Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7th SST AnswerKey 25aug-102825202034311 PDF
7th SST AnswerKey 25aug-102825202034311 PDF
Uploaded by
Mitanshu Mittal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesThe document is about the structure and composition of the Earth. It discusses:
1) The Earth is divided into three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and is made of rocks and soil. The mantle lies below the crust and is composed of molten rock. The core is the innermost layer and is made of iron and nickel.
2) There are three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks form from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from other rocks being changed by heat and pressure.
3) Fossil
Original Description:
Original Title
7th_SST_AnswerKey_25Aug-102825202034311.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is about the structure and composition of the Earth. It discusses:
1) The Earth is divided into three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and is made of rocks and soil. The mantle lies below the crust and is composed of molten rock. The core is the innermost layer and is made of iron and nickel.
2) There are three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks form from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from other rocks being changed by heat and pressure.
3) Fossil
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pages7th SST AnswerKey 25aug-102825202034311 PDF
7th SST AnswerKey 25aug-102825202034311 PDF
Uploaded by
Mitanshu MittalThe document is about the structure and composition of the Earth. It discusses:
1) The Earth is divided into three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and is made of rocks and soil. The mantle lies below the crust and is composed of molten rock. The core is the innermost layer and is made of iron and nickel.
2) There are three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks form from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from other rocks being changed by heat and pressure.
3) Fossil
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
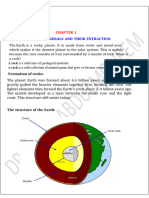
Ch-2 (Inside Our Earth)
Class: 7th Subject:-Social Science Date: 25-08-2020
Answer Key
A. Explain the following terms :
(a) Crust : The topmost layer of the Earth’s surface which is made-up of rocks and soil is called the crust.
(b) Mantle : The mantle is a layer between the crust and the outer core of the earth.
(c) Core : The innermost layer of the Earth is called core. The core is made-up of Nickel (Ni) and Iron (Fe).
The core is extremely hot (3000°C to 6000°C) and pressure on the core is extremely high.
(d) Sial : It is the upper crust comprising of continental masses. It is made of light weight material. It is
mainly composed of two minerals—Silica (Si) and Aluminium (Al). That is why it is called Sial.
(e) Sima : It is the lower part of the crust comprising of thin and fragile ocean floor. It is denser than the
continental crust. It is composed of minerals like Silicon (Si) and Magnesium (Ma). That is why it is
called Sima.
(f) Nife : It is the innermost layer of the Earth. It is composed of minerals like Nickel (Ni) and Iron (Fe).
That is why it is called Nife.
(g) Magma : The molten material in the lower mantle is called magma. The average temperature of this
molten material is 2200°C. It flows out of the earth during volcanic eruptions.
(h) Lava : During volcanic eruptions magma is released on the surface of the earth. It is called Lava. This
molten lava flows out through a lava tube.
(i) Fossil Fuel : Minerals that are formed from the remains of dead and decomposed animals and plants
trapped inside the earth long, long ago are called fossil fuels. They are non-renewable resources of
energy.
(j) Minerals : Minerals are naturally occurring substances having definite structure and physical
properties. They are not made by human beings. Each mineral has a chemical composition. For
example mica, quartz, feldspar, diamond are some minerals.
B. Multiple Choice Questions :
1. (a) crust 2. (b) Nife 3. (a) molten material
4. (b) solid metal 5. (b) Ores 6. (c) Diamond
7. (a) Marble 8. (a) Clay
C. Answer the following :
1. The earth is divided into three main layers :
(a) Crust : The topmost layer of the earth’s surface which is made up of rocks and soil is called the
crust. It is this layer that supports life.
(b) Mantle : Most of the earth’s interior is made up of the layer of the molten rock. It lies between
the solid crust and the hot and dense core.
(c) Core : The innermost layer of the earth is called the core. The core is made up of Nickel (Ni) and
Iron (Fe). The Pressure on the core is extremely high.
2. The rocks which are formed by the internal heat of the earth are called igneous rocks. Igneous
rocks were the first to be formed on the surface of the earth so they are called primary rocks. All
other rocks are formed from them.
3. (a) Igneous rocks are formed from molten magma found abundantly in the interior of the earth.
Magma cools and solidifies into rock.
