Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Surgery Card 56
Oral Surgery Card 56
Uploaded by
Eppy KaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Surgery Card 56
Oral Surgery Card 56
Uploaded by
Eppy KaCopyright:
Available Formats
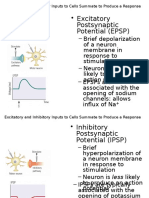
• sodium ions
Local anesthetics selectively inhibit the peak permeability of sodium, whose value is normally
about five to six times greater than the minimum necessary for impulse conduction. The
following sequence is a proposed mechanism of action of local anesthetics:
1. Displacement of sodium ions from the sodium channel receptor site, which permits...
2. Binding of local anesthetic molecule to this receptor site, which thus produces...
3. Blockade of the sodium channel, and a...
4. Decrease in sodium conductance, which leads to...
5. Depression of the rate of electrical depolarization, and a...
6. Failure to achieve the threshold potential level, along with a...
7. Lack of development of propagated action potentials, which is called...
8. Conduction blockade
The mechanism whereby sodium ions gain entry to the axoplasm of the nerve, thereby initiating an
action potential, is altered by local anesthetics. The nerve membrane remains in a polarized state
because ionic movements responsible for the action potential fail to develop. Nerve block produced
by local anesthetics is called a nondepolarizing nerve block.
1. Local anesthetics reversibly block nerve impulse conduction and produce
Notes reversible loss of sensation at their administration site. The site of action of local
anesthetics is at the lipoprotein sheath of the nerves.
2. Local anesthetics are clinically effective on both axons and free nerve endings.
3. Important: Small, unmyelinated nerve fibers that conduct pain and temperature
sensations are affected first, followed by touch, proprioception, and skeletal muscle
tone.
4. Emergence from a local anesthetic nerve block follows the same diffusion patterns
as induction; however, it does so in reverse order.
5. Recovery is usually a slower process than induction because the anesthetic is bound
to the drug receptor site in the sodium channel and, therefore, is released more slowly
than it is absorbed.
6. Conductance of potassium, calcium, and chloride remains unchanged.
You might also like
- Biofact Sheet Nerves SynapsesDocument4 pagesBiofact Sheet Nerves SynapsesJonMortNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument35 pagesNeurophysiology in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryPriya ManimalaNo ratings yet
- BadfishDocument8 pagesBadfishMelisa SanchezNo ratings yet
- OS Local AnesthesiaDocument25 pagesOS Local AnesthesiaJha SujitNo ratings yet
- Os 4Document6 pagesOs 4مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- 5 - Local AnetheticsDocument30 pages5 - Local AnetheticsCorry QyNo ratings yet
- Cours 3 - Pain ControlDocument50 pagesCours 3 - Pain ControlMadi LazarNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2Document23 pagesNeuro 2yomanNo ratings yet
- Local AnesthesiaDocument121 pagesLocal AnesthesiaGabriela Cocieru Motelica100% (2)
- Local AnasthesiaDocument121 pagesLocal AnasthesiaD YasIr Mussa100% (1)
- Synapse, The Concept of Antidote, Curare and Exotoxins PoisoningDocument39 pagesSynapse, The Concept of Antidote, Curare and Exotoxins PoisoningCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiDocument12 pages3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Local AnaestheticsDocument17 pagesLocal AnaestheticsShantanu RewatkarNo ratings yet
- #Local Anesthetic DrugsDocument26 pages#Local Anesthetic DrugsTripti Padalia100% (1)
- Neuropharmacology Notes (Part 1)Document5 pagesNeuropharmacology Notes (Part 1)Rawan AlshammaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia 1Document78 pagesAnesthesia 1hamza.betatNo ratings yet
- Local Anestgesia and ComplicationsDocument73 pagesLocal Anestgesia and Complicationslionel andreaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes SynapseDocument4 pagesBio Notes SynapseLeeroy MafuruseNo ratings yet
- DR - Vinay Jain PG1 YearDocument76 pagesDR - Vinay Jain PG1 YearNeelesh BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia 1Document90 pagesAnesthesia 1hamza.betatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.3Document5 pagesTutorial 4.3Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Neuro Muscular Junction NNDocument68 pagesNeuro Muscular Junction NNAnak AyamNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia I LectureDocument44 pagesLocal Anesthesia I LectureMavisNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic Pharmacology LecDocument16 pagesLocal Anesthetic Pharmacology LecFazira EkmaNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia: Presented By-: Harsh Jain Mds I YearDocument40 pagesLocal Anaesthesia: Presented By-: Harsh Jain Mds I YearRiya JainNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular BlockersDocument15 pagesNeuromuscular BlockersBharane DharranNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Local AnaestheticsDocument19 pagesMechanism of Action of Local AnaestheticsSumit Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Principles of Neural and Hormonal CommunicationDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Neural and Hormonal CommunicationAmmar SmadiNo ratings yet
