Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Uploaded by
Arturo León CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Warm Up PDFDocument217 pagesThe Warm Up PDFProfe Borda100% (10)
- Psychology NotesDocument18 pagesPsychology NotesSamantha NeaveNo ratings yet
- The Developing BrainDocument8 pagesThe Developing BrainAca AvNo ratings yet
- Reverse: EngıneeringDocument8 pagesReverse: EngıneeringNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience of Learning and Development1 PDFDocument18 pagesNeuroscience of Learning and Development1 PDFmemememe100% (1)
- Lesson 6 - C4 Neurons & The BrainDocument11 pagesLesson 6 - C4 Neurons & The BrainSariniya SelvamohanNo ratings yet
- PSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesPSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceAngelica TumlodNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusDocument17 pagesNeuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusCLAIRE DENISSE DEVISNo ratings yet
- Mod 3Document41 pagesMod 3AchNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitFrom EverandBrain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitNo ratings yet
- Development of Neurons From Birth To AdulthoodDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Neurons From Birth To Adulthoodelizabethtorio1892No ratings yet
- Mr. Phinoj K Abraham (Moth) : Assistant Professor, SRM College of Occupational TherapyDocument34 pagesMr. Phinoj K Abraham (Moth) : Assistant Professor, SRM College of Occupational TherapyKazi AijazNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (STD 9) Lesson Plan - Zeenat GaziDocument4 pagesNervous System (STD 9) Lesson Plan - Zeenat GaziZest SpiritNo ratings yet
- Neural Development: Lic. Ruth Lopez Angie Colindres Ahtziri FloresDocument21 pagesNeural Development: Lic. Ruth Lopez Angie Colindres Ahtziri FloresManuel Colindres 2.0No ratings yet
- Miller2012 Braqin TeasersDocument1 pageMiller2012 Braqin Teasersiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The NeuroneDocument17 pagesLesson 4 - The NeuroneArgie M. EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Transplante Neuronas en Base A Celulas MadreDocument13 pagesTransplante Neuronas en Base A Celulas MadreRudy PerezNo ratings yet
- Document 25Document8 pagesDocument 25AroojNo ratings yet
- Perspectives: From The Neuron Doctrine To Neural NetworksDocument11 pagesPerspectives: From The Neuron Doctrine To Neural NetworksKira SAANo ratings yet
- Neurotransmission: "Muscle Messages": Set-UpDocument8 pagesNeurotransmission: "Muscle Messages": Set-UpDoris SmithNo ratings yet
- LABANDADocument3 pagesLABANDA22101051No ratings yet
- BD Research ReportDocument23 pagesBD Research Reportmrahaman.nbmcNo ratings yet
- Neuro Transm I SoresDocument30 pagesNeuro Transm I SoresAnonymous kpeMfIej9No ratings yet
- Brain AnatomyDocument2 pagesBrain AnatomyÖzge ŞenNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Research Paper 3Document11 pagesNeuroscience Research Paper 3post.office.document007No ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Ctivity ODocument4 pagesNervous Tissue: Ctivity OHannah MondillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 - Neural Signaling (Complete)Document20 pagesChapter 41 - Neural Signaling (Complete)Liana Glorian G. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Elife 77470 v2Document25 pagesElife 77470 v2ttqnhu.rhmNo ratings yet
- Acuerdo 038 de 2015Document6 pagesAcuerdo 038 de 2015rodrigo rodriguez pachonNo ratings yet
- How Learning WorksDocument3 pagesHow Learning WorksRubens RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NeuroplasticityDocument6 pagesUnit 2 NeuroplasticityKhushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Cognitive P. Chapter 2Document4 pagesCognitive P. Chapter 2May AloNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing Cell StainDocument2 pagesMost Amazing Cell StainJessieNo ratings yet
- Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesCognitive NeurosciencejanamsheikNo ratings yet
- Option A - Neurobiology and BehaviourDocument29 pagesOption A - Neurobiology and Behaviour玛丽娜No ratings yet
- Texto Unidad I - Cerebro y CondcutaDocument19 pagesTexto Unidad I - Cerebro y CondcutaDes ADNo ratings yet
- Demystifying The Adolescent BrainDocument7 pagesDemystifying The Adolescent Brainapi-609689257No ratings yet
- Brainwave Article A Squishy Wonder Brain Structure and Function FINALDocument4 pagesBrainwave Article A Squishy Wonder Brain Structure and Function FINALaritrayeebarman05No ratings yet
