Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Uploaded by
Khairuddin MzainMrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2Document39 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2AngeloRofelTabundaNava50% (18)
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocument63 pagesThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28172% (25)
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Electric Fields & Potential WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectric Fields & Potential WorksheetFandy Ardy50% (2)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument42 pagesThermal Power PlantAravind C.KNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDocument5 pages1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Document13 pagesUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- Power Plant EquipmentDocument54 pagesPower Plant EquipmentJoy PalitNo ratings yet
- T Project ReportDocument63 pagesT Project ReportArif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Document21 pagesCfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Shruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliTanveer AzizNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument6 pagesThermal Power StationAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocument21 pagesLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- Physics 4.Document5 pagesPhysics 4.SOLAIMANNo ratings yet
- Explain The Principles of Operation of Steam TurbiDocument9 pagesExplain The Principles of Operation of Steam Turbielrefaimohamed293No ratings yet
- Power StationDocument5 pagesPower StationHimanshu RajNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFPPDocument34 pagesIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power StationDocument157 pagesThermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power Stationgteklay100% (1)
- Geothermal powerDocument3 pagesGeothermal poweralisalihosman12No ratings yet
- PPT4 Coal FiredDocument31 pagesPPT4 Coal FiredWinston LibangaNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power PlantDocument4 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power Plantuikeshekhar610No ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument7 pagesGeothermalGilbert Sta BrigidaNo ratings yet
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesPP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesThermal Power PlantAnudeep ChittluriNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document11 pagesLab Report 3Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantsuganyaNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working of Thermal Power Plantdibyenindus100% (1)
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- Dry Cooling Systems1.2Document40 pagesDry Cooling Systems1.2paragmishra1986No ratings yet
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- Honorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadDocument50 pagesHonorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument36 pagesThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Power PlantDocument27 pagesPower PlantaloknegiNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantsDocument18 pagesSteam Power Plantscan canNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocument22 pagesBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument35 pagesThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Notes - OrganizedDocument107 pagesPower Plant Engineering Notes - Organizeddeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- CoalDocument48 pagesCoallekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsDocument21 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsSiman NapstervkkNo ratings yet
- Power System ComponentsDocument17 pagesPower System ComponentsbobidmrNo ratings yet
- SIREreport 118ee0297Document13 pagesSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 3Document4 pagesLecture No 3Musa KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocument32 pagesUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngDocument93 pagesPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (3)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 2 - Geomorphology and WeatheringDocument24 pagesLecturer 2 - Geomorphology and WeatheringJoseph Zotoo100% (1)
- Green Hospital: by DR - Mahboob Ali Khan PHDDocument34 pagesGreen Hospital: by DR - Mahboob Ali Khan PHDPeter AsaneNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper About Tourism ImpactsDocument5 pagesReflection Paper About Tourism ImpactsRenz John AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Sinavy Pem Fuel CellDocument12 pagesSinavy Pem Fuel CellArielDanieli100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE Section 4 Notes PDFDocument8 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Section 4 Notes PDFInês Da CostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Steam Cycle TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter-2 Steam Cycle TheorybhaskarNo ratings yet
- Structural DataDocument328 pagesStructural DataHarsh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Suez Ozonia Cfs Uk AntonyDocument4 pagesSuez Ozonia Cfs Uk AntonyantonyglzNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Cls VIIA ChemistryDocument3 pagesCH 5 Cls VIIA ChemistryTrixxy CarterNo ratings yet
- Module #4 WEATHERING AND SOIL-FORMING ROCKS AND MINERALSDocument2 pagesModule #4 WEATHERING AND SOIL-FORMING ROCKS AND MINERALSMa. Diana Joy MamansagNo ratings yet
- Retrospective of 70 Years o F Organic Geochemistry 2005 KvenvoldenDocument11 pagesRetrospective of 70 Years o F Organic Geochemistry 2005 KvenvoldenMario GarciaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument16 pagesPPTRizza0% (1)
- SSC-JE 2022: Staff Selection Commision-Junior EngineerDocument15 pagesSSC-JE 2022: Staff Selection Commision-Junior EngineerAsheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Environment in Jordan MoEDocument56 pages2 Environment in Jordan MoEkaramn3matNo ratings yet
- Biodegradability of Plastics Challenges and MisconceptionsDocument3 pagesBiodegradability of Plastics Challenges and MisconceptionsShivam SamaiyaNo ratings yet
- Bondoc Richel G. (CWTS Project MRF)Document9 pagesBondoc Richel G. (CWTS Project MRF)RICHEL BONDOCNo ratings yet
- Steam Table: Mollier ChartDocument8 pagesSteam Table: Mollier ChartabdcivilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PE AM - 003Document17 pagesMechanical PE AM - 003Guru Raja Ragavendran NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Extrusion of Soft Clay Through A Retaining Wall: NotesDocument7 pagesExtrusion of Soft Clay Through A Retaining Wall: NotesRabindra ChaulagaiNo ratings yet
- Iceland Trade Mission: Mt. Princeton Geothermal LLCDocument31 pagesIceland Trade Mission: Mt. Princeton Geothermal LLCAlleyTreeNo ratings yet
- Potential of Waste To Energy in African Urban Areas 2475 7675 1000162Document12 pagesPotential of Waste To Energy in African Urban Areas 2475 7675 1000162Emmanuel Anosisye MwangomoNo ratings yet
- M0712101104 - Ktra Do Nong ChayDocument4 pagesM0712101104 - Ktra Do Nong ChayTịch MịchNo ratings yet
- All About Prehistoric Era To Celebrate US National Fossil Day by Slidesgo - 1Document56 pagesAll About Prehistoric Era To Celebrate US National Fossil Day by Slidesgo - 1Justin SeagullNo ratings yet
- Literary ReviewDocument5 pagesLiterary Reviewapi-549216833No ratings yet
- CSBS 105 Unit-I Oscillations AssainmentDocument4 pagesCSBS 105 Unit-I Oscillations AssainmentDeepam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic EraDocument3 pagesCenozoic EraJudith Vengano AguilarNo ratings yet
- Quiz 002 100%Document14 pagesQuiz 002 100%jrence100% (1)
- Global Warming EssayDocument8 pagesGlobal Warming Essaykhuranakrish100% (1)
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Uploaded by
Khairuddin MzainMrafiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Components of The Combined Cycle Power Plant
Uploaded by
Khairuddin MzainMrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
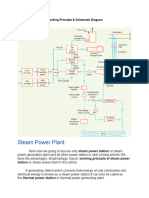
Components of the Combined Cycle Power Plant.