(b) When igneous rocks are exposed on the surface, due to the action of wind, water, plants or
animals, they break down into smaller pieces called sediments. Wind and water carry these
sediments and deposit them in different places. With time the sediments get buried and
compressed resulting into layered rocks with wave like patterns known as sedimentary rocks.
(c) Metamorphic rocks are formed when the sedimentary or igneous rocks get buried deep into
the earth. Heat and pressure inside the earth bakes the rock, changing it into something new.
4. Minerals that are formed from the remains of dead and decomposed animals and plants trapped
inside the earth long, long ago are called fossil fuels. These minerals are important sources of
energy and are of non-renewable nature. Coal, petroleum and natural gas are examples of fossil
fuels.
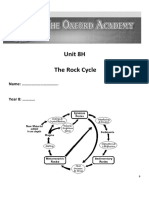
5. The continuous process in which a rock changes from one kind to another is called rock cycle.
(i) Cooling of magma results in the formation of igneous rocks.
(ii) Forces of nature, like sunrays, rain, wind disintegrate these rocks.
(iii) The broken rocks get deposited on the floor of seas, oceans, lakes and rivers and form
sedimentary rocks.
(iv) Extreme heat and pressure inside the earth changes sedimentary rocks into metamorphic
rocks.
(v) Due to extreme heat and pressure inside the earth, sometimes metamorphic and sedimentary
rocks melt to form magma.
(vi) Magma comes out through cracks in the crust of the earth, cools and solidifies to form igneous
rocks.
(vii) In this way rock cycle goes on.
6. Importance of rocks :
(i) Hard rocks are extensively used in construction.
(ii) Minerals like coal and petroleum are sources of fossil fuels.
(iii) Rocks provide metallic ores which are used in the industry.
(iv) Some rocks are sources of precious and semi-precious stones and gems used in jewellery.
(v) Minerals in the rocks provide nutrients needed by the plants.
Hots :
1. Igneous rocks are formed from molten magma found abundantly in the interior of the earth.
Magma cools and solidifies into rock. Igneous rocks are hard and non-porous. They do not allow
remains of dead and decomposed animals and plants get embedded and compressed in the layers
of these rocks.
2. Certain rocks contains metals which can be extracted economically and can be used for the
construction purposes. These rocks are called ores. For example, Bauxite is an ore of Aluminium.
Haematite is an ore of Iron.
D. Distinguish between the following : (a)
Intrusive rocks Extrusive rocks
1. These rocks are formed 1. These rocks are formed
when molten magma gets when lava, coming out of
trapped inside the earth. volcano, reaches the surface
of the earth.
2. These rocks take a very long 2. These rocks rapidly cool
time to cool down and down and solidify.
solidify.
3. These types of rocks have 3. These types of rocks have a
larger grains, for example, fine grained structure, for
Granite. example, Basalt rocks.
Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks
1. Igneous is derived from Latin word 1. Sedimentary is derived from Latin
‘ignis’ meaning ‘fiery’. word ‘sedimentum’ meaning
‘settle down’.
2. These are formed from molten 2. These are formed from the
(b) magma. fragments of other rocks.
3. These are formed by the internal 3. These are formed by weathering of
heat of the earth. igneous rocks by action of wind,
water, plants or animals.
4. These are known as primary rocks. 4. These are known as secondary
rocks.
5. These are good sources of metallic 5. These are good sources of fossil
ores like gold, silver and iron ore. fuels like coal, petroleum and
natural gas.
Organic Minerals Inorganic Minerals
1. These are living minerals. 1. These were never living.
(c) 2. Organic minerals can 2. These cannot be easily
easily break down into broken down.
materials. 3. Electrons spin in anti-
3. Electrons spin in clockwise direction.
clockwise directions.
Give two examples of each of the following types of rocks :
Igneous rocks : Basalt, Granite Metamorphic rocks :
Marble, Quartzite Sedimentary rocks :
Limestone, Sandstone
E. Match the rocks to its features :
These rocks have ribbon like layers. Metamorphic
rock (Last
image)
These rocks have small shiny Igneous rock,
or sparkly crystals. Basalt Vth
image
The layered rocks with Sedimentary
wave like patterns. rock (Ist
image)
Some of these rocks are not rough, but Granite
smooth and shiny like glass. (IV
image)
These rocks are good source of Coal
fossil fuels. (IIIrd
image)
These are formed when Sandston
grains of sand get e (IInd
compressed over a long image)
period of time.