- Use It or Lose It - How Neurogenesis Keeps The Brain Fit For LearningDocument20 pagesUse It or Lose It - How Neurogenesis Keeps The Brain Fit For Learningmadalena limaNo ratings yet
- Miss Tanimowo Neuroplasticity PresentationDocument50 pagesMiss Tanimowo Neuroplasticity PresentationtanimowoodunayoNo ratings yet
- The Function of Mirror Neurons in The Learning Process: 1 NeurosciencesDocument7 pagesThe Function of Mirror Neurons in The Learning Process: 1 NeurosciencesJuliano MainardesNo ratings yet
- NeuronDocument11 pagesNeuronSaaraNo ratings yet
- Ajbsr MS Id 000960Document14 pagesAjbsr MS Id 000960TrishaNo ratings yet
- Brain Development The Human Brain: Adapted For Learning Meanings From Other PeopleDocument16 pagesBrain Development The Human Brain: Adapted For Learning Meanings From Other PeopleMaria Sílvia CintraNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Brain (Burrell 2016)Document4 pagesUnlocking The Brain (Burrell 2016)MaxNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurDocument3 pagesNeuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurluizetteNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Psych 140 NotesDocument16 pagesPsych 140 Notesjsjarabejo1No ratings yet
- The Scientist-What Do New Neurons in The Brains of Adults Actually DoDocument8 pagesThe Scientist-What Do New Neurons in The Brains of Adults Actually DoAna Paula Dantas PassosNo ratings yet
- Vogel2012-Can We Make Our Brains More PlasticDocument3 pagesVogel2012-Can We Make Our Brains More Plasticiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- AC3 UNIT 01 TextbookDocument22 pagesAC3 UNIT 01 TextbookAbigail QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Science of TheDocument60 pagesNeuroscience Science of TheALA Meditation - Relaxing MusicNo ratings yet
- Neuroscie3nce Core ConceptsDocument10 pagesNeuroscie3nce Core ConceptsDante AvilésNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Brain PDFDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Brain PDFRuxandra Laura VladNo ratings yet
- Neural and Social NetworkDocument49 pagesNeural and Social NetworkGL M. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument49 pagesPDF DocumentKhushi ThaparNo ratings yet
- Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument2 pagesLearning To Be A Better Studentsilfi.dalleNo ratings yet
- Fncir 10 00023Document13 pagesFncir 10 00023shivang patelNo ratings yet
- SFN Neuroscience Core Concepts2Document10 pagesSFN Neuroscience Core Concepts2Nicole VitalariuNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
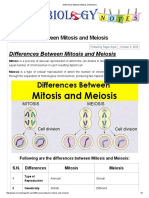
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisMeri SunderNo ratings yet
- How Do Muscles Grow - The Science of Muscle GrowthDocument5 pagesHow Do Muscles Grow - The Science of Muscle Growthamir17012076No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 - Science - NTSE (Biology) Quiz - 18Document4 pagesCBSE Class 10 - Science - NTSE (Biology) Quiz - 18Rajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- BIOL 3140 Lab Report 3Document21 pagesBIOL 3140 Lab Report 3Tabashir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13Document13 pages2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13italofgNo ratings yet
- Greenfield Convent School Syllabus 2022-2023Document4 pagesGreenfield Convent School Syllabus 2022-2023MarveliteNo ratings yet
- 15th Week Minerals 2023Document40 pages15th Week Minerals 2023VizhiNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document55 pagesDay 1ivancalderon867374No ratings yet
- Gastric Lavage: Intermittent Open SystemDocument1 pageGastric Lavage: Intermittent Open SystemSyabie YassinNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- Lignin, Lignocellulose, LigninaseDocument12 pagesLignin, Lignocellulose, LigninasectnbsNo ratings yet
- CC ReviewerDocument2 pagesCC ReviewerMerill Harrelson LibanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Asthma WordDocument4 pagesPediatric Asthma Wordraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument4 pagesSYLLABUSKhuLetzx GhuRlNo ratings yet
- TUBESDocument1 pageTUBESXamantha ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Poisons and PoisoningDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Poisons and PoisoningKhar Mel GoNo ratings yet
- Five Phase Treatments DR ManakaDocument20 pagesFive Phase Treatments DR ManakaKoa Carlos CastroNo ratings yet
- Limf NodeDocument34 pagesLimf NodeNika MtsituriNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RN, Manc Anatomy and Physiology InstructorDocument133 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RN, Manc Anatomy and Physiology InstructorHypothalamus1No ratings yet
