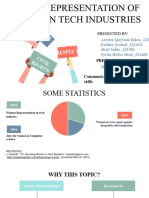
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Social Discrimination Is The Unfair or Prejudicial Treatment of Individuals and Groups On The Basis of Characteristics Such As Race
Social Discrimination Is The Unfair or Prejudicial Treatment of Individuals and Groups On The Basis of Characteristics Such As Race
Uploaded by
Shourovs Shourov0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesSocial discrimination refers to unfair or prejudicial treatment based on characteristics like race, gender, age, or sexual orientation. It exists in both direct and indirect forms. While there is no consensus on the root causes, discrimination is generally viewed as a learned behavior shaped by parents, teachers, media, and social institutions. Efforts to reduce discrimination include multicultural education, civil rights laws, and policies aimed at promoting inclusion and equal treatment in areas like employment. The effects of social discrimination are reflected in issues like gender discrimination, religious discrimination, and age discrimination in the workplace, all of which can negatively impact people's lives and opportunities. Social discrimination poses a threat to democracy and violates principles of human rights and equal worth.
Original Description:
Original Title
Social discrimination is the unfair or prejudicial treatment of individuals and groups on the basis of characteristics such as race
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSocial discrimination refers to unfair or prejudicial treatment based on characteristics like race, gender, age, or sexual orientation. It exists in both direct and indirect forms. While there is no consensus on the root causes, discrimination is generally viewed as a learned behavior shaped by parents, teachers, media, and social institutions. Efforts to reduce discrimination include multicultural education, civil rights laws, and policies aimed at promoting inclusion and equal treatment in areas like employment. The effects of social discrimination are reflected in issues like gender discrimination, religious discrimination, and age discrimination in the workplace, all of which can negatively impact people's lives and opportunities. Social discrimination poses a threat to democracy and violates principles of human rights and equal worth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesSocial Discrimination Is The Unfair or Prejudicial Treatment of Individuals and Groups On The Basis of Characteristics Such As Race
Social Discrimination Is The Unfair or Prejudicial Treatment of Individuals and Groups On The Basis of Characteristics Such As Race
Uploaded by
Shourovs ShourovSocial discrimination refers to unfair or prejudicial treatment based on characteristics like race, gender, age, or sexual orientation. It exists in both direct and indirect forms. While there is no consensus on the root causes, discrimination is generally viewed as a learned behavior shaped by parents, teachers, media, and social institutions. Efforts to reduce discrimination include multicultural education, civil rights laws, and policies aimed at promoting inclusion and equal treatment in areas like employment. The effects of social discrimination are reflected in issues like gender discrimination, religious discrimination, and age discrimination in the workplace, all of which can negatively impact people's lives and opportunities. Social discrimination poses a threat to democracy and violates principles of human rights and equal worth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Causes of Social Discrimination
Social Discrimination is a threat to society
Social discrimination is the unfair or prejudicial treatment of individuals and groups on the basis of
characteristics such as race, sex, age or sexual orientation.
There are many forms of Social discrimination, in addition to the more familiar forms such as race and
gender, based on ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, age, disability or handicap and sexual harassment.
The above qualification refers to a situation of direct Social discrimination, in which a person suffers
unfavorable treatment directly on the basis of a prohibited ground. Indirect Social discrimination refers to
a situation in which an apparently neutral provision or practice has discriminatory effects. In addition to
direct and indirect social discrimination, we can use the term institutional Social discrimination.
In terms of root cause, social discrimination does not appear to be a clear acceptance of any theory of
causation, but such social discrimination often causes a chain reaction of harm. For example, it should be
noted that there is also a link between social discrimination and social distancing, as it is often
psychologically easier to discriminate against people with whom one is not familiar.
While there is no general consensus on the “cause” of social discrimination, there is consensus that it
constitutes learned behavior. The internalization of discrimination begins with parents and then with
teachers, the main groups in shaping attitudes in children. The media and social institutions reinforce
discriminatory attitudes, giving them social legitimacy, since discrimination is learned. At best,
discrimination can be reduced. Society more frequently relies on education and legislation to combat
social discrimination; For reasons that are not yet clearly understood, intergroup contact alone is not
enough to reduce social discrimination. On the one hand, multicultural education, whether direct or
indirect, constitutes the backbone of educational efforts aimed at eliminating social discrimination. On the
other hand, a focus on civil rights, enlightened immigration policies and hiring quota mandates are the
cornerstone of legal approaches to mitigate the effects of social discrimination. The most overlooked area
in resolving social discrimination issues lies in the network of close relationships where true feelings of
love can be encouraged and strengthened.