1) Gas turbine
- The gas turbine uses natural gas or various other fuels, such as No. 2 diesel or kerosene
compresses air and mixes it with fuel that is heated to a very high temperature. The hot air-fuel
mixture moves through the gas turbine blades, making them spin.
- The fast-spinning turbine drives a generator that converts a portion of the spinning energy into
electricity.
2) Compressor
- draws air into the engine, pressurizes it, and feeds it to the combustion chamber at speeds of
hundreds of miles per hour. The combustion system, typically made up of a ring of fuel injectors
that inject a steady stream of fuel into combustion chambers where it mixes with the air.
3) Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG)
- removes heat from the hot exhaust of the gas turbine to turn water into superheated steam. This
is done by directing the hot exhaust across finned tubes filled with water.
- This water absorbs the heat and turns into saturated steam. The steam rises up to the drum, and
the moisture in the saturated steam is removed by mechanical separators; it is then sent through
piping to another set of finned tubes to superheat it. This superheated steam is sent to the steam
turbine.
-The hot exhaust from the gas turbine exits the “hersig” through an exhaust stack to atmosphere.
4) Steam turbine
- The steam turbine receives superheated steam from the “hersig” in order to turn the steam
turbine rotor, which is connected to a generator to make electricity. The superheated steam is
directed to the steam turbine from the “hersig” by steam piping.
- After the superheated steam is used to operate the steam turbine, it is exhausted into the
condenser.
5) Generator
- The spinning of the gas and steam turbine drives the generator rudder to spin and coverting
mechanical energy into electrical energy.
6) Condenser
- receive steam that has been exhausted from the steam turbine and condense it back to water. This
is performed by running cooling water through tubes in the condenser, which absorbs heat from
the exhausted steam in order to turn it back to water. This water is then pumped from the
condenser to either a deaerator or the low-pressure steam drum by the condensate pumps.
7) Cooling Tower
- Cooling towers are a special type of heat exchanger that allows water and air to come in contact
with each other to lower the temperature of the hot water.
- During this process, small volumes of water evaporate, lowering the temperature of the water
that's being circulated throughout the cooling tower.
8) Bus Duct
- the main conduit for power distribution in a power generation facility that gets from the
generator to the power grid
9) Transformer
- trades voltage for current in a circuit, while not affecting the total electrical power. This means it
takes high-voltage electricity with a small current and changes it into low-voltage electricity with
a large current, or vice versa.
10) Power Grid
- Generate the electricity current from the power plant to houses, premises, etc.