F. Label the Diagram :
l Crust
l Mantle
l Outer Core
l Inner Core
You might also like
- Engineering Materials Note by Me For Ctevt-1Document20 pagesEngineering Materials Note by Me For Ctevt-1VedhPrakas Gupta71% (7)
- Iodometric Determination of CopperDocument13 pagesIodometric Determination of CopperAidil RanggaNo ratings yet
- pdf1620720198270 5 11 2021 1 33 20 PMDocument4 pagespdf1620720198270 5 11 2021 1 33 20 PMSukhman veer SinghNo ratings yet
- Inside Our Earth: CrustDocument32 pagesInside Our Earth: CrustDheeraj SainiNo ratings yet
- Geo L7 Rocks & Rock TypesDocument7 pagesGeo L7 Rocks & Rock TypesYogesh DhanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Rocks Jkchrome ComDocument2 pagesRocks Jkchrome ComSomu SinghNo ratings yet
- Gess 202Document5 pagesGess 202Kalpavriksha1974100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Inside Our EarthDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Inside Our EarthGaming ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- The Interior of The Earth: WOW TRP - Class 7 - Social Science Binder - Indd 250 19-Oct-18 12:57:03 PMDocument2 pagesThe Interior of The Earth: WOW TRP - Class 7 - Social Science Binder - Indd 250 19-Oct-18 12:57:03 PMJimins lost jamsNo ratings yet
- Class-VII SST Notes-3 Inside Our EarthDocument4 pagesClass-VII SST Notes-3 Inside Our Earthdivyaansh.aroraNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument12 pagesInterior of The Earthunwantedaccountno1No ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 10Document10 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 10megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- 7 Geo CH 2 Notes 2023-24Document8 pages7 Geo CH 2 Notes 2023-24sumi devuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. RocksDocument4 pagesUnit 4. Rocksmcarmendgj74No ratings yet
- RocksDocument5 pagesRocksthndlovuNo ratings yet
- MolaveDocument14 pagesMolavereiirhayNo ratings yet
- Tema RocksDocument4 pagesTema Rocksmcarmendgj74No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Chapter 2 - Inside Our Earth - .Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Chapter 2 - Inside Our Earth - .pamckjstarNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Document2 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Aya CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous RocksDocument5 pagesIntrusive and Extrusive Igneous RocksShaurya ManiktalaNo ratings yet
- Stem Dakahlia Geology Club: - Skills: - Learning Outcome: 4Document17 pagesStem Dakahlia Geology Club: - Skills: - Learning Outcome: 4romaehab201912No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bokaro Steel City: Class Vii Sub: Geography - Ch-2 Inside Our Earth Topic: Rocks and MineralsDocument14 pagesDelhi Public School Bokaro Steel City: Class Vii Sub: Geography - Ch-2 Inside Our Earth Topic: Rocks and MineralsPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument47 pagesROCKSClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Notes - Provide by Shayam - WWW - Arjun00.com - NPDocument126 pagesEngineering Materials Notes - Provide by Shayam - WWW - Arjun00.com - NPYoukesh GautamNo ratings yet
- DNDKJQJQJWJDocument4 pagesDNDKJQJQJWJSaanish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Gess 202Document5 pagesGess 202api-309501342No ratings yet
- Petgeo MidtermsDocument169 pagesPetgeo MidtermsGilian Joy Mari PerezNo ratings yet
- (Ii) Very Short Answer QuestionDocument3 pages(Ii) Very Short Answer QuestionChandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- From Mineral To Rock: Minerals All Around UsDocument2 pagesFrom Mineral To Rock: Minerals All Around UsFiveOfThreeNo ratings yet
- Environmental ManagementDocument10 pagesEnvironmental ManagementAgostina Padovan67% (3)
- Rocks and MineralsDocument8 pagesRocks and MineralsSuvashreePradhanNo ratings yet
- Inside Our Earth 1. Write Briefly About Each of The Three Layers of The Earth. Illustrate Your Answer With A Suitable Diagram. A. CrustDocument3 pagesInside Our Earth 1. Write Briefly About Each of The Three Layers of The Earth. Illustrate Your Answer With A Suitable Diagram. A. CrustNagul JagatheeswaranNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument33 pagesIgneous RocksuunsyNo ratings yet
- Cabuyao Institute of Technology: Core 4 - Earth Science 3 Types of RocksDocument11 pagesCabuyao Institute of Technology: Core 4 - Earth Science 3 Types of RocksJulius Michael DicheNo ratings yet
- Rocks - Teachers NotesDocument5 pagesRocks - Teachers NotesSaman AkramNo ratings yet