The effects of social discrimination in society are reflected in social discrimination based on sex, gender,
religion and disability.
Gender discrimination means unequal treatment between men and women. It is a big problem in our
country. It begins at birth and continues throughout a woman's life. Social prejudices, customs and ills of
dowry systems are the causes of gender discrimination.
Religious discrimination involves treating people differently in their jobs because of their religion,
religious beliefs and practices, and / or their request for accommodation (a change in a rule or policy in
the workplace). their religious beliefs and practices.
Age discrimination, also known as age discrimination in the workplace, is a complex issue that can affect
many areas of government policy and can have many influences on individuals themselves. Age
discrimination can arise through employment and can affect young, old and young. This could affect
employment opportunities, promotion opportunities and growth. Age can also be a factor when employers
decide who should be selected for the layoff.
Social discrimination goes against the most fundamental values of a modern society. In fact, it is a threat
to democracy, which is based on the idea of a society in which hierarchies and arbitrary preferences based
on, for example, gender, ethnicity and wealth have been. eliminated in order to achieve equality.
Democracy recognizes the value and equal rights of all, so equality prohibits social discrimination, which
is also the cornerstone of human rights.
Social discrimination poses not only a threat to society, but also to the individual who is subjected to such
unfavorable treatment, as it is a direct denial of the equal worth of the victim. It is a violation of a person's
identity. The consequences of social discrimination coincide with the seriousness of the crime, a causal
link with alienation
You might also like
- Falling Behind How Rising Inequality PDFDocument2 pagesFalling Behind How Rising Inequality PDFNicholasNo ratings yet
- DiscriminationDocument7 pagesDiscriminationMarianne CortesNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of DiscriminationDocument3 pagesCauses and Effects of DiscriminationJane Gregorio ChanNo ratings yet
- The Cause of DiscriminationDocument3 pagesThe Cause of DiscriminationIrene EspejoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesMidterm Reflection PaperAriannaNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - Gender and SocietyDocument6 pagesFinal Paper - Gender and Societyeventories.phNo ratings yet
- Suggest Ways To Address Social Inequalities G 5Document16 pagesSuggest Ways To Address Social Inequalities G 5Ronald PurigayNo ratings yet
- Student NameDocument3 pagesStudent NameIbrahim AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Homophobia AssignmentDocument3 pagesHomophobia AssignmentcindrellajohnsoncjNo ratings yet
- HomosexualDocument2 pagesHomosexualJenalyn BenolariaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionYusef HamedNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument2 pagesThesisCarlos MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper DISSDocument8 pagesResearch Paper DISSKia LeighNo ratings yet
- Speaking Project - Gender Discrimination - EditedDocument1 pageSpeaking Project - Gender Discrimination - Editedbrilhantebeatriz2007No ratings yet
- English Speech Society ProblemDocument2 pagesEnglish Speech Society ProblemMeena “Ruby” SaravananNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality Is A Pervasive SoDocument6 pagesGender Inequality Is A Pervasive SoAftab KazmiNo ratings yet
- Social Evils Are Deeply Ingrained Issues Within A Society That Undermine Its WellDocument1 pageSocial Evils Are Deeply Ingrained Issues Within A Society That Undermine Its WellTHE MoonlightNo ratings yet
- Docfile of SST Project ResearchDocument20 pagesDocfile of SST Project Researchkeerat preet kaurNo ratings yet
- Eaap Acad-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesEaap Acad-Wps OfficeDanz Axl BondocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NoelDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Noelalphashane FloresNo ratings yet
