Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infinitives PDF
Infinitives PDF
Uploaded by
jair zepedaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument35 pagesGerunds and Infinitivesedlira100% (1)
- Sintesis de Periodo Grado DecimoDocument13 pagesSintesis de Periodo Grado DecimoEnglish Teacher GCSSNo ratings yet
- Ing To PDFDocument2 pagesIng To PDFCristina Fonte100% (1)
- Infinitive-Gerund ExerciseDocument1 pageInfinitive-Gerund ExerciseReNSsNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument5 pagesInfinitive and GerundFATHIMAH MINHAH EL FITHRI Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesGerund or InfinitivejanetNo ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsHoshi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Everything About Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesEverything About Gerunds and InfinitivesRonald Coras GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Gerund or Infinitive Task 3Document5 pagesGerund or Infinitive Task 3Gaby ArceNo ratings yet
- Non - Finite VerbsDocument4 pagesNon - Finite Verbsmohitguptabtech100% (1)
- Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Document5 pagesInfinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Erickk MendezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesdindaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Your Work) To See How The Phrase Modifies and Focuses The NounDocument8 pagesSubject: Your Work) To See How The Phrase Modifies and Focuses The NounLia NovarinaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitive and GerundsMonica TiriraNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument16 pagesVerb Patternssamir.khwajazada786No ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pages3.1.2 Gerunds and InfinitivesErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument3 pagesInfinitive and GerundNgọc LinhNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitiveDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitiveHildha Nurmalasari DewiNo ratings yet
- Gerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Document12 pagesGerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Lukas PavardisNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and Gerund in EnglishDocument3 pagesInfinitive and Gerund in EnglishRaul Wal SchNo ratings yet
- Class 11 InfinitiveDocument14 pagesClass 11 InfinitiveKamrul Islam1996No ratings yet
- Grammar Task I Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Document6 pagesGrammar Task I Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Evelia Gar RojNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives With Verbs Part 1Document7 pagesGerunds and Infinitives With Verbs Part 1EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesKatherine JuleNo ratings yet
- Infiniteves & - Ing Forms EFL MaterialDocument6 pagesInfiniteves & - Ing Forms EFL MaterialJaryn CapekNo ratings yet
- Grammar Course Lecture Four Infintive PhrasesDocument5 pagesGrammar Course Lecture Four Infintive Phrasesfarawella09No ratings yet
- Verbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningDocument3 pagesVerbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningBeatrice FanareanuNo ratings yet
- To InfinitivesDocument30 pagesTo InfinitivesReza NoviandaNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument17 pagesGerund or InfinitiveFebriantiKomalasariNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeDocument14 pagesAuxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeMaxi ygn100% (1)
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument3 pagesGerund or InfinitiveNORMA ZOGHEIBNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument51 pagesVerbalsnemat.muhammadi786No ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsCARLOS ANDRES HOSTIA VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- NP C8 CD8.1 ScriptDocument5 pagesNP C8 CD8.1 ScriptGinko KuinNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Rules: Infinitive and GerundDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules: Infinitive and GerundAlde AndroNo ratings yet
- Bare InfinitiveDocument4 pagesBare Infinitivesammer30No ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: English Grammar TodayDocument6 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: English Grammar TodayVeronica Sucino RomeroNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitivesDocument24 pagesGerund and InfinitivesSeptiana Dewi AlhabbiyNo ratings yet
- G I: T N R: Erunds AND Nfinitives Heir OUN OlesDocument8 pagesG I: T N R: Erunds AND Nfinitives Heir OUN OlesSix minutesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bad HabitDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Bad HabitJabal Thoriq Ibrahim 1F-D3 ADBISNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1ELAINE OPPENo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument18 pagesTrabajo de InglesLuisAntonioMagallanesMartinezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de InglesDocument6 pagesEjercicios de InglesEDWIN ALONSO SANCHEZ BUTRONNo ratings yet
- Non-Finite-Forms - Infinitive & G.Document13 pagesNon-Finite-Forms - Infinitive & G.JosephinaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and GeruDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by An Infinitive and Gerunestor caroNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument15 pagesGerund and InfinitiveRosario CibrianNo ratings yet
- Ing or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesIng or Infinitivemilenerato2240No ratings yet