- Inside Our Earth Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesInside Our Earth Questions and AnswersKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- 4-Core Subhect-Science-11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module-4Document25 pages4-Core Subhect-Science-11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module-4agnes joy cepeNo ratings yet
- G 7 Understanding The EarthDocument6 pagesG 7 Understanding The EarthzoyaNo ratings yet
- Geography CSS and PMS Chapter 1 and 2Document25 pagesGeography CSS and PMS Chapter 1 and 2Ismail BarakzaiNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument3 pagesRock CycleImene KhaznadjiNo ratings yet
- LAS ES W2-LC6and7Document8 pagesLAS ES W2-LC6and7nana.No ratings yet
- Earthscience Week 2Document14 pagesEarthscience Week 2Mykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesReviewer Earth ScienceinamowtoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesEarth Science: Rocks and MineralsTakanashiNo ratings yet
- Study of The Interior of The Earth Is Done by GeologistDocument3 pagesStudy of The Interior of The Earth Is Done by GeologistSourya DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Earth Science 2Document11 pagesReviewer Earth Science 2Stephanie GraceNo ratings yet
- CL 7 - SST (G)Document4 pagesCL 7 - SST (G)K BhaiNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals - NotesDocument4 pagesRocks and Minerals - NotesgvzmqbkpyhNo ratings yet
- 3 Rock Worksheet AnswersDocument1 page3 Rock Worksheet AnswersCristina Maquinto100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our EarthDocument4 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our EarthvijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The EarthDocument9 pagesUnderstanding The EarthEesha BhokareNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 and 2Document2 pagesActivity 1 and 2Kavish DayaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Notes EnviromentalDocument45 pagesCHAPTER 1 Notes Enviromentalazeen.zanzoonNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 2ndDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography 2ndAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- Unit 8H The Rock Cycle: Name: .Document11 pagesUnit 8H The Rock Cycle: Name: .irene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Science 11 ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience 11 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- Rock FormationDocument5 pagesRock FormationabigailbornillaNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument14 pagesRocksNovrei YucsonNo ratings yet
- 1 Educator Answer 1 Educator Answer 1 Educator Answer 1 Educator AnswerDocument6 pages1 Educator Answer 1 Educator Answer 1 Educator Answer 1 Educator AnswerJasmin SaricalaNo ratings yet
- 7th - WORKSHEET 4-1021121202031311 PDFDocument2 pages7th - WORKSHEET 4-1021121202031311 PDFMitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 7th Maths - 1021027202024214Document2 pagesWORKSHEET 7th Maths - 1021027202024214Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- ICAI CA Found. Eco & BCK Paper 30.07.2021Document14 pagesICAI CA Found. Eco & BCK Paper 30.07.2021Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- 7th - SST Answer Key ch5 Civics 1-1021030202030056 PDFDocument4 pages7th - SST Answer Key ch5 Civics 1-1021030202030056 PDFMitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Class-7 Subject-Social Science: Chapter: Hydrosphere (Geography)Document3 pagesAnswer Key Class-7 Subject-Social Science: Chapter: Hydrosphere (Geography)Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- 11th and 12th Test Schedule-10211122020122925Document2 pages11th and 12th Test Schedule-10211122020122925Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 3: Chapter - 8 (Comparing Quantities)Document1 pageWorksheet - 3: Chapter - 8 (Comparing Quantities)Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- What Is A Poster-10298202060439Document4 pagesWhat Is A Poster-10298202060439Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 ch5 History-10299202025932Document1 pageWorksheet 6 ch5 History-10299202025932Mitanshu Mittal100% (1)