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2Document39 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2AngeloRofelTabundaNava50% (18)
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocument63 pagesThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28172% (25)
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Electric Fields & Potential WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectric Fields & Potential WorksheetFandy Ardy50% (2)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument42 pagesThermal Power PlantAravind C.KNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDocument5 pages1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Document13 pagesUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- Power Plant EquipmentDocument54 pagesPower Plant EquipmentJoy PalitNo ratings yet
- T Project ReportDocument63 pagesT Project ReportArif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Document21 pagesCfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Shruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliTanveer AzizNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument6 pagesThermal Power StationAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocument21 pagesLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- Physics 4.Document5 pagesPhysics 4.SOLAIMANNo ratings yet
- Explain The Principles of Operation of Steam TurbiDocument9 pagesExplain The Principles of Operation of Steam Turbielrefaimohamed293No ratings yet
- Power StationDocument5 pagesPower StationHimanshu RajNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFPPDocument34 pagesIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power StationDocument157 pagesThermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power Stationgteklay100% (1)
- Geothermal powerDocument3 pagesGeothermal poweralisalihosman12No ratings yet
- PPT4 Coal FiredDocument31 pagesPPT4 Coal FiredWinston LibangaNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power PlantDocument4 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power Plantuikeshekhar610No ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument7 pagesGeothermalGilbert Sta BrigidaNo ratings yet
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesPP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesThermal Power PlantAnudeep ChittluriNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document11 pagesLab Report 3Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantsuganyaNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working of Thermal Power Plantdibyenindus100% (1)
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- Dry Cooling Systems1.2Document40 pagesDry Cooling Systems1.2paragmishra1986No ratings yet
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- Honorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadDocument50 pagesHonorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument36 pagesThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Power PlantDocument27 pagesPower PlantaloknegiNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantsDocument18 pagesSteam Power Plantscan canNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocument22 pagesBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument35 pagesThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Notes - OrganizedDocument107 pagesPower Plant Engineering Notes - Organizeddeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- CoalDocument48 pagesCoallekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsDocument21 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsSiman NapstervkkNo ratings yet
- Power System ComponentsDocument17 pagesPower System ComponentsbobidmrNo ratings yet
- SIREreport 118ee0297Document13 pagesSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 3Document4 pagesLecture No 3Musa KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocument32 pagesUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngDocument93 pagesPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (3)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 2 - Geomorphology and WeatheringDocument24 pagesLecturer 2 - Geomorphology and WeatheringJoseph Zotoo100% (1)
- Green Hospital: by DR - Mahboob Ali Khan PHDDocument34 pagesGreen Hospital: by DR - Mahboob Ali Khan PHDPeter AsaneNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper About Tourism ImpactsDocument5 pagesReflection Paper About Tourism ImpactsRenz John AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Sinavy Pem Fuel CellDocument12 pagesSinavy Pem Fuel CellArielDanieli100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE Section 4 Notes PDFDocument8 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Section 4 Notes PDFInês Da CostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Steam Cycle TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter-2 Steam Cycle TheorybhaskarNo ratings yet
- Structural DataDocument328 pagesStructural DataHarsh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Suez Ozonia Cfs Uk AntonyDocument4 pagesSuez Ozonia Cfs Uk AntonyantonyglzNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Cls VIIA ChemistryDocument3 pagesCH 5 Cls VIIA ChemistryTrixxy CarterNo ratings yet
- Module #4 WEATHERING AND SOIL-FORMING ROCKS AND MINERALSDocument2 pagesModule #4 WEATHERING AND SOIL-FORMING ROCKS AND MINERALSMa. Diana Joy MamansagNo ratings yet
- Retrospective of 70 Years o F Organic Geochemistry 2005 KvenvoldenDocument11 pagesRetrospective of 70 Years o F Organic Geochemistry 2005 KvenvoldenMario GarciaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument16 pagesPPTRizza0% (1)
- SSC-JE 2022: Staff Selection Commision-Junior EngineerDocument15 pagesSSC-JE 2022: Staff Selection Commision-Junior EngineerAsheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Environment in Jordan MoEDocument56 pages2 Environment in Jordan MoEkaramn3matNo ratings yet
- Biodegradability of Plastics Challenges and MisconceptionsDocument3 pagesBiodegradability of Plastics Challenges and MisconceptionsShivam SamaiyaNo ratings yet
- Bondoc Richel G. (CWTS Project MRF)Document9 pagesBondoc Richel G. (CWTS Project MRF)RICHEL BONDOCNo ratings yet
- Steam Table: Mollier ChartDocument8 pagesSteam Table: Mollier ChartabdcivilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PE AM - 003Document17 pagesMechanical PE AM - 003Guru Raja Ragavendran NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Extrusion of Soft Clay Through A Retaining Wall: NotesDocument7 pagesExtrusion of Soft Clay Through A Retaining Wall: NotesRabindra ChaulagaiNo ratings yet
- Iceland Trade Mission: Mt. Princeton Geothermal LLCDocument31 pagesIceland Trade Mission: Mt. Princeton Geothermal LLCAlleyTreeNo ratings yet
- Potential of Waste To Energy in African Urban Areas 2475 7675 1000162Document12 pagesPotential of Waste To Energy in African Urban Areas 2475 7675 1000162Emmanuel Anosisye MwangomoNo ratings yet
- M0712101104 - Ktra Do Nong ChayDocument4 pagesM0712101104 - Ktra Do Nong ChayTịch MịchNo ratings yet
- All About Prehistoric Era To Celebrate US National Fossil Day by Slidesgo - 1Document56 pagesAll About Prehistoric Era To Celebrate US National Fossil Day by Slidesgo - 1Justin SeagullNo ratings yet
- Literary ReviewDocument5 pagesLiterary Reviewapi-549216833No ratings yet
- CSBS 105 Unit-I Oscillations AssainmentDocument4 pagesCSBS 105 Unit-I Oscillations AssainmentDeepam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic EraDocument3 pagesCenozoic EraJudith Vengano AguilarNo ratings yet
- Quiz 002 100%Document14 pagesQuiz 002 100%jrence100% (1)
- Global Warming EssayDocument8 pagesGlobal Warming Essaykhuranakrish100% (1)