- Gerunds Vs InfinitivesDocument19 pagesGerunds Vs InfinitivesRoosevelt SantosNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and InfinitiveReuben VarnerNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument7 pagesGerund or InfinitiveQue Verbo BataNo ratings yet
- GERUNDDocument8 pagesGERUNDValentine NNo ratings yet
- GuideDocument14 pagesGuideedmondusNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and Infinitivezaenal mfdNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and Infinitivezaenal mfdNo ratings yet
- GerundsDocument18 pagesGerundsAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument5 pagesGerund or InfinitiveVICTOR MANUEL VAZQUEZ MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Gerunds & InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds & InfinitivesM TZONo ratings yet
- Simple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sFrom EverandSimple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Word Translation Example SentenceDocument2 pagesWord Translation Example Sentencejair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Suki 2Document1 pageSuki 2jair zepedaNo ratings yet
- PASADOPDocument1 pagePASADOPjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Jaqueline Ramirez Felix: Word Translation Example SentenceDocument3 pagesJaqueline Ramirez Felix: Word Translation Example Sentencejair zepedaNo ratings yet
- How Could We Change The WorldDocument6 pagesHow Could We Change The Worldjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Present Past Past Participle GerundDocument7 pagesPresent Past Past Participle Gerundjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Get PhrasesDocument1 pageGet Phrasesjair zepedaNo ratings yet
Infinitives PDF
Infinitives PDF
Uploaded by
jair zepedaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infinitives PDF
Infinitives PDF
Uploaded by
jair zepedaCopyright:
Available Formats
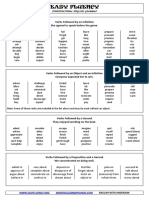
INFINITIVES
Infinitives are forms like (to) write, (to) stand. Unlike verb tenses (e. g. writes, stood), infinitives do not usually
show the actual times of actions or events. They usually refer to actions and events in a more general way,
rather like –ing forms.
Infinitives have many functions. An infinitive can be used, for example:
A. After do or a modal auxiliary verb, as part of the verb phrase.
Do you think she´s ready? You must get some more light bulbs.
B. As a subject or complement of a clause
To watch him eating really gets on my nerves.
The main thing is to stay in calm. It´s nice to talk to you.
In older English, an infinitive could be the subject of a sentence.
To make mistakes is easy. To wait for people who were late made him angry.
In modern English is more often use it as a “preparatory subject” and put the infinitive later.
It´s easy to make mistakes.
It made him angry to wait for people who were late.
C. To express person´s purpose
He comes to London to look for work. They went to the supermarket to buy food
She called her father to say happy birthday
D. As object or complement of a verb, adjective or noun.
I don´t want to go to bed. You have the right to remain silent.
I´m anxious to contact your brother.
After many non-auxiliary verbs, we can use the infinitives of other verbs.
It´s beginning to rain. I don´t want to see you again.
She seems to be crying. I expect to have finished by tomorrow evening.
The car needs to be cleaned.
Common verbs that can be followed by infinitives.
Afford Agree Appear Ask Be sure Care
Choose Continue Decide Expect Forget Help
Hope Learn Like Need Offer order
Plan Prepare Refuse Regret Remember Seem
Teach Try Want wish Would like
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument35 pagesGerunds and Infinitivesedlira100% (1)
- Sintesis de Periodo Grado DecimoDocument13 pagesSintesis de Periodo Grado DecimoEnglish Teacher GCSSNo ratings yet
- Ing To PDFDocument2 pagesIng To PDFCristina Fonte100% (1)
- Infinitive-Gerund ExerciseDocument1 pageInfinitive-Gerund ExerciseReNSsNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument5 pagesInfinitive and GerundFATHIMAH MINHAH EL FITHRI Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesGerund or InfinitivejanetNo ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsHoshi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Everything About Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesEverything About Gerunds and InfinitivesRonald Coras GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Gerund or Infinitive Task 3Document5 pagesGerund or Infinitive Task 3Gaby ArceNo ratings yet
- Non - Finite VerbsDocument4 pagesNon - Finite Verbsmohitguptabtech100% (1)
- Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Document5 pagesInfinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Erickk MendezNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesdindaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Your Work) To See How The Phrase Modifies and Focuses The NounDocument8 pagesSubject: Your Work) To See How The Phrase Modifies and Focuses The NounLia NovarinaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundsDocument4 pagesInfinitive and GerundsMonica TiriraNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument16 pagesVerb Patternssamir.khwajazada786No ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pages3.1.2 Gerunds and InfinitivesErick GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument3 pagesInfinitive and GerundNgọc LinhNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitiveDocument6 pagesGerunds and InfinitiveHildha Nurmalasari DewiNo ratings yet
- Gerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Document12 pagesGerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Lukas PavardisNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and Gerund in EnglishDocument3 pagesInfinitive and Gerund in EnglishRaul Wal SchNo ratings yet
- Class 11 InfinitiveDocument14 pagesClass 11 InfinitiveKamrul Islam1996No ratings yet
- Grammar Task I Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Document6 pagesGrammar Task I Infinitive and Gerund Infinitive: After An Adjective After Certain Verbs (With To)Evelia Gar RojNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives With Verbs Part 1Document7 pagesGerunds and Infinitives With Verbs Part 1EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument5 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesKatherine JuleNo ratings yet
- Infiniteves & - Ing Forms EFL MaterialDocument6 pagesInfiniteves & - Ing Forms EFL MaterialJaryn CapekNo ratings yet
- Grammar Course Lecture Four Infintive PhrasesDocument5 pagesGrammar Course Lecture Four Infintive Phrasesfarawella09No ratings yet
- Verbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningDocument3 pagesVerbs That Are Normally Followed by The Gerund Form:-: With No Change in MeaningBeatrice FanareanuNo ratings yet
- To InfinitivesDocument30 pagesTo InfinitivesReza NoviandaNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument17 pagesGerund or InfinitiveFebriantiKomalasariNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeDocument14 pagesAuxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeMaxi ygn100% (1)
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument3 pagesGerund or InfinitiveNORMA ZOGHEIBNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument51 pagesVerbalsnemat.muhammadi786No ratings yet
- TenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsDocument11 pagesTenorioIslas Elizabeth Infinitives and GerundsCARLOS ANDRES HOSTIA VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- NP C8 CD8.1 ScriptDocument5 pagesNP C8 CD8.1 ScriptGinko KuinNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Rules: Infinitive and GerundDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules: Infinitive and GerundAlde AndroNo ratings yet
- Bare InfinitiveDocument4 pagesBare Infinitivesammer30No ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: English Grammar TodayDocument6 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: English Grammar TodayVeronica Sucino RomeroNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitivesDocument24 pagesGerund and InfinitivesSeptiana Dewi AlhabbiyNo ratings yet
- G I: T N R: Erunds AND Nfinitives Heir OUN OlesDocument8 pagesG I: T N R: Erunds AND Nfinitives Heir OUN OlesSix minutesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bad HabitDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Bad HabitJabal Thoriq Ibrahim 1F-D3 ADBISNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1ELAINE OPPENo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument18 pagesTrabajo de InglesLuisAntonioMagallanesMartinezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de InglesDocument6 pagesEjercicios de InglesEDWIN ALONSO SANCHEZ BUTRONNo ratings yet
- Non-Finite-Forms - Infinitive & G.Document13 pagesNon-Finite-Forms - Infinitive & G.JosephinaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by An Infinitive and GeruDocument2 pagesVerbs Followed by An Infinitive and Gerunestor caroNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument15 pagesGerund and InfinitiveRosario CibrianNo ratings yet
- Ing or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesIng or Infinitivemilenerato2240No ratings yet
- Gerunds Vs InfinitivesDocument19 pagesGerunds Vs InfinitivesRoosevelt SantosNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and InfinitiveReuben VarnerNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument7 pagesGerund or InfinitiveQue Verbo BataNo ratings yet
- GERUNDDocument8 pagesGERUNDValentine NNo ratings yet
- GuideDocument14 pagesGuideedmondusNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and Infinitivezaenal mfdNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument18 pagesGerund and Infinitivezaenal mfdNo ratings yet
- GerundsDocument18 pagesGerundsAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument5 pagesGerund or InfinitiveVICTOR MANUEL VAZQUEZ MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Gerunds & InfinitivesDocument6 pagesGerunds & InfinitivesM TZONo ratings yet
- Simple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sFrom EverandSimple English: Phrasal Verbs: 100s of examples + MP3sRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Word Translation Example SentenceDocument2 pagesWord Translation Example Sentencejair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Suki 2Document1 pageSuki 2jair zepedaNo ratings yet
- PASADOPDocument1 pagePASADOPjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Jaqueline Ramirez Felix: Word Translation Example SentenceDocument3 pagesJaqueline Ramirez Felix: Word Translation Example Sentencejair zepedaNo ratings yet
- How Could We Change The WorldDocument6 pagesHow Could We Change The Worldjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Present Past Past Participle GerundDocument7 pagesPresent Past Past Participle Gerundjair zepedaNo ratings yet
- Get PhrasesDocument1 pageGet Phrasesjair zepedaNo ratings yet