- Neural PhysiologyDocument45 pagesNeural PhysiologyHakim Asif Haider100% (1)
- 4.neural and HormonalDocument40 pages4.neural and HormonalRulani PrinceNo ratings yet
- PSYC 2410 DE S12 Textbook Notes Chapter 04 PDFDocument14 pagesPSYC 2410 DE S12 Textbook Notes Chapter 04 PDFKatarina GruborovićNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationDocument39 pagesA Level Biology: Nervous CoordinationAhmedNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics 2019-2020 2nd YrDocument54 pagesLocal Anesthetics 2019-2020 2nd YrJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 8 Coordination Response and Gene Technology - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelDocument13 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 8 Coordination Response and Gene Technology - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A Levelsathmi gurusingheNo ratings yet
- DR - Siddharth Dhanaraj Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon: Composition Properties & Mechanism of Local AnestheticsDocument68 pagesDR - Siddharth Dhanaraj Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon: Composition Properties & Mechanism of Local AnestheticsSiddharth DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi NerveDocument5 pagesFisiologi Nervenurul armaliaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Mariam KidwaiDocument20 pagesNervous Tissue: Mariam KidwaiMariam KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and Gene TechnologyDocument13 pagesCoordination, Response and Gene Technologymii chanrNo ratings yet
- Synaptic TransmissionDocument17 pagesSynaptic Transmissionyanaasv05No ratings yet
- Presentation NeuronDocument18 pagesPresentation NeuronrushnaNo ratings yet
- Nerve Impulse-Week 4-5Document69 pagesNerve Impulse-Week 4-5COPY PAPAGAJKANo ratings yet
- Neuronal CommunicationDocument29 pagesNeuronal CommunicationSamantha CNo ratings yet
- PHS 221Document18 pagesPHS 221tewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Local AnestheticsDocument21 pagesLocal AnestheticsVishwas BansalNo ratings yet
- Wa0020.Document32 pagesWa0020.Safura IjazNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics2Document36 pagesLocal Anesthetics2sonapradhan14No ratings yet
- Dharmani Devi Murugan PHD Department of PharmacologyDocument33 pagesDharmani Devi Murugan PHD Department of PharmacologyYong MxNo ratings yet
- Summary Biological PsychologyDocument133 pagesSummary Biological PsychologyAnastasia100% (1)
- NO B.SC 2002Document27 pagesNO B.SC 2002Sergio AraujoNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: DR - Jagadish JenaDocument109 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agents: DR - Jagadish Jenavvb_frndNo ratings yet
- Local AnaestheticsDocument31 pagesLocal AnaestheticsNodi NodiNo ratings yet
- 3.8. The Nervous SystemDocument6 pages3.8. The Nervous SystemGentiana GashiNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle ContractionDocument14 pagesInvestigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contractiongeddy D.No ratings yet
- Nerve ImpulseDocument8 pagesNerve ImpulseAsadNo ratings yet
- 111 Week 2 WorksheetDocument4 pages111 Week 2 WorksheetjabyleynesNo ratings yet
- L.A in Dentistary 2021Document44 pagesL.A in Dentistary 2021A MNo ratings yet
- Ans 1Document21 pagesAns 1Navnath HatvateNo ratings yet
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachFrom EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachNo ratings yet
- Oral SurgeryDocument1 pageOral SurgeryEppy KaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Arrangement of Artificial TeethDocument22 pagesPreliminary Arrangement of Artificial TeethEppy KaNo ratings yet
- Face-Bow Instructions: Bite-Tab Strip Away From Backing Sheet. Do NotDocument14 pagesFace-Bow Instructions: Bite-Tab Strip Away From Backing Sheet. Do NotEppy KaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Aging On The Edentulous StateDocument17 pagesThe Effects of Aging On The Edentulous StateEppy KaNo ratings yet
- 3 Sequelae of Denture WearingDocument41 pages3 Sequelae of Denture WearingEppy Ka50% (4)
- 3 Sequelae of Denture WearingDocument41 pages3 Sequelae of Denture WearingEppy Ka50% (4)
- Anatomy TourDocument70 pagesAnatomy TourEppy KaNo ratings yet