- Differ and Deeper: Social Discrimination and Its Effects To The Grade 10 Students of Bauan Technical High SchoolDocument5 pagesDiffer and Deeper: Social Discrimination and Its Effects To The Grade 10 Students of Bauan Technical High SchoolElleNo ratings yet
- PR1 Ni FrenzDocument4 pagesPR1 Ni FrenzHeavenlymeNo ratings yet
- E: Tnomngcoyiya@ufh - Ac.zaDocument18 pagesE: Tnomngcoyiya@ufh - Ac.zaviweNo ratings yet
- Stop BullyingDocument2 pagesStop BullyinganinoiualexiaelenaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Norms and Practices Are The Shared Expectations and Rules That Guide The Behavior of A Group of PeopleDocument4 pagesCultural Norms and Practices Are The Shared Expectations and Rules That Guide The Behavior of A Group of PeopleMary Antonette LoterteNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE 5 PPT For ReviewerDocument12 pagesQ2 MODULE 5 PPT For ReviewerCharlyn Maristela AguilarNo ratings yet
- Term OutputDocument3 pagesTerm OutputPolpol DiamononNo ratings yet
- Personal ReflectionDocument2 pagesPersonal Reflectionapi-665360074No ratings yet
- Gender DiscriminationDocument2 pagesGender DiscriminationDaniel BuarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Definition of Social IssuesDocument17 pagesLiterature Review: Definition of Social Issueswali ahmedNo ratings yet
- DiscriminationDocument2 pagesDiscrimination6A DS //No ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Gender ExpressionDocument2 pagesSexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Gender ExpressionXijhyve ManganaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument14 pagesResearch PaperMugiwara JenroNo ratings yet
- Ramos (GS)Document1 pageRamos (GS)MJ ArazasNo ratings yet
- Forms of DiscriminationDocument1 pageForms of DiscriminationKerisia WayneNo ratings yet
- Wit Soc Group 3Document30 pagesWit Soc Group 3Diana ParkerNo ratings yet
- Social IssuesDocument7 pagesSocial IssuesNandya sankarNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesReaction PaperKhyla joy anne AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Social Issues of SocietyDocument85 pagesSocial Issues of SocietyArcely GundranNo ratings yet
- Phemia - Strategies To Address DevianceDocument5 pagesPhemia - Strategies To Address DeviancePhemiaNo ratings yet
- Gender PPT 1Document178 pagesGender PPT 1Abuki TemamNo ratings yet
- SOC 1502 Written Assignment Unit 4Document5 pagesSOC 1502 Written Assignment Unit 4Cherry HtunNo ratings yet
- UCSP RESEARCH Group 2 Async ActDocument4 pagesUCSP RESEARCH Group 2 Async ActKhian PinedaNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Change Communication On Sexual HarrasmentDocument19 pagesBehaviour Change Communication On Sexual HarrasmentMilcahNo ratings yet
- DiscriminationDocument2 pagesDiscriminationMary Joy FanikerNo ratings yet
- Stigma and Discrimination Against Gay MenDocument1 pageStigma and Discrimination Against Gay MenAron Shane AureaNo ratings yet
- Ass. Sociology 2Document3 pagesAss. Sociology 2tawas20No ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5 Ucsp HandoutDocument16 pagesQ2 Module 5 Ucsp HandoutrhainsophiaNo ratings yet
- How To YayDocument3 pagesHow To YayAlper Tamay ArslanNo ratings yet
- Position Paper (Kate)Document4 pagesPosition Paper (Kate)Nash CasunggayNo ratings yet
- Social IssuesDocument7 pagesSocial IssuesUsman waseemNo ratings yet
- Sexualbehavior BeckcomDocument5 pagesSexualbehavior Beckcomabbybeckcom5No ratings yet
- The Awareness of Sex Education To Young PeopleDocument4 pagesThe Awareness of Sex Education To Young Peoplewanash1669No ratings yet
- Eapp Concept PaperDocument10 pagesEapp Concept PaperNicole MonesNo ratings yet
- Making Connections Between Texts To Particular Social Issues 2Document46 pagesMaking Connections Between Texts To Particular Social Issues 2mobileveejay3No ratings yet