- Triage Level 5Document78 pagesTriage Level 5DanielKnows100% (1)
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Document8 pagesLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To MetabolismDocument15 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To MetabolismMkhahlelwaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument17 pagesApproach To The Patient With Endocrine Disordersseun williamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 14 NotesRhianon Annie McDowellNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Scale Up of Industrial Fermentation ProcessesDocument11 pagesOptimization and Scale Up of Industrial Fermentation ProcessesFauzan PutraNo ratings yet
- Abductor Muscles and Their FunctionDocument2 pagesAbductor Muscles and Their Functionstargazerlilies07No ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise: General Types of Aerobic ExercisesDocument2 pagesAerobic Exercise: General Types of Aerobic ExercisesPAULINE DEOCAMPONo ratings yet
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Uploaded by
Arturo León CastroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Habits & Triggers: Neuroplasticity
Uploaded by
Arturo León CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
Teaching an Old Dog
New Tricks
Previously, scientists thought that the
brain's structure was hard-wired and
immutable. Brain-damaged patients
rarely made full recoveries and the
living brain’s microscopic activities
-i - i
were unobservable. The widely held >
belief was that the brain was a machine:
machines are capable o f many things,
but they do not change and grow.
New research has taught us that the brain is actually plastic, it is able to change based on
experiences. Even in old age. the adult brain retains neuroplasticity and is able to change its
structure and function. It turns out you can teach an old dog new tricks!
Dendrite
N eurons
Neurons process and transmit
information through electrical
and chemical signals.
There are around 86 billion
neurons in the human brain.
Synapses
Synapses are the small gaps Neurotransmitter
between neurons. They allow molecules F Dendrite
information to pass from one
neuron to the next.
Synapse
Birth 3 vrs old
,
Adult Brain
Approx. 2.500 Approx. 15.000 Use it or lose it: 50% o f
synapses synapses neurons do not survive into
Infant brain: large adulthood as rarelv used .
capacity for growth synapses are eliminated Nerve
ending
throughout adolescence.
N eu ro g en esis
The production o f neurons, beginning week 3 o f human
development at a rate o f 250,000/niinute until birth.
Previous thought...
Neurons cannot reproduce after the first tew years ot life
. .
New research: neurogenesis may continue The Future: there is growing hope that
to occur throughout human life span. science will discover an effective way
In 1999. researchers at the Salk Institute. to guide the process o f neuronal growth
San Diego discovered neurogenesis to repair areas o f the brain that are iI
occurring in the brain o f a 72-year-old adult! damaged by injury or disease.
/
Pathw ays N e u ro p la sticity
Neural pathways connect relatively
distant areas o f the brain or nervous
New thoughts and
system, each pathway is associated
skills carve out new
with a particular action or behavior.
pathways.
a
Repetition and
practice strengthen
these pathways,
forming new habits.
I
Old pathways get used
*
less and weaken.
Every time we think, feel or do something,
we strengthen this pathway. Habits are With repeated and direct attention
well travelled pathways - our brain finds towards a desired change, we all have
these things easy to do. the ability to rewire our brains.
Pleasure & Reward
The Mesolimbic Dopamine System
/
The brain's reward pathway encourages us to seek out activities essential to species survival.
Food & Drink Shelter Sex Nurturing
The reward pathway is activated, the brain floods with dopamine.
We feel good, we seek to repeat the activity.
"Hey, this cake is really good.
I ’m going to remember that fo r the future. "
Dopamine Hippocampus lays Desire
reward down memories to eat more
!/
H ijackin g the brain
,
Dopamine release and behaviors essential to survival take place in the midbrain.
which always trumps the cerebral cortex.
The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, thought and consciousness.
Substance Reward system Hippocampus
is consumed floods with remembers rapid
dopamine sense of satisfaction
Prefrontal cortex Hippocampus
Drives user to seek Remembers
out the substance rapid sense
o f satisfaction
Amygdala
Q Remembers environmental
Nucleus accumbens T. cues (people, places.