- 7th Hindi WorkSheet 882020-10288202034442Document1 page7th Hindi WorkSheet 882020-10288202034442Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- YS School: REPORT CARD-CLASS: 7th B (2020-21)Document1 pageYS School: REPORT CARD-CLASS: 7th B (2020-21)Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Gyan Punj Awp For 10TH Eng PDFDocument21 pagesGyan Punj Awp For 10TH Eng PDFMitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: AnswerDocument5 pagesClass Notes: AnswerMitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Class XII SECTION - A (Reading)Document45 pagesPractice Questions For Class XII SECTION - A (Reading)Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 English Writing Skills - Notice: What Is A Notice?Document8 pagesClass 12 English Writing Skills - Notice: What Is A Notice?Mitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- English: Gyan Devi Salwan Public School Summer Holiday Homework, 2020-21 Class XiDocument16 pagesEnglish: Gyan Devi Salwan Public School Summer Holiday Homework, 2020-21 Class XiMitanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Detergents PDFDocument10 pagesDetergents PDFThirumani SelvamNo ratings yet
- 9, Hydrocarbon DerivativesDocument86 pages9, Hydrocarbon Derivativesina stanevaNo ratings yet
- Surface Modification of PEEKDocument9 pagesSurface Modification of PEEKMuhammad Ahmed SaleemNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Redox ReactionsDocument92 pagesStoichiometry and Redox ReactionsHjkkNo ratings yet
- Biochemical MetabolismmDocument11 pagesBiochemical MetabolismmJessela EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Condensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationDocument3 pagesCondensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Methanol To Olefins (MTO) : Development of A Commercial Catalytic ProcessDocument98 pagesMethanol To Olefins (MTO) : Development of A Commercial Catalytic ProcessРоман ЗахаровNo ratings yet
- GCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsDocument30 pagesGCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsShaheer HashmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (1) .1 - Igneous RockDocument64 pagesChapter 3 (1) .1 - Igneous RockLia AmeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S138589472102742X MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S138589472102742X MainSara ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Structur e Prefix Suffix: - C - C O Alkoxy Carbonyl or CarbalkoxyDocument40 pagesFunctional Group Structur e Prefix Suffix: - C - C O Alkoxy Carbonyl or CarbalkoxyMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Special Publication No.4 of The Society For Geology Applied To Mineral DepositsDocument602 pagesSpecial Publication No.4 of The Society For Geology Applied To Mineral DepositsAlexandra VasileNo ratings yet
- 19 Volumetric Analysis Involving Acids and Alkalis Teacher PDFDocument63 pages19 Volumetric Analysis Involving Acids and Alkalis Teacher PDFVanessa LeungNo ratings yet
- My Periodic Table AssignmentDocument1 pageMy Periodic Table Assignmentapi-290100812No ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry UNIT II: Corrosion ScienceDocument13 pagesApplied Chemistry UNIT II: Corrosion ScienceViswa NathanNo ratings yet
- Diamond Catalogo Consumibles PDFDocument20 pagesDiamond Catalogo Consumibles PDFleopa78No ratings yet
- QP - Class X - Science - Mid-Term - Assessment - 2021 - 22 - Oct - 21Document6 pagesQP - Class X - Science - Mid-Term - Assessment - 2021 - 22 - Oct - 21Ashish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Luting Agents For Fixed Prosthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument37 pagesLuting Agents For Fixed Prosthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of PlasticsDocument2 pagesA Brief History of PlasticsAntSWNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem Is 02Document930 pagesAnalytical Chem Is 02BoseNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortarDocument10 pagesFactors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortaraikalessNo ratings yet
- 22) Protein GelatinDocument33 pages22) Protein GelatinAnuj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Codan Chemical Resistance 2015Document4 pagesCodan Chemical Resistance 2015Gokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Toxicology of Textile DyesDocument31 pagesToxicology of Textile DyesWilson Anandaraj100% (5)
- Special StainsDocument18 pagesSpecial StainsJil BellaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Document4 pagesBonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Mel Patricia M. CabreraNo ratings yet
- ChemorgoDocument42 pagesChemorgoYasmin ZaherNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Experiment No.10 Potassium CarbonateDocument3 pagesGroup 1 Experiment No.10 Potassium CarbonateBlazy InhumangNo ratings yet
- S5 CHEM (The S-Block Elements)Document30 pagesS5 CHEM (The S-Block Elements)Mwesigwa HannahNo ratings yet