Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Ability To Perform Two Tasks Together Depends On Their Difficulty
The Ability To Perform Two Tasks Together Depends On Their Difficulty
Uploaded by
LoraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Ability To Perform Two Tasks Together Depends On Their Difficulty
The Ability To Perform Two Tasks Together Depends On Their Difficulty
Uploaded by
LoraCopyright:
Available Formats
Divided Attention
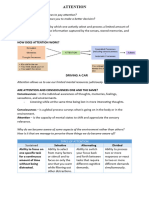
The ability to attend to multiple stimuli simultaneously and to perform multiple tasks at the same time
Task Similarity
The participant is more likely to be successful if the task involves different stimulus or response
modalities
Task Difficulty
The ability to perform two tasks together depends on their difficulty
Practice
The demands placed on attentional resources may be reduced if the task or action is practiced
Selective Attention
The ability to focus on a single stimulus, even while other stimuli are occurring simultaneously
Spotlight Model of Attention
Attention as having a focus, a margin, and a fringe, like a spotlight
Resource Model of Attention
We have limited resources when it comes to attention
Cocktail Party Effect
The phenomenon of being able to focus one's auditory attention on a particular stimulus while filtering
out a range of other stimuli
Inattentional Blindness
The event in which an individual fails to perceive an unexpected stimulus that is in plain sight
Change Blindness
A perceptual phenomenon that occurs when a change in a visual stimulus is introduced and the
observer does not notice it
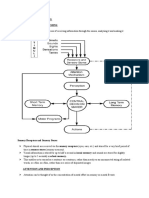
Distal Stimuli
Any physical object or event in the external world that reflects light
Proximal Stimuli
The patterns of stimuli from these objects and events that actually reach your senses
Covert Orienting
The act to mentally shifting one's focus without moving one's eyes
Overt Orienting
The act of selectively attending to an item or location over others by moving the eyes to point in that
direction
Attentional Capture
The unintentional focusing of attention, for example by a change in a stimulus, which interrupts other
processing
Neglect Syndrome
A neuropsychological condition in which, after damage to one hemisphere of the brain is sustained, a
deficit in attention to and awareness of one side of the field of vision is observed
Vigilance Attention
The ability to maintain concentrated attention over prolonged periods of time
Executive Attention
Refers to a subfunction of attention that includes processes for monitoring and resolving conflicts that
arise among internal processes
Speech Shadowing
An experimental technique in which subjects repeat speech immediately after hearing it, usually
through earphones
You might also like
- Unit 3: AttentionDocument18 pagesUnit 3: AttentionlNo ratings yet
- Psy 6 Attention FullDocument6 pagesPsy 6 Attention FullAndrea Aya CardinozaNo ratings yet
- Attending the WorldDocument16 pagesAttending the WorldmissionabhiyasinfoNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument9 pagesAttentionJuma GullNo ratings yet
- Types of Attention MaterialDocument14 pagesTypes of Attention MaterialSanjhanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Cognitive ProcessDocument29 pagesUnit 6 Cognitive ProcessHetal Pandya100% (1)
- Unit-II Lesson 4 Attention Concept and MechanismDocument13 pagesUnit-II Lesson 4 Attention Concept and MechanismDr Yashpal AzadNo ratings yet
- Attention and ConsciousnessDocument28 pagesAttention and Consciousnesspedretti spaghettiNo ratings yet
- All About Attentional ControlDocument2 pagesAll About Attentional Controllilj12No ratings yet
- What Is Divided Attention?Document50 pagesWhat Is Divided Attention?LoraNo ratings yet
- Processing Capacity and Selective Attention: Change DeafnessDocument5 pagesProcessing Capacity and Selective Attention: Change DeafnessVidisha KandwalNo ratings yet
- Psychology NotesDocument17 pagesPsychology NotesravibhargavaraamNo ratings yet
- Psy Assignment No 3Document5 pagesPsy Assignment No 3FAIZ ANJUMNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Iftekhar Hossain, Professor and Head, Department of Psychology, Patna UniversityDocument10 pagesDr. Md. Iftekhar Hossain, Professor and Head, Department of Psychology, Patna UniversityfanNo ratings yet
- Attention: Dr. Bouchefra Miloud Cognitive Psychlogylevel: 3 Year Academic Year: 2017-2018Document5 pagesAttention: Dr. Bouchefra Miloud Cognitive Psychlogylevel: 3 Year Academic Year: 2017-2018amiraNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting AttentionDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting AttentionQasim MunawarNo ratings yet
- SEM 1 UNIT 3 - MGU Attention-Notes PDFDocument9 pagesSEM 1 UNIT 3 - MGU Attention-Notes PDFBhoomika VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Acr 2310300816 1146388970 2Document52 pagesAcr 2310300816 1146388970 2sssssssssssNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument35 pagesAttentionDr-Marudhar MarudharNo ratings yet
- Attension Psychology AIDocument46 pagesAttension Psychology AIezaat.shalbyNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Process: Set of All Mental Abilities ProcessesDocument34 pagesCognitive Process: Set of All Mental Abilities ProcessesSwagata BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- HF Subjective Questions 1. Information ProcessingDocument5 pagesHF Subjective Questions 1. Information ProcessingraviNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument43 pagesAttentionSuhana KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AttentionDocument19 pagesChapter 4 AttentionJean GuirnaldoNo ratings yet
- Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual ProcessesDocument14 pagesSensory, Attentional and Perceptual ProcessesNemesha PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual ProcessesDocument42 pagesChapter 5 - Sensory, Attentional and Perceptual ProcessesSwapnil MauryaNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument37 pagesAttentionAkshi chauhanNo ratings yet