* * Dopamine released JJ sights, sounds)
Environmental cues create intense cravings
“ The reward pathway is intimately connected to our judgm ent
and emotional areas. Judgm ent becomes distorted and the
brain begins to treat the substance as necessary fo r survival. ”
David Sm ith. M .D . co-author o f Unchain Your Brain
j.
The A d d ict's Brain
What makes a substance / behavior addictive?
Speed o f Intensity o f Reliability of V
dopamine release dopamine release dopamine release
Addictive drugs can release 2 to 10 times the amount o f dopamine
.
that natural rewards do and they do it more quickly and more reliably.
D eve lo p in g Tolerance
Repeated Number o f Original Dosage has to Eventually, high
overstimulation dopamine dosage gives be increased doses are required
receptors less reward to achieve just to stave off
<
« r reduced original high withdrawal
HAB I TS & T R I G G E R S
'__'•
“Habits play an important role in our health. Understanding the
biology o f how we develop routines that may be harmful to us.
and how to break those routines and embrace new ones, could
help us change our lifestyles and adopt healthier behaviors. ”
Dr. Nora Volkow - National Institute of Health
Recognize and ayoid triggers:
Enyironniental Social Emotional
triggers triggers triggers
Places, locations, Family, friends, Depression, stress,
smells, sounds other users exhaustion, frustration,
anger, anxiety, loneliness
$
T rig g e rs cause a dow nw ard spiral
i
R eco gnizing trig g e rs
.
“F o r relapse prevention, it is crucial to understand the
environmental cues that trigger cravings. Recovery is
rechanneling the brain so that when those cues come, you r
brain is channeled to brain-healthy activities. Eventually,
when the craving occurs, the brain returns to homeostasis
much more readily.-
Recovetw .
becomes
i
more natural, and
you get the healthy reward. ”
** , ,
David Sm ith. M .D . co-author of Unchain S our Brain
R E W I R I N G T H E BRAIN
Neuroplasticity
‘Neuro ’ = brains ‘Plastic ’ = changeable
a
Neuroplasticity promises a new understanding o f what it means
to be human: we can rew ire our brains ju st by thinking!
Practice, P ractice, Practice!
“Rewiring requires setting new goals and practicing the healthy
pursuit o f reward while the brain is creating new pathways. ”
David Sm ith. M .D . co-author o f Unchain S our Brain
N e u ro p la sticity
Set goals Recognise Make Seek pleasure New pathway New healthy
triggers conscious and reward is strengthened habit is formed
decisions from healthv
pursuits
P rep aratio n
Ayoid Leam to live a Exercise, try Seek support from
substances comfortable and yoga and peers and take care
that provide responsible life in meditation o f yourself:
unhealthy rewards which your brain don’ t get too tired,
is rewarded by too hungry, too
healthy pursuits lonely, too angry
Brain Training
If we don’t learn new skills, we don’t engage our brain's plasticity.
Highly focused activities help keep the brain in good shape, why not try:
Learning a Career Logistical Newr
new language change puzzles environments
“ When everything else is controlled fo r, bilinguals who
come down with Alzheim er's do so about 4 .5 years later
than monolinguals. ”
Dr. Thomas Bak University o f Edinburgh
You might also like
- The Warm Up PDFDocument217 pagesThe Warm Up PDFProfe Borda100% (10)
- Psychology NotesDocument18 pagesPsychology NotesSamantha NeaveNo ratings yet
- The Developing BrainDocument8 pagesThe Developing BrainAca AvNo ratings yet
- Reverse: EngıneeringDocument8 pagesReverse: EngıneeringNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience of Learning and Development1 PDFDocument18 pagesNeuroscience of Learning and Development1 PDFmemememe100% (1)
- Lesson 6 - C4 Neurons & The BrainDocument11 pagesLesson 6 - C4 Neurons & The BrainSariniya SelvamohanNo ratings yet
- PSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesPSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceAngelica TumlodNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusDocument17 pagesNeuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusCLAIRE DENISSE DEVISNo ratings yet
- Mod 3Document41 pagesMod 3AchNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitFrom EverandBrain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitNo ratings yet
- Development of Neurons From Birth To AdulthoodDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Neurons From Birth To Adulthoodelizabethtorio1892No ratings yet