- Project On Sociology of Gender and SexualityDocument17 pagesProject On Sociology of Gender and SexualityBonface ZadockNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Social Impact of Inequalities of GenderDocument7 pagesEvaluate The Social Impact of Inequalities of GenderMaisha ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Feminism: Sexism andDocument10 pagesFeminism: Sexism andNesty Yangga SarsateNo ratings yet
- Social Inequality NotesDocument4 pagesSocial Inequality NotesgabrielNo ratings yet
- Gender Based ViolenceDocument23 pagesGender Based ViolenceFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Survival Guide for Racially Abused Persons: Boosting self-esteem amid racial abuseFrom EverandSurvival Guide for Racially Abused Persons: Boosting self-esteem amid racial abuseNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Racism From Rachel ShineDocument16 pagesA Presentation On Racism From Rachel ShineMyNorthwest0% (1)
- Reservation in Govt Service in RajasthanDocument102 pagesReservation in Govt Service in RajasthanDpi Elansezhian RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Hernandez Melissa Gender Discrimination EssayDocument5 pagesHernandez Melissa Gender Discrimination Essayapi-271489519No ratings yet
- Communication and PresentationDocument11 pagesCommunication and PresentationsaneuhNo ratings yet
- CNY Segregation MapsDocument13 pagesCNY Segregation MapsTim KnaussNo ratings yet
- Upsc Essay 2023 Model Answers WebDocument22 pagesUpsc Essay 2023 Model Answers WebstuDYmateriALNo ratings yet
- ADP Workforce View 2018 FRDocument32 pagesADP Workforce View 2018 FRjaffresNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology Survey Report Presentation Topic - Reservation in Education SystemDocument21 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology Survey Report Presentation Topic - Reservation in Education SystemDoomer PenNo ratings yet
- Review of Recent Literature On Socio Economic Status and LearningDocument10 pagesReview of Recent Literature On Socio Economic Status and LearningafdtbwkhbNo ratings yet
- Noise Pollution TeluguDocument8 pagesNoise Pollution Telugucherukuri GroupNo ratings yet
- Social StratificationDocument30 pagesSocial StratificationIsmail ChahineNo ratings yet
- Housing Shit EdxDocument8 pagesHousing Shit EdxTsuki KoNo ratings yet
- Global IssuesDocument2 pagesGlobal IssuesAyaanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Journal of African Elections v11n1 Gender Politics 2011 Elections EisaDocument26 pages2012 Journal of African Elections v11n1 Gender Politics 2011 Elections EisannubiaNo ratings yet
- Calc Project 3Document4 pagesCalc Project 3api-457258209No ratings yet
- MDSSS BrochureDocument8 pagesMDSSS BrochureJaimon C UthupNo ratings yet
- Ucsp11 q2 Mod8 Globalinequality v1Document23 pagesUcsp11 q2 Mod8 Globalinequality v1Thinthin AraqueNo ratings yet
- ReservationDocument9 pagesReservationShreya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Artículo InterseccionalidadDocument6 pagesArtículo InterseccionalidadGabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4kajal adhikaryNo ratings yet
- Basavaraju Reservation Under The Constitution of India Issues and PerspectivesDocument9 pagesBasavaraju Reservation Under The Constitution of India Issues and PerspectivesK ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier-I ResultDocument157 pagesSSC CGL Tier-I ResultGowtham MekapotulaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Revised Fig On PG 7Document76 pagesCh. 5 Revised Fig On PG 7ibmepuneNo ratings yet
- Defending Equality of OutcomeDocument33 pagesDefending Equality of OutcomeGokul KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Social MobilityDocument5 pagesWhat Is Social MobilityDK BalochNo ratings yet
- P6 UK Bank CustomersDocument180 pagesP6 UK Bank CustomersPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- Anth 1012, Units 4-6, Revised, Post-Covid, Jan. 2021Document86 pagesAnth 1012, Units 4-6, Revised, Post-Covid, Jan. 2021Abdulmejd Kelil Shifa (Techkelster)No ratings yet
- Globalisation, Society and Inequalities: Harish WankhedeDocument6 pagesGlobalisation, Society and Inequalities: Harish WankhedesofiagvNo ratings yet
- Disability Inclusion: Topic GuideDocument54 pagesDisability Inclusion: Topic GuidesineNo ratings yet