- Psychology AssignmentDocument7 pagesPsychology AssignmentAngelie AngelNo ratings yet
- DPSY-534 - 3 and 4 - AttentionDocument34 pagesDPSY-534 - 3 and 4 - AttentionDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Attention Lecture BssDocument18 pagesAttention Lecture Bssmoeed malikNo ratings yet
- Attention ShahzebDocument3 pagesAttention Shahzebumer rahimoonNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Attention Perception Learning Memory and ForgettingDocument163 pagesUnit 5 Attention Perception Learning Memory and ForgettingvivekNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AttentionDocument16 pagesUnit 5 AttentionvaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior (Perception)Document5 pagesHuman Behavior (Perception)Arna Francis Amor CosidoNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument34 pagesAttentionSTRANGE KHANNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument22 pagesAttentionNimra Bashir CheemaNo ratings yet
- BA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 1Document26 pagesBA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 1GPRNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument8 pagesAttentionKhushbooNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2getaravindh11No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6Crina MariaNo ratings yet
- Attention Process Nature DetermineneDocument21 pagesAttention Process Nature DetermineneAli A HusainiNo ratings yet
- Aattention. SameDocument5 pagesAattention. Sameycq5s9jdgnNo ratings yet
- Concentration and AttentionDocument7 pagesConcentration and AttentionAina KhanNo ratings yet
- ATTENTIONDocument12 pagesATTENTIONaritrayeebarman05No ratings yet
- Geetanjali Medical College and HospitalDocument25 pagesGeetanjali Medical College and HospitalAshish Doot100% (1)
- Cognition - Arnold Lewis Glass (1) (2) - Copia-137-186Document50 pagesCognition - Arnold Lewis Glass (1) (2) - Copia-137-186Regina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Attention - JF - 2024Document44 pagesTopic 7 - Attention - JF - 2024sadnimassin2No ratings yet
- Attention in PsychologyDocument10 pagesAttention in PsychologyJohn henryNo ratings yet
- Attention, Perception, Learning, Memory, & ForgettingDocument319 pagesAttention, Perception, Learning, Memory, & ForgettingKarthika M TharakanNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definition of AttentionDocument4 pagesMeaning and Definition of AttentionPlacement officerNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of School Psychology: AttentionDocument8 pagesEncyclopedia of School Psychology: AttentionAlonso Raymundo Chavarria RamirezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Attention: Cognitive PsychologyDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Attention: Cognitive Psychologyjai HindNo ratings yet
- Psychology Unit III PDFDocument34 pagesPsychology Unit III PDFOmprakash SwamiNo ratings yet
- AttentionDocument26 pagesAttentionKarn KunteNo ratings yet
- Ob Book4Document4 pagesOb Book4janvi singapuriNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPersonal DevelopmentFaevriseNo ratings yet
- Sensory, Attentional & Perceptual Processes: Main HighlightsDocument5 pagesSensory, Attentional & Perceptual Processes: Main HighlightsRitu DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Complex Cognitive Processes What Is Cognition ?: Two General Modes of CognitionDocument9 pagesComplex Cognitive Processes What Is Cognition ?: Two General Modes of CognitionAhmad ShahNo ratings yet
- Stenberg 1999 Attention Acts As A Means of Focusing Limited Mental Resources On The Information and Cognitive Processes That Are Most Salient at A Given MomentDocument3 pagesStenberg 1999 Attention Acts As A Means of Focusing Limited Mental Resources On The Information and Cognitive Processes That Are Most Salient at A Given MomentNadia Chan0% (1)
- Boost Your Concentration: Beat distractions and learn to focus on any taskFrom EverandBoost Your Concentration: Beat distractions and learn to focus on any taskRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Perception, Prejudice, and Bias FlashcardsDocument72 pagesPerception, Prejudice, and Bias FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- Motivation and AttitudesDocument2 pagesMotivation and AttitudesLoraNo ratings yet
- Three Components of Emotion Physiological Cognitive Behavioral Universal Emotions James-Lange TheoryDocument1 pageThree Components of Emotion Physiological Cognitive Behavioral Universal Emotions James-Lange TheoryLoraNo ratings yet
- Prior Exposure To A Stimulus Unfavorably Influences The Response To The Same StimulusDocument3 pagesPrior Exposure To A Stimulus Unfavorably Influences The Response To The Same StimulusLoraNo ratings yet
- Memory FlashcardsDocument98 pagesMemory FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- Language FlashcardsDocument52 pagesLanguage FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- Emotion FlashcardsDocument18 pagesEmotion FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- The Feeling of Disorientation Experienced by Someone Who Is Suddenly Subjected To An Unfamiliar Culture, Way of Life, or Set of AttitudesDocument1 pageThe Feeling of Disorientation Experienced by Someone Who Is Suddenly Subjected To An Unfamiliar Culture, Way of Life, or Set of AttitudesLoraNo ratings yet
- Cognition FlashcardsDocument92 pagesCognition FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- Culture FlashcardsDocument36 pagesCulture FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- OCHEMDocument9 pagesOCHEMLoraNo ratings yet
- Acid DerivativesDocument1 pageAcid DerivativesLoraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Flashcards AllDocument1 pageGeneral Chemistry Flashcards AllLoraNo ratings yet