- Mr. Phinoj K Abraham (Moth) : Assistant Professor, SRM College of Occupational TherapyDocument34 pagesMr. Phinoj K Abraham (Moth) : Assistant Professor, SRM College of Occupational TherapyKazi AijazNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (STD 9) Lesson Plan - Zeenat GaziDocument4 pagesNervous System (STD 9) Lesson Plan - Zeenat GaziZest SpiritNo ratings yet
- Neural Development: Lic. Ruth Lopez Angie Colindres Ahtziri FloresDocument21 pagesNeural Development: Lic. Ruth Lopez Angie Colindres Ahtziri FloresManuel Colindres 2.0No ratings yet
- Miller2012 Braqin TeasersDocument1 pageMiller2012 Braqin Teasersiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The NeuroneDocument17 pagesLesson 4 - The NeuroneArgie M. EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Transplante Neuronas en Base A Celulas MadreDocument13 pagesTransplante Neuronas en Base A Celulas MadreRudy PerezNo ratings yet
- Document 25Document8 pagesDocument 25AroojNo ratings yet
- Perspectives: From The Neuron Doctrine To Neural NetworksDocument11 pagesPerspectives: From The Neuron Doctrine To Neural NetworksKira SAANo ratings yet
- Neurotransmission: "Muscle Messages": Set-UpDocument8 pagesNeurotransmission: "Muscle Messages": Set-UpDoris SmithNo ratings yet
- LABANDADocument3 pagesLABANDA22101051No ratings yet
- BD Research ReportDocument23 pagesBD Research Reportmrahaman.nbmcNo ratings yet
- Neuro Transm I SoresDocument30 pagesNeuro Transm I SoresAnonymous kpeMfIej9No ratings yet
- Brain AnatomyDocument2 pagesBrain AnatomyÖzge ŞenNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Research Paper 3Document11 pagesNeuroscience Research Paper 3post.office.document007No ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Ctivity ODocument4 pagesNervous Tissue: Ctivity OHannah MondillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 - Neural Signaling (Complete)Document20 pagesChapter 41 - Neural Signaling (Complete)Liana Glorian G. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Elife 77470 v2Document25 pagesElife 77470 v2ttqnhu.rhmNo ratings yet
- Acuerdo 038 de 2015Document6 pagesAcuerdo 038 de 2015rodrigo rodriguez pachonNo ratings yet
- How Learning WorksDocument3 pagesHow Learning WorksRubens RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NeuroplasticityDocument6 pagesUnit 2 NeuroplasticityKhushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Cognitive P. Chapter 2Document4 pagesCognitive P. Chapter 2May AloNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing Cell StainDocument2 pagesMost Amazing Cell StainJessieNo ratings yet
- Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument10 pagesCognitive NeurosciencejanamsheikNo ratings yet
- Option A - Neurobiology and BehaviourDocument29 pagesOption A - Neurobiology and Behaviour玛丽娜No ratings yet
- Texto Unidad I - Cerebro y CondcutaDocument19 pagesTexto Unidad I - Cerebro y CondcutaDes ADNo ratings yet
- Demystifying The Adolescent BrainDocument7 pagesDemystifying The Adolescent Brainapi-609689257No ratings yet
- Brainwave Article A Squishy Wonder Brain Structure and Function FINALDocument4 pagesBrainwave Article A Squishy Wonder Brain Structure and Function FINALaritrayeebarman05No ratings yet
- Use It or Lose It - How Neurogenesis Keeps The Brain Fit For LearningDocument20 pagesUse It or Lose It - How Neurogenesis Keeps The Brain Fit For Learningmadalena limaNo ratings yet
- Miss Tanimowo Neuroplasticity PresentationDocument50 pagesMiss Tanimowo Neuroplasticity PresentationtanimowoodunayoNo ratings yet
- The Function of Mirror Neurons in The Learning Process: 1 NeurosciencesDocument7 pagesThe Function of Mirror Neurons in The Learning Process: 1 NeurosciencesJuliano MainardesNo ratings yet
- NeuronDocument11 pagesNeuronSaaraNo ratings yet
- Ajbsr MS Id 000960Document14 pagesAjbsr MS Id 000960TrishaNo ratings yet
- Brain Development The Human Brain: Adapted For Learning Meanings From Other PeopleDocument16 pagesBrain Development The Human Brain: Adapted For Learning Meanings From Other PeopleMaria Sílvia CintraNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Brain (Burrell 2016)Document4 pagesUnlocking The Brain (Burrell 2016)MaxNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurDocument3 pagesNeuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurluizetteNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Psych 140 NotesDocument16 pagesPsych 140 Notesjsjarabejo1No ratings yet
- The Scientist-What Do New Neurons in The Brains of Adults Actually DoDocument8 pagesThe Scientist-What Do New Neurons in The Brains of Adults Actually DoAna Paula Dantas PassosNo ratings yet
- Vogel2012-Can We Make Our Brains More PlasticDocument3 pagesVogel2012-Can We Make Our Brains More Plasticiulia andreeaNo ratings yet
- AC3 UNIT 01 TextbookDocument22 pagesAC3 UNIT 01 TextbookAbigail QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Science of TheDocument60 pagesNeuroscience Science of TheALA Meditation - Relaxing MusicNo ratings yet
- Neuroscie3nce Core ConceptsDocument10 pagesNeuroscie3nce Core ConceptsDante AvilésNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Brain PDFDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Brain PDFRuxandra Laura VladNo ratings yet
- Neural and Social NetworkDocument49 pagesNeural and Social NetworkGL M. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument49 pagesPDF DocumentKhushi ThaparNo ratings yet
- Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument2 pagesLearning To Be A Better Studentsilfi.dalleNo ratings yet
- Fncir 10 00023Document13 pagesFncir 10 00023shivang patelNo ratings yet
- SFN Neuroscience Core Concepts2Document10 pagesSFN Neuroscience Core Concepts2Nicole VitalariuNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisMeri SunderNo ratings yet
- How Do Muscles Grow - The Science of Muscle GrowthDocument5 pagesHow Do Muscles Grow - The Science of Muscle Growthamir17012076No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 - Science - NTSE (Biology) Quiz - 18Document4 pagesCBSE Class 10 - Science - NTSE (Biology) Quiz - 18Rajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- BIOL 3140 Lab Report 3Document21 pagesBIOL 3140 Lab Report 3Tabashir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13Document13 pages2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13italofgNo ratings yet
- Greenfield Convent School Syllabus 2022-2023Document4 pagesGreenfield Convent School Syllabus 2022-2023MarveliteNo ratings yet
- 15th Week Minerals 2023Document40 pages15th Week Minerals 2023VizhiNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document55 pagesDay 1ivancalderon867374No ratings yet
- Gastric Lavage: Intermittent Open SystemDocument1 pageGastric Lavage: Intermittent Open SystemSyabie YassinNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- Lignin, Lignocellulose, LigninaseDocument12 pagesLignin, Lignocellulose, LigninasectnbsNo ratings yet
- CC ReviewerDocument2 pagesCC ReviewerMerill Harrelson LibanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Asthma WordDocument4 pagesPediatric Asthma Wordraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument4 pagesSYLLABUSKhuLetzx GhuRlNo ratings yet
- TUBESDocument1 pageTUBESXamantha ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Poisons and PoisoningDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Poisons and PoisoningKhar Mel GoNo ratings yet
- Five Phase Treatments DR ManakaDocument20 pagesFive Phase Treatments DR ManakaKoa Carlos CastroNo ratings yet
- Limf NodeDocument34 pagesLimf NodeNika MtsituriNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RN, Manc Anatomy and Physiology InstructorDocument133 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RN, Manc Anatomy and Physiology InstructorHypothalamus1No ratings yet
- Triage Level 5Document78 pagesTriage Level 5DanielKnows100% (1)
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Document8 pagesLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To MetabolismDocument15 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To MetabolismMkhahlelwaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument17 pagesApproach To The Patient With Endocrine Disordersseun williamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 14 NotesRhianon Annie McDowellNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Scale Up of Industrial Fermentation ProcessesDocument11 pagesOptimization and Scale Up of Industrial Fermentation ProcessesFauzan PutraNo ratings yet
- Abductor Muscles and Their FunctionDocument2 pagesAbductor Muscles and Their Functionstargazerlilies07No ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise: General Types of Aerobic ExercisesDocument2 pagesAerobic Exercise: General Types of Aerobic ExercisesPAULINE DEOCAMPONo ratings yet