCH 3-Moulding and Core Makinggosaye desalegn100% (3)
- Lesson 2 MINERAL AGGREGATESDocument10 pagesLesson 2 MINERAL AGGREGATESDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- Sand MouldingDocument62 pagesSand Mouldingdhruvmistry300No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process-I MouldsDocument46 pagesManufacturing Process-I MouldsRahul Deb PalNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4Document61 pagesWeek 3 and 4israrisroo10No ratings yet
- Pavement Materials NotesDocument105 pagesPavement Materials NotesProf. Nagarjun Gowda B SNo ratings yet
- Advanced Concrete Design Module 1 KtuDocument28 pagesAdvanced Concrete Design Module 1 Ktushalu R FNo ratings yet
- MCWT PDFDocument173 pagesMCWT PDFhrishikeshlahudkar18No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mould MakingDocument54 pagesChapter 3 Mould Makingjoy fulNo ratings yet
- Sand Casting Fall 2023Document36 pagesSand Casting Fall 2023Ahmed AmeerNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 AGGREGATES: Origin, Classification, Requirements, Properties and Tests On Road AggregatesDocument109 pagesUnit - 1 AGGREGATES: Origin, Classification, Requirements, Properties and Tests On Road AggregatesAnil Suryawanshi100% (1)
- TY MCWT Moulding SandDocument47 pagesTY MCWT Moulding SandHrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Molding and Core Sands: Types of Molding SandDocument15 pagesMolding and Core Sands: Types of Molding SandSaroj Kumar KaparNo ratings yet
- Mouldingsand 170509114249 PDFDocument49 pagesMouldingsand 170509114249 PDFAnything You Could ImagineNo ratings yet
- Casting Series 3Document23 pagesCasting Series 3Janmayjoy Halder SwagataNo ratings yet
- Requirements of Bituminous MixesDocument2 pagesRequirements of Bituminous MixesRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Sand CastingDocument42 pagesSand Castingshar8awy 506No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Aggregates: Concrete TechnologyDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Aggregates: Concrete TechnologyAnonymous WalvB8No ratings yet
- Manufactured Sand As AggregateDocument17 pagesManufactured Sand As AggregateMANISHA SURVENo ratings yet
- Casting: Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingDocument109 pagesCasting: Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingasitacharyaNo ratings yet
- MOUDLING SAND IngredDocument3 pagesMOUDLING SAND Ingredvijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- PATTERN MTL 3Document3 pagesPATTERN MTL 3vijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- Moulding Process and Materials: Good Castings Cannot Be Made Without Good MouldsDocument2 pagesMoulding Process and Materials: Good Castings Cannot Be Made Without Good Mouldsvijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- Pattern AllowancesDocument4 pagesPattern Allowancesvijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- Need For WeldingDocument5 pagesNeed For Weldingvijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- Boiler QuestionsDocument39 pagesBoiler Questionssk3146100% (11)
- Desktop Computer Theme PPT Template - GEMO EDITSDocument15 pagesDesktop Computer Theme PPT Template - GEMO EDITSD GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mark R. Schoeberl Et Al - Estimation of Stratospheric Age Spectrum From Chemical TracersDocument18 pagesMark R. Schoeberl Et Al - Estimation of Stratospheric Age Spectrum From Chemical TracersRemazzzNo ratings yet
- Marine BoilerDocument30 pagesMarine BoilerCarloNo ratings yet
- The Electrical StabilityDocument2 pagesThe Electrical StabilityGua MimiNo ratings yet
- Rainbow in A Jar: ProblemDocument1 pageRainbow in A Jar: ProblemPrayogo DidiNo ratings yet
- Lexe8179 02Document2 pagesLexe8179 02Pankaj KambleNo ratings yet
- Chhabra Thermal Power StationDocument18 pagesChhabra Thermal Power StationAmit Agarwal100% (1)
- Overview of Centrifugal PumpsDocument5 pagesOverview of Centrifugal Pumpsrahul_choubey_9No ratings yet
- Life Cycle Cost of Using On Site Renewable Energy For The Electrification of Industrial Buildings in Sri LankaDocument122 pagesLife Cycle Cost of Using On Site Renewable Energy For The Electrification of Industrial Buildings in Sri LankaBimsara MalithNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Ingeniería EconómicaDocument2 pagesEjercicios de Ingeniería EconómicaDiego MoralesNo ratings yet
- National Adaptation Plan: ExecutiveDocument32 pagesNational Adaptation Plan: ExecutiveEka Dyana100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 4 EXTERNAL FLOWDocument40 pagesFluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 4 EXTERNAL FLOWsam19961No ratings yet
- #1 Dissociation of Propionic Acid DimerDocument14 pages#1 Dissociation of Propionic Acid DimerCharity QuinnNo ratings yet
- American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, IncDocument11 pagesAmerican Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, Incfjflores26No ratings yet
- NotesAcademy - Year 3&4 ChemistryDocument119 pagesNotesAcademy - Year 3&4 Chemistrydarkadain100% (1)
- Francis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesDocument5 pagesFrancis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesfahadNo ratings yet
- Big Coal's Dirty SecretsDocument10 pagesBig Coal's Dirty SecretsAppalachian VoiceNo ratings yet
- Corrected Factor For GT Performance CalculationDocument12 pagesCorrected Factor For GT Performance Calculationijal1984No ratings yet
- Able To Use Superlatives.: Types of Natural DisastersDocument3 pagesAble To Use Superlatives.: Types of Natural DisastersGabriela CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Paper (Climate Change)Document2 pagesEarth Science Paper (Climate Change)Ray Harvey CapunoNo ratings yet
- CHISHAWASHA Soil TestsDocument3 pagesCHISHAWASHA Soil TestsSitche ZisoNo ratings yet
- 1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument28 pages1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studiesyadavmansi1101997No ratings yet
- Kinetics of The Cao/Ca (Oh) Hydration/Dehydration Reaction For Thermochemical Energy Storage ApplicationsDocument33 pagesKinetics of The Cao/Ca (Oh) Hydration/Dehydration Reaction For Thermochemical Energy Storage ApplicationsAnonymous Hy5Ir9QXNo ratings yet
- As 2243.4-1998 Safety in Laboratories Ionizing RadiationsDocument9 pagesAs 2243.4-1998 Safety in Laboratories Ionizing RadiationsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Project Study ThermoelectricDocument54 pagesProject Study Thermoelectriczakibrant23No ratings yet
- Biology Notes PDFDocument211 pagesBiology Notes PDFamar lalNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Eletric Vehicle Notes 1Document10 pagesHybrid Eletric Vehicle Notes 1Anandhu ANo